Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Dug Wells
Hochgeladen von
PrinceEnopiaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Dug Wells
Hochgeladen von
PrinceEnopiaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
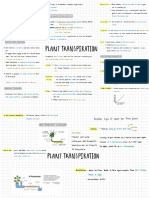
DUG WELLS- 15 METERS DEPTH
Dug wells are made by constructing a large hole into the earth to a depth greater than the ground water
level. A reservoir is created by lining the walls of the hole with rocks, brick, wood, or concrete pipe to
prevent cave-in. In some conditions the hole may be back filled with coarse gravel with a feed line
installed. In this situation the gravel area acts as the reservoir. As long as ground water is present, a dug
well will yield results. Water is extracted from the reservoir and replenished naturally from the aquifer. The
wells recharge and use capacities are directly related to the permeability of the soil into which the well is
constructed . Dug wells are typically limited to a depth of 25 - 30, and are practical only when the water
table is near the surface of the earth. Because of the dug wells method of construction and shallow depth,
contamination from surface drainage and sub surface seepage is common. In many areas dug wells are
prohibited by law.
BORED WELLSBored wells are constructed by means of an auger which bores a cylindrical hole into the earth. After water
is reached , soil samples are collected to determine the permeability of the soil. If a suitable permeable soil
is encountered, a screen or filtering device is attached to a casing and lowered into the bore hole . The
casing is driven or pushed to the desired depth. The well is developed, and water is extracted from the soil.
DRIVEN WELLS
Driven wells consist of a series of tightly coupled pipe lengths installed below the water table with a well
point or screen at the lower end. The well point may be forced into the ground by a series of driven blows
directed upon the pipe above it or telescoped into the well after the pipe is driven and soil samples are
collected. The permeability of the soil is the determining factor for the feasibility of the well. Water is
extracted directly from the soil.
DRILLED WELLS-1000 METERS
Drilled wells typically are used in areas of geologically poor soil conditions. Drilled wells are commonly
drilled by one of two methods: The first is known as cable tool or percussion method. It involves a
machine that alternately lifts and drops a long chisel -shaped bit within the bore hole . The hole is
deepened as the bit cuts and breaks the rock. A bailer is used to extract the cuttings as necessary. The
second is called the rotary well drilling method. A rotating bit is fixed to the end or the drill pipe. The
rotary action of this bit chews into the rock or other earth materials. Air or water is used to transport the
cuttings to the surface. Water seeps into the bore hole through cracks or seams in the rock, and is
extracted from the bore hole by means of a submersible pump typically installed to a depth greater than
that of the water bearing seam
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 13 Dewatering of FoundationsDokument65 Seiten13 Dewatering of FoundationsZahoor AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water WellsDokument20 SeitenWater Wellsashraf habibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Water BasicsDokument5 SeitenWell Water Basicsbontu gadisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draining for Profit, and Draining for HealthVon EverandDraining for Profit, and Draining for HealthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit II DewateringDokument13 SeitenUnit II Dewateringadhishankar50Noch keine Bewertungen
- DEWATERINGDokument14 SeitenDEWATERINGChaidir Sai LusterNoch keine Bewertungen
- DewateringDokument6 SeitenDewateringIsife OlisaemekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tube Well and Designs Assigmnt and Presentation (Group1)Dokument39 SeitenTube Well and Designs Assigmnt and Presentation (Group1)Abdullah100% (1)
- A Building Without Water Supply Is Unfit For Human HabitationDokument9 SeitenA Building Without Water Supply Is Unfit For Human Habitationjurhym doteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dewatering Us UnvstyDokument17 SeitenDewatering Us Unvstyengr_atulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Well ConstructionDokument5 SeitenWater Well ConstructionrramadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 - Excavation & TimberingDokument35 Seiten03 - Excavation & TimberingSaurav ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Private Water SupplyDokument7 SeitenPrivate Water SupplyNick Zeet RasonableNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Types of DewateringDokument2 SeitenWhat Are Types of Dewateringmp_babu_2100% (4)
