Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Nmat Review Physics 1 (Module 1 Exercise) : DIRECTIONS: Select The Best Answer To Each of The
Hochgeladen von
Mia0%(1)0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
264 Ansichten3 SeitenThis document provides a review for a physics exam covering topics like vectors, Newton's laws of motion, kinematics, work, energy, and momentum. It consists of 35 multiple choice questions testing understanding of concepts like resultant vectors, forces, motion, work, energy, impulse, and more. An example question asks the student to determine the direction of the normal force exerted on a box being pushed up an inclined plane based on a diagram.
Originalbeschreibung:
p6
Originaltitel
Physics 1 M-1 AK
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document provides a review for a physics exam covering topics like vectors, Newton's laws of motion, kinematics, work, energy, and momentum. It consists of 35 multiple choice questions testing understanding of concepts like resultant vectors, forces, motion, work, energy, impulse, and more. An example question asks the student to determine the direction of the normal force exerted on a box being pushed up an inclined plane based on a diagram.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0%(1)0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
264 Ansichten3 SeitenNmat Review Physics 1 (Module 1 Exercise) : DIRECTIONS: Select The Best Answer To Each of The
Hochgeladen von
MiaThis document provides a review for a physics exam covering topics like vectors, Newton's laws of motion, kinematics, work, energy, and momentum. It consists of 35 multiple choice questions testing understanding of concepts like resultant vectors, forces, motion, work, energy, impulse, and more. An example question asks the student to determine the direction of the normal force exerted on a box being pushed up an inclined plane based on a diagram.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
NMAT REVIEW
PHYSICS 1
(MODULE 1 EXERCISE)
Figure for Number 8.
DIRECTIONS: Select the best answer to each of the
following questions and blacken the appropriate space on
your answer sheet.
Quantities, Vectors, Newtons Law of Motion
1. length : meter :: _______ : Ampere
a. time
c. luminous intensity
b. temperature
d. current
2. Vector A has a magnitude of 5 in the leftward direction
and B has magnitude of 2 in the rightward direction. What
is the value of 2A B?
a. 12 in the leftward direction
b. 10 in the leftward direction
c. 8 in the leftward direction
d. 8 in the rightward direction
3. Mike is riding his bike at 3 m/s when Carl overtakes
with his bike at 5 m/s. What is Mikes speed relative to
Carls?
a. -2 m/s
b. +2 m/s
c. -8 m/s
d. +8 m/s
4. A single vector that can describe an entire set of
vectors is called:
a. Vector Displacement
c. Resultant Vector
b. Vector Force
d. Vector Arrow
5. Which of the following describes the direction of the
resultant vector, 4 m North of East?
a.
c.
b.
d.
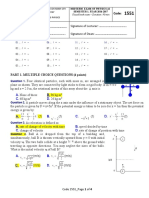
8. A mover pushes a box up an inclined plane, as shown in
the figure. Which of the following shows the direction of
the normal force exerted by the plane on the box?
a.
c.
b.
d.
9. What is the direction
of the force of gravity
on the pendulum bob?
(Refer to the figure)
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
6. _________ is the force with which the Earth pulls an
object on its surface towards its center.
a. Friction Force
c. Weight
b. Normal Force
d. Tension
10. A force F applied to a mass m1 accelerates the body
by a1, what will be the new acceleration if the mass is
doubled and the same force is applied?
a. half the original value
b. the same as the original value
c. double the original value
d. three times the original value
7. What is the resultant vector of the figure below?
A = 17 N
11. A man is pulling a cart full of gravel. What is the
direction of the frictional force of the cart?
a.
c.
B=5N
a. 12 N, due East
b. 12 N, due West
b.
c. 22 N, due East
d. 22 N, due West
d.
107
12. A. 30-kg boy sits down on one side of a see-saw, 2.0
m from the fulcrum. Where must a 40-kg boy sit on the
other side to keep the see-saw balanced?
