Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Al06 01
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous yewQtGOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Al06 01
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous yewQtGCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
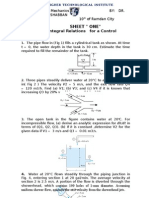
KMEM 3119
Active Learning
Chapter 6 Exercise 1
Problem 1
(Icy
Oil
10C
0.5 m/s
lake, 0C)
D = 0.4 m
Te
L = 300 m
Figure 6-1-1 (Problem 1)
Consider the flow of oil at 10C in a 40-cm-diameter pipeline at an average velocity of 0.5 m/s as in figure 61-1. A 1500-m-long section of pipeline passes through icy waters of lake at 0. Measurements indicate that
the surface of the pipe is nearly 0C. Disregarding the thermal resistance of the pipe material, determine,
(a) the temperature of the oil when the pipe leaves the lake
(b) the rate of heat transfer from the oil
(c) the pumping power required to overcome the pressure losses and to maintain the oil flow in the pipe
Problem 2
Inlet
15C
Water
=3cm
m
Exit
65C
10L/min
L=5m
Figure 6-1-2 (Problem 2)
Water is to be heated from 15C to 65C as it flows through a 3-cm-internal diameter 5-m-long tube as in
figure 6-1-2. The tube is equipped with an electric resistance heater that provides uniform heating
throughout the surface of the tube. The outer surface of the heater is well insulated, so that in steady
operation all the heat generated in the heater is transferred to water in the tube. If the system is to provide
hot water at a rate of 10L/min,
(a) Determine the power rating of the resistance heater.
(b) Estimate the inner surface temperature of the tube at the exit
Problem 3
Glass
cover
20C
Air
30C
0.15 m3/min
60C
Collector
plate
(insulated)
Figure 6-1-3 (Problem 3)
Consider an air solar collector that is 1-m-wide and 5-m-long and has constant spacing of 3-cm between the
glass cover and collector plate as in figure 6-1-3. Air enters the collector at 30C at a rate of 0.15m3/s
through the 1-m-wide edge and flows along the 5-m-long passage way. If the average temperature of the
glass cover and the collector plate are 20C and 60C, respectively, determine
(a) the net rate of heat transfer to the air in the collector
(b) the temperature rise of air as it flows through the collector
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Tutorial Slides (Only Questions) - Internal Forced Convection & Natural ConvectionDokument10 SeitenTutorial Slides (Only Questions) - Internal Forced Convection & Natural ConvectionVivaan SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home Assignment-7 - (Assignment Problems)Dokument2 SeitenHome Assignment-7 - (Assignment Problems)Rounak MajumdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeatTransfer Sheet 4 ForcedConvection QDokument3 SeitenHeatTransfer Sheet 4 ForcedConvection QmondyelgabryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 5Dokument3 SeitenTutorial 5abu fahmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Sheet 4 - Internal Forced Convection - WatermarkDokument1 SeiteProblem Sheet 4 - Internal Forced Convection - WatermarkUzair KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Heat and Mass TransferDokument2 SeitenAdvanced Heat and Mass TransferIbmWasuserNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A14403 Fluid Mechanics & Heat TransferDokument8 Seiten9A14403 Fluid Mechanics & Heat TransfersivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 5Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 5Blue SkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8TUTORIAL5PDFDokument5 Seiten8TUTORIAL5PDFBlue SkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- r5220303 Mechanics of FluidsDokument1 Seiter5220303 Mechanics of FluidssivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 1Dokument4 SeitenSheet 1mohelg83Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 2-Pressure DropDokument2 SeitenSheet 2-Pressure Dropmohelg83Noch keine Bewertungen
- r5220303 Mechanics of FluidsDokument1 Seiter5220303 Mechanics of FluidsSaitheja SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid-Term Test (2022-2023) CHE F343Dokument2 SeitenMid-Term Test (2022-2023) CHE F343Vehaan HandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Tutorials On Convection Heat TransferDokument2 SeitenClass Tutorials On Convection Heat TransferSimon OsemboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 8Dokument4 SeitenAssignment 8Abhilash TilakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angeles - Momentum TransferDokument16 SeitenAngeles - Momentum TransferJaden BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid B SheetDokument7 SeitenFluid B SheetAmr Mustafa MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- PS 3Dokument9 SeitenPS 3naverfallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3 PDFDokument7 SeitenAssignment 3 PDFRima ChinnasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture#5 - Problem SolvingDokument22 SeitenLecture#5 - Problem SolvingAlicann CannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q.1 A Pressure Vessel Contains A Gas at An Initial Pressure of 3.5 MN/MDokument2 SeitenQ.1 A Pressure Vessel Contains A Gas at An Initial Pressure of 3.5 MN/MSUGEET SOODNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial CondensationDokument1 SeiteTutorial Condensationeja70Noch keine Bewertungen