- Water WellsDokument8 SeitenWater WellsJanine Arielle DanaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dewatering For ConstructionDokument14 SeitenDewatering For ConstructionpabulumzengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Completion Development and Maintenance of WellsDokument33 SeitenWell Completion Development and Maintenance of WellsArun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand Dug WellDokument29 SeitenHand Dug WellMelikteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Well Group 4Dokument29 SeitenWater Well Group 4Alvin DeliroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 7 Construction Dewatering and Ground FreezingDokument17 SeitenLesson 7 Construction Dewatering and Ground FreezingRsjBugtongNoch keine Bewertungen
- DewateringDokument51 SeitenDewateringShashikanta SahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type of WellsDokument10 SeitenType of WellsAddrien Daniel100% (1)
- Drainage & DewateringDokument18 SeitenDrainage & DewateringPranav KdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tubewellsandtheirdesign 160625145100Dokument60 SeitenTubewellsandtheirdesign 160625145100Tara Chandra PanjiyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- WellsDokument25 SeitenWellsTHEJSWINoch keine Bewertungen
- Dewatering TechniquesDokument17 SeitenDewatering TechniquesTrudeep DaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of DewateringDokument11 SeitenMethods of DewateringjinkumalakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DewateringtechniquespptDokument45 SeitenDewateringtechniquespptMadhu AsopaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec-04 & 05 Draiage & DewateringDokument33 SeitenLec-04 & 05 Draiage & DewateringRahat fahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module2 DrainageMethodsDokument7 SeitenModule2 DrainageMethodsJaisuryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Wells Are Drilled - by American Ground Water TrustDokument2 SeitenHow Wells Are Drilled - by American Ground Water Trusthbpr9999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ground Improvement Techniques UNIT-1Dokument23 SeitenGround Improvement Techniques UNIT-1Raghuram Vadiboyena VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nikhil HydrologyDokument16 SeitenNikhil HydrologynavoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DewateringDokument13 SeitenDewateringTejay TolibasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Track DrainageDokument12 SeitenTrack DrainageBook JkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 - Fundamentals of Water Supply Systems 2Dokument88 SeitenLecture 1 - Fundamentals of Water Supply Systems 2Ronstedt Rutherford Molina100% (1)
- Drainage Structures: Water Resources EngineeringDokument80 SeitenDrainage Structures: Water Resources EngineeringMg CanoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 9Dokument10 SeitenCH 9salmanistiaq0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Road Drainage-1Dokument27 SeitenRoad Drainage-1RISHABHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well DesignDokument5 SeitenWell DesignJoshie WishyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - Private Water Supply SourceDokument20 Seiten3 - Private Water Supply SourceE&N CommissionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slideshare Upload Login SignupDokument26 SeitenSlideshare Upload Login SignupAbok AduogoNoch keine Bewertungen
- WELLSDokument10 SeitenWELLSlloyd louies ferrerasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Pan For Runoff Water Harvesting PDFDokument4 SeitenWater Pan For Runoff Water Harvesting PDFmulwa2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embankment DamDokument63 SeitenEmbankment DamRanjan Dhungel100% (1)
- Continuation On WellsDokument22 SeitenContinuation On WellsvictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dewatering of FoundationsDokument20 SeitenDewatering of FoundationsFizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DewateringDokument11 SeitenDewateringNeda Shakil100% (1)
- Subject-Water Resources Engineering: Wells, Types of WellsDokument27 SeitenSubject-Water Resources Engineering: Wells, Types of Wellschauhansukant52Noch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Dewatering Excavations at Construction SiteDokument26 SeitenMethods of Dewatering Excavations at Construction SiteRajesh Khadka100% (2)
- DewateringDokument6 SeitenDewateringDrishti Jain100% (1)
- Types of Tube Wells & Its ConstructionDokument51 SeitenTypes of Tube Wells & Its Constructionrbroy_dwsd88% (8)