30 kg
40 kg
2m
a. on the fulcrum
b. 1.5 m from the fulcrum
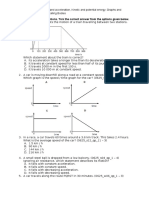
20. How is the v-t graph best described?
a. constants velocity
v
b. constant acceleration
c. constant deceleration
d. zero acceleration
?m
c. 2.0 m from the fulcrum
d. 2.67 m from the fulcrum
13. What will be the new force of gravitation if the mass
of body A is halved and the mass of body B is doubled,
while the separation beetween them increases to thrice
the original?
1
a. the original
c. 3 times the original
9
1
b. the original
d. 9 times the original
3
14. How far should an 18-kg sphere be from a 2-kg
sphere if their force of gravitation must be equal to the
gravitational constant G? (G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2)
a. 1 m
b. 3 m
c. 6 m
19. A car travels 50 km from Manila to Laguna for 40
mins. But due to heavy traffic, the return trip took him 60
mins. What is the average speed of the car (in km/hr)
during the whole trip?
a. Zero
b. 57.5 km/hr
c. 60 km/hr
d. 62.5 km/hr
d. 9 m
15. If the gravitational force of a certain planet is
21. Which motion is characterized by a constant speed?
a. uniformly accelerated motion
b. uniform circular motion
c. constant deceleration
d. zero acceleration
22. A climbers bag might fall from a cliff. If he is 45 m
above, how long will it take his bag to reach the ground?
a. 1.5 s
b. 3.0 s
c. 6.0 s
d. 9.0 s
23. How fast is the bag as it is about to reach the ground?
a. 15 m/s
b. 30 m/s
c. 60 m/s
d. 90 m/s
24. Which of the following statement is/are true about a
particle undergoing free fall?
I. If a particle is thrown vertically upward with a speed of
5 m/s, the speed of the particle as it hits the same spot on
its way down is also 5 m/s.
II. The gravitational acceleration of a particle is the same
on Earth and on the moon.
III. In free fall, the lighter particle will fall faster than the
heavier particle.
IV. The constant acceleration g means that the velocity of
a particle falling down and undergoing free fall increases
by g every second.
a. I and II
b. III and IV
c. II and III
d. I and IV
that of
4
the Earth, what will be the weight of an object in that
planet if the object has a mass of m on Earth?
1
3
4
a. (mg)
b. (mg)
c. 2 (mg)
d. (mg)
2
4
3
25. A bungee jumper started from the ramp with an initial
horizontal velocity of 10 m/s. If the ramp is 100 m high
and he was able to touch the ground, how long will it take
for him to touch the ground?
a. 4.5 s
b. 9.0 s
c. 13.5 s
d. 18.0 s
Kinematics, Linear Motion, Projectile and
Uniform Circular Motion
26. From number 25, how far would he be from the ramp?
a. 45 m
b 90 m
c. 135 m
d. 180 m
16. Which of the following are fundamental units of
physical mechanics?
a. mass, time and length
b. mass, temperature and speed
c. time, length and speed
d. time, temperature and speed
17. A boy starts from their house and walks around a
square block, and ends up in front of his house again. If
one side of a block is around 100 m, what is the total
distance travelled by the boy?
a. Zero
b. 100 m
c. 200 m
d. 400 m
18. What is the displacement of the boy?
a. Zero
b. 100 m
c. 200 m
d. 400 m
27. A motorcycle rides off the edge of a cliff. Just at the
edge, its velocity is horizontal, with a magnitude of 8 m/s.
