Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
hhECA9 PDF
Hochgeladen von
jajajajaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
hhECA9 PDF
Hochgeladen von
jajajajaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ovid: Anatomy & Physiology: An Incredibly Easy!
Workout
Page 1 of 8
Authors: Springhouse
Title: Anatomy & Physiology: An Incredibly Easy! Workout, 1st Edition
Copyright 2009 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
> Table of Contents > 2 - Genetics and chemical organization
2
Genetics and chemical organization
i
P.8
Warm-up
Genetics and chemical organization review
Genetic facts
Genetics is the study of heredity
Inherited traits are transmitted from parents to offspring in germ cells, or gametes
Human gametes are eggs (or ova) and sperm
Inheritance is determined at fertilization
Chromosomes
Each contains a strand of genetic material called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Each trait a person inherits is carried in the genes
Chromosomescomposed of DNA and protein
Human ovum and sperm each contain 23 chromosomes
When ovum and sperm unite, the result is a fertilized cell with 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) in the
nucleus
Femaleshave two X chromosomes
Maleshave an X and a Y chromosome
Meiosiscell-division process that forms ova and sperm
Genes
Genotypegenetic information of a person
Phenotyperecognizable traits associated with a specific genotype
Allelesvariations of a gene (such as brown, green, or blue eye color) that can occupy a
particular gene locus
Trait predominance
Each parent contributes one set of chromosomes
Homozygousidentical alleles on each chromosome
Heterozygousdifferent alleles on each chromosome
Autosomal inheritance
Autosomal dominantmore powerful gene and more easily expressed
Autosomal recessiveless powerful gene and less easily expressed
Sex-linked inheritance
file:///C:/Users/chall/AppData/Local/Temp/~hhECA9.htm
1/10/2017
Ovid: Anatomy & Physiology: An Incredibly Easy! Workout
Page 2 of 8
The male has only one copy of most genes on the X chromosome; inheritance of those genes is
called X-linked
A man transmits one copy of each X-linked gene to his daughters and none to his sons
A woman transmits one copy of each X-linked gene to each child, male or female
Some recessive genes on X chromosomes act dominant in females
Genetic defects
Teratogensenvironmental agents that can cause congenital, structural, or functional defects
Mutations
Permanent change in genetic material
May cause serious defects, such as congenital anomalies
Autosomal disorders
Single-gene disorderserror at a single gene site on DNA
Most hereditary disorders are caused by autosomal defects
Autosomal dominant transmission and autosomal recessive inheritanceusually affects male and
female offspring equally
Sex-linked disorders
Usually recessive traits caused by genes located on the sex chromosomes (most on X
chromosome)
Single X-linked recessive gene can cause disorder to be exhibited in a male
All daughters of an affected male are carriers
Multifactorial disorders
Result from a less-than-optimum expression of many different genes, not from a specific error
Examples apparent at birth (cleft lip, cleft palate) or later (type II diabetes mellitus, hypertension)
Chromosome defects
Congenital anomalies, or birth defectsaberrations in chromosome structure or number
Types
Translocationrelocation of a segment of a chromosome to a nonhomologous chromosome
Disjunctionnormal separation of chromosomes during both meiosis and mitosis
Nondisjunctionfailure to separate that causes unequal distribution of chromosomes between the
two resulting cells
Principles of chemistry
Matteranything that has mass and occupies space
P.9
file:///C:/Users/chall/AppData/Local/Temp/~hhECA9.htm
1/10/2017
Ovid: Anatomy & Physiology: An Incredibly Easy! Workout
Page 3 of 8
Energythe capacity to do work (put mass into motion)
Potentialstored energy; kineticenergy of motion
Typeschemical, electrical, and radiant
Chemical composition
Elementmatter that can't be broken down into simpler substances by normal chemical reactions
Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen account for 96% of the body's total weight
Atomic structure
Atomsmallest unit of matter involved in chemical reactions
Atoms of a single type constitute an element
Subatomic particles
Protons (p+)
Positively charged particles
Each element has a distinct number of protons
Neutrons (n)
Uncharged, or neutral, particles
Electrons (e)
Negatively charged particles
Play a key role in chemical bonds and reactions
Chemical bonds
Force of attraction that binds a molecule's atoms together
Formationrequires energy; breakupreleases energy
Types
Hydrogentwo atoms associate with a hydrogen atom
Ionicvalence electrons transfer from one atom to another
Covalentatoms share pairs of valence electrons
Chemical reactions
One of two events occurs:
Unpaired electrons from the outer shell of one atom transfer to the outer shell of another
atom
