Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
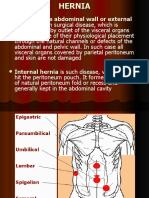
6.examination of Inguinal Swelling
Hochgeladen von
Muvenn KannanOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
6.examination of Inguinal Swelling
Hochgeladen von
Muvenn KannanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Examination of Inguinal Swelling
1.When examining an inguinal swelling,extra test are required to be done to detect hernia.
2.Thus,when examining an inguinal swelling,it is also required to include the steps used in
Examination of Lumps,and the additional steps specific to inguinal swelling.
3.In this section,the additional steps will be discussed.
Inspection-Done when the patient is standing
1.Extent-Whether is it localized to the specific site or extends into the scrotum(Inguinoscrotal
hernia)
2.Visible peristalsis-May be visualized in inguinal hernia,not in femoral hernia or other
swellings
3.Cough impulse-Ask the patient to cough will inspecting the superficial inguinal ring
-Positive if a mass bulges or any existing mass expands.Specific for hernia.
Palpation
1.Determine if it is a Hernia,and its content
i)Cough impulse-A finger is placed on the swelling,and patient coughs
-Positive if a mass can be felt bulging or expanding.Specific for hernia
*In irreducible hernias,cough impulse may be negative
ii)Reducibility-Done to determine the nature of the hernia(Reducible or irreducible hernia)
-Also to determine the content of the hernia
a)Omentocele- When reducing hernia, initially it is easy but eventually it gets
harder
-Gurgling sound is absent
-Doughy consistency
b)Enterocele- When reducing hernia, initially it is hard but eventually it gets
easier
-Gurgling sound is present
-Cystic consistency
2.Differentiate Inguinal from Femoral hernia
i)Pubic tubercle-The pubic tubercle is palpated and the swelling is inspected in relation to
the pubic tubercle
-Inguinal hernia is medial to it,femoral hernia is lateral to it.
3.Type of inguinal hernia (Direct vs indirect hernia)
i)Ring occlusion test-Done in the standing position,and the hernia is first reduced
-A thumb is pressed on the deep inguinal ring,and the patient is asked to
cough
-In indirect hernia,the swelling will not bulge.For direct hernia,the
swelling will bulge medial to the deep inguinal ring.
*For femoral hernia,this is done at the saphenous opening(4 cm below and lateral to pubic
tubercle).It will be positive.
ii)Invagination test
-Locate superficial inguinal ring from bottom of scrotum upwards
-Reduce the hernia, put finger on the ring, then ask patient to cough
-If indirect hernia, hernia bulge will hit the tip of the finger (can be blocked)
-If direct hernia, hernia bulge will hit the pulp of finger (cannot be blocked)
4.Inguinoscrotal hernia vs Scrotal swelling(Only done for inguinoscrotal hernia)
i)To get above the mass-Done in presence of inguinoscrotal extention.
-The scrotum is held with thumb in front,and other fingers
behind.The scrotum is carefully felt and palpated form bottom to top
-In isolated scrotal swelling,can get above.In inguinal hernia,mass
cannot be felt above
Percusion-Resonant if hernia consists of enterocele.Dull if hernia consist of omentocele.
Auscultation-Bowel sounds can be heard if hernia consists of enterocele
At the end of examination, describe the findings
1. Right or Left
2. Inguinal or Femoral
3. Direct or Indirect
4. Content Enterocele or Omentocele
5. How far it go?
Complicated or Uncomplicated(Irreducible,obstructed,strangulated)
Differential Diagnosis of inguinal Swelling
1.Inguinal hernia-Medial to pubic tubercle
i)Direct hernia-Deep ring occlusion test is negative
ii)Indirect hernia-Deep ring occlusion test is positive
2.Femoral Hernia-Lateral to the pubic tubercle
-Cough impulse is positive when the saphenous opening is located
-Deep occlusion test is positive if the saphenous opening is occluded
3.Spermatic cord enlargement
i)Encysted hydrocele of the cord-A cystic swelling.Fluctuation and translucency is positive
ii)Lymph varix-A condition where lymphatic vessels of the cord becomes dilated due to
obstruction caused by filariasis
-Palpation,it is cystic.Cough impuse is thrill like,rather than expansile.