What is the initial downward velocity of the motorcycle?
a. 0 m/s
c. 8 m/s
b. 4 m/s
d. cannot be determined
28. What is the horizontal component of the final velocity
as the motorcycle hits the ground on number 29?
a. 0 m/s
c. 8 m/s
b. 4 m/s
d. cannot be determined
Work, Energy, Power & Impulse and Momentum
29. Which of the following does not belong to the group?
a. energy
b. force
c. power
d. work
108
30. By what factor was the kinetic energy changed if the
mass is doubled and the velocity is halved?
a. Same as the original
c. One-fourth of the original
b. Four times the original
d. One-Half of the original
31. Norman is driving his car to work when the engine
stopped 5 m from the parking lot. If he pushes the car in
the direction of motion with a constant force of 7 kN, how
much work is done on the car?
a. 35 J
b. 35 kJ
c. 70 J
d. 70 kJ
32. To an ordinary person, carrying a load while walking
across a level ground is performing a work. To a physicist,
there is no work done in carrying the load because
_______
a. there is no force on the load
b. there is no displacement of the load
c. the force on the load is perpendicular to its
displacement
d. the force on the load is opposite to the displacement
33. What is the kinetic energy of a 2.0-kg object moving
at 10 m/s?
a. 10 J
b. 20 J
c. 100 J
d. 200 J
34. Which of the following does not show work?
a. climbing a flight of stairs
b. lifting a chair
c. pulling a toy truck
d. rocking on a rocking chair
35. The diagram below shows a 50-kg crate on a
frictionless plane at angle 0 to the horizontal. The crate is
pushed at constant speed up the incline from point A to
point B by force F.
If angle 0 were increased, what would be the effect on the
magnitude of force F and the total work W done on the
crate as it is moved from A to B ?
a. W would remain the same and the magnitude of F
would decrease.
b. W would remain the same and the magnitude of F
would increase.
c. W would increase and the magnitude of F would
decrease.
d. W would increase and the magnitude of F would
increase.
109
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Physics 71 1 Long Sample ExamDokument4 SeitenPhysics 71 1 Long Sample ExamManna Pinto100% (1)
- MIDTERM EXAMINATION in GENERAL PHYSICS 1 TEST IDokument12 SeitenMIDTERM EXAMINATION in GENERAL PHYSICS 1 TEST Izamora pegafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector and Kinematics Problems AnswersDokument14 SeitenVector and Kinematics Problems AnswersAhmed aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics I Quiz #2 - Kinetic and Potential Energy ProblemsDokument9 SeitenPhysics I Quiz #2 - Kinetic and Potential Energy ProblemsNathaly SosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors PhysicsDokument6 SeitenVectors PhysicsFurqan HyderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro Physics Instructors Guide Semester1 AppendixADokument63 SeitenIntro Physics Instructors Guide Semester1 AppendixAGfour Maserati50% (2)
- Kinematics and DynamicsDokument16 SeitenKinematics and DynamicsmartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Test in Grade 9 ScienceDokument3 SeitenSummative Test in Grade 9 ScienceApolonio Pamittan Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sem1 Exam GPDokument3 SeitenSem1 Exam GPJumz BoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MT2 Practice Fall 07Dokument3 SeitenMT2 Practice Fall 07Seljen AceNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExIF04 PDFDokument13 SeitenExIF04 PDFAB:brilliant thanks alot sir. G4MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For College Physics 8th EditionDokument24 SeitenTest Bank For College Physics 8th EditionAlbert Ascher100% (34)
- 4TH Quarter - Science 9Dokument7 Seiten4TH Quarter - Science 9MARIA THERESA TULALINoch keine Bewertungen
- Sem 1 Practice FinalDokument32 SeitenSem 1 Practice FinalJuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- REVISION QUESTIONS PHY094 CHAPTER 1-4Dokument8 SeitenREVISION QUESTIONS PHY094 CHAPTER 1-4NURUL FARRAH LIEYANA BT SHAMSUL BAHARINoch keine Bewertungen