- ADokument5 SeitenAKrishna DheerajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 2Venkitaraj K PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer QuestionsDokument8 SeitenHeat Transfer QuestionsSaeed AlshamsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ass 7Dokument4 SeitenAss 7Puneet MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Forced Convection Question ONLYDokument2 SeitenInternal Forced Convection Question ONLYIzzudin HusseinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of HXDokument5 SeitenDesign of HXvikirhythmNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME Con-2Dokument8 SeitenME Con-2Divyanshu YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Problems StatementDokument21 SeitenTutorial Problems StatementAbni AbhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HEAT TRANSFER 2011 JNTUH Question PaperDokument8 SeitenHEAT TRANSFER 2011 JNTUH Question PaperAnil Frivolous AbstemiousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Department Fluid Mechanics (1), SheetDokument2 SeitenFayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Department Fluid Mechanics (1), SheetMo 16Noch keine Bewertungen
- MEHB323 Tutorial Assignment 7 PDFDokument2 SeitenMEHB323 Tutorial Assignment 7 PDFNirmal Chandra0% (1)
- 3 Avaliacao Grupo1 PDFDokument3 Seiten3 Avaliacao Grupo1 PDFPedro Henrique Fauro De AraujoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME436: Heat Transfer: 1 Flow Over A Flat PlateDokument3 SeitenME436: Heat Transfer: 1 Flow Over A Flat Platerewqrewq5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Dokument4 SeitenQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Ameer Hakeem Primus100% (1)
- ExamDokument3 SeitenExamBiyadgie AlebelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1 (ME206)Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 1 (ME206)deshrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal KONDUKTIVITASDokument2 SeitenSoal KONDUKTIVITASSupriyantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compri QuestionsDokument2 SeitenCompri QuestionsCheryl ChaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 7th and 8thDokument7 SeitenAssignment 7th and 8thSaurabh DeopuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow of Hot Oil Over A Flat Plate:: External Forced ConvectionDokument8 SeitenFlow of Hot Oil Over A Flat Plate:: External Forced Convectionvarshasdm1987100% (1)
- Tutorial Problems-Ch 3Dokument4 SeitenTutorial Problems-Ch 3Aryan NayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serth ProblemsDokument7 SeitenSerth ProblemsRuel CedeñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 6Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 6Vii VyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.forced External ConvectionDokument9 Seiten1.forced External Convectionvarshasdm19870% (1)
- Đề các nămDokument10 SeitenĐề các nămMinh AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2 Heat TransferDokument5 SeitenAssignment 2 Heat TransferolenbearNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tut 3Dokument4 SeitenTut 3SamarthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathcad Project (ChE)Dokument9 SeitenMathcad Project (ChE)UKissMeowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid B SheetDokument7 SeitenFluid B SheetmustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 8Dokument3 SeitenTutorial 8CHANDAN RAJNoch keine Bewertungen
- II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsDokument8 SeitenII B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsAshok DaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example From JB SlidesDokument14 SeitenExample From JB SlidesSangetha Chelladorai0% (3)
- ConvectionDokument2 SeitenConvectionSanith RenjalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cycle Test SOMDokument7 SeitenCycle Test SOMRyan GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Engines Machinery's Reference Series, Number 70Von EverandSteam Engines Machinery's Reference Series, Number 70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison On Types of PipeDokument3 SeitenComparison On Types of PipeAnonymous yewQtGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enter First Line of Text Here Enter Second Line of Text Here Enter Third Line of Text HereDokument1 SeiteEnter First Line of Text Here Enter Second Line of Text Here Enter Third Line of Text HereAnonymous yewQtGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1: Topic: Buildings: Types and FunctionsDokument1 SeiteTutorial 1: Topic: Buildings: Types and FunctionsAnonymous yewQtGNoch keine Bewertungen
- AL1 KEM140039.vi: Upper LimitDokument1 SeiteAL1 KEM140039.vi: Upper LimitAnonymous yewQtGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulate Signal Express VI' To Waveform Graph')Dokument5 SeitenSimulate Signal Express VI' To Waveform Graph')Anonymous yewQtGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Questions Chapter 5 1. 2Dokument1 SeiteReview Questions Chapter 5 1. 2Anonymous yewQtGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Feature (Hole)Dokument2 SeitenInternal Feature (Hole)Anonymous yewQtGNoch keine Bewertungen
- By Parts EgDokument8 SeitenBy Parts EgAnonymous yewQtGNoch keine Bewertungen