- Dewatering of Soil: Group No 1Dokument10 SeitenDewatering of Soil: Group No 1Sikander KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- WatersupplyDokument5 SeitenWatersupplySourendra KaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuya Albert Anyange ENG-217-036/2018 Assignment 3 Foundation Construction and Management of DamsDokument10 SeitenKuya Albert Anyange ENG-217-036/2018 Assignment 3 Foundation Construction and Management of DamsDeAndre mtekoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laying and Testing of SewersDokument13 SeitenLaying and Testing of SewersBedatrayee05100% (1)
- Building Construction I Lecture 3 Chapter 2Dokument38 SeitenBuilding Construction I Lecture 3 Chapter 2Narayan Paudel BkNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual Ovograder 05 EDokument131 SeitenUser Manual Ovograder 05 EPrinceEnopiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Power FactorDokument49 SeitenAutomatic Power FactorR Sathish Kumar KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spare Parts For Feeding SystemDokument27 SeitenSpare Parts For Feeding SystemPrinceEnopiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 1Dokument2 SeitenExam 1PrinceEnopia100% (1)
- GFGDokument2 SeitenGFGPrinceEnopiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 1Dokument2 SeitenExam 1PrinceEnopia100% (1)
- 2014 - 003 The 22 Basic Principles of PlumbingDokument59 Seiten2014 - 003 The 22 Basic Principles of Plumbingnica tam50% (6)
- The New National Building CodeDokument16 SeitenThe New National Building Codegeanndyngenlyn86% (50)
- 2014 - 001 Introduction To House PlumbingDokument16 Seiten2014 - 001 Introduction To House PlumbingRon Julienne RebugioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 - 008 Domestic Cold Water Supply SystemDokument94 Seiten2014 - 008 Domestic Cold Water Supply SystemPrinceEnopiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PD856 Sanitation CodeDokument44 SeitenPD856 Sanitation CodejbonvierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine National Standards For Drinking Water (PNSDW) 2007 PDFDokument35 SeitenPhilippine National Standards For Drinking Water (PNSDW) 2007 PDFraymundvaj73% (15)
- Farm Tools and Their UsesDokument10 SeitenFarm Tools and Their UsesPrinceEnopia86% (7)
- Implementing Rules and Regulations of Republic Act 9003Dokument70 SeitenImplementing Rules and Regulations of Republic Act 9003PrinceEnopiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evil Twin LyricsDokument5 SeitenEvil Twin LyricsPrinceEnopiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angel of Peace PrayerDokument1 SeiteAngel of Peace PrayerPrinceEnopiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BP 344Dokument58 SeitenBP 344Ultrabuilders Const100% (14)
- FlowersDokument2 SeitenFlowersPrinceEnopiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Folds&Faults PresentationDokument17 SeitenFolds&Faults Presentationcrown212Noch keine Bewertungen
- Skardu ReportDokument77 SeitenSkardu ReportkazimmehdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uge1 Activity 4Dokument2 SeitenUge1 Activity 4Vhon MisakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coral Reef ConservationDokument33 SeitenCoral Reef ConservationPrathamesh ParabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank ICSE Class 10th GeographyDokument6 SeitenQuestion Bank ICSE Class 10th GeographyKaramveer Singh100% (1)
- Ramsar Convention PDFDokument11 SeitenRamsar Convention PDFGishan SanjeewaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 275-Chemosphere 2022 (Review TPH)Dokument19 Seiten275-Chemosphere 2022 (Review TPH)Olumide AjayiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green City, Clean Waters: Implementing Philadelphia's Combined Sewer Overflow Long Term Control Plan UpdateDokument57 SeitenGreen City, Clean Waters: Implementing Philadelphia's Combined Sewer Overflow Long Term Control Plan UpdateKirk BarrettNoch keine Bewertungen
- PlantDokument4 SeitenPlant5/1-07 Kornkanokod ChoopongwaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topographic Map of WallisDokument1 SeiteTopographic Map of WallisHistoricalMapsNoch keine Bewertungen
- USGS Volcano Threat AssessmentDokument50 SeitenUSGS Volcano Threat AssessmentHNNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kern County Mines and Minerals ResourcesDokument368 SeitenKern County Mines and Minerals ResourcesRussell HartillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine TyphoonDokument21 SeitenPhilippine TyphoonBethlehem CuradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Hydrometeorological Hazards PDFDokument88 Seiten6 Hydrometeorological Hazards PDFArciete DyrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science-8-SIM-Q2-Module 5 - Week 5Dokument32 SeitenScience-8-SIM-Q2-Module 5 - Week 5Irene SivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journey To The End of The Earth - Day 2Dokument14 SeitenJourney To The End of The Earth - Day 2anita josephNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS (Stevie Wonder)Dokument2 SeitenAS (Stevie Wonder)Ananda Satya100% (5)