iii)Diffuse lipoma-Irreducible,no impulse on coughing
4.Testis
i)Undescended testis-Usually within the inguinal canal
ii)Ectopic testis-Usually above and lateral to the superficial inguinal ring
Important landmarks
1.Pubic tubercle-2.5 cm lateral to the pubic symphysis(midline)
2.Superficial inguinal ring3.Deep inguinal ring- Midway between ASIS and pubic tubercle,2-3 cm above that point
4.Saphenous opening-3-4 cm inferiorly and laterally to pubic tubercle
5.Inguinal ligament-Runs from pubic tubercle to ASIS
-Formed by aponeurosis of external oblique,and continues as fascia lata of
the thigh
Differential Diagnosis of Femoral Hernia
1.Saphena varix-Saccular enlargement of the termination of the long saphenous
vein.Associated with varicose vein
-Schwartzs test:Percussion of the varicose vein will transmit impulse to the
saphena varix,which can be felt by the fingers
2.Enlarged lymph node-A serch for infection should be made
3.Femoral aneurysm-There will be expansile pulsation
4.Psoas abscess-Cold abscess which tracks down from Potts Disease
5.Lipoma
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandGastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Inguinal Hernia EditedDokument34 Seiten1 Inguinal Hernia EditedNadhirah ZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyVon EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hernia: Inguinal - Surgical Anatomy, Presentation, Treatment, ComplicationsDokument43 SeitenHernia: Inguinal - Surgical Anatomy, Presentation, Treatment, ComplicationsFobin VargheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hernia Examination SchemeDokument4 SeitenHernia Examination Schemeatribecalledquest20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Systemic Surgery NuggetsDokument17 SeitenSystemic Surgery NuggetsAhmad UsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSCE Checklist - Hernia Examination-1Dokument1 SeiteOSCE Checklist - Hernia Examination-1singhurvashi365Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stoma Examination OSCE GuideDokument5 SeitenStoma Examination OSCE GuideEssa AfridiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LEC 15.1 - Abdominal HerniasDokument37 SeitenLEC 15.1 - Abdominal HerniasTudor CorneaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Diagnosis Pain Right HypochondriumDokument35 SeitenDifferential Diagnosis Pain Right HypochondriumDrArish Mahmood100% (1)
- MCQingeneralsurgeryforundergraduates PDFDokument259 SeitenMCQingeneralsurgeryforundergraduates PDFNAVANEETHAKRISHNANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases of Esophagus & Dysphagia: Dr. Vishal SharmaDokument146 SeitenDiseases of Esophagus & Dysphagia: Dr. Vishal SharmaMohamed KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carcinoma StomachDokument43 SeitenCarcinoma StomachRukman Mecca100% (1)
- Case Presentation Lump Right HypochondriumDokument22 SeitenCase Presentation Lump Right HypochondriumNANDAN RAINoch keine Bewertungen
- SurgeryDokument14 SeitenSurgeryVinit ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatric Surgery 2Dokument38 SeitenPaediatric Surgery 2عمار عارفNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical History For ULCER & LumpDokument94 SeitenSurgical History For ULCER & LumpAbdullah MatarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Examination of The AbdomenDokument13 SeitenClinical Examination of The AbdomenNur Miladiyah100% (1)
- History Taking For CholelithiasisDokument6 SeitenHistory Taking For CholelithiasisToria053Noch keine Bewertungen
- PeritonitisDokument19 SeitenPeritonitisAditya SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Abscess Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDokument2 SeitenLiver Abscess Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsAdi Kurnia100% (1)
- ANDI DR Louis Jordaan - 2Dokument9 SeitenANDI DR Louis Jordaan - 2aprooolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question: 1 of 100 / Overall Score: 80%: True / FalseDokument84 SeitenQuestion: 1 of 100 / Overall Score: 80%: True / FalseGalaleldin AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- HerniaDokument11 SeitenHerniaRizka JamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal Pain EmqDokument2 SeitenAbdominal Pain EmqZohaib Iqbal100% (1)
- Powerpoint: Disorders of The EsophagusDokument65 SeitenPowerpoint: Disorders of The Esophagusj.doe.hex_8782% (11)
