Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Case
Hochgeladen von
Elaine MateoCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Case
Hochgeladen von
Elaine MateoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
3
CASE STUDY
Instruction:
Review the following 2015 Balance Sheet and Income Statement for T. F. Baker
Cosmetics, Inc.
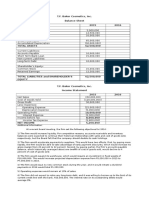
T.F. Baker Cosmetics, Inc.
Balance Sheet
As of December 31, 2015
ASSETS
Current Assets:
Cash
Accounts Receivable
Inventory
Total Current Assets
5,000,000
12,500,000
10,000,000
27,500,000
Non-Current Asset:
Gross Fixed Asset
Accumulated Depreciation
65,000,000
30,000,000
Total Assets
35,000,000
P
62,500,000
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS EQUITY
Current Liabilities:
Accounts Payable
Short Term Bank Loan
Total Current Liabilities
10,000,000
15,000,000
25,000,000
Non-Current Liability:
Long-Term Debt
Shareholders Equity:
Common Stock
Retained Earnings
Total Shareholders Equity
Total Liabilities and Shareholders Equity
10,000,000
15,000,000
12,500,000
27,500,000
P 62,500,000
T.F. Baker Cosmetics, Inc.
Income Statement
For the year ended December 31, 2015
Net Sales
Cost of goods sold
Gross profit
Expenses:
Operating Expenses
Depreciation Expense
Interest Expense
P 150,000,000
(120,000,000)
30,000,000
15,000,000
5,000,000
2,000,000
22,000,000
Income before Tax
Income Tax Expense (35%)
Net Income
8,000,000
(2,800,000)
P
5,200,000
Additional Information:
At a recent board meeting, the firm set the following objectives for 2016:
1) The firm would increase liquidity. For competitive reasons, accounts receivable and
inventory balances were expected to continue their historical relationships with sales and
cost of goods sold, respectively, but the Board felt that the company should double its
cash holdings.
2) The firm would accelerate payments to suppliers. This would have two effects. First, by
paying more rapidly, the firm would be able to take advantage of early payment
discounts, which would increase its gross margin from 20 percent to 22 percent. Second,
by paying earlier, the firms accounts payable balance, which historically averaged about
one twelfth of cost of goods sold, would decline to 4 percent of cost of goods sold.
3) The firm would expand its warehouse, which would require an investment in fixed assets
of P10,000,000. This would increase projected depreciation expense from P5,000,000 in
2015 to P7,000,000 in 2016.
4) The firm would issue no new common stock during the year, and it would initiate a
dividend payments in 2016 would total P1,200,000.
5) Operating expenses would remain at 10% of sales.
6) The firm did not expect to retire any long-term debt, and it was willing to borrow up to
the limit of its current credit line with the bank, P20,000,000. The interest rate on its
outstanding debts would average 8%.
7) The firm set a sales target for 2016 of P200,000,000.
Requirement: Develop a set of Pro Forma Financial Statements to determine whether or not T.F.
Baker Cosmetics can achieve all these goals simultaneously.
ANSWERS
T.F. Baker Cosmetics, Inc.
Income Statement
Net Sales
Cost of Goods Sold
Gross Profit
Less: Expenses:
Operating Expense
Depreciation Expense
Operating Profit
Interest Expense
Income before Tax
Income Tax Expense
NET INCOME
2015
150,000,000
(120,000,000)
30,000,000
2016
200,000,000
(156,000,000)
44,000,000
(15,000,000)
(5,000,000)
10,000,000
(2,000,000)
8,000,000
(2,800,000)
5,200,000
(20,000,000)
(7,000,000)
17,000,000
(2,400,000)
14,600,000
(5,110,000)
9,490,000
T.F. Baker Cosmetics, Inc.
