Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
2012 Mid Autumn EC21103 PDF
Hochgeladen von
IndranilOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
2012 Mid Autumn EC21103 PDF
Hochgeladen von
IndranilCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, KHARAGPUR
Date: ............ , FN/AN, Time: 2/3- Hrs., Full Marks: 30, No of students: 351
Majors: ECE/CSEIEEIIE/QE, 2nd yr B.Tech(H)/B.Areh(II)!M.-5e
Mid Semester Examination, Semester: Autumnl8pftftg, 2017
Subject: Introduction to Electronics (EC21103)
NOTE:
1. All waveform sketches I diagrams must be neatly drawn and clearly labeled.
2. The final answers (numerical values with unit) should be underlined or enclosed within I box 1.
3. Answers must be brief and to the point. Partial cr~dit will be awarded for correct attempt.
4. For every problem, start your answer from a new page. Avoid writing answers of the various parts of a
single question at different locations in your answer-script.
5. Assume the following parameter values, unless a parameter value is specifically given with the problem:
Dielectric constants: t:o = 8.854 x 10- [Fim],
t:r ofSi02 =3.9
Boltzmann Constant, k = 1.38 x 10- 23 (JI K]
= 8.617 x 10-5 [eVI K]
Chargeofanelectron,q = -1.602 x 10- 19 (C]
At room temperature or 300K:
Intrinsic carrier concentration, ni = 10 10 (cm- 3 ]
Thermal voltage, VrH = 25.9 X w- 3 (V]
Mobility of the electrons, P.n ='= 1400(cm2 IV.s]
Mobility of the holes P.v = 500(cm IV.s]
P-N junction reverse saturation current, Is = 10- 15 (A]
P-N junction forward cut-in voltage, V-y = 0. 7(V]
P-N junction forward-bias ON-voltage, VDoN = 0. 7[V]
Diode large-signal forward resistance, Rt = O(D]
Diode break-down voltage, VBR = oo(V]
Early voltage of BIT, VA = oo(V]
Gate-oxidecapacitance,Cox = 3 x 10-8 (Ficm 2]
Channel-length modulation parameter,..\ = o(V- 1 ]
6. For any value related to any device parameter or circuit parameter, which you may find not given with a
problem, assume suitable value for such parameter.
1. Select the correct answer and give proper justification:
(5 x 1.5 marks)
(a) The built-in potential (Vbi) of a p-n junction depends largely on temperature (T) as:
(i) 0( JT.
(ii) ocT.
(iii) oc T 2
(iv) independent ofT.
(v) None of the others.
(b) A voltage v. = 10sin(l001rt + 1rI 4)V is given to the input of a half-wave rectifier circuit with a resistive load
(R) = 1KD and a capacitative load (C) = 20p,F. What will be the peak-to-peak ripple voltage of the output
waveform?
(i) 9.3 v
(ii) 4.65 v
(iii) 5.88 v
(iv) 3.65 V
(v) None of the others.
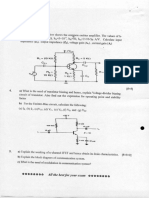
(c) Which circuit out of Fig. l(i) through Fig. l(iv) corresponds to the input voltage and output voltage waveforms
ofFig. 1(c)?
(d) The npn transistor of Fig. 1(d) is operating in forward active mode, where VeE= 1 V. Assume f3
is the value of R?
(i) 2000 n
(ii) 1900 n
(iii) 2100 n
(iv) 100 n
(v) None of the others.
= 100. What
(e) The circuit in Fig. l(e) has one silicon diode (Dl, V-y = 0.7 V) and one germanium diode (D2, V-y = 0.2 V).
Find Vout
(i) 3.14mVpp
(ii) 0.203 v pp
CONTINUED
"'-
-2(iii) 795 j.Lv pp
(iv) 3I4 p.V pp
(v) None of the others.