- Экз. воп для 5-го курса на англ. 200 вопросовDokument32 SeitenЭкз. воп для 5-го курса на англ. 200 вопросовKumar AdityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examination of Abdominal Lump: DR Rajesh P SDokument20 SeitenExamination of Abdominal Lump: DR Rajesh P SdrrajeshpsmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyloric StenosisDokument23 SeitenPyloric StenosisRama ItachiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of OesophagusDokument25 SeitenAnatomy of OesophagusRabi SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neck Examination PDFDokument2 SeitenNeck Examination PDFNizam Mischievous'Lovely Schremo BoyysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scrotal SwellingDokument40 SeitenScrotal Swellingeirene simbolonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal Pain Content PDFDokument71 SeitenAbdominal Pain Content PDFyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Abdomen &peritonitisDokument63 SeitenAcute Abdomen &peritonitisSamar Ahmad100% (1)
- Intestinal Atresia and StenosisDokument7 SeitenIntestinal Atresia and StenosisMichael NafarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pancreatic Cancer: Aziz Ahmad, MD Surgical Oncology Mills-Peninsula Hospital April 23, 2011Dokument18 SeitenPancreatic Cancer: Aziz Ahmad, MD Surgical Oncology Mills-Peninsula Hospital April 23, 2011mywifenoor1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Surgery: Review Questions: Self-Assessment in General SurgeryDokument3 SeitenPediatric Surgery: Review Questions: Self-Assessment in General Surgerymkct111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Benign Anorectal Conditions: Ahmed Badrek-AmoudiDokument20 SeitenBenign Anorectal Conditions: Ahmed Badrek-AmoudiAna De La RosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Omphalocelevsgastroschisis 160810122732Dokument23 SeitenOmphalocelevsgastroschisis 160810122732LNICCOLAIO100% (1)
- Approach To Patients With Inguinoscrotal Masses: Section of Urology Department of Surgery The Medical CityDokument43 SeitenApproach To Patients With Inguinoscrotal Masses: Section of Urology Department of Surgery The Medical CityKevin Eric SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgery - Pediatric GIT, Abdominal Wall, Neoplasms - 2014ADokument14 SeitenSurgery - Pediatric GIT, Abdominal Wall, Neoplasms - 2014ATwinkle SalongaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SURGERYFinals - 1. The AppendixDokument10 SeitenSURGERYFinals - 1. The AppendixRenatoCosmeGalvanJuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic - Diaphragmatic HerniasDokument13 SeitenTopic - Diaphragmatic HerniasOlga CerlatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculous Biliary DiseaseDokument71 SeitenCalculous Biliary DiseaseMinnossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgery BookDokument95 SeitenSurgery BookKhaled Mahmud100% (1)
- Inguinal Hernia SlidesDokument42 SeitenInguinal Hernia SlidesEzekiel Arteta100% (1)
- Perforated Gastric UlcerDokument18 SeitenPerforated Gastric UlcerNorshahidah IedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Large Bowel Obstruction by Nic MDokument42 SeitenLarge Bowel Obstruction by Nic MRisky OpponentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benign Prostatic HypertrophyDokument111 SeitenBenign Prostatic HypertrophyOnkar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examination of Salivary GlandsDokument29 SeitenExamination of Salivary GlandsSamchristy MammenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breast QDokument6 SeitenBreast Qfatima chrystelle nuñalNoch keine Bewertungen
- HyphemaDokument19 SeitenHyphemaLiyanti RinceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gall Stone Disease: DR M.farhad General SurgeonDokument56 SeitenGall Stone Disease: DR M.farhad General SurgeondrelvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case of Obstructive JaundiceDokument38 SeitenCase of Obstructive JaundiceadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 - Gallbladder StonesDokument71 Seiten17 - Gallbladder StonesRashed Shatnawi100% (1)
- Pyloric StenosisDokument14 SeitenPyloric Stenosisgangguan hepatobilierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anal Fissure: BY Alisha SaleemDokument7 SeitenAnal Fissure: BY Alisha Saleemashar khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Right Ventricular Myocardial InfarctionDokument43 SeitenRight Ventricular Myocardial Infarctionrudresh m g0% (2)