- I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDokument3 SeitenI. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerNeil VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test of Competence: A. Cross Out The Correct Answer. (35 Points)Dokument4 SeitenTest of Competence: A. Cross Out The Correct Answer. (35 Points)Ms Yosela MaharaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Phys C Fall Final Web RevDokument12 SeitenAP Phys C Fall Final Web RevNadhya FadlillahNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPH4C Physics Grade 12 College Exam Review Package Unit 1 MotionDokument30 SeitenSPH4C Physics Grade 12 College Exam Review Package Unit 1 MotionKhristine Khate Odiaman MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINAL EXAMINATION FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCEDokument2 SeitenFINAL EXAMINATION FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCEbernadeth m. barajasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2007 EUEEDokument8 SeitenPhysics 2007 EUEElikinaw demisieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviwer in Gen. Physics 1Dokument4 SeitenReviwer in Gen. Physics 1Romero, Ken Angelo B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDokument3 SeitenI. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerNeil VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced PhysicsDokument5 SeitenAdvanced PhysicsMichelle MalataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics MCQDokument6 SeitenEngineering Mechanics MCQeafz111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test-Questions-Physics IDokument7 SeitenTest-Questions-Physics INheszie Cortez MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Examination in General Physics 1Dokument10 SeitenMidterm Examination in General Physics 1zamora pegafi100% (2)
- Gravity and Energy Multiple Choice PracticeDokument11 SeitenGravity and Energy Multiple Choice PracticeJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 201 (003N) Fall 2010 - Midterm I.AnswersDokument7 SeitenPhysics 201 (003N) Fall 2010 - Midterm I.AnswersXiao LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 11 Pop Quiz Jan 2013Dokument4 SeitenGrade 11 Pop Quiz Jan 2013Jerrord ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force, Motion and EnergyDokument18 SeitenForce, Motion and EnergyTushitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Physics sp01Dokument19 Seiten11 Physics sp0138 Ritik GurjarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Test in General Physics Multiple ChoiceDokument4 SeitenUnit Test in General Physics Multiple ChoiceDina Mita100% (1)
- Sample Midterm Sum 12Dokument7 SeitenSample Midterm Sum 12Mt RushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Cumulative Review: Part I: KinematicsDokument38 SeitenMultiple Choice Cumulative Review: Part I: Kinematics张书Noch keine Bewertungen
- AGA KHAN SCHOOLS, SOUTH First Term Examination, November 2020 Physics Class IX (Science Group) Paper I (ADokument12 SeitenAGA KHAN SCHOOLS, SOUTH First Term Examination, November 2020 Physics Class IX (Science Group) Paper I (AHaseeb MirzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Energy and PowerDokument14 SeitenWork Energy and Powerfakintunde912Noch keine Bewertungen
- Force and Motion: Key Concepts of Forces, Moments, Equilibrium, Energy, Work and PowerDokument62 SeitenForce and Motion: Key Concepts of Forces, Moments, Equilibrium, Energy, Work and PowerMerin0% (1)
- (UPOU) PHYSICS Pre-TestDokument14 Seiten(UPOU) PHYSICS Pre-TestMon Belle AmourNoch keine Bewertungen
- 103 F 05 Exam 1Dokument7 Seiten103 F 05 Exam 1Raufzha AnandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 UreviewDokument34 Seiten4 Ureviewumchemist2Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Summative Test Science 9Dokument3 Seiten4th Summative Test Science 9odette carzanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Physics SPDokument4 Seiten11 Physics SPvikas vyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nsci 111Dokument70 SeitenNsci 111Ed Pasion100% (2)
- 2100ex2s03 PDFDokument7 Seiten2100ex2s03 PDFAnubhav SwaroopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Test I Kinematics MCQDokument10 SeitenModel Test I Kinematics MCQKarlie NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex3mech 2019Dokument8 SeitenEx3mech 2019Nasim RazaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers Foundations and Connections 1St Edition Katz Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument41 SeitenPhysics For Scientists and Engineers Foundations and Connections 1St Edition Katz Test Bank Full Chapter PDFBrendaTaylorwzab100% (7)
