Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
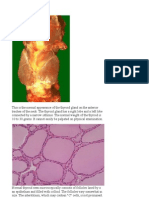
Thyroid Disease
Hochgeladen von
Ziyad0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
241 Ansichten1 SeiteObGyn
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenObGyn
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
241 Ansichten1 SeiteThyroid Disease
Hochgeladen von
ZiyadObGyn
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
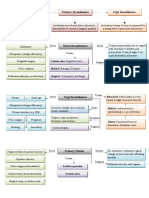
Accurate method of estimating
thyroid function compensates for
GFR Iodine by 50%
Free T4 conc. Thyroid Function Pregnanc
test THYROID DISEASE y
Serum bound T3 and T4
Iodide (freely cross placenta)
Freely
Cross Placent <10 w no iodine in
TSH-Ab (cause fetal thyroid al
thyroid
Transf 11 to 12 w produce T4
Fetal Thyroid
T4 (important for neural Function
development in first trimester >12 w Able to concentrate
Limit
before mature fetal thyroid) ed iodine, and Fetal TSH, T4,
TRH (low circ. levels, not and free T4 mature thyroid
TSH (DOES NOT CROSS) Do Not
Cross
Prematurity Complicati Maternal Hyperthyroidism Incidence 1 per 500
ons pregnancies
IUGR Graves’ disease (most)
Investigatio Treatment
Sympto
ns
Superimposed PET ms
Difficult (many S&S are
Serum free T4 Propylthiouracil (PUT) &
Stillbirth present in normal euthyroid
Methimazole cross
pregnancies)
Neonatal M&M TSH levels placenta (can cause fetal Resting pulse > 100 bpm
hypothyroidism) give (fails to slow with Valsalva
Precipitating minimal dose for within maneuver)
Thyroid Storm factors Radioactive iodine Rx Eye changes, Weight loss,
S&S Heat intolerance
Infection
Surgical Rx only if Medical fails
Hyperthermia Labor
Marked tachycardia Cesarean
Perspiration Noncompliance Maternal Hypothyroidism
Complicati
High output failure Investigati
Treatment on ons
Severe dehydration Spontaneous Abortion
TSH levels (imp)
Propanolol
PET
Neonatal Sodium iodide Neonatal
Abruption
PTU
1% (due to TSH-Ab Congenital Hypothyroidism LBW/Stillbirth
Dexamethesone
Lasts 2 – 3 months Generalized Developmental Lower IQ (cretinism)
Fluid replacement
16% neonatal mortality Etiology: thyroid dysgenesis, inborn
Hypothermic
Fetal HR continently > Most common cause of neonatal goiter
Fetal goiter seen on US is maternal ingestion of iodideds
present in cough syrup
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Lecture 29 30 Thyroid TherapeuticsDokument3 SeitenLecture 29 30 Thyroid TherapeuticsAhmed MashalyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Treatment of HypertensionDokument7 Seiten3 Treatment of HypertensiontiaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionDokument1 SeitePathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionMicroposterNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.1d - Pathology of The Pituitary - Nov.10 - Dr. GalangDokument4 Seiten4.1d - Pathology of The Pituitary - Nov.10 - Dr. GalangMiel Raphael AranillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alarm Symptoms of Hematoonco in Pediatrics: Dr. Cece Alfalah, M.Biomed, Sp.A (K) Pediatric Hematology and OncologyDokument22 SeitenAlarm Symptoms of Hematoonco in Pediatrics: Dr. Cece Alfalah, M.Biomed, Sp.A (K) Pediatric Hematology and OncologyMuhammad ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step 1 DrugsDokument46 SeitenStep 1 DrugsZebram ZeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abx FinalDokument3 SeitenAbx Finalyanks1120Noch keine Bewertungen
- STEP 1 ChecklistDokument11 SeitenSTEP 1 ChecklistHasan Khan RoudbaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemotherapyDokument11 SeitenChemotherapyNedaAbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMDokument8 SeitenApproximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMakane ryuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti FungalsDokument5 SeitenAnti FungalskakuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultimate Pharm GuideDokument41 SeitenUltimate Pharm GuideeanguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, ArrhythmiaDokument14 SeitenWeek 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, Arrhythmiashivani patel100% (1)
- A To Z Diseases LISTS For NEETPGDokument5 SeitenA To Z Diseases LISTS For NEETPGQworldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step1 Review TopicsDokument32 SeitenStep1 Review TopicsAsif AbidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne 2.6 - Benign and Malignant Tumors of The Ovaries and Fallopian TubesDokument8 SeitenGyne 2.6 - Benign and Malignant Tumors of The Ovaries and Fallopian TubesVon HippoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolyte Imbalance Cause Signs and Symptoms Intervention ConnectionDokument6 SeitenElectrolyte Imbalance Cause Signs and Symptoms Intervention ConnectionmkninnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Lab Values (USMLE Step 1)Dokument12 SeitenNormal Lab Values (USMLE Step 1)nmp274Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 2 - Blood VesselsDokument12 SeitenLec 2 - Blood VesselsJeffrey LübbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartDokument6 SeitenMicrobiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartM Patel100% (1)