- Acute Limb IschemiaDokument16 SeitenAcute Limb IschemiaMohammad Husni BanisalmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Trauma and Life Support (Atls) : by Anu Sandhya PG Ward 3Dokument34 SeitenAdvanced Trauma and Life Support (Atls) : by Anu Sandhya PG Ward 3Muvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Age Related Macular DegenerationDokument35 SeitenAge Related Macular DegenerationMuvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.hypertensive Disorders in PregnancyDokument8 Seiten2.hypertensive Disorders in PregnancyMuvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pleural Effusion OSPEDokument2 SeitenPleural Effusion OSPEMuvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatoid Arthritis MEQDokument3 SeitenRheumatoid Arthritis MEQMuvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastric Carcinoma: H. Pylori InfectionDokument7 SeitenGastric Carcinoma: H. Pylori InfectionMuvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meq 1 Paediatrics: Marks)Dokument4 SeitenMeq 1 Paediatrics: Marks)Muvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Changes in Chamber EnlargementDokument16 SeitenECG Changes in Chamber EnlargementMuvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supraventricular Arrhythmias (Seminar)Dokument29 SeitenSupraventricular Arrhythmias (Seminar)Muvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colorectal CancerDokument39 SeitenColorectal CancerMuvenn Kannan100% (2)
- Intestinal Obstruction 4Dokument25 SeitenIntestinal Obstruction 4Muvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocular Emergencies: Pisit Preechawat, MD Department of Ophthalmology, Ramathibodi HospitalDokument86 SeitenOcular Emergencies: Pisit Preechawat, MD Department of Ophthalmology, Ramathibodi HospitalBenny Franclin SuripattyNoch keine Bewertungen
- IV FluidsDokument47 SeitenIV FluidsMuvenn Kannan100% (1)
- Causes of Chorea, Athetosis, HemiballismusDokument10 SeitenCauses of Chorea, Athetosis, HemiballismusMuvenn Kannan0% (1)
- Supervised by DR Hisham Prepared by Anwariah Aris Noor Mohammad SafwanDokument50 SeitenSupervised by DR Hisham Prepared by Anwariah Aris Noor Mohammad SafwanMuvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Membrane ExamDokument9 SeitenBiology Membrane ExamMuvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breastfeeding - CompiledDokument81 SeitenBreastfeeding - CompiledMuvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Changes in Chamber EnlargementDokument16 SeitenECG Changes in Chamber EnlargementMuvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afrm Sample Questions Module 1-19-11 2012Dokument16 SeitenAfrm Sample Questions Module 1-19-11 2012Muvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Spine Clearance Ortho 3 Journal ClubDokument31 SeitenC Spine Clearance Ortho 3 Journal ClubMuvenn KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal System 4Dokument2 SeitenGastrointestinal System 4Dian AngrianyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Athletic Pubalgia (Sports Hernia) .Basu PDFDokument18 SeitenAthletic Pubalgia (Sports Hernia) .Basu PDFPrabhu ashvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dextile Anatomical Mesh BrochureDokument6 SeitenDextile Anatomical Mesh BrochurercortesflowmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- ERN Intercoll MRCS Bk2Dokument48 SeitenERN Intercoll MRCS Bk2Rocita HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Abdominal Wall and HerniasDokument113 SeitenChapter 9 Abdominal Wall and HerniasMACON824Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal HydroceleDokument14 SeitenJurnal HydroceleDedian FajarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inguinal Hernia Ultrasound 2Dokument6 SeitenInguinal Hernia Ultrasound 2savingtaviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- أسئلة امتحان الإقامة تكنوDokument10 Seitenأسئلة امتحان الإقامة تكنومحمد حميدانNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgery EORDokument76 SeitenSurgery EORAndrew BowmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hernia NotesDokument2 SeitenHernia NotesEdaManatadNoch keine Bewertungen
- SURGERY Lecture 3 - Abdominal Hernia (Dr. Mendoza)Dokument12 SeitenSURGERY Lecture 3 - Abdominal Hernia (Dr. Mendoza)Medisina101100% (1)
