Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Quarterly Test in g9 Science 2nd Grading
Hochgeladen von
Rolly MiñonCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Quarterly Test in g9 Science 2nd Grading
Hochgeladen von
Rolly MiñonCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Division of Romblon
Romblon
SECOND QUARTERLY TEST
Grade 9 SCIENCE
School Year 2016-2017
Name: __________________________________Date: _____________________________
Grade/Section: ___________________________
_____________________________
Score:
______________________________________________________________________________
GENERAL DIRECTIONS: Read the sentences or questions carefully. Encircle
the letter that corresponds to the best answer.
1. Which type of bond is formed when an atom of sodium transfers an
electron to an iodine atom?
a. polar covalent
c. metallic
b. ionic
d. nonpolar covalent
2. When strontium reacts with oxygen to form strontium oxide, each
strontium atom
a. loses two ions
c. loses two electrons
b. gains two electrons
d. gains two ions
4. Which one of the following is most likely to be a covalent compound?
a. Rb2S
c. SrCl2
c.
b. CaO
d.NCl3
5. Which one of the following is most likely to be an ionic compound?
a. NO2
b.LiCl
c.NaB
d.SO
6. Which pairs of atoms will share electrons when a bond is formed between
them?
a. Ba and I
b. Li and I
c. K and Cl
d. C and O
7. Which of these is a correct compound name?
a. chloro hydride
c. calcium bromine
b. lead sodide
d. argon sulfide
8. A bond in which an atom contributes two electrons is:
a. a double covalent bond c. a polar covalent bond
b. an ionic bond
d. a coordinate covalent bond
9. A bond formed between two atoms in which each atom contributes a
bonding electron is called a:
a. polar bond
c. coordinate covalent bond
b. double covalent bond
d. single covalent bond
10. A covalent bond formed between two elements that have an
electronegativity difference of 1.6 would be:
a. a non polar bond
c. moderately polar bond
b. a very polar bond
d. an ionic bond
11. Which of the following molecules is polar?
a. O2
c. CO2
b. Cl2
d. HCl
12. We would expect a bond formed between a silicon atom and an oxygen
atom to be:
a. an ionic bond
c. a polar covalent bond
b. a coordinate covalent bond d. a nonpolar covalent bond
13. Which of the following is not a covalent compound?
a. SCl2
b. KCl
b. c. HCl
d. S2Cl2
14. If a bonding pair of electrons is shared unequally between two atoms,
the bond is:
a. Ionic
c. coordinate covalent
b. nonpolar covalent
d. polar covalent
15. Electron Affinity is
a. The energy required to remove an electron from an atom
b. The measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to
attract electrons
c. The energy change when an electron is acquired by a neutral
atom
d. The distance between radii of adjacent atoms
16. Electronegativity is
a. The energy required to remove and electrons from an atom
b. The measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to
attract electrons
c. The energy change when an electron is acquired by a neutral
atom
d. The distance between radii of adjacent atoms
17. Ionization Energy is
a. The energy required to remove an electron from an atom
b. The measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to
attract electrons
c. The energy change when an electron is acquired by a neutral
atom
d. The distance between radii of adjacent atoms
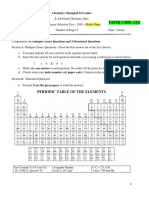
18. Which element has the highest electronegativity?
a. Fluorine
c. iodine
b. Lithium
d. rubidium
19. The letters s, p. d, or f are used to designate a particular______ within
an energy level.
a. sublevel,
c. space
b. Spin
d. color.
20. The space that may be occupied by a pair of electrons within a
sublevel is a(n):
a. Orbital
c. Planks space
b. Heisenbergs probability position.
21. Electron affinity:
a. energy needed to lose one electron from a compound,
b. (b) energy needed to lose one electron,
c. (c) energy needed to add an electron to a gaseous atom.
22. Which of the following would correctly characterize a nonmetal?
a. low ionization energy, low electron affinity
b. high ionization energy, low electron affinity
c. high ionization energy, high electron affinity
d. low ionization energy, high electron affinity.
23. When a metallic atom ionizes:
a. it gains electrons,
c. it loses electrons
b. it neither gains nor loses electrons.
24.
The ___ have the lowest electronegativities.
a. nonmetals
c. metalloids
b. metals
25.