One atom shares its unpaired electrons with another atom
Types: Synthesis, decomposition, exchange, reversible
Inorganic compounds
Water
Body's most abundant substance
Permits the transport of solvents
file:///C:/Users/chall/AppData/Local/Temp/~hhECA9.htm
1/10/2017
Ovid: Anatomy & Physiology: An Incredibly Easy! Workout
Page 4 of 8
Acts as lubricant in mucus and other bodily fluids
Helps regulate body temperature
Electrolytes
Compounds whose molecules consist of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged
ions (anions)
Acids, bases, and salts
Acidsseparate into a positively charged hydrogen ion and a negatively charged anion
Basesseparate into negatively charged hydroxide ions and positively charged cations
Saltsform when acids react with bases
Body fluids must attain acid-base balance for homeostasis
More hydrogen ions = more acidic solution
More hydroxide ions = more basic (alkaline) solution
Organic compounds
Compounds that contain carbon or carbon-hydrogen bonds
Carbohydrates
Sugars, starches, glycogen, and cellulose
Release and store energy
Three types:
Monosaccharides (ribose and deoxyribose)
Disaccharides (lactose and maltose)
Polysaccharides (glycogen)
Lipids
Water-insoluble biomolecules
Triglyceride
Most abundant lipid in food and the body
Insulates and protects
Body's most concentrated energy source
Phospholipids
Major structural components of cell membranes
Sterolssimple lipids with no fatty acids in their molecules
Bile saltsemulsify fats during digestion and aid absorption of the fat-soluble vitamins (A,
D, E, K)
Male and female sex hormonesresponsible for sexual characteristics and reproduction
Cholesterola part of animal cell membranesneeded to form all other sterols
Vitamin Dhelps regulate calcium concentration
Lipoproteinshelp transport lipids throughout the body
Eicosanoids
Prostaglandins (modify hormone responses, promote inflammatory response, open airways)
Leukotrienes (play role in allergic and inflammatory responses)
file:///C:/Users/chall/AppData/Local/Temp/~hhECA9.htm
1/10/2017
Ovid: Anatomy & Physiology: An Incredibly Easy! Workout
Page 5 of 8
Proteins
Most abundant organic compound in the body
Composed of amino acids
Polypeptidemany amino acids linked together
One or more polypeptides form a protein
Nucleic acids
Composed of nitrogenous bases, sugars, and phosphate
DNA
Primary hereditary molecule
RNA
Transmits genetic information from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm
Guides protein synthesis from amino acids
P.10
Boxing match
Fill in the answers to the clues below by using all of the syllables in the box. The number of syllables for
each answer is shown in parentheses. Use each syllable only once. The first answer has been provided
for you as an example.
i
1. Genetic constitution of individual
(3) G E N O T Y P E
2. Study of heredity
(3) __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
(3) __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
3. Outward manifestation of genotype
4. Germ cell
(2) __ __ __ __ __ __
5. Structures of nucleus in each germ cell
(3) __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
6. Complete set of chromosomes
(2) __ __ __ __ __ __
7. Location of gene on a chromosome
(2) __ __ __ __ __
8. Permanent change in genetic information
(3) __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
9. Cell division process by which sperm and ova form(3) __ __ __ __ __ __ __
(2) __ __ __ __ __ __ __
10. Variations of the same gene
Hit or miss
Some of the following statements about chromosomes are true; the others are false. Mark each
accordingly.
_____ 1. A fertilized human ovum contains 23 chromosomes.
_____ 2. When an ovum and a sperm unite, corresponding chromosomes pair up.
_____ 3. Each pair of chromosomes contains information that determines a person's gender.
_____ 4. In a female, both sex chromosomes are relatively large, and each is designated by the
letter X.
_____ 5. In a male, one sex chromosome is an X chromosome and one is a smaller chromosome,
designated by the letter Y.
_____ 6. Each gamete produced by a male contains both an X and a Y chromosome.
_____ 7. When a sperm with an X chromosome fertilizes an ovum, the offspring may be male or
female.
_____ 8. Genes are segments of a DNA chain, arranged in sequence on a chromosome.
_____ 9. The location of a specific gene on a chromosome varies from person to person.
file:///C:/Users/chall/AppData/Local/Temp/~hhECA9.htm
1/10/2017
Ovid: Anatomy & Physiology: An Incredibly Easy! Workout
Page 6 of 8
P.11
Coaching session
Gene expression
Gene expression refers to a gene's effect on cell structure or function. Types include:
Dominant: Expressed even if only one parent passes the gene
Recessive: Expressed only if both parents pass the gene
Codominant: Allow equal expression of two alleles
Sex-linked: Carried on sex chromosomes (most on X and are recessive; those on Y are dominant)
Strike out
The following statements pertain to genes and gene expression. Cross out all of the untrue statements.