Balance Sheet
Current Assets
Cash
Accounts Receivable
Inventory
Non-current Assets:
Gross Fixed Asset
Accumulated Depreciation
TOTAL ASSETS
Current Liabilities:
Accounts Payable
Short Term Bank Loan
Non-current Liabilities:
Long-Term Debt
Shareholders Equity:
Common Stock
Retained Earnings
*External Financing Required
TOTAL LIABILITIES and SHAREHOLDERS
EQUITY
SOLUTIONS
2015
2016
5,000,000
12,500,000
10,000,000
10,000,000
16,666,667
13,000,000
65,000,000
(30,000,000)
62,500,000
75,000,000
(37,000,000)
77,666,667
10,000,000
15,000,000
6,240,000
20,000,000
10,000,000
10,000,000
15,000,000
12,500,000
15,000,000
20,790,000
5,636,667
77,666,667
62,500,000
COST OF GOODS SOLD
Sales
2015
Gross
Profit
Gross
Margin
150,000,00
0
30,000,000
Sales
2016
Gross
Margin
Gross
Profit
200,000,00
0
22%
Sales
2016
COGS
(squeeze)
Gross
Profit
200,000,00
0
156,000,00
0
44,000,000
20%
=5,000,000 x 2
=10,000,000
ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE
PERCENTAGE OF SALES
= ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE
2015 / SALES 2015
=12,500,000 / 150,000,000
=0.8333333333 OR 8.33333333%
ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE
=SALES 2016 X 8.3333%
=200,000,000 X 8.33333%
=16,666,667
INVENTORY
PERCENT OF COGS
=10,000,000 / 120,000,000
=0.08333333 OR 8.333333%
INVENTORY 2016
=COGS 2016 X 0.8333333%
=156,000,000 X 0.83333333%
=13,000,000
GROSS FIXED ASSET
65,000,000 + 10,000,000
=75,000,000
ACCUMULATED
DEPRECIATION
=30,000,000 + 7,000,000
=37,000,000
ACCOUNTS PAYABLE
=COGS X 4%
=156,000,000 X 4%
=6,240,000
SHORT TERM BANK LOAN
The firm was willing to borrow up to
the limit of its credit line with the
bank, 20,000,000
RETAINED EARNINGS
=RETAINED EARNINGS 2015 +
NET PROFIT DIVIDEND
PAYMENT
=12,500,000 + 9,490,000
1,200,000 =20,790,000
44,000,000
OPERATING EXPENSES
=SALES 2016 X 10%
=200,000,000 X 10%
=20,000,0000
CASH
INTEREST EXPENSE
=OUTSTANDING DEBTS X 8%
=(SHORT TERM BANK LOAN +
LONG TERM DEBT) X 8%
=(20,000,000 + 10,000,000) X 8%
=2,400,000
INCOME TAX EXPENSE
=INCOME TAX EXPENSE 2015
/INCOME BEFORE TAX 2015
=2,800,000 / 8,000,000
=0.35 OR 35%
INCOME TAX EXPENSE 2016
=14,600,000 X 35%
=5,110,000
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Grange Fencing Garden Products Brochure PDFDokument44 SeitenGrange Fencing Garden Products Brochure PDFDan Joleys100% (1)
- UntitledDokument17 SeitenUntitledSedat100% (1)
- (Essential Skills For Nurses Series) Philippa Sully - Joan Dallas-Essential Communication Skills For Nursing and Midwifery-Mosby - Elsevier (2010) PDFDokument250 Seiten(Essential Skills For Nurses Series) Philippa Sully - Joan Dallas-Essential Communication Skills For Nursing and Midwifery-Mosby - Elsevier (2010) PDFRetno SumaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volleyball Unit PlanDokument4 SeitenVolleyball Unit Planapi-214597204Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Social Networking Sites To The Academic Performance of The College Students of Lyceum of The Philippines - LagunaDokument15 SeitenThe Impact of Social Networking Sites To The Academic Performance of The College Students of Lyceum of The Philippines - LagunaAasvogel Felodese Carnivora64% (14)
- Sample Engagement LetterDokument5 SeitenSample Engagement Letterprincess_camarilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Related Literature and Related StudiesDokument23 SeitenReview of Related Literature and Related StudiesReynhard Dale100% (3)
- BZY Series Tension Meter ManualDokument29 SeitenBZY Series Tension Meter ManualJORGE SANTANDER0% (1)
- DU30Dokument5 SeitenDU30Elaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5ec7660621062 - 1590126086 - Cpa Dreams Recommended Schedule For Self ReviewDokument15 Seiten5ec7660621062 - 1590126086 - Cpa Dreams Recommended Schedule For Self ReviewElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco 200 - Principles of Macroeconomics: Chapter 6: National Income AccountingDokument10 SeitenEco 200 - Principles of Macroeconomics: Chapter 6: National Income AccountingElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5ec7660621062 - 1590126086 - Cpa Dreams Recommended Schedule For Self ReviewDokument15 Seiten5ec7660621062 - 1590126086 - Cpa Dreams Recommended Schedule For Self ReviewElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5: The Public SectorDokument15 SeitenChapter 5: The Public SectorJudz SawadjaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CaseDokument5 SeitenCaseElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Able of Ontents: Cash Flow and