The factor(s) that influence electronegativity is/are ____
a. nuclear charge of the atom
c. atomic radius of the atom
b. the shielding effect
d. all of the preceding.
26. The ability to conduct electricity readily is a property of:
a. nonmetals
c. semiconductors
b. metals
d. halogens.
27. 87. The particle that results when two or more atoms form covalent
bonds is a:
a. single charged atom
c. atomic ion
b. molecule
28. 88. The strength of the bond between two atoms ___ as the difference
in their electronegativities become larger.
a. decreases
c. increases
b. remains constant
d.could increase or decrease.
29.
compounds are normally solids at STP and tend to be soluble in water.
a. Hydrogen
c. metallic
b. covalent
d. Ionic.
30.
The London dispersion force is:
a. attraction between positive and negative ions
b. attraction between nonpolar molecules,
c. attraction between polar molecules,
d. measure of attraction for electrons.
31.
When two atoms combine by sharing electrons, where one has a
bigger share, in order to obtain a stable octet they form a ___ bond.
a. Ionic
c.polar covalent
b. non-polar covalent.
32. When two atoms combine by transfer of electrons the opposite charges
of the ions attract resulting in a____ bond.
a. Ionic
c. polar covalent
b. non-polar covalent.
33.
What type of bond has an electronegativity difference of 3.1?
a. Non-polar covalent
c. Polar covalent
b. Ionic
d. Polar ionic
34. The chemical bond formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of
electrons is a(n)
a. Ionic bond
c. Orbital bond
b. Polar bond
d. Covalent bond
35.
Which of the following bonds are insoluble?
a. ionic
C. nonpolar covalent
b. polar covalent
D. none of the above
36. Which of the following bonds are important in organic systems because
they
form chains of bonds that create organic molecules of life?
a. ionic
C. hydrogen
b. polar covalent
D. nonpolar covalent
37.
A bond in which an atom contributes two electrons is:
a. a double covalent bond
c. a polar covalent bond
b. an ionic bond
d. a coordinate covalent bond
38. A bond formed between two atoms in which each atom contributes a
bonding electron is called a:
a. polar bond
c. coordinate covalent bond
b. double covalent bond
d. single covalent bond
39.
The electron dot structure for hydrogen sulfide, H2S, is:
a. H S
c. H S
b. b. H S H
d. H H S
40. A covalent bond formed between two elements that have an
electronegativity difference of 1.6 would be:
a. a nonpolar bond
c. a moderately polar bond
b. a very polar bond
d. an ionic bond
41. Which of the following is not a covalent compound?
a. a. SCl2
c. KCl
b. HCl
d. S2Cl2
42. If a bonding pair of electrons is shared unequally between two atoms,
the bond is:
a. Ionic
c. coordinate covalent
b. nonpolar covalent
d. polar covalent
43. Which element has the abbreviated electron configuration, [Ar]
4s2,3d10,4p6?
a. Krypton
c. Xenon
b. Zinc
d. Lead
44. What is the total number of valence electrons in an atom with the electron
configuration 2-8-5?
a. 2
c .5
b. 8
d. 15
45. What term refers to the region of an atom where an electron is most likely to
be found?
a. quantum
c. spectrum
b. orbital
d. orbit
46. What is the total number of electrons in an Mg+2 ion?
a. 10
c. 24
b. 2
d. 12
47.
Which of the following bond(s) can be described as being weak and
often transient
electrical attractions between two atoms bearing partial electrical
charges?
a. ionic
c. polar covalent
b. nonpolar covalent
d. all of the bove
48. In the following molecular formula, how many of each atom is present?
C6H12O6
a. C = 6, H = 12, O = 6
c. C = 12, H = 24, O = 12
b. C = 1, H = 6, O = 12
d. none of the above
49.
All atoms try to complete the number of ________ in their outer orbital.