Dominant genes can be expressed and transmitted to the offspring even if only one parent
possesses the gene.
Recessive genes are expressed only under the influence of environmental factors.
Males have more genetic material than females.
Sex-linked genes are carried on sex chromosomes.
Almost all sex-linked genes appear on the X chromosome and are recessive.
Because sex-linked genes are recessive, they are rarely expressed.
Some genes are only expressed under certain environmental conditions.
i
Parallel bars
Complete each of the analogies below by determining the relationship between the given word pair and
then determining the missing term in the second word pair.
Egg : _______________ : : Sperm : Spermatozoa
Female : XX : : Male : _______________
Inside : Genotype : : Outside : _______________
Homozygous : Identical : : _______________ : Different
More : _______________ : : Less : Recessive
One too many : Trisomy : : One too few : _______________
P.12
Jumble gym
Use the clues to help you unscramble words related to genetic defects. Then use the circled letters to
answer the question posed.
Question: Which term is used to describe a disorder that results from an error at a single gene site?
Permanent change in genetic material
ANTIMUTO
i
__
__ __ __ __ __ __
Type of disorder resulting from a number of genes and environmental influences acting together
C A M L I AT F L U T I R O
file:///C:/Users/chall/AppData/Local/Temp/~hhECA9.htm
1/10/2017
Ovid: Anatomy & Physiology: An Incredibly Easy! Workout
Page 7 of 8
__ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
__ __ __ __
Class of disorders resulting from aberrations in chromosome structure or number
ACONTINGLESEALAMION
__ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
__ __ __ __
__ __ __ __
The relocation of a segment of a chromosome to a nonhomologous chromosome
CANTORLASTION
__ __ __ __ __ __ __
__ __ __ __
Condition in which the number of chromosomes present is one less than normal
OMMYSOON
__ __ __ __
__ __ __
The presence of an extra chromosome
MISTYOR
__ __ __ __ __
__
Occurs when chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis or mitosis, resulting in an
unequal distribution of chromosomes between the two resulting cells
SICUNDOJINNTON
__
__ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
Answer: __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
Pep talk
Energy and persistence conquer all things.
Benjamin Franklin
P.13
Cross-training
Complete the following crossword puzzle to test your knowledge of body chemistry.
Across
1. Matter that can't be broken down into simpler substances by normal chemical reactions
5. Dynamic equilibrium of the body
7. A form of an atom that has a different number of neutrons and, therefore, a different atomic
weight
9. Compounds containing carbon
10. Formed by the combination of the atoms of two different elements
12. Most abundant organic compound in the body
13. Dense central core of an atom
14. Smallest unit of matter that can take part in a chemical reaction
15. The capacity to do work
Down
1. Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in shells
2. Anything that has mass and occupies space
3. An atom's ability to combine with other atoms
4. Uncharged particles in the atom's nucleus
file:///C:/Users/chall/AppData/Local/Temp/~hhECA9.htm
1/10/2017
Ovid: Anatomy & Physiology: An Incredibly Easy! Workout
Page 8 of 8
6. Compounds without carbon
8. Combination of two or more atoms
11. Positively charged particles in the atom's nucleus
i
P.14
Match point
Match the terms on the left with the definitions on the right.
1. Water _______
A. Force of attraction that binds a molecule's atoms
together
2. Electrolytes _______
B. Help transport lipids to various parts of the body
C. Compounds whose molecules consist of positively
3. Salts _______
and negatively charged ions that separate in solution
4. Carbohydrates _______
D. Main function is to release and store energy
5. Triglycerides _______
E. Most abundant substance in the body
F. Neutral fats that insulate and protect
6. Phospholipids _______
7. Lipoproteins _______
G. Major structural components of cell membranes
8. Peptide bonds _______
H. Form when acids react with bases
9. Polypeptide _______
I. Emulsify fats during digestion and aid absorption of
the fat-soluble vitamins
10. Bile salts _______
J. Link amino acids together
11. Nucleic acid containing two long chains of K. Many amino acids linked together
deoxyribonucleotides _______
12. Nucleic acid having a single-chain structure L. RNA
_______
13. Chemical bond _______
M. DNA
i
You make the call
Using the space provided, describe the four basic types of chemical reactions.