- Farming Systems and Sustainable Agriculture PDFDokument35 SeitenFarming Systems and Sustainable Agriculture PDFPrince GrimmjowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Roof Energy Calculator - Urban Climate Research CenterDokument2 SeitenGreen Roof Energy Calculator - Urban Climate Research CenterAcoperisuri verzi OdúNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbonate Depo SystemsDokument244 SeitenCarbonate Depo Systemsshamshad_meNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drain Design (Proag) PDFDokument12 SeitenDrain Design (Proag) PDFAppavoo DeelenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Guide SampleDokument11 SeitenLearning Guide Samplelj BoniolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geography - WikipediaDokument15 SeitenGeography - WikipediaLorenzo E.MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Snapshots LLDA 9-30-2015Dokument2 SeitenWave Snapshots LLDA 9-30-2015Gerome RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stratigraphy and Sedimentology of The Chert Unit of The Semanggol FormationDokument9 SeitenStratigraphy and Sedimentology of The Chert Unit of The Semanggol FormationgeomagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urban Landscape: Transforming in IndiaDokument94 SeitenUrban Landscape: Transforming in IndiaMruga RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gist of NCERT GeographyDokument116 SeitenThe Gist of NCERT GeographyKishore Kumar100% (1)
- Water A Precious ResourceDokument5 SeitenWater A Precious ResourceBIMAN MONDALNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2301 - PREZENTARE Geografia Romaniei PDFDokument47 Seiten2301 - PREZENTARE Geografia Romaniei PDFman666onNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final EIA Report of Netrakona EZDokument332 SeitenFinal EIA Report of Netrakona EZTawseef HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersVon EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesVon EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (21)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseVon EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (69)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastVon EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (31)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterVon EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincVon EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (137)
- When the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeVon EverandWhen the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- The Big Burn: Teddy Roosevelt and the Fire that Saved AmericaVon EverandThe Big Burn: Teddy Roosevelt and the Fire that Saved AmericaBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (9)
- Exploring Creation with Physical Science, 3rd EditionVon EverandExploring Creation with Physical Science, 3rd EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Civilized To Death: The Price of ProgressVon EverandCivilized To Death: The Price of ProgressBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (215)
- Survival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosVon EverandSurvival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- A Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight ChaptersVon EverandA Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight ChaptersBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (113)
- The World Beneath: The Life and Times of Unknown Sea Creatures and Coral ReefsVon EverandThe World Beneath: The Life and Times of Unknown Sea Creatures and Coral ReefsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- A Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeVon EverandA Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- The Earth Prescription: Discover the Healing Power of Nature with Grounding Practices for Every SeasonVon EverandThe Earth Prescription: Discover the Healing Power of Nature with Grounding Practices for Every SeasonBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Pitfall: The Race to Mine the World’s Most Vulnerable PlacesVon EverandPitfall: The Race to Mine the World’s Most Vulnerable PlacesNoch keine Bewertungen
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesVon EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- So Others May Live: Coast Guard's Rescue Swimmers Saving Lives, Defying DeathVon EverandSo Others May Live: Coast Guard's Rescue Swimmers Saving Lives, Defying DeathBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- Run the Storm: A Savage Hurricane, a Brave Crew, and the Wreck of the SS El FaroVon EverandRun the Storm: A Savage Hurricane, a Brave Crew, and the Wreck of the SS El FaroBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (39)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeVon EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (9)