Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Williamson PDF
Hochgeladen von
Arwah FerozeOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Williamson PDF
Hochgeladen von
Arwah FerozeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
3/4/14
Amphibian
Immunology
Heather
Williamson
University
of
Tennessee
Department
of
Microbiology
March
4,
2014
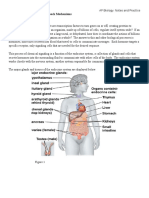
Vertebrate Immunology
Lymphoid Organs
3/4/14
Immunity
First Line of Defense
3/4/14
Innate Immunity: Terminology
Antigen: something foreign or toxic to the cell or body
Macrophages: Big-eater
-role is to phagocytose
-stimulate lymphocytes
-attach foreign substances, infectious
microbes, and cancer cells
Dendritic Cells: Process antigen and present it to cell
surface of T cells of the immune system
-Messengers between innate and adaptive
Natural Killer Cells: Cytotoxic lymphocyte
-rapid response
-release cytokines (signals and
chemicals)
Innate Immunity: Terminology
Pattern Recognition Receptors
-primitive part of the immune system
-found on host cell surface
-recognize pathogen-associated molecular
patterns
Pathogen-associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs)
-molecules associated with groups of pathogens
-activate immune responses
Antimicrobial and serum proteins
-potent, broad spectrum antibiotics
-enhance immunity
3/4/14
Innate Immunity Summary
Non-specic defense mechanisms
Immediately or within hours of anGgen
appearance
Physical barriers, chemicals in the blood,
immune system cells
AcGvated by chemical properGes of the
anGgen (PAMPs)
Adaptive Immunity
3/4/14
Adaptive Immunity: Terminology
T cells (mature in Thymus)
-TC
-TH1
-TH2
Major Histocompatibility Complex Proteins
(Found on Host Cells)
Antigen presenting cell
B cells (produced in the bone marrow)
Antibody
T cells
Type of lymphocyte
Matures in the thymus
CD4 T cells-Helper T cells
-TH1: promote macrophage activation and
cytotoxic T cell proliferation
-TH2: Evoke strong antibody response
CD8 T cells-Cytotoxic T cells
-kills infected/dysfunctional cells
3/4/14
Major Histocompatibility
Complex
Series
of
genes
that
code
for
cell
surface
proteins
controlling
the
adapGve
immune
response.
Class
I
MHC
contains
three
genes;
proteins
from
these
genes
are
expressed
on
almost
all
cells.
Class
II
MHC
genes
contain
3
genes
whose
proteins
are
expressed
on
anGgen-presenGng
macrophages,
dendriGc
cells
and
B
cells.
3/4/14
AnGgen PresenGng Cell (APCs)
Cell that displays foreign antigens complexed with
MHCs on their surfaces (called antigen
presentation
T cells recognize using their T-cell receptors
(TCRs).
Most cells in the body can present antigen to CD8+
(cytotoxic) T cells via MHC class I molecules and
act as APCs
Term is often limited to specialized
cells(macrophages, dendritic cells and B cells) that
generally express MHC class I and II and
stimulate CD4+ (Helper) and CD8+ (cytotoxic) T
cells
3/4/14
B
cells
Formed
in
the
bone
marrow
Has
B
cell
receptor
protein
that
allows
B
cell
binding
to
specic
anGgen
Makes
anGbodies
Develops
into
memory
cells
Memory
3/4/14
AcGve Immune Response Summary
An-gen specic immune response
More complex than innate
AnGgen must rst be processed and
recognized
Once recognized, specic cells a]ack specic
anGgen
Also includes memory
Tolerance
Ability to discriminate self versus non-self
-prevents over reactivity to environmental
stimuli (allergens, normal microbes, etc)
-Important for fetus, organ transplants,
skin grafts
Amphibian Immunity
3/4/14
Xenopus
ConnecGng
taxon
that
links
ancient
vertebrates
and
mammals
ComparaGve
model
of
choice
for
immunological
studies
Li]le
is
known
of
other
amphibians
Great Model
Southern Leopard Frog Eggs
Differences between developmental
stages
10
3/4/14
Juvenile Immunity
11
3/4/14
Larval Immunology
Competent Innate Immune System
Weak Adaptive Immune System
-Small amount of T cells and B cells in
larvae
-NK cells only right before metamorphosis
Immune Remodeling During
Metamorphosis
What is going on during
Metamorphosis?
