Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Uppp1 2016 Sem 3
Hochgeladen von
ThilagaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Uppp1 2016 Sem 3
Hochgeladen von
ThilagaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
Section A [15 marks]
Answer all questions in this section. Write your answer in the table given.
1.
Which of the following molecule does not contain a bond?
A
Benzene
B
Ethene
C
Methanal
D
Methane
2.
Which of the following organic compunds have the same empirical and molecular formulae?
A
CH3CH=CH2
B
CH2=CHCH=CHCH=CH2
C
CH2OHCHOHCH2OH
D
CH3CH2CH2COOH
3.
Which of the following statements about geometrical isomerism is true?
A
The molecule must be planar.
B
The melting point of the cis and trans isomers is different.
C
The chemical properties of the cis and trans isomers are different.
D
Two groups of atoms must be on each carbon atom that is covalently bonded by a
single bond.
4.
Which of the following compounds is isometric with propanoic acid?
A
CH3COOCH2CH3
B
CH2=CH-O-COCH3
C
CH3OCH2CH2OH
D
HOCH2CH2CHO
5. Which of the following
CH3CH(NH2)COOH
ClCH=CHCl
A
Optical
B
Geometric
C
Geometric
D
Optical
6.
isomerisms
are
shown
by
compounds
CH3CH(NH2)COOH
Optical
Optical
Geometric
Geometric
Which of the following best explains the function of OH- ion as a nucleophile?
A
It is alkaline.
B
It is negatively charged.
C
It has lone pair electrons.
D
It has a highly electronegative oxygen atom.
ClCH=CHCl,
7. In which of the following series, are the compounds arranged in the order of increasing basic
strength?
A
B
8. Which of the following reactions involves an electrophilic reagent?
CH3CH2Cl + HCl
A CH3CH3 + Cl2
B CH3Br + NaOH
CH3OH + NaBr
C CH3CH=CH2 + HBr
CH3CHBrCH3
D CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH
CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2O
9. Which of the following formulae does not represent an alkane?
A
C6H14
B
C13H28
C
C18H36
D
C36H74
10. What is the IUPAC name for (CH3)3CCH2CH3
A
1,1,1 - trimethylpropane
B
1,1,2 - trimethylpropane
C
2 - methylpentane
D
2,2 - dimethylbutane
11. Alkane has low reactivity because
A
it is a unsaturated hydrocarbon
B
it is a saturated hydrocarbon
C
it have a charge centre
D
its molecule is polar
12. What is the major product for the reaction of propene and hydrogen halide such as ?
A
Bromine
B
Propane
C
1-bromopropane
D
2-bromopropane
13. What is the reaction between ethene and hydrogen bromide?
A
Nucleophilic addition
B
Electrophilic addition
C
Nucleophilic substitution
D
Electrophilic substitution
14. Hydrocarbons undergo various reactions. One of the reactions involving 3,3-dimethyloctane is
shown below.
X
3,3-Dimethyloctane
Products
X could be
A
450 C, Al2O3 / SiO2
B
H2SO4(conc), 180 C
C
NaOH(aq), reflux
D
KCN(aq)/ethanol, reflux
15. Which of the following compounds is the product obtained when ethene is oxidised by
oxygen at 300 C using silver catalyst?
A
HOCH2CH2OH
HC
ll
O
H2C
CH
ll
O
CH2
O
O
H2C
CH2
O O
Section A [15 marks]
No
Answer
No
Answer
No
11
12
13
14
10
15
Answer
Section B [15 marks]
Answer all questions in this section.
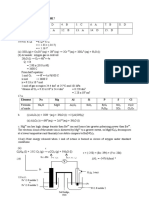
16. (a) The compound C5H12 exhibits isomer pentane, 2-methylbutane and 2,2-dimethylpropane.
The table below shows the boiling point of the isomers.
Compound
pentane
2-methylbutane
2,2-dimethylpropane
Boiling point/ C
36.3
29.7
9.5
(i) Explain this boiling point trend.
[2 marks]
(b) pKa values of some compounds are given as follows.
pKa values: 15.5, 10.0 and 4.74
Compound
CH3OH
C6H5OH
CH3COOH
pKa
(i) Fill in the blanks with the correct pKa.
[1 mark]
(ii)Arrange the compounds in increasing order of their acidic strength.
[1 mark]
(ii)Explain your answer.
[3 marks]
17. Photochemical smog is a type of air pollution which is formed from the reaction of gases
from internal combustion of engines of vehicles, in the atmosphere in the presence of sunlight.
(a) Name the gases formed from the internal combustion of engines of vehicles which
contribute to the formation of photochemical smog.
[2 marks]
(b) A measure taken to reduce these pollutant gases is to install catalytic converter