50.
a. protons
c. electrons
b. neutrons
d. all of the above
Which of the following bonds are insoluble?
a. ionic
c. nonpolar covalent
b. polar covalent
d. none of the above
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Second Quarter Test With Answer in Grade 9 ScienceDokument5 SeitenSecond Quarter Test With Answer in Grade 9 ScienceRenalyn F. Andres80% (15)
- 2ND Summative Test - Science9 - 2022-2023Dokument3 Seiten2ND Summative Test - Science9 - 2022-2023Karen Bargayo Deloraso67% (3)
- 2nd Periodical Examination in Sci g9Dokument4 Seiten2nd Periodical Examination in Sci g9george barnachea100% (5)
- Science 9 PT 2ndQDokument3 SeitenScience 9 PT 2ndQMaria Elaine Feranil100% (1)
- Quarterly Test in g9 Science 2nd GradingDokument4 SeitenQuarterly Test in g9 Science 2nd GradingPedro GenosasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 2nd QuarterDokument2 SeitenScience 9 2nd QuarterJocelyn Acog Bisas Mestizo100% (1)
- Test Questions ScienceDokument4 SeitenTest Questions ScienceEsmeey Castañares100% (1)
- 2nd Quarterly Test in g9 ScienceDokument5 Seiten2nd Quarterly Test in g9 ScienceLIWLIWA SUGUITAN100% (1)
- Science 9 2nd QTR Exam With Answer KeyDokument3 SeitenScience 9 2nd QTR Exam With Answer KeyKatrina Lourdes SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCE 9 EXAM (2nd Quarter) QuestionsDokument3 SeitenSCIENCE 9 EXAM (2nd Quarter) QuestionsKert Cyrel RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second GradingDokument4 SeitenSecond GradingBillones Rebalde MarnelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- High School Science Exam Covers Atoms, Bonds, Organic CompoundsDokument5 SeitenHigh School Science Exam Covers Atoms, Bonds, Organic CompoundsKelly Ann Panganiban81% (26)
- Summative Test Science Grade 9 Module 1 and 2Dokument3 SeitenSummative Test Science Grade 9 Module 1 and 2Jamie Cea92% (49)
- Second Grading Examination Science 9Dokument5 SeitenSecond Grading Examination Science 9jtxbny100% (1)
- Department of Education Region X Division of Bukidnon District of Manolo Fortich II DAMILAG INTEGRATED SCHOOL SECOND PERIODICAL EXAMDokument4 SeitenDepartment of Education Region X Division of Bukidnon District of Manolo Fortich II DAMILAG INTEGRATED SCHOOL SECOND PERIODICAL EXAMAllan Roloma100% (1)
- Third Quarter Examination Grade 9 RegularDokument6 SeitenThird Quarter Examination Grade 9 RegularFelisa Andamon60% (5)
- Third Quarter Test in Grade 9 ScienceDokument3 SeitenThird Quarter Test in Grade 9 ScienceCherrie Ann GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Quarterly Examination in Science 9Dokument4 SeitenFirst Quarterly Examination in Science 9Chai Barcelon86% (7)
- Examining ScienceDokument5 SeitenExamining ScienceEncluna Lindon Jay100% (3)
- Third Quarter Test in Grade 9 ScienceDokument4 SeitenThird Quarter Test in Grade 9 ScienceCherrie Ann Go100% (4)
- 1st SUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 9 Q2Dokument5 Seiten1st SUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 9 Q2Sabnahis Batongbuhay Extension100% (1)
- Grade 9 Science Periodical Test ReviewDokument3 SeitenGrade 9 Science Periodical Test ReviewRowena Sta Maria83% (18)
- 1st Quarter Exam Science 9Dokument4 Seiten1st Quarter Exam Science 9Christian Mark Almagro Ayala100% (3)
- Answer Sheet Grade 9 Second QuarterDokument1 SeiteAnswer Sheet Grade 9 Second QuarterAlbert Rosete100% (3)
- Science 9 Second Quarter ExamDokument3 SeitenScience 9 Second Quarter ExamMARY ROSE D. BORINAGANoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 3rd Grading ExamDokument6 SeitenScience 9 3rd Grading ExamJessica Rosatase Gemang100% (2)
- 2nd Quarter First Summative Grade 9Dokument2 Seiten2nd Quarter First Summative Grade 9Apple Samoy100% (3)
- Third Quarter Exam in Grade - 9Dokument3 SeitenThird Quarter Exam in Grade - 9Amabelle Agsolid82% (44)
- Grade 9 Science 1st Periodical TestDokument7 SeitenGrade 9 Science 1st Periodical TestJay Ronnie PranadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 Constellation SummativeDokument1 SeiteScience 9 Constellation SummativeJane Limsan Paglinawan100% (4)