Financial Planning Title PageDokument1 SeiteAble of Ontents: Cash Flow and Financial Planning Title PageElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnswerDokument1 SeiteAnswerElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CopyDokument2 SeitenCopyElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Objectives: A. Objectives of Cash Flow StatementDokument2 SeitenLearning Objectives: A. Objectives of Cash Flow StatementElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Programming LanguangeDokument13 SeitenBasic Programming LanguangeElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AteDokument19 SeitenAteElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Objectives: A. Objectives of Cash Flow StatementDokument2 SeitenLearning Objectives: A. Objectives of Cash Flow StatementElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pro Forma Statements: John Mark Emerson G. Dizon BSA-3BDokument22 SeitenPro Forma Statements: John Mark Emerson G. Dizon BSA-3BElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IFRS8Dokument11 SeitenIFRS8Elaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Able of Ontents: Cash Flow and Financial Planning Title PageDokument1 SeiteAble of Ontents: Cash Flow and Financial Planning Title PageElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cash PlanningDokument3 SeitenCash PlanningElaine Mateo100% (1)
- ProblemsDokument7 SeitenProblemsElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Define TaxationDokument3 SeitenDefine TaxationElaine MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Rice Research Newsletter Vol12 No.4Dokument67 SeitenInternational Rice Research Newsletter Vol12 No.4ccquintosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Regional PlanningDokument27 SeitenIntroduction To Regional Planningadeeba siddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interection 2 Reading Teacher's Book PDFDokument165 SeitenInterection 2 Reading Teacher's Book PDFتركي الزهراني0% (1)
- Introduction To Physiotherapy PracticeDokument22 SeitenIntroduction To Physiotherapy PracticejNoch keine Bewertungen
- APS PresentationDokument32 SeitenAPS PresentationRozack Ya ZhackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Mine Ventialtion ProblemDokument3 SeitenChapter 3 Mine Ventialtion ProblemfahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Bms8n2 e LowDokument58 SeitenManual Bms8n2 e Lowzoranbt80_324037655Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gel Electrophoresis Worksheet Teacher AnswersDokument3 SeitenGel Electrophoresis Worksheet Teacher AnswersChris FalokunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stating Like and DislikesDokument2 SeitenStating Like and DislikesDavid ArdiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Problems On Gas TurbineDokument9 SeitenReview Problems On Gas TurbinejehadyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- DTS Nozzles R3Dokument2 SeitenDTS Nozzles R3meilia teknikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of Vectors Prepared By: Victor Rea OribeDokument17 SeitenComponents of Vectors Prepared By: Victor Rea OribeGerone Tolentino AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auburn Bsci ThesisDokument5 SeitenAuburn Bsci Thesisafksaplhfowdff100% (1)
- File 1) GRE 2009 From - Nov - 18 PDFDokument84 SeitenFile 1) GRE 2009 From - Nov - 18 PDFhuyly34Noch keine Bewertungen
- QLD Plan Draft Review Raw DataDokument242 SeitenQLD Plan Draft Review Raw DataRohit Jain100% (1)
- Basic: M1736N Model: MW73VR Model Code: Mw73Vr/BwtDokument42 SeitenBasic: M1736N Model: MW73VR Model Code: Mw73Vr/Bwtsantiago962Noch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller Velocity TrianglesDokument2 SeitenImpeller Velocity TrianglesLorettaMayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019q123.ev3-Descon Engro Level Gauges-QDokument7 Seiten2019q123.ev3-Descon Engro Level Gauges-Qengr_umer_01Noch keine Bewertungen
- MT4 EA Installation Guide Digital - EnglishDokument7 SeitenMT4 EA Installation Guide Digital - EnglishThe Trading PitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portfolio Eelco Maan - 06-2017Dokument25 SeitenPortfolio Eelco Maan - 06-2017tungaas20011Noch keine Bewertungen
- The King's Avatar - Chapter 696 - Guild Feature - Gravity TalesDokument5 SeitenThe King's Avatar - Chapter 696 - Guild Feature - Gravity TalesMayhaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPA NCP Technical Notebook PDFDokument191 SeitenEPA NCP Technical Notebook PDFlavrikNoch keine Bewertungen