_____________________________________
1. Synthesis reaction (anabolism)
Hint: A + B AB
_____________________________________
_____________________________________
2. Decomposition reaction (catabolism)
_____________________________________
Hint: AB A + B
_____________________________________
_____________________________________
3. Exchange reaction
_____________________________________
Hint: AB + CD A + B + C + D AD + BC_____________________________________
_____________________________________
_____________________________________
4. Reversible reaction
Hint: A + B AB
_____________________________________
_____________________________________
file:///C:/Users/chall/AppData/Local/Temp/~hhECA9.htm
1/10/2017
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The FDA Group - Preparing For A Life Science Validation ProjectDokument11 SeitenThe FDA Group - Preparing For A Life Science Validation ProjectEmmanuel-Landry N'Gotta Amp67% (3)
- Lab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesDokument16 SeitenLab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesOtto ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composite Beam Simply Supported DesignDokument21 SeitenComposite Beam Simply Supported DesignTharanga Pradeep100% (1)
- VP Gaming GuideDokument32 SeitenVP Gaming GuidejajajajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standards of PlayDokument5 SeitenStandards of PlayjajajajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bellagio Casino Gaming GuideDokument28 SeitenBellagio Casino Gaming Guidestefan_1989Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sixty VI Need G-WPS OfficeDokument1 SeiteSixty VI Need G-WPS OfficejajajajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaye Validator AVS User ManualDokument170 SeitenKaye Validator AVS User ManualjajajajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sixty VI Need G-WPS OfficeDokument1 SeiteSixty VI Need G-WPS OfficejajajajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple PDFDokument2 SeitenA Simple PDFJaheer MakalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coin and Currency in The: Casino IndustryDokument16 SeitenCoin and Currency in The: Casino IndustryjajajajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- hhECA9 PDFDokument8 SeitenhhECA9 PDFjajajajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 2AbhinavJain100% (1)
- Halliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics: Classroom Response System QuestionsDokument51 SeitenHalliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics: Classroom Response System QuestionsOlimpiade InfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.4-Rotational Mechanical System Transfer Functions: Table 3Dokument5 Seiten2.4-Rotational Mechanical System Transfer Functions: Table 3طه حسن شاكر محمودNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dosimetry Materials BrochureDokument4 SeitenDosimetry Materials BrochureVictor Manuel Suyco CasaperaltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotor Dynamics Without Equations - NelsonDokument9 SeitenRotor Dynamics Without Equations - NelsonItalo LinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter4 e Slides - 4Dokument79 SeitenChapter4 e Slides - 4azizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 30 PhysicsDokument29 SeitenChapter 30 Physicseg40340% (1)
- ConvectionDokument27 SeitenConvectionVinoth Malaikani100% (2)
- Bond GraphDokument5 SeitenBond GraphMila Dhari NovianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Inductors Engl 03-08Dokument12 SeitenPower Inductors Engl 03-08Bernard OdipoNoch keine Bewertungen
- POLEDokument18 SeitenPOLEJosue HasbunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interview QuestionsDokument13 SeitenInterview QuestionsJoseph George100% (1)
- Powder DiffractionDokument9 SeitenPowder DiffractionGary TrumpNoch keine Bewertungen
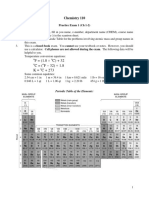
- CHEM110 Practice Exam 1Dokument3 SeitenCHEM110 Practice Exam 1Zama MtnNoch keine Bewertungen
- MomentumDokument23 SeitenMomentumAlbieJane CatotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Powder Processing TechniquesDokument26 SeitenMetal Powder Processing TechniquesAzhar Ali0% (1)
- 1.0 PT STP1 - BQDokument46 Seiten1.0 PT STP1 - BQdenny yusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pil Unit Review2015 KeyDokument6 SeitenPil Unit Review2015 Keyapi-296347043Noch keine Bewertungen
- CPX/SDX-751: Low-Profile Intelligent Plug-In Smoke DetectorDokument2 SeitenCPX/SDX-751: Low-Profile Intelligent Plug-In Smoke DetectordurokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Undersaturated Oil-Gas Simulation - Impes Type Solution: o Os GS So oDokument9 SeitenUndersaturated Oil-Gas Simulation - Impes Type Solution: o Os GS So onaefmubarakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Note Mw31 90nmDokument0 SeitenApplication Note Mw31 90nmammayi9845_930467904Noch keine Bewertungen
- GravitationDokument6 SeitenGravitationInfrion MatiqueonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boundary Layer FlowsDokument28 SeitenBoundary Layer FlowsAmy RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Media Tension 10Dokument19 SeitenMedia Tension 10EdgardV1024Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding and Explaining Surface Tension and CDokument12 SeitenUnderstanding and Explaining Surface Tension and CKatiaPeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of ThermodynamicsDokument55 SeitenFundamentals of Thermodynamicsudoye kachiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinema TicsDokument61 SeitenKinema TicsApex Institute33% (6)