- 1st Periodic Test - Science 9Dokument4 Seiten1st Periodic Test - Science 9Lani Bernardo Cuadra100% (1)
- 3rd Final Exam Sci 9 2017Dokument4 Seiten3rd Final Exam Sci 9 2017Jeng Sanchez100% (7)
- 1st Periodical Test (Grade 9)Dokument4 Seiten1st Periodical Test (Grade 9)Alison Barrero87% (239)
- 2nd Periodical Exam English 9Dokument3 Seiten2nd Periodical Exam English 9Sherryl81% (31)
- 3rd Periodical Exam Science 9Dokument4 Seiten3rd Periodical Exam Science 9Sher Sherwin82% (11)
- Republic of the Philippines Science 9 Table of SpecificationDokument3 SeitenRepublic of the Philippines Science 9 Table of SpecificationCaryl Ann C. Sernadilla80% (5)
- Grade 9 (2nd Quarter Exam)Dokument5 SeitenGrade 9 (2nd Quarter Exam)Edward Almazan90% (31)
- FORCE AND MOTIONDokument4 SeitenFORCE AND MOTIONMark Ryan J Bacus75% (4)
- 4th Periodical Exam Science 9Dokument5 Seiten4th Periodical Exam Science 9Sher Sherwin70% (10)
- Grade 9 Science 1st Quarter 2016Dokument4 SeitenGrade 9 Science 1st Quarter 2016Keanu Ribs86% (21)
- 1st Quarter Exam Review in Grade 9 ScienceDokument4 Seiten1st Quarter Exam Review in Grade 9 ScienceMeljean Kalaw Castillo100% (1)
- Exam 2Dokument3 SeitenExam 2Limar Anasco EscasoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 First Quarter Exam SY 2021-2022Dokument5 SeitenScience 9 First Quarter Exam SY 2021-2022Encluna Lindon JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Quarter Examination in Science 9.vhanDokument3 Seiten3rd Quarter Examination in Science 9.vhanVhan Panilagao MendebilNoch keine Bewertungen
- DepEd English 9 Second Quarter TestDokument4 SeitenDepEd English 9 Second Quarter TestCharity Anne Camille Penaloza82% (11)
- Philippine Science Test Covers Volcanoes, Stars, ClimateDokument2 SeitenPhilippine Science Test Covers Volcanoes, Stars, ClimateChristine Joy E. Sanchez-Castelo100% (1)
- Volcanoes Summative TestDokument2 SeitenVolcanoes Summative Testjoan marie Pelias100% (3)
- 2nd Quarter 3rd Summative Science 9Dokument2 Seiten2nd Quarter 3rd Summative Science 9Apple SamoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rizal National High School Table of Specification Third Summative Test in Science 9Dokument5 SeitenRizal National High School Table of Specification Third Summative Test in Science 9Christine Joy DelaPena Sanico100% (20)
- My secret crush revealed in rhymeDokument4 SeitenMy secret crush revealed in rhymeArlhine Danga GalleboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pretest in Grade 9 ScienceDokument3 SeitenPretest in Grade 9 ScienceEj Rafael58% (12)
- 1 Periodical Exam 1 Grading Period Science 9 Name: - Score: - Grade & Section: - DateDokument3 Seiten1 Periodical Exam 1 Grading Period Science 9 Name: - Score: - Grade & Section: - Datejoy100% (2)
- Science 9 Quarter IIIDokument2 SeitenScience 9 Quarter IIIArvin Arne Rodrigo67% (3)
- Name: - Section: - Date: - Score: - Pre-Test First Quarter Grade 9 Science and TechnologyDokument2 SeitenName: - Section: - Date: - Score: - Pre-Test First Quarter Grade 9 Science and TechnologyJan IceNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Quarter Exam in Science 9Dokument3 SeitenFirst Quarter Exam in Science 9Ronalyn CajudoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 9 Science Exam ReviewDokument4 SeitenGrade 9 Science Exam ReviewJ R Caballero Dubluis100% (5)
- Summative Test Science 9 q4 WK 1-2Dokument3 SeitenSummative Test Science 9 q4 WK 1-2Joel Bagoyo100% (1)
- SCIENCE Grade 9: Quarter 2 - Module 3 Ionic CompoundDokument16 SeitenSCIENCE Grade 9: Quarter 2 - Module 3 Ionic CompoundRosalia Busca100% (1)
- 1st PT in Science 9 With TOS 2022 2023Dokument7 Seiten1st PT in Science 9 With TOS 2022 2023paulyn espino100% (1)