1\
I \
Fig.l(c)
T
Fig. l(i)
Fig. l(ii)
Fig. l(iii)
Fig. l(iv)
2. Consider a sawtooth waveform with period T, which is given by v(t) = 2t V for 0 ~ t < T and v(t + nT) = v(t) for
t;::::: T, n E {1, 2, 3, ... }. Find the ripple factor, which can be defined as Vr(rms)/Vdc
(3 marks)
3. Prove that f3 = gmr1r for the hybrid-1r BJT small signal model. Where f3 =common emitter BIT current gain, 9m
= common emitter BIT transconductance, r,. = small signal equivalent resistance between emitter and base terminals.
(3 marks)
4. Find the currents (I) for the following two configurations, where lengths (L 1 = 1 em, L 2 = 2 em), cross-section areas
(A 1 = 1 mm2 , A 2 = 0.25 mm2 ) and doping densities (Nn = 10 17 fcm 3 , NA = 10 16 fcm 3 ) are given. The reverse
saturation current of a p-njunction is given by Is = qAni 2 ( LDNP
+ LDNn
). Lp = I 0 em, Ln = I em.
(2,2 marks)
p
A
n
D
'
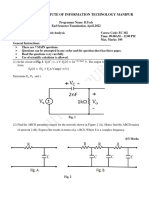
5. In the circuit diagram ofFig. 5 find (a) the conduction angle ofD5, (b) the PIV (peak inverse voltage) ofD5. (c) Draw
(2,2,I marks)
the voltage waveform across the capacitor for two cycles of the input waveform.
6. Draw the voltage transfer characteristics (vouT vs. VJN) of the circuit given in Fig.6 for the input voltage range of
(0 V-12 V). Identify the different ranges of VJN and vour for which the transistor is in cutoff, forward active and
(5 marks)
saturation respectively. f3 = 100.
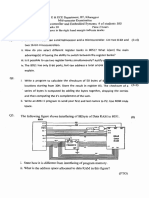
7. Calculate the small-signal input resistance (~n) and small-signal output resistance (Rout) of the circuit given in Fig.
7. f3n = 100, f3v = 50, VAnpn = 100 V, VApnp = 80 V.
(2.5,2.5 marks)
8. Prove that in= ~(p.nCox)('[)[(vos- Vt)vDs-~vns 2 ] for an NMOS transistorin the triode region.
(2.5marks)
-3-
Rt
3K!l
1 K!l
100 p.tF
r---""'-r""--.,...-..--.!~
1"1
+
vout
D1
Fig: 1 (e)
Fig. 1 (d)
~
VIN
..
Ll
rl ~}
..
('f)
.............
M~
~
0
0
Fig. 4(a): n-n type
Lt
VIN
pi.
D2
L2
..
EJ ru1
Vs
.~
...-(
t/)
0,..........
Fig. 4(b): p-n type
Fig. 5
l2V
12V
SKQ
VBB
230KQ
2KQ
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesVon EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Edinburgh College of Science and Engineering School of Engineering and ElectronicsDokument15 SeitenUniversity of Edinburgh College of Science and Engineering School of Engineering and ElectronicsSyed Fasih Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BE 1st Midterm Sep2009Dokument3 SeitenBE 1st Midterm Sep2009YASHNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6002x FinalReview S2012 CleanDokument80 Seiten6002x FinalReview S2012 CleanGemini GntNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digi Anal5Dokument4 SeitenDigi Anal5NGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Rahman Tutorial 1Dokument5 SeitenRahman Tutorial 1John Wanyoike MakauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jntu Hyd 2 2ece PDC Set 2Dokument18 SeitenJntu Hyd 2 2ece PDC Set 2Krishna RamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical, Digital and Industrial Circuits: Second Sequence ExamDokument4 SeitenElectrical, Digital and Industrial Circuits: Second Sequence ExamNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical Engineering EE 8342: Personal and Mobile CommunicationsDokument4 SeitenGeorgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical Engineering EE 8342: Personal and Mobile CommunicationsAnjana SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems (Solution)Dokument6 SeitenCommunication Systems (Solution)Rana FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- E & TC ECN Que PaperDokument1 SeiteE & TC ECN Que PaperChidambar GuravNoch keine Bewertungen
- E & TC ECN Que PaperDokument1 SeiteE & TC ECN Que PaperChidambar GuravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sant Longowal Institute of Engineering & Technology Department of Electronics & Communication EngineeringDokument2 SeitenSant Longowal Institute of Engineering & Technology Department of Electronics & Communication EngineeringRajesh PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- NET201 Network Theory Set-A AS2019Dokument7 SeitenNET201 Network Theory Set-A AS2019SofelNoch keine Bewertungen
