Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
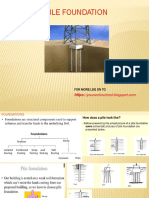
Rotary Bored Piles: Technique Sheet
Hochgeladen von
ValentVeeOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Rotary Bored Piles: Technique Sheet
Hochgeladen von
ValentVeeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
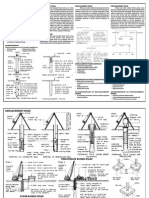
TECHNIQUE SHEET
ROTARY BORED PILES
Rotary Bored Piles can be used to support any structure where the highest load carrying
capacity is required. Balfour Beatty Ground Engineering has developed specialist expertise
to deliver large, complex and technically challenging projects.
BASIC TECHNIQUE
Drilling tools, including augers and buckets, are
used to excavate the soils to form an open hole to
the required depth. Where unstable ground
conditions are present, commonly within made
ground and in granular layers, a steel casing is used
to provide temporary support. This casing is either
screwed in using the rig or vibrated into place.
A reinforcing cage is then installed into the open
bore and concrete is poured via a delivery tube or
tremmie pipe. If a steel casing was used it is later
withdrawn.
ROTARY BORED PILE CONSTRUCTION SEQUENCE
STRENGTHS
Minimal ground disturbance - with limited risk
of damage to adjacent structures
Suitable for all soil types
Simple and efficient installation process
Ability to drill through most obstructions and
socket into rock
Ideal for insitu cast retaining walls where high
levels of reinforcement and tight drilling
tolerances are needed
TECHNIQUE SHEET
CAD IMAGE OF ROTARY BORED PILING RIG
ARISINGS FROM ROTARY BORED PILING
TECHNIQUE ENHANCEMENTS
Use of Oscillator
Where minimum disturbance is critical (e.g. close
to an existing building or railway line), an oscillator
can be used to install the steel casing with great
precision.
Hollow Piles
BBGE have developed piles with a hollow core,
saving concrete and steel with no loss in
performance, in collaboration with City University.
Under-reams
In stable soils the base of the pile can be extended
up to a 6.3m diameter to form an inverted cone,
which delivers a very high load-bearing capacity.
This allows piles to be founded at a shallower
depth, potentially avoiding lower unstable soils.
Plunge Columns
Standard H section beams, as well as fabricated
steel box or H sections, can be plunged into the pile
following concrete placement. These columns are
commonly used for top-down construction, which
enables simultaneous superstructure construction
and basement excavation, or where temporary
propping or support is required to adjacent
structures. This technique can significantly reduce
the overall build cycle.
Drilling Fluids
Where unstable ground exists at depth, and it
becomes uneconomical or impractical to use
casing, a vinyl polymer - or bentonite drilling fluid
can be introduced to support the bore during
excavation. When the concrete is being tremmied
into the bore, the polymer or bentonite fluid is
displaced and pumped out before being cleaned
and recycled for use in the next pile.