- Physics 4A Conceptual Questions on Vectors and KinematicsDokument6 SeitenPhysics 4A Conceptual Questions on Vectors and KinematicsdsowmNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Phys1 Kinematics 2 D Practice Problems 2016-10-06Dokument17 SeitenAP Phys1 Kinematics 2 D Practice Problems 2016-10-06JabeenAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS SUMMATIVE TESTDokument5 SeitenPHYSICS SUMMATIVE TESTJasmin SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- XI Mock TestDokument15 SeitenXI Mock TestDont KnowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Exam 2016-2017-01Dokument4 SeitenMidterm Exam 2016-2017-01Gia Hân EmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ on Force and MomentDokument26 SeitenMCQ on Force and MomentKolakotla Sharath chandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For College Physics 8th EditionDokument24 SeitenTest Bank For College Physics 8th EditionlouisadonaldlwrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Grade 9 TQDokument9 SeitenScience Grade 9 TQLae GadgudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 11Dokument9 SeitenPhysics 11NasimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Reyes Part 2Dokument4 SeitenReyes Part 2MiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reyes Part 2Dokument4 SeitenReyes Part 2MiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical ChemistryDokument2 SeitenClinical ChemistryMiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histopathology PDFDokument1 SeiteHistopathology PDFMiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reyes Part 2Dokument4 SeitenReyes Part 2MiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phlebotomy WorksheetDokument1 SeitePhlebotomy WorksheetMiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 27aDokument228 SeitenChapter 27aMiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reyes Part 2Dokument4 SeitenReyes Part 2MiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacte Summary 2Dokument9 SeitenBacte Summary 2Gio Tamaño Balisi100% (2)
- Unit 1. Introduction To Clinical Chemistry 1Dokument107 SeitenUnit 1. Introduction To Clinical Chemistry 1MiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical MicrosDokument2 SeitenClinical MicrosMiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Banking and SerologyDokument9 SeitenBlood Banking and SerologyMiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CL Application Form 24mar08Dokument5 SeitenCL Application Form 24mar08MiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuotqsheethemaDokument3 SeitenQuotqsheethemakthmntsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 HemaDokument35 Seiten1 HemaMiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hours 8 24 16 OFF 24 OFF Post Sero 8-4 HEMA 4-8 Xmatch F24D Xmatch FND 8-4 SERO 4-8 Xmatch F24DDokument1 SeiteHours 8 24 16 OFF 24 OFF Post Sero 8-4 HEMA 4-8 Xmatch F24D Xmatch FND 8-4 SERO 4-8 Xmatch F24DMiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medtech LawDokument16 SeitenMedtech LawClaudine David0% (1)
- Hours 8 24 16 OFF 24 OFF Post Sero 8-4 HEMA 4-8 Xmatch F24D Xmatch FND 8-4 SERO 4-8 Xmatch F24DDokument1 SeiteHours 8 24 16 OFF 24 OFF Post Sero 8-4 HEMA 4-8 Xmatch F24D Xmatch FND 8-4 SERO 4-8 Xmatch F24DMiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biostat Laboratory Activity2Dokument2 SeitenBiostat Laboratory Activity2MiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sleep Deprivation Lowers Teen Hemoglobin LevelsDokument1 SeiteSleep Deprivation Lowers Teen Hemoglobin LevelsMiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biostatistics Reflection 2Dokument1 SeiteBiostatistics Reflection 2MiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fresh Tissue Examination and Fixation MethodsDokument9 SeitenFresh Tissue Examination and Fixation MethodsKate Alyssa Caton100% (11)