Tadpoles are free-living so must be protected
against potential pathogens
During metamorphosis, they acquire adult
specific molecules
Must show tolerance to new self molecules
T cell function becomes impaired
Express different antibody repertoire
Lessening of skin graft tolerance
The appearance of MHC class I antigens
Persistence of immunological memory
12
3/4/14
Adult Immunology
Immune system becomes complete 2-3 weeks
after metamorphosis
Strong Innate and adaptive immune responses
-Antimicrobial peptides
-NK cells
-Complement
Adaptive Immune system similar to other
mammals
-Except B cells differentiate mostly in the liver
and spleen (instead of bone marrow)
13
3/4/14
Temperature and Immune Status
Helminth clearance is slower at 15C that 25C
Skin grafts are rejected faster at 27C than at
21C
These and other data suggest selective inhibitory
effect of low temperature on T-cell function
Other modulators of immune
response
Temperature
UV
pH
Predators
Man-made modulators
Psychosocial factors
Xenobiotics
Susceptibility of amphibians
to infectious diseases
14
3/4/14
Review of what you just learned
First defenses of pathogens through the
skin and digestive tract are anti-microbial
peptides
Pathogens are killed by chemical
cascades (complement) and/or
macrophages
Adaptive immune response requires time
to activate in the presence of antigen
-highly specific
-generation of memory cells
Increases in Susceptibility not
simply due to poor immunity
Exposure to new, highly virulent
pathogens
New pathogens are immunosuppressive
Pathogen bloom
Stress response
Environmental contaminants
15
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Transfer Factors: Properties, Mechanism of Action and Its Clinical ApplicationsVon EverandTransfer Factors: Properties, Mechanism of Action and Its Clinical ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunity 2022Dokument53 SeitenImmunity 2022Craft Hachz By dhiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental CariesDokument88 SeitenDental CariesSharlene OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- It 4 - Sel Dan Jaringan Sistim ImunDokument90 SeitenIt 4 - Sel Dan Jaringan Sistim Imunezra soNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSB - Overview of Immune System - Innate and Adaptive - UndergraduatesDokument70 SeitenBSB - Overview of Immune System - Innate and Adaptive - UndergraduatesBumba ArnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 21 - Immunity - NotesDokument60 SeitenChapter 21 - Immunity - NotesLavian Nguyen100% (1)
- IS3 - Antigens and The Major Histocompatibility ComplexDokument30 SeitenIS3 - Antigens and The Major Histocompatibility ComplexnasarcedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Immune System & Lymphoid Organs: Bulseco, Carino, Dinglasan, SalanguitDokument88 SeitenThe Immune System & Lymphoid Organs: Bulseco, Carino, Dinglasan, SalanguitVanessa CarinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptive ImmunityDokument59 SeitenAdaptive ImmunityRowie WanawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptive ImmunityDokument18 SeitenAdaptive Immunityandrewmaleto155Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit II Cells & Organs of ImmuneDokument69 SeitenUnit II Cells & Organs of ImmuneSAMUELNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Immune System - Ksu+Dokument17 SeitenThe Immune System - Ksu+Amit BhadhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptive ImmunityDokument30 SeitenAdaptive ImmunitySedqamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptive Immunity: DR Arsalan Uqaili M.Phil (Physiology)Dokument37 SeitenAdaptive Immunity: DR Arsalan Uqaili M.Phil (Physiology)USAMA AHMEDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Immunology (Revision) : DR Z MakatiniDokument51 SeitenBasic Immunology (Revision) : DR Z MakatiniEstee van WykNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ImmunologyDokument41 SeitenIntroduction To ImmunologyFYMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complement SystemDokument70 SeitenComplement SystemSarvesh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology - Basic Immunology RevisedDokument6 SeitenMicrobiology - Basic Immunology RevisedfilchibuffNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Week Imunologi Sound ADokument26 Seiten4th Week Imunologi Sound AWidya NingsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImmunityDokument27 SeitenImmunityMuhammad Fawad100% (1)
- The Immune SystemDokument150 SeitenThe Immune SystemAshish ChangediyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells and Organs of The Immune SystemDokument34 SeitenCells and Organs of The Immune SystemEmanuel MgheniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antigens: Shashi AnandDokument50 SeitenAntigens: Shashi AnandDil NavabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immune System To Agent InfectionDokument70 SeitenImmune System To Agent Infectionliza yunitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Immune SystemDokument15 SeitenThe Immune SystemAslak Torgersen100% (1)
- Basic Immunology: Dr. Fitriyah Mayorita, SP - PKDokument46 SeitenBasic Immunology: Dr. Fitriyah Mayorita, SP - PKFadhila RizkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immune Response: Cell Biology and Its Application BI-1202Dokument35 SeitenImmune Response: Cell Biology and Its Application BI-1202Eriani Wulandari100% (1)