TECHNICAL CAPABILITIES ROTARY BORED PILES
Specification
From
To
Practical Depth
N/A
70m
Diameter
0.45m
3.0m
Typical Load Capacity
1000kN
30,000kN
Rig Height
12.5m
28m
Rig Weight
37,000kg
140,000kg
Rig Length
7m
10m
Rid Width
3m
5m
Noise Profile at 10m
85db
90db
CONTACT US
Balfour Beatty Ground Engineering
Pavilion B, Ashwood Park, Ashwood Way, Basingstoke RG23 8BG
T: 01256 400400 | W: www.bbge.com | E: info@bbge.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Soosan Hydraulic Breaker Part List PDFDokument44 SeitenSoosan Hydraulic Breaker Part List PDFValentVee89% (9)
- Metro Clark Waste ManagementDokument7 SeitenMetro Clark Waste ManagementEloiza Acosta GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Driven Cast in Situ PilesDokument17 SeitenDriven Cast in Situ PilesSonu KumawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- UnderpinningDokument11 SeitenUnderpinningAhmad Mustanir HadadakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retaining Walls and Basement OnstructionDokument18 SeitenRetaining Walls and Basement Onstructionreemadepon0% (1)
- Types of FoundationDokument69 SeitenTypes of FoundationAsadullah Khan GhalibNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Build a Global Model Earthship Operation II: Concrete WorkVon EverandHow to Build a Global Model Earthship Operation II: Concrete WorkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete in Highway Engineering: International Series of Monographs in Civil EngineeringVon EverandConcrete in Highway Engineering: International Series of Monographs in Civil EngineeringBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- Su Series CatalogueDokument4 SeitenSu Series CatalogueValentVee0% (1)
- The Management of Cyanide in Gold ExtractionDokument44 SeitenThe Management of Cyanide in Gold ExtractionYiannis BarasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level 3 Food Safety and HygieneDokument85 SeitenLevel 3 Food Safety and HygieneNikade Confidence100% (2)
- Different Methods of Deep Foundation DesignDokument7 SeitenDifferent Methods of Deep Foundation DesignMuhammad ArhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Foundation PilingDokument3 SeitenDeep Foundation PilingVishnuPSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Foundation: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument9 SeitenDeep Foundation: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAzhar HussinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of PilesDokument40 SeitenTypes of PilesMohamad HanifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unique Solutions in Geotechnical WorksDokument72 SeitenUnique Solutions in Geotechnical WorksAlphaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0 Pile FoundationDokument15 Seiten0 Pile FoundationGANGADHARAIAH SNNoch keine Bewertungen
- GuniteDokument46 SeitenGuniteprasad perkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Construction 5 To 7Dokument30 SeitenBuilding Construction 5 To 7GeraldineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pin Piles UnderpinningDokument13 SeitenPin Piles UnderpinningsenhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 FoundationsDokument62 Seiten2008 FoundationsMani Kandan ArunachalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piled Foundation ReportDokument7 SeitenPiled Foundation ReportDijo Mathews100% (1)
- Bearing Piles and GroupsDokument36 SeitenBearing Piles and Groupsjologscresencia100% (1)
- (FRANKI) Displacement PilesDokument18 Seiten(FRANKI) Displacement PilesHatta RizqNoch keine Bewertungen
- PilesDokument47 SeitenPilesnurulselangorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2625 Deep Foundations For High Rise Buildings in Hong KongDokument11 Seiten2625 Deep Foundations For High Rise Buildings in Hong KongJulio MzpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile and Mat FoundationDokument9 SeitenPile and Mat FoundationMuhamad SafeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0 Piles: Piles Foundation Is Used WhenDokument11 Seiten1.0 Piles: Piles Foundation Is Used WhenMind RipNoch keine Bewertungen
- PilingDokument8 SeitenPilinghgor100% (1)
- BAUER Bored Cast-In-place Concrete PilesDokument12 SeitenBAUER Bored Cast-In-place Concrete Pilesjoaonunes.405443Noch keine Bewertungen
- TKBT Anchor EquipmentDokument32 SeitenTKBT Anchor EquipmentLuca Brandi100% (1)