- BloodlustDokument1 SeiteBloodlustRazzab BbanurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Historical Background and Key People in MicrobiologyDokument2 SeitenHistorical Background and Key People in MicrobiologyMiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino AcidsDokument3 SeitenAmino AcidsMiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biostat Laboratory Activity2Dokument2 SeitenBiostat Laboratory Activity2MiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gynecologist CV TemplateDokument6 SeitenGynecologist CV TemplateSingh ViratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histopathologic TechniquesDokument60 SeitenHistopathologic TechniquesMiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCL ReflectionDokument1 SeiteSCL ReflectionMiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Noether TheoremDokument5 SeitenNoether Theoremmikolaj_bugzillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Consevation of MoventumDokument77 Seiten11 Consevation of MoventumRamachandranPerumalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legrangian FormalismDokument12 SeitenLegrangian FormalismSreelakshmi AnilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetic Energy and the Possibility of Over UnityDokument11 SeitenKinetic Energy and the Possibility of Over Unitylzk2d2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic Solution of Euler's Equations of Motion For An Asymmetric Rigid BodyDokument18 SeitenAnalytic Solution of Euler's Equations of Motion For An Asymmetric Rigid Bodyheavy-metalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lathe Cutting Tool Displacement RankingDokument8 SeitenLathe Cutting Tool Displacement RankingVogelNoch keine Bewertungen
- PST 3dplotDokument67 SeitenPST 3dplotMedina HalidovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frontiers in Relativistic Celestial MechDokument372 SeitenFrontiers in Relativistic Celestial MechCarl MarksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter5A TorqueDokument32 SeitenChapter5A TorqueShuq Faqat al-FansuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy 101 Mega Solved FileDokument281 SeitenPhy 101 Mega Solved FileShahbaz Naeem0% (2)
- Chapter 14 Kinetics of Particle - Work & EnergyDokument37 SeitenChapter 14 Kinetics of Particle - Work & Energyحزيفہ اعظمNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equation SheetDokument2 SeitenEquation Sheettw2121100% (1)
- DIMENSIONINGDokument30 SeitenDIMENSIONINGTsa ChaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HKDSE Physics Part - 2 MechanicsDokument17 SeitenHKDSE Physics Part - 2 MechanicsdexterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics I Problems PDFDokument1 SeitePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ilo emDokument4 SeitenIlo emAnonymous 3VNugnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 7 Long TestDokument1 SeiteScience 7 Long TestKarena WahimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speed, Velocity and Acceleration: Graphs, Equations and Falling BodiesDokument4 SeitenSpeed, Velocity and Acceleration: Graphs, Equations and Falling Bodieskeyur.galaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Circular MotionDokument43 SeitenChapter 7 Circular MotionMuhammad ZuhilmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior General Physics 1 q1 Module 3Dokument26 SeitenSenior General Physics 1 q1 Module 3arcyeliefaithcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extra Physics Rotational ProblemsDokument4 SeitenExtra Physics Rotational ProblemsjohnnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Electrodynamics of Spinning Magnets PDFDokument5 SeitenOn The Electrodynamics of Spinning Magnets PDFMenelao ZubiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worm HoleDokument6 SeitenWorm Holedevilboyz_raj1835Noch keine Bewertungen
- GoT PDFDokument182 SeitenGoT PDFUma Bhattacharyya100% (1)
- Spatial Database Practicum Topology ModuleDokument18 SeitenSpatial Database Practicum Topology ModulegiokruthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular Motion ProblemsDokument11 SeitenCircular Motion ProblemsPiyush PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Quiz 2 - CIV191.PDF Version 1Dokument1 SeiteFinal Quiz 2 - CIV191.PDF Version 1Harvey MorosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difficulties With The Klein-Gordon Equation: Apeiron, Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2004 1Dokument18 SeitenDifficulties With The Klein-Gordon Equation: Apeiron, Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2004 1shiravandNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Scalars and VectorsDokument3 Seiten02 Scalars and VectorsomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alexander Burinskii - Two Stringy Systems of The Kerr Spinning ParticleDokument22 SeitenAlexander Burinskii - Two Stringy Systems of The Kerr Spinning ParticleSteam29Noch keine Bewertungen