Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Exam 02-03
Hochgeladen von
Jai Gaizin0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
7 Ansichten3 SeitenDigital Comp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenDigital Comp
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
7 Ansichten3 SeitenExam 02-03
Hochgeladen von
Jai GaizinDigital Comp
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
9000011975
HONOOOE OY
UNIVERSITY OF HERTFORDSHIRE
Session: 2002/2003
Semester: A
Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences
Department of Electronic, Communications and Electrical Engineering
‘Module Code: 2ELE0037
gital Capture and Manipulation
DURATION OF EXAM: 2 hours
THE FOLLOWING IS PROVIDED FOR THIS EXAMINATION:
‘One answer book
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
Candidates are required to answer three questions. All questions carry equal marks.
Use of University approved calculators is ALLOWED
‘The mark allocations indicated are approximate only, and are intended to guide
candidates on how much time to spend on each part.
This paper consists of FIVE questions on THREE pages,
Page 1 of 3
@
(o)
©
@
©
@
()
©
@
©
@
(>)
©
Explain the difference between a continuous and a discrete signal.
(20%)
What are the advantages of digital signals compared with analogue
ones?
(20%)
What is the sampling theorem?
(15%)
What is a band-limited signal?
(15%)
‘When one sine wave is modulated with another, two frequencies are
produced. How are they related to the two original frequencies? Using
this answer, explain the sampling theorem in terms of additional
frequencies created as a result of the sampling process.
(30%)
Explain what is meant by luminance. State the equation for luminance in
terms of its RGB colour components.
(20%)
Explain how the remaining colour information is transmitted
(15%)
With the aid of a diagram give an analysis of a composite video signal
(25%)
Explain the differences between PAL and NTSC.
(10%)
Explain the principles of magnetic recording,
(30%)
Discuss the stages of JPEG encoding
(40%)
Draw the following discrete cosine transforms:
(i) DC component
(ii) Horizontal DC, maximum frequency vertical
(iii) Vertical DC, Maximum horizontal frequency
(iv) Maximum frequency both vertical and horizontal
(20%)
Which of the above is most likely to have the highest energy level?
(6%)
Page 2 of 3
@
©
@
()
@
0)
Outline the different types of MPEG pictures, their features and how
they are used for motion compression.
(25%)
Why is picture reordering needed?
(10%)
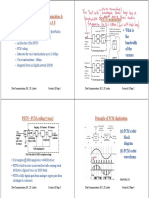
Four sinusoidal signals (Si, S2, Ss and $4) with equal amplitude but
different frequencies. Signal S; has 10 Hz frequency, signal S; has 20
Hz frequency, signal S has 50 Hz frequency and signal S, has 100 Hz
frequency. The four signals have been added to each other to produce a
fifth signal D as expressed by the equation:
D=S,+S2+83+S
The signal D is filtered in order to pass one or more of the signals $1, S2,
Ss and S, and attenuate the rest of the signals. The signal D has been
applied to a filter, which has ideal characteristics, to get the signal F
where F is the output of the Filter.
‘Suppose that the filters’ costs can be ranked as follows starting with the
cheapest filter: low pass filter, high pass filter, band pass filter and band
stop filter, You are required to use the cheapest possible filter if
possible.
In the following cases determine the filter type to be used and draw its
frequency response. Also annotate the x-axis of the frequency response
of each filter you use.
@ FRS
(i) F=S,
Gi) F=S:+S5
(iv) F=Si+S,
(60%)
Draw a block diagram of a second order finite impulse response (FIR)
digital filter.
(40%)
Explain in detail the anatomy of an mp3 file.
(0%)
Explain the ripping principles of a compact disk (CD) and state one too!
(program) to achieve this.
(50%)
Page 3 of 3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Link IntroDokument12 SeitenLink IntroJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- NLP Week 2 Rationalist and Empiricist Paradigms in Natural Language ProcessingDokument28 SeitenNLP Week 2 Rationalist and Empiricist Paradigms in Natural Language ProcessingJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course WorkDokument2 SeitenCourse WorkJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Computer ScienceDokument2 SeitenDepartment of Computer ScienceJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAI Week3Dokument16 SeitenDAI Week3Jai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Link ReferenceDokument12 SeitenLink ReferenceJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAI Week3Dokument6 SeitenDAI Week3Jai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAI Week2Dokument7 SeitenDAI Week2Jai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAI Week3Dokument16 SeitenDAI Week3Jai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAI Week1Dokument6 SeitenDAI Week1Jai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MScDCOM-Lec09v3 With AnnotationsDokument6 SeitenMScDCOM-Lec09v3 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MScDCOM-Lec03v3 With AnnotationsDokument3 SeitenMScDCOM-Lec03v3 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument46 SeitenLecture 1Jai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MScDCOM-Lec07v2 With AnnotationsDokument5 SeitenMScDCOM-Lec07v2 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MScDCOM-Lec06v2 With AnnotationsDokument5 SeitenMScDCOM-Lec06v2 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAI Week1Dokument12 SeitenDAI Week1Jai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MScDCOM-Lec08v2 With AnnotationsDokument7 SeitenMScDCOM-Lec08v2 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MScDCOM-Lec04v3 With AnnotationsDokument4 SeitenMScDCOM-Lec04v3 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MScDCOM-Lec05v2 With AnnotationsDokument3 SeitenMScDCOM-Lec05v2 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISAD Tutorial ERM Week7Dokument1 SeiteISAD Tutorial ERM Week7Jai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MScDCOM-Lec01V3 With AnnotationsDokument4 SeitenMScDCOM-Lec01V3 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MScDCOM-Lec02v3 With AnnotationsDokument2 SeitenMScDCOM-Lec02v3 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 PrototypingDokument1 Seite12 PrototypingJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Access Commands - Accessible From The Help' Menu: Input MaskDokument6 SeitenAccess Commands - Accessible From The Help' Menu: Input MaskJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Motion4Dokument9 SeitenLinear Motion4Jai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Detailed DesignDokument6 Seiten11 Detailed DesignJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 System DesignDokument5 Seiten10 System DesignJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear EqnDokument6 SeitenLinear EqnJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 PrototypingDokument1 Seite12 PrototypingJai GaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)