- Pin Piles For Building FoundationsDokument15 SeitenPin Piles For Building FoundationsAntonio MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile Foundation - Based On MaterialDokument36 SeitenPile Foundation - Based On MaterialAvani JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep FoundationDokument10 SeitenDeep Foundationvinod_commentNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0526 BT PccpilesDokument4 Seiten0526 BT Pccpilesrmorton03Noch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Basement ExcavationDokument4 SeitenDeep Basement Excavationmypenta2008Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.pile Foundation: Q1. Write Down Functions and Classification of Pile FoundationDokument9 Seiten1.pile Foundation: Q1. Write Down Functions and Classification of Pile FoundationSuhail AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of FoundationDokument77 SeitenTypes of FoundationThammu Tulasiram100% (1)
- Pile Foundation: For More Log On ToDokument35 SeitenPile Foundation: For More Log On ToBRAIN OF AN ARCHITECT100% (1)
- BACLIG, LORNA G. (BSCE 4-2) - CENGR 4220 Assignment No. 4Dokument14 SeitenBACLIG, LORNA G. (BSCE 4-2) - CENGR 4220 Assignment No. 4LORNA BACLIGNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNDERPINNING Text MaterialDokument14 SeitenUNDERPINNING Text MaterialYoga RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- UnderpinningDokument30 SeitenUnderpinningAimi Athirah ZahibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile Foundations Lecture Note 1 PDFDokument99 SeitenPile Foundations Lecture Note 1 PDFMalbattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile Foundation ReportDokument11 SeitenPile Foundation ReportEduardo OrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil NailingDokument6 SeitenSoil Nailingvinodreddy146Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of FoundaitonsDokument75 SeitenTypes of FoundaitonsHina MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plunge ColumnsDokument4 SeitenPlunge Columnschandar70Noch keine Bewertungen
- I. Deep Foundation: A. PileDokument7 SeitenI. Deep Foundation: A. PileNikol CapulongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constech SelekDokument17 SeitenConstech Seleknur asyiqinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Under Reamed Pile-5108Dokument12 SeitenUnder Reamed Pile-5108anku510880% (5)
- Types of FootingDokument3 SeitenTypes of FootingRonald DolorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portal FrameDokument46 SeitenPortal Frameakm100% (1)
- Pile Foundations Ii - CHP3-1Dokument37 SeitenPile Foundations Ii - CHP3-1Uveys kavakliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precast ConcreteDokument69 SeitenPrecast Concretejaffna100% (2)
- Gabion Wall and Sheet PilesDokument18 SeitenGabion Wall and Sheet PilesVasanthapragash NadarajhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Castinsituplace154 150108061806 Conversion Gate01Dokument6 SeitenCastinsituplace154 150108061806 Conversion Gate01Anjumara HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet PilingDokument24 SeitenSheet PilingniyatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10B UnderpinningDokument24 Seiten10B UnderpinningAlma AinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prestress ConcreteDokument135 SeitenPrestress ConcreteNishant AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- JFE SheetPile CatalogDokument24 SeitenJFE SheetPile Cataloghutuguo100% (1)
- Turf Wall Architecture and Turf Furniture Assembly GuideVon EverandTurf Wall Architecture and Turf Furniture Assembly GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionVon EverandReinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Log Cabins and Outbuildings: A Guide to Building Homes, Barns, Greenhouses, and MoreVon EverandLog Cabins and Outbuildings: A Guide to Building Homes, Barns, Greenhouses, and MoreBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Fixed Invoice PDFDokument1 SeiteFixed Invoice PDFValentVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Tanker Truck 1Dokument1 SeiteWater Tanker Truck 1ValentVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema Audio CarDokument1 SeiteSkema Audio CarValentVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fixed Invoice PDFDokument1 SeiteFixed Invoice PDFValentVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Denah KantinDokument1 SeiteDenah KantinValentVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- H Series Service ManualDokument134 SeitenH Series Service ManualValentVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airman Products: More Options, Better SolutionsDokument6 SeitenAirman Products: More Options, Better SolutionsValentVee100% (1)