- Second Periodical Exam Science 9Dokument2 SeitenSecond Periodical Exam Science 9Michelle Mae HoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.6 BondingDokument17 Seiten1.6 BondingMahmoud TahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Lewis Dot Structure and Types of BondDokument71 Seiten4 Lewis Dot Structure and Types of BondEren Micaella100% (1)
- Homework CH 1-5Dokument2 SeitenHomework CH 1-5Brian DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sishugriha Senior School Chemical BondDokument4 SeitenSishugriha Senior School Chemical BondNARENDRAN SNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 TJC Promo Exam MCQ Answers CHEMISTRYDokument2 Seiten2013 TJC Promo Exam MCQ Answers CHEMISTRYgohjwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Chemistry An Atoms First ApproachDokument609 SeitenIntroductory Chemistry An Atoms First ApproachVirginia Jimnez100% (1)
- Bonding Jeopardy: Provided byDokument52 SeitenBonding Jeopardy: Provided byThe Electric DolphinNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.SC - BiochemistryDokument39 SeitenB.SC - BiochemistryJaseena AlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding Project 1Dokument2 SeitenChemical Bonding Project 1Queen ErellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of h2 Chemistry DefinitionsDokument7 SeitenList of h2 Chemistry Definitionsapi-342193969100% (1)
- Types of Bonds WorksheetDokument3 SeitenTypes of Bonds WorksheetKenji Munsuro100% (2)
- 1st Year Chemistry Sc1 ChemistryDokument896 Seiten1st Year Chemistry Sc1 Chemistrybiranchi satapathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classifying Compounds by Physical PropertiesDokument15 SeitenClassifying Compounds by Physical PropertiesTeddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Olympiad Model Paper 2018Dokument9 SeitenOlympiad Model Paper 2018deeyamullaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesDokument9 SeitenScience: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesAriel Lomugdang PatricioNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEASDokument48 SeitenGEASJonar MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry HandoutDokument2 SeitenOrganic Chemistry HandoutHonleth Jheney MamarilNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry Notes For SHS PDFDokument20 SeitenGeneral Chemistry Notes For SHS PDFAlwyn Dave Ambatali100% (4)
- Tampus Ppt-Ionic&covalentDokument51 SeitenTampus Ppt-Ionic&covalentjeneca tampusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elementary Science of Metals - Martin (Wykeham Publications Ltd. 1969) PDFDokument77 SeitenElementary Science of Metals - Martin (Wykeham Publications Ltd. 1969) PDFMichael Long100% (1)
- Ionic and Covalent BondsDokument5 SeitenIonic and Covalent Bondsapi-233981890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scrap Book in ChemistryDokument12 SeitenScrap Book in ChemistryReymond Jude PagcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Chemistry General Organic and BiologicalDokument1.236 SeitenIntroduction To Chemistry General Organic and BiologicalEstebanPartida100% (4)
- Ap Chem - Chapter 1 Reading GuideDokument21 SeitenAp Chem - Chapter 1 Reading Guideapi-475547739Noch keine Bewertungen
- 0620 w11 QP 33 PDFDokument12 Seiten0620 w11 QP 33 PDFMinakshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Chemistry NotesDokument70 SeitenIGCSE Chemistry NotesCrystal Wong93% (40)
- Solution Manual For Human Biology 16th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael WindelspechtDokument36 SeitenSolution Manual For Human Biology 16th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael Windelspechtoverspinmeetklac40100% (46)
- PERIOD 3 OXIDE PROPERTIESDokument6 SeitenPERIOD 3 OXIDE PROPERTIESCHEE HONG CHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2003 Local Chemistry Olympiads Exam Question PapersDokument7 Seiten2003 Local Chemistry Olympiads Exam Question PapersRSLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mod 1 Properties & Structure of Matter NotesDokument16 SeitenMod 1 Properties & Structure of Matter NotesVed PatelNoch keine Bewertungen