- DE57J12Dokument4 SeitenDE57J12tutulkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Sem 2022 MidsemDokument6 Seiten4th Sem 2022 MidsemAditya KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENEL2EEH1 - Electrical & Electronic EngineeringDokument7 SeitenENEL2EEH1 - Electrical & Electronic EngineeringqanaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH CT 403 Electronics - FsDokument5 SeitenPH CT 403 Electronics - Fsप्रियरंजन सिंह राजपूतNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A02406 Network TheoryDokument8 Seiten9A02406 Network TheorysivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jntu Hyd 2 2ece Eca Set 2Dokument18 SeitenJntu Hyd 2 2ece Eca Set 2Travis BennettNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019-Dec EC-101 232Dokument2 Seiten2019-Dec EC-101 232Rajesh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MELZG632 Analog IC Design MidSem Make-Up 1573297948961Dokument3 SeitenMELZG632 Analog IC Design MidSem Make-Up 1573297948961VEMURI RAVI TEJANoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Board-XII Physics - Paper - SolutionDokument15 SeitenCBSE Board-XII Physics - Paper - SolutionMichelle DennisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coimbatore Institute of TechnologyDokument3 SeitenCoimbatore Institute of TechnologyMani BharathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- r059210202 Pulse and Digital CircuitsDokument11 Seitenr059210202 Pulse and Digital CircuitsSrinivasa Rao GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Within : Indian Institute of TechnologyDokument2 SeitenWithin : Indian Institute of TechnologyIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Circuit Analysis - II 2 Question PapersDokument8 SeitenElectrical Circuit Analysis - II 2 Question Paperssrinu247Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics June 2012Dokument4 SeitenElectronics June 2012bkvuvce8170Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Circuits &electronics Device Question PaperDokument5 SeitenElectric Circuits &electronics Device Question PaperSalai Kishwar JahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OXFORD LEARNING HUB vst-2Dokument3 SeitenOXFORD LEARNING HUB vst-2Hemanta JenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of ZimbabweDokument6 SeitenUniversity of ZimbabweTatenda BizureNoch keine Bewertungen
- NET201 Network Theory Set-A AS2018Dokument6 SeitenNET201 Network Theory Set-A AS2018SofelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 29 QusDokument16 Seiten29 QusAsafAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prework Questions For KI-1Dokument5 SeitenPrework Questions For KI-1Danial SadiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Circuit Analysis II: Center For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electronics LabDokument8 SeitenElectric Circuit Analysis II: Center For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electronics LabIrfan HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Es - 101Dokument8 SeitenEs - 101Subrata PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Proficiency Examination: Caribbean Examinations CouncilDokument15 SeitenAdvanced Proficiency Examination: Caribbean Examinations Councilpetey78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 5 PDFDokument3 SeitenSheet 5 PDFMajid HelmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duration: Three HoursDokument18 SeitenDuration: Three HoursjeetendrasidhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE - PHysics - 2009Dokument18 SeitenGATE - PHysics - 2009saravanamoorthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ade QuestionDokument11 SeitenAde QuestionClone CloneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical, Digital and Industrial Circuits: First Sequence TestDokument2 SeitenElectrical, Digital and Industrial Circuits: First Sequence TestNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Engg Dec 20 Reg-WkdDokument4 SeitenBasic Engg Dec 20 Reg-WkdDesmond Owusu- AnsahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analogue ElectronicsDokument7 SeitenAnalogue ElectronicsrizwanahbNoch keine Bewertungen
- FORM TP 22247: Caribbean Examinat Advanced Proficiency Physics Ions Coun ExaminationDokument19 SeitenFORM TP 22247: Caribbean Examinat Advanced Proficiency Physics Ions Coun Examinationpetey78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eec Final Set 2Dokument3 SeitenEec Final Set 2Said RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics MQP Ii Puc 2023-24Dokument4 SeitenElectronics MQP Ii Puc 2023-24sanjaykashiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preparatory PhysicsDokument4 SeitenPreparatory PhysicsExcel PU CollegeNoch keine Bewertungen