- Immune SystemDokument45 SeitenImmune SystemShi XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Concept and Components of The Immune SystemDokument25 SeitenBasic Concept and Components of The Immune Systemadankhadija6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 Adaptive Immunity BABS3041 2024Dokument30 SeitenLecture 5 Adaptive Immunity BABS3041 2024pvrajk7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class 05-06Dokument64 SeitenClass 05-06Vinoth Kanna ANoch keine Bewertungen
- General Features of Immune SystemDokument37 SeitenGeneral Features of Immune SystemKiruba HaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 생명 블루오션 강의3 면역Dokument20 Seiten생명 블루오션 강의3 면역kimjihoo778Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elements of The Immune System and Their Roles in DefenseDokument55 SeitenElements of The Immune System and Their Roles in Defensenokate konkoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Mediated ImmunityDokument22 SeitenCell Mediated ImmunityDrJoko SulistyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immuno3 & 4 Q Innate Immunity & ComplementDokument41 SeitenImmuno3 & 4 Q Innate Immunity & Complementmmoney1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of Immunology and Immune SystemsDokument18 SeitenBasic Principles of Immunology and Immune SystemsVictoria &BeautifulPeopleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptive DefenseDokument27 SeitenAdaptive Defenseayesha sanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of The Immune SystemDokument30 SeitenOverview of The Immune SystemNitish SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology: Combined Class (Mental Health Psichatry, Clinical Anastasia, & Clinical Sciences) Year 2 30/03/2022Dokument30 SeitenImmunology: Combined Class (Mental Health Psichatry, Clinical Anastasia, & Clinical Sciences) Year 2 30/03/2022Derick NKANDU KALUBANoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Lecture - Innate Immune Response (2022)Dokument56 SeitenIntegrated Lecture - Innate Immune Response (2022)Nabilah DENoch keine Bewertungen
- Course 11 - ImunochemistryDokument31 SeitenCourse 11 - ImunochemistryPopa NicuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunity 16-1Dokument63 SeitenImmunity 16-1Jude ChinecheremNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Immune SystemDokument31 SeitenThe Immune SystemYesiana Lilis Sugiarti100% (1)
- Foundations in Microbiology: TalaroDokument63 SeitenFoundations in Microbiology: Talaromertx013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Immune OrgansDokument49 SeitenImmune OrgansdenyqueronoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pattern RecognitionDokument22 SeitenPattern RecognitionNadia NasrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunity: Dr. Abhijith D, Assistant Professor, Department of Biochemistry, JSS Medical College, MysooruDokument55 SeitenImmunity: Dr. Abhijith D, Assistant Professor, Department of Biochemistry, JSS Medical College, MysooruSneha ManoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecules, of The Immune SystemDokument39 SeitenMolecules, of The Immune SystemFaith MbasaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction Is S2 Reg 2022Dokument48 SeitenIntroduction Is S2 Reg 2022Al Moazer Abdulaal AbdulateefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immune System: Innate ImmunityDokument5 SeitenImmune System: Innate ImmunityDea EmpamanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic ImmunologyDokument57 SeitenBasic ImmunologyRonalyn UgatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology PDFDokument70 SeitenImmunology PDFstancy thomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImmunityDokument44 SeitenImmunityHam Za100% (1)
- Transplantation and RejectionDokument20 SeitenTransplantation and Rejectionwtapranjal.123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Properties and Overview of Immune ResponsesDokument30 SeitenProperties and Overview of Immune ResponsesVivien KasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- BBC2 Molecular Immunology 2019Dokument24 SeitenBBC2 Molecular Immunology 2019tasyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immune Response and Immunity: Envr 133 Mark D. SobseyDokument27 SeitenImmune Response and Immunity: Envr 133 Mark D. SobseyRochman MujayantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innate & Adaptive Immunity: Innate Immunity Exposure To The Microbe (Antigen) - It Is Nonspecific andDokument14 SeitenInnate & Adaptive Immunity: Innate Immunity Exposure To The Microbe (Antigen) - It Is Nonspecific andSAKARIYE MAXAMEDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 - Intro and Overview of The Immune ResponseDokument67 SeitenTopic 1 - Intro and Overview of The Immune ResponseAmber ChenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mac Peds FormularyDokument45 SeitenMac Peds FormularyLUIS MIGUEL CASTILLA MORANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranialnerve 180324181201 PDFDokument44 SeitenCranialnerve 180324181201 PDFArwah FerozeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranialnerve 180324181201 PDFDokument44 SeitenCranialnerve 180324181201 PDFArwah FerozeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranialnerve 180324181201 PDFDokument44 SeitenCranialnerve 180324181201 PDFArwah FerozeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEDokument18 SeitenCEArwah FerozeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examiners' Report/ Principal Examiner Feedback January 2015Dokument10 SeitenExaminers' Report/ Principal Examiner Feedback January 2015Raiyan RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyrexia of Unknown Origin: Mohd Hanafi RamleeDokument42 SeitenPyrexia of Unknown Origin: Mohd Hanafi RamleeArwah FerozeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyrexia of Unknown Origin: Mohd Hanafi RamleeDokument42 SeitenPyrexia of Unknown Origin: Mohd Hanafi RamleeArwah FerozeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 536 BPG Assessment Foot Ulcer 1Dokument115 Seiten536 BPG Assessment Foot Ulcer 1FebricaPutriArthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Detailed Lesson Plan Practical Research 2Dokument29 SeitenA Detailed Lesson Plan Practical Research 2Erica CanonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Download Test Bank For Ebersole and Hess Gerontological Nursing and Healthy Aging 2nd Canadian Edition by Touhy PDF Full ChapterDokument36 SeitenFull Download Test Bank For Ebersole and Hess Gerontological Nursing and Healthy Aging 2nd Canadian Edition by Touhy PDF Full Chapteradrianblackiadxetkrqm100% (15)
- Persistent Prelethal Stress Leads To Cellular AdaptationDokument14 SeitenPersistent Prelethal Stress Leads To Cellular AdaptationMalliga SundareshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ectopic PregnancyDokument54 SeitenEctopic Pregnancypatriciaatan1497Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tips No Naturally Cure Hemorrhoids FastDokument26 SeitenTips No Naturally Cure Hemorrhoids FastK.l. DhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legends About The Discovery of Fire Key IncludedDokument2 SeitenLegends About The Discovery of Fire Key IncludedSilvia MontesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zat Aktif & PBFDokument153 SeitenZat Aktif & PBFnabilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Winter 2010 Natural FarmerDokument48 SeitenWinter 2010 Natural FarmerV1xWqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Science Competition Practise Questions Years 11 - 12Dokument4 SeitenBig Science Competition Practise Questions Years 11 - 12Happy4314Noch keine Bewertungen
- Community Theatre and AIDS Studies in International Performance PDFDokument194 SeitenCommunity Theatre and AIDS Studies in International Performance PDFgabriella feliciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cataract Consent FormDokument4 SeitenCataract Consent FormHitesh Sharma100% (1)
- GIT Fluid BalanceDokument33 SeitenGIT Fluid BalanceMaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tony Gaddis Python BookDokument5 SeitenTony Gaddis Python BookArslan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Do No Harm by Henry Marsh ExtractDokument15 SeitenDo No Harm by Henry Marsh ExtractAyu Hutami SyarifNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOX-SICK by Suzanne Somers - ExcerptDokument19 SeitenTOX-SICK by Suzanne Somers - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group100% (1)
- Circulatory Disease ProjectDokument2 SeitenCirculatory Disease Projectapi-517831630Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.ALS Algorithms Advanced Life SupportDokument1 Seite3.ALS Algorithms Advanced Life SupportLucian Alin DinuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Samar Deb Easy and Interesting ADokument846 SeitenSamar Deb Easy and Interesting ACharlieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atrial Fibrillation PathophysiologyDokument2 SeitenAtrial Fibrillation PathophysiologyanabbabarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medsurg 3 Exam 1Dokument55 SeitenMedsurg 3 Exam 1Melissa Blanco100% (1)
- Excretion and Homeostasis.Dokument70 SeitenExcretion and Homeostasis.philomenanjuguna72Noch keine Bewertungen
- Budget Justification Fy2021Dokument418 SeitenBudget Justification Fy2021Lisa FabianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal FatigueDokument40 SeitenAdrenal FatigueNimmi Nims67% (3)
- The Endocrine System and Feedback MechanismsDokument8 SeitenThe Endocrine System and Feedback MechanismsJame SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate of Analysis, Quality and Conformity: Certified: ISO 9001:2008, ISO 13485-2003 and WHO GMPDokument3 SeitenCertificate of Analysis, Quality and Conformity: Certified: ISO 9001:2008, ISO 13485-2003 and WHO GMPMitha AriantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatic Encephalopathy and DkaDokument6 SeitenHepatic Encephalopathy and Dkajames garciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.RTRI Principle and Performance 8may2019Dokument34 Seiten5.RTRI Principle and Performance 8may2019ABCDeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dystolic Dysfunction Ppt. SalmanDokument42 SeitenDystolic Dysfunction Ppt. SalmanMustajab MujtabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wild and Ancient Fruit - Is It Really Small, Bitter, and Low in Sugar - Raw Food SOSDokument73 SeitenWild and Ancient Fruit - Is It Really Small, Bitter, and Low in Sugar - Raw Food SOSVictor ResendizNoch keine Bewertungen