Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
B Unit 6 Notes
Hochgeladen von
api-327072135Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
B Unit 6 Notes
Hochgeladen von
api-327072135Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
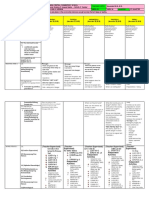
BUSINESS NOTES FOR UNIT 6: MOTIVATING WORKERS
Why people work
1. Money: to pay for necessities and luxuries
2. Security: a sense of security, for ex: knowing that your job and pay are
safe- you are not likely to lose your job
3. Social needs (affiliation): feeling part of a group or organization,
meeting people, making friends at work
4. Esteem needs (self- importance): feeling important, feeling your job is
important
5. Job satisfaction: enjoyment is derived from feeling that you have done
a good job
High productivity of business comes from a workforce that is motivated to
work effectively and from this comes increased profits.
Well- motivated workers high productivity increased output higher
profits
`Motivation theories
F. W. Taylor (1911): Money is the main motivator
all individuals are motivated by personal gain and therefore, if they are
paid more, they will work more effectively.
Criticisms against:
1. The idea is to simplistic- employees are motivated by many things
beside money.
2. If workers are unfulfilled by their work in some way, there will be no
increase the workforce, therefore no productivity will be gained.
3. A practical problem arises if you cant easily measure an employees
output.
Maslow (1954): Hierarchy of needs
Hierarchy of needs:
1. Physiological needs: food, rest, recreation, shelter, wages high enough
to pay weekly bills
2. Safety/ security needs: protection against danger, poverty; fair
treatment
3. Social needs: friendship, sense of belonging to a team, work colleagues
that support you at work
4. Esteem needs: having status and recognition achievement,
independence, being given recognition for a job well done
5. Self- actualization: succeeding to your full potential, feeling you have
done a good job for financial and personal reward, being promoted and
given more responsibility
Herzberg (1959) Hygiene and motivators
According to Herzberg, human have 2 sets of needs; one is for the basic
animal needs (hygiene factors) and the second is for a human being to be
able to grow psychologically (motivational needs or motivators).
Motivators
Achievement
Recognition
Personal growth/ development
Advancement/ promotion
Work itself
Hygiene (or maintenance) factors
Status
Security
Work conditions
Company policies and administration
Relationship with supervisor
Relationship with subordinates
Salary
Motivating factors financial rewards/ motivators
Three factors which can motivate employees:
Financial rewards
Non- financial rewards
Introducing ways to give job satisfaction
FINACIAL REWARDS
Pay may give incentives to employees to encourage them to work harder
and more effectively. There are 4 main forms of payment:
Wages: often paid every week, sometimes in cash or into a bank
account
workers get paid on a regular
basis & dont have to wait
long for their money
workers can get extra
payment for working overtime
weekly calculations are
required which takes time &
money
wages clerks perform this task
Time rate: payment by the hour (payment for a period of time
Easy to calculate wages
Workers know exactly what
they will be paid for working a
certain period of time
The system required takes
time
Good and bad workers get
paid the same
More supervisors are
demanded to watch the
workers
Clocking- in system is needed
to determine number of hours
worked by the employees
Piece rate: depending on the quantity of products made by workers;
can also come with additional money
Encourages workers to work
faster and produce more
goods
Negatively affects the quality
=>
1. quality control system is
needed = expensive
2. damage the reputation of
the business
can be not fair for careful
workers
if machinery breaks down,
employees may earn less
money
Salaries: are paid monthly normally straight into a bank account, not
paid in cash. Rewards can be added to the basic salary:
Commission
Profit sharing
Often paid to sales staff
Similar to piece rate
If sales staffs are persuasive
and try to make customers
buy what they dont really
want, this can bring bad
reputation and long- term
decrease in sale
Can be stressful for workers
Often used in service where
Bonus
Performance- related pay
Share ownership
its difficult to know an
individuals contribution to the
increased profit but do benefit
the business
A lump sum paid to workers
At the end of year or intervals
during year
Linked to the effectiveness of
their work
Often used when output cant
be measured
Use system of appraisal where
immediate superior observe a
workers work, talk to their
colleagues and have an
interview with them about
their result
Shares are given to workers
They can get dividends if the
company does well
Improves employee loyalty as
they will be more responsible
and important to the company
Motivating factors non- financial rewards
They can be called perks or fringe benefits and may include:
Company vehicle
Discounts on the firms products
Health care paid for
Childrens education fees paid
Free accommodation
Share options
Generous expense accounts
Pension paid for
Free trip abroad/ holidays
Job satisfaction
Pay
Opportunities for promotion
Working conditions
Fringe benefits or non- financial rewards
How employees are treated or managed
Working hours
Colleagues
Nature of work
Level of responsibility
Sense of achievement derived from job
Recognition for achievements
Chance for training
Status of the job
Job rotation involves workers swapping round and doing a certain task for a
limited amount of time and then changing again.