- Brochure Tjs BBPP 2012Dokument8 SeitenBrochure Tjs BBPP 2012ValentVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iota Engineering: Refer To Lumen Reference Chart For List of Compatible LampsDokument2 SeitenIota Engineering: Refer To Lumen Reference Chart For List of Compatible LampsValentVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nippon Hycote 665Dokument3 SeitenNippon Hycote 665ValentVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carmix 5.5 XLDokument1 SeiteCarmix 5.5 XLValentVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexible Solutions: Let Us Be Part of Your LifeDokument2 SeitenFlexible Solutions: Let Us Be Part of Your LifeValentVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- RoundingDokument5 SeitenRoundingValentVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maspion PVC Pipe and FittingDokument6 SeitenMaspion PVC Pipe and FittingValentVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Introduction To Quality and Productivity (General) : Quality in Business, Engineering and Manufacturing Has ADokument10 Seiten1-Introduction To Quality and Productivity (General) : Quality in Business, Engineering and Manufacturing Has AAnupama SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC SamsungDokument57 SeitenAC SamsungMihai MargineanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Juan TambanDokument72 SeitenJuan TambanEmmanuel Rona100% (4)
- Answer Key Class 8thDokument3 SeitenAnswer Key Class 8thdeepti varshneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trends2 Ank Wbspa 16387Dokument12 SeitenTrends2 Ank Wbspa 16387Constantino CAAMAÑONoch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Sor 19-5-14Dokument55 SeitenTraffic Sor 19-5-14Saurabh Pednekar100% (1)
- Code of Basic Requirements For Water Supply, Drainage and Sanitation (Fourth Revision)Dokument15 SeitenCode of Basic Requirements For Water Supply, Drainage and Sanitation (Fourth Revision)Kishore Ainavilli100% (1)
- Chapter 11 - ExcretionDokument46 SeitenChapter 11 - Excretionapi-372850875% (4)
- CE6605 Environmental Engineering IIDokument19 SeitenCE6605 Environmental Engineering IIunknown noNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muda, Mura, Muri in The Lean Lexicon ©Dokument3 SeitenMuda, Mura, Muri in The Lean Lexicon ©Michael ThompsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technology Developers v. CA RESOLUTIONDokument3 SeitenTechnology Developers v. CA RESOLUTIONStradivariumNoch keine Bewertungen
- CWTS 1 Module 4Dokument21 SeitenCWTS 1 Module 4Janna Marie GeronimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kip 700 Product Information GuideDokument24 SeitenKip 700 Product Information Guidechrisban35Noch keine Bewertungen
- EIA - Sumathi - Eng - Environmental Impect Analysis Steel Rolling MillDokument13 SeitenEIA - Sumathi - Eng - Environmental Impect Analysis Steel Rolling MillsarashviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Araling Panlipunan: Self-Learning ModuleDokument21 SeitenAraling Panlipunan: Self-Learning ModuleRoshelle Ann DulcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drawings - Baakline Stormwater ProjectDokument11 SeitenDrawings - Baakline Stormwater ProjectyaseenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local and Worldwide Sustainable BenchmarksDokument13 SeitenLocal and Worldwide Sustainable Benchmarksmansi sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 3 (Hyundai)Dokument12 Seiten1 3 (Hyundai)lastking_king17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Exchanger Gaskets 1 PDFDokument2 SeitenHeat Exchanger Gaskets 1 PDFMuhammad Aftab AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic of The Philippines Tanggapan NG Sangguniang Panlungsod City of NagaDokument5 SeitenRepublic of The Philippines Tanggapan NG Sangguniang Panlungsod City of NagaDhessa Mae MendiolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Manual Parts List: 1500VMC (FANUC 0iMD)Dokument261 SeitenOperating Manual Parts List: 1500VMC (FANUC 0iMD)apodsh100% (1)
- GPSNP Final Esmf 24 04 18Dokument135 SeitenGPSNP Final Esmf 24 04 18ANIKET BABUTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Turnaround Project Planning PrimerDokument6 SeitenTurnaround Project Planning PrimerSuresh Haldipur100% (1)
- Chemical and Environmental Mock TestDokument6 SeitenChemical and Environmental Mock TestRugi Vicente RubiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sika Grout 212 215 212hp - MsdsDokument5 SeitenSika Grout 212 215 212hp - MsdsMohd MustafhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accomplishment in Waste SegregationDokument6 SeitenAccomplishment in Waste SegregationJaime Daileg100% (3)