- Management of Common Cases in Emergency MedicineDokument55 SeitenManagement of Common Cases in Emergency MedicinemonpyitharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharm C Exam 10 Drug ListDokument2 SeitenPharm C Exam 10 Drug ListVokdadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kathynotes PDFDokument103 SeitenKathynotes PDFvarrakeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106Dokument47 SeitenPharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106sean liyanageNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Aid PharmacoDokument61 SeitenFirst Aid PharmacogirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic GuideDokument6 SeitenAntibiotic GuideAnnTran100% (1)
- Antimicrobial Drugs TableDokument19 SeitenAntimicrobial Drugs TableLaylee ClareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport of Critically Ill Adults 2011Dokument1 SeiteTransport of Critically Ill Adults 2011velocity25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Female Genital Tract CancersDokument5 SeitenFemale Genital Tract CancersSolomon Seth SallforsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Medicine #1Dokument167 SeitenInternal Medicine #1Nikhil RayarakulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases - BiochemDokument4 SeitenDiseases - BiochemJay FeldmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meninges, Ventricles - CSF - Study GuideDokument3 SeitenMeninges, Ventricles - CSF - Study Guideshivani patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Chem 1Dokument5 SeitenBio Chem 1Reynaldo RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology TableDokument9 SeitenPharmacology TableMaryam KhushbakhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY WebpathDokument35 SeitenENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY Webpathapi-3766657Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug-Drug InteractionDokument9 SeitenDrug-Drug InteractionHo Shi XianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Medicine Quick TablesDokument276 SeitenInternal Medicine Quick Tablesjoey plouffeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsDokument3 SeitenPatent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsKIANA LOUISE ROMANONoch keine Bewertungen
- Poliomyelitis Haemophilus Influenzae Type B VariecellaDokument4 SeitenPoliomyelitis Haemophilus Influenzae Type B VariecellaJeanna Chong100% (1)
- Classification of The Epilepsies: Purpose: For Clinical DiagnosisDokument25 SeitenClassification of The Epilepsies: Purpose: For Clinical Diagnosisayu rifqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of AnemiaDokument4 SeitenClassification of AnemiaEna PaparićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Path Concept MapsDokument113 SeitenPath Concept MapsAndleeb ImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test LFTsDokument2 SeitenTest LFTsostarburstoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PnemoniaDokument4 SeitenPnemoniadhavalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antifungal Agents: EchinocandinsDokument2 SeitenAntifungal Agents: EchinocandinsCourtney TownsendNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeDokument5 SeitenPost-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeEben Ezar Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immuno Micro VirologyDokument15 SeitenImmuno Micro VirologyReynaldo RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SketchyPath ChecklistDokument1 SeiteSketchyPath ChecklistFajar Raza100% (1)
- Vasculitis MindnodeDokument1 SeiteVasculitis MindnodeToño VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chart - WBC DisordersDokument1 SeiteChart - WBC DisordersSamuel RothschildNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semester 2 Drug ListDokument7 SeitenSemester 2 Drug ListNam_Pham_6481Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trusted Evidence For Confident Clinical Decisions: Resources For Medication, Disease, and ToxicologyDokument10 SeitenTrusted Evidence For Confident Clinical Decisions: Resources For Medication, Disease, and ToxicologyCurcubeuAuroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology A - NSAIDSDokument14 SeitenPharmacology A - NSAIDSselflessdoctorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics Dysmorphology in Pediatrics - MedicoNotesDokument1 SeiteGenetics Dysmorphology in Pediatrics - MedicoNotesJ KPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antimycobacterial Drugs PDFDokument3 SeitenAntimycobacterial Drugs PDFCas BuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolic MRCPCHDokument11 SeitenMetabolic MRCPCHJawwad Masood AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotics in ActionDokument1 SeiteAntibiotics in Actionjuan esteban MonroyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staph. Aureus Staph. Epidermidis Staph. SaprophyticusDokument5 SeitenStaph. Aureus Staph. Epidermidis Staph. SaprophyticusTom PedersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cancer Drugs Drugs Indication Adverse Effects Interaction and ContraindicationDokument5 SeitenCancer Drugs Drugs Indication Adverse Effects Interaction and ContraindicationOndari gisemba OSINDENoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDokument1 SeiteCyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 - Toronto Notes 2011 - GynecologyDokument52 Seiten14 - Toronto Notes 2011 - GynecologyZiyad100% (4)
- Fluid Management in PediatricsDokument3 SeitenFluid Management in PediatricsZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDokument2 SeitenAcyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseZiyad100% (1)