Increases variety in work
Easier for manager to organize when problem occurs
Job enlargement is where extra tasks are added to a workers job
description. This doesnt mean extra work or responsibility but greater
variety to the work and increases job satisfaction.
Job enrichment involves looking at jobs and adding tasks required more
skill and responsibility. Extra training may be needed.
Autonomous work groups or team- working
Workers can be more involved in the decision making and be more
responsible
Feel committed
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Human Relations in NursingDokument15 SeitenHuman Relations in NursingOm VaishNav100% (1)
- Building An IMC Campaign IMC Plan Pro DiskDokument22 SeitenBuilding An IMC Campaign IMC Plan Pro DiskPisica Andreea RoxanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 CP 03 - Critical ReadingDokument10 SeitenModule 3 CP 03 - Critical ReadingMishael InfanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potom KovaDokument31 SeitenPotom Kovamanish_198797682Noch keine Bewertungen
- NegOr Q3 CESC Module5 v2Dokument14 SeitenNegOr Q3 CESC Module5 v2Joevarie JunioNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To The Competing Values FrameworkDokument4 SeitenAn Introduction To The Competing Values FrameworknmandavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sports CultureDokument9 SeitenSports CultureNanbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write A Project ProposalDokument20 SeitenHow To Write A Project ProposalIrsani Fenilia100% (2)
- Consciousness and Self-ConsciousnessDokument21 SeitenConsciousness and Self-Consciousnessantonio_ponce_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- INSDSG Project Management For Instructional DesignersDokument16 SeitenINSDSG Project Management For Instructional DesignersApostolos KoutropoulosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aghayedo, Elmi-Homework 6Dokument3 SeitenAghayedo, Elmi-Homework 6faizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 28 Ways To Stop ProcrastinatingDokument5 Seiten28 Ways To Stop ProcrastinatingAnonymous n5EmHGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overcoming Resistance To ChangeDokument29 SeitenOvercoming Resistance To ChangeHani Law100% (2)
- Transactional AnalysisDokument4 SeitenTransactional Analysisapi-498183825Noch keine Bewertungen
- Special Meeting 8.14.15 Agenda and Materials Website1 - 8Dokument452 SeitenSpecial Meeting 8.14.15 Agenda and Materials Website1 - 8KOLD News 13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Masculinities in TrumpetDokument10 SeitenMasculinities in TrumpetYumi MeeksGiz SawabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legacies of DerridaDokument37 SeitenLegacies of DerridaR_TeresaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Inner Game + QualityDokument102 SeitenCore Inner Game + Qualityosher26100% (4)
- Masterclass of Loomis and Bargue Facial and Figure DrawingDokument5 SeitenMasterclass of Loomis and Bargue Facial and Figure DrawingLuciano Carvalho100% (1)
- Hylda Baktiar Octaviana - TM 10 - Kel 4Dokument4 SeitenHylda Baktiar Octaviana - TM 10 - Kel 4Hylda Octavia100% (2)
- Human Resouces PlanningDokument30 SeitenHuman Resouces Planningmeme_qanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 PEriodical ExamDokument4 SeitenGrade 8 PEriodical ExamDaniel FabianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outline and Evaluate The Role of Neural Mechanisms of Controlling EatingDokument2 SeitenOutline and Evaluate The Role of Neural Mechanisms of Controlling Eatingsam_282284953100% (1)
- Emotional: Winaldi Angger Pamudi (2213510017) M.khalil Gibran Siregar (2213510001) Ririn Alfitri (2213510009)Dokument8 SeitenEmotional: Winaldi Angger Pamudi (2213510017) M.khalil Gibran Siregar (2213510001) Ririn Alfitri (2213510009)lolasafitriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDokument1 SeiteDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesRonalaine IrlandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Test 1Dokument2 SeitenUnit Test 1Margerie FrueldaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 25 New Kinder DLL From New TG 2018Dokument10 SeitenWeek 25 New Kinder DLL From New TG 2018Ecyoj Bantaculo Casilac100% (1)
- Vedanta-Part 1Dokument8 SeitenVedanta-Part 1arul_ramalingam4903Noch keine Bewertungen
- Most Common Job Interview QuestionsDokument2 SeitenMost Common Job Interview QuestionsFlavio MondragónNoch keine Bewertungen
- 77-Article Text-218-1-10-20220630Dokument16 Seiten77-Article Text-218-1-10-20220630EDIT VLOGNoch keine Bewertungen