- B1 Ece2002 50030 50290 50369Dokument4 SeitenB1 Ece2002 50030 50290 50369NanduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code No: 45010Dokument8 SeitenCode No: 45010SRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Exercises 0: The Basics: E1001 Electronic Circuits Prof P BayvelDokument7 SeitenTutorial Exercises 0: The Basics: E1001 Electronic Circuits Prof P BayvelraihanserajNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC Con-2Dokument8 SeitenEC Con-2Prabhu SakinalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dethi DTTT2Dokument2 SeitenDethi DTTT2anhtainguyenluuNoch keine Bewertungen
- DP-Assignment Brief A1 - 16ED2 - UpdatedDokument17 SeitenDP-Assignment Brief A1 - 16ED2 - UpdatedBaru Su100% (1)
- Neet Set PDokument28 SeitenNeet Set PRocktotpal KonwarhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Circuit END Sem) Analysis 2022Dokument3 SeitenElectrical Circuit END Sem) Analysis 2022Udit RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisVon EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyVon EverandOrganic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsVon EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsDokument2 SeitenMicrocontroller and Embedded SystemsIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsDokument2 SeitenMicrocontroller and Embedded SystemsIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 End Spring EC21004Dokument2 Seiten2012 End Spring EC21004IndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC31 006 Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsDokument2 SeitenEC31 006 Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALL The EIGHT Questions: Indian Ins-R:Itl:Jte of Technology, KharagpurDokument2 SeitenALL The EIGHT Questions: Indian Ins-R:Itl:Jte of Technology, KharagpurIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid Spring 2016 EC31006 PDFDokument2 SeitenMid Spring 2016 EC31006 PDFIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF and Microwave EngineeringDokument3 SeitenRF and Microwave EngineeringIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 Mid Spring EV20001Dokument1 Seite2014 Mid Spring EV20001IndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 End Autumn EC31003Dokument3 Seiten2015 End Autumn EC31003IndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Signal ProcessingDokument2 SeitenDigital Signal ProcessingIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS, CH, MF,: Section-2Dokument2 SeitenCS, CH, MF,: Section-2anirudtNoch keine Bewertungen
- EP60042 Engineering Design ProcessDokument1 SeiteEP60042 Engineering Design ProcessIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 Mid Spring BS20001Dokument6 Seiten2014 Mid Spring BS20001IndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC31008 Digital Signal ProcessingDokument1 SeiteEC31008 Digital Signal ProcessingIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid Spring 2016 EC31006 PDFDokument2 SeitenMid Spring 2016 EC31006 PDFIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC31008 Digital Signal ProcessingDokument1 SeiteEC31008 Digital Signal ProcessingIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsDokument2 SeitenMicrocontroller and Embedded SystemsIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 Mid Spring BS20001Dokument6 Seiten2014 Mid Spring BS20001IndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- EP60042 Engineering Design ProcessDokument1 SeiteEP60042 Engineering Design ProcessIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid Spring 2016 EC31006 PDFDokument2 SeitenMid Spring 2016 EC31006 PDFIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- #Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur: Answer The QuestionsDokument1 Seite#Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur: Answer The QuestionsIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- EP60042 Engineering Design ProcessDokument1 SeiteEP60042 Engineering Design ProcessIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC31 006 Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsDokument2 SeitenEC31 006 Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC31008 Digital Signal ProcessingDokument1 SeiteEC31008 Digital Signal ProcessingIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid Spring 2016 EC31006 PDFDokument2 SeitenMid Spring 2016 EC31006 PDFIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 Mid Autumn EC21107Dokument2 Seiten2010 Mid Autumn EC21107IndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microcontroller and Embedded Systems - 1Dokument1 SeiteMicrocontroller and Embedded Systems - 1IndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC31 006 Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsDokument2 SeitenEC31 006 Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsIndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 Mid Autumn EC21107Dokument2 Seiten2012 Mid Autumn EC21107IndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 End Autumn MA21007Dokument2 Seiten2011 End Autumn MA21007IndranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hitachi HDDs Repair Scheme Based On MRT ProDokument21 SeitenHitachi HDDs Repair Scheme Based On MRT ProvicvpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No. 2 Rockwell Hardness Test IntroductionDokument3 SeitenExperiment No. 2 Rockwell Hardness Test IntroductionAhmad Abd100% (1)
- L4 Subdivision of PlotsDokument20 SeitenL4 Subdivision of PlotsKenny BoatNoch keine Bewertungen
- LBX 6513DS VTMDokument4 SeitenLBX 6513DS VTMsergiocuencascribNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disc Brake System ReportDokument20 SeitenDisc Brake System ReportGovindaram Rajesh100% (1)
- Practice Question ElectricityDokument3 SeitenPractice Question ElectricityIvan SetyawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allison 1,000 & 2,000 Group 21Dokument4 SeitenAllison 1,000 & 2,000 Group 21Robert WhooleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packages in JavaDokument4 SeitenPackages in JavaKummeta KeerthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5R55W-S Repair DiagnosisDokument70 Seiten5R55W-S Repair Diagnosisaxallindo100% (2)
- Big Data Analytics & Technologies: HbaseDokument30 SeitenBig Data Analytics & Technologies: HbaseWong pi wenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech LND 17.0 M06 Response Spectrum AnalysisDokument64 SeitenMech LND 17.0 M06 Response Spectrum AnalysisKubilayNoch keine Bewertungen
- MathDokument2 SeitenMathWessam ElmongyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SkyCiv Beam - Hand Calculations - AJW8CTBuLE8YKrkKaG8KTtPAw8k74LSYDokument13 SeitenSkyCiv Beam - Hand Calculations - AJW8CTBuLE8YKrkKaG8KTtPAw8k74LSYsaad rajawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5ROS Underslung BSaverTROUGHS25Dokument1 Seite5ROS Underslung BSaverTROUGHS25jonodo89Noch keine Bewertungen
- OK Flux 231 (F7AZ-EL12) PDFDokument2 SeitenOK Flux 231 (F7AZ-EL12) PDFborovniskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atmel 2565 Using The Twi Module As I2c Slave - Applicationnote - Avr311Dokument14 SeitenAtmel 2565 Using The Twi Module As I2c Slave - Applicationnote - Avr311m3y54mNoch keine Bewertungen
- P 130881757895329843Dokument44 SeitenP 130881757895329843Vijay MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- I C Engine LabDokument3 SeitenI C Engine LabDevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shaping Plastic Forming1Dokument24 SeitenShaping Plastic Forming1Himan JitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Selections - WhiteBackgroundDokument67 SeitenChapter 3 Selections - WhiteBackgroundyowzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polya Problem Solving StrategiesDokument12 SeitenPolya Problem Solving StrategiesGwandaleana VwearsosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sentinel Visualizer 6 User GuideDokument227 SeitenSentinel Visualizer 6 User GuideTaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wacker Neuson Light Towers LTN 6l Parts Manual 348628422Dokument23 SeitenWacker Neuson Light Towers LTN 6l Parts Manual 348628422kellyholland180884pnc100% (61)
- Narayana Xii Pass Ir Iit (2023 24) PDFDokument16 SeitenNarayana Xii Pass Ir Iit (2023 24) PDFRaghav ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Command - HPUXDokument5 SeitenNetwork Command - HPUXRashid NihalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Database Programming With SQL 12-3: DEFAULT Values, MERGE, and Multi-Table Inserts Practice ActivitiesDokument2 SeitenDatabase Programming With SQL 12-3: DEFAULT Values, MERGE, and Multi-Table Inserts Practice ActivitiesFlorin CatalinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cep MPDokument1 SeiteCep MPAzmat HabeebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 4 - Lesson 15 Tuples: Python Mini-Course University of Oklahoma Department of PsychologyDokument20 SeitenDay 4 - Lesson 15 Tuples: Python Mini-Course University of Oklahoma Department of PsychologyhuseyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- More Practice Multiple ChoiceDokument3 SeitenMore Practice Multiple ChoiceHiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICSDokument24 SeitenPHYSICS21SO204 AnvithaNoch keine Bewertungen