- "Most Common's" in Pediatric CardiologyDokument1 Seite"Most Common's" in Pediatric CardiologyZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Typical CSF Findings in Pediatric MeningitisDokument1 SeiteTypical CSF Findings in Pediatric MeningitisZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruments & IndicationsDokument11 SeitenInstruments & IndicationsZiyad100% (2)
- EndometriosisDokument1 SeiteEndometriosisZiyad100% (1)
- Prenatal Assessment of FetusDokument1 SeitePrenatal Assessment of FetusZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetric BleedingDokument1 SeiteObstetric BleedingZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary IncontinenceDokument1 SeiteUrinary IncontinenceZiyad100% (1)
- BreechDokument1 SeiteBreechZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS Musculoskeletal ReviewDokument12 SeitenMS Musculoskeletal ReviewShayesra-Radina Laja SahibadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology ProjectDokument18 SeitenBiology Projectladheedha69% (13)
- Elbow InjuriesDokument8 SeitenElbow Injuriesapi-3716867100% (2)
- Kumpulan Tugas: Disusun Oleh: Revi Adestika 2008730105Dokument1 SeiteKumpulan Tugas: Disusun Oleh: Revi Adestika 2008730105Revi AdestikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSE Bulletin - March 2024 - RamadanDokument2 SeitenHSE Bulletin - March 2024 - RamadanraiavaniranjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Pathophysiology 6th Edition Jacquelyn L BanasikDokument3 SeitenTest Bank For Pathophysiology 6th Edition Jacquelyn L BanasikKenneth Maestas100% (27)
- Ultraformer Info After CareDokument2 SeitenUltraformer Info After CareFruity FruitcakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRCP Revision NotesDokument14 SeitenMRCP Revision NotesSharanyMustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- USMLE High Yield Internal Medicine Notes-Part I 2020Dokument19 SeitenUSMLE High Yield Internal Medicine Notes-Part I 2020usmlematerials.netNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kajian Pemanfaatan Wolbachia Terhadap Pengendalian DBD Studi Literatur Dan Studi Kasus Pemanfaatan Wolbachia Di YogyakartaDokument14 SeitenKajian Pemanfaatan Wolbachia Terhadap Pengendalian DBD Studi Literatur Dan Studi Kasus Pemanfaatan Wolbachia Di Yogyakartajihan OktafianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDokument2 SeitenNursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverThirdy Aquino82% (28)
- Cardiology WorkBookDokument102 SeitenCardiology WorkBookCastleKGNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSYC 210 Abnormal Psychology: Introduction To Psychology (PSYC 101) or Equivalent Is Strongly Recommended. StudentsDokument8 SeitenPSYC 210 Abnormal Psychology: Introduction To Psychology (PSYC 101) or Equivalent Is Strongly Recommended. StudentsAriadne MangondatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics Practice NCLEX Questions HandoutDokument6 SeitenGenetics Practice NCLEX Questions HandoutAlvin L. Rozier100% (3)
- Muscle and Bone Strenthening ActivitiesDokument14 SeitenMuscle and Bone Strenthening ActivitiesSussy BakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Invasive Diagnostic Instruments: By. Kailash - Pandey Aditya - MayekarDokument32 SeitenNon Invasive Diagnostic Instruments: By. Kailash - Pandey Aditya - MayekarkrupalithakkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder SectionDokument19 SeitenObsessive-Compulsive Disorder Sectionark1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laryngeal CleftDokument4 SeitenLaryngeal CleftjuicyprunesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review 02Dokument2 SeitenReview 02Vicki KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- DfahDokument7 SeitenDfahexpert 60Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guia 6. Trastorno Motor y SensitivoDokument47 SeitenGuia 6. Trastorno Motor y SensitivoLorna Varela ArquinNoch keine Bewertungen
- NRC - Skill Competency Checklist - PainAsessmentOlderAdults - SkillChecklistDokument2 SeitenNRC - Skill Competency Checklist - PainAsessmentOlderAdults - SkillChecklist紅玉練Noch keine Bewertungen
- Happy Family FloaterformDokument5 SeitenHappy Family FloaterformWealthMitra Financial ServicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ortho Neck FemurDokument28 SeitenOrtho Neck FemurgebyfondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Campy Lo Bacterio SisDokument14 SeitenCampy Lo Bacterio SisHarikrishnan NamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canine LeishmaniasisDokument77 SeitenCanine LeishmaniasisPilar Sanchez GuiraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For: Diabetes, High Blood Sugar, Hyperglycemia, DKA, Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Fluid and Electrolytes ImbalanceDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For: Diabetes, High Blood Sugar, Hyperglycemia, DKA, Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Fluid and Electrolytes ImbalanceFhai EscioNoch keine Bewertungen
- XXXXXX 121Dokument11 SeitenXXXXXX 121AndriantkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rodney Vs Death Rabies RadioLab Homework AssignmentDokument1 SeiteRodney Vs Death Rabies RadioLab Homework AssignmentLula Sims 14Noch keine Bewertungen