- Hi-Yield Notes in SurgeryDokument18 SeitenHi-Yield Notes in SurgeryJohn Christopher Luces50% (2)
- Inguinal Herniotomy With The Mitchell-Banks' Technique Is Safe in Older Children.Dokument3 SeitenInguinal Herniotomy With The Mitchell-Banks' Technique Is Safe in Older Children.Berliana Kurniawati Nur HudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleo - Agustin - Pathophysiology of Inguinal HerniaDokument3 SeitenCleo - Agustin - Pathophysiology of Inguinal HerniaCleobebs Agustin100% (2)
- Free Tension HernioraphyDokument43 SeitenFree Tension HernioraphyrositasholekhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Cases in SurgeryDokument115 SeitenShort Cases in Surgerynit524100% (2)
- Review Article: The Onstep Method For Inguinal Hernia Repair: Operative Technique and Technical TipsDokument8 SeitenReview Article: The Onstep Method For Inguinal Hernia Repair: Operative Technique and Technical TipsKaterina TsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Mini NetterDokument13 SeitenMaterial Mini NetterVALENTINA ALBORNOZ BASTÍASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tloy Inguinal Hernias Doc MedinaDokument11 SeitenTloy Inguinal Hernias Doc MedinaJAM CHRISTINE MABBUNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inguinal Scrotal SwellingsDokument23 SeitenInguinal Scrotal SwellingsAzmyza Azmy100% (1)
- Question ListDokument65 SeitenQuestion Listridin007Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Consideration Inguinal Hernias: Femoral Hernia Incisional Hernia Umbilial Hernia Hernia of Linea AlbaDokument30 SeitenGeneral Consideration Inguinal Hernias: Femoral Hernia Incisional Hernia Umbilial Hernia Hernia of Linea Albainna3003Noch keine Bewertungen
- GIT-III Module PDFDokument9 SeitenGIT-III Module PDFFaiz MansoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCFHS Diagnostic Radiology ExamsDokument123 SeitenSCFHS Diagnostic Radiology ExamsDr-Khaled Shaaban100% (1)
- AbdWall, Hernia Atbp - AnnoDokument34 SeitenAbdWall, Hernia Atbp - AnnoJuan Lorenzo RequironNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resident Hernia LectureDokument106 SeitenResident Hernia Lecturesgod34Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modified by MAW 2009: MRCS Clinical Examination Scheme & Test InterpretetionDokument62 SeitenModified by MAW 2009: MRCS Clinical Examination Scheme & Test InterpretetionFA Rinku PatwaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes General SurgeryDokument16 SeitenLecture Notes General SurgeryHamsa VeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Mesh Repair of Femoral Hernia: Lloyd M. Nyhus, MD, and Jose E Patifio, MD?Dokument10 SeitenNon-Mesh Repair of Femoral Hernia: Lloyd M. Nyhus, MD, and Jose E Patifio, MD?marquete72Noch keine Bewertungen
- 38 Abdominal WallDokument20 Seiten38 Abdominal WallAlucardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Von EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionVon EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (404)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (31)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (42)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDVon EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (82)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryVon EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (46)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaVon EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesVon EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (1412)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsVon EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Von EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (110)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsVon EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (170)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (8)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessVon EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (328)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassVon EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (27)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingVon EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1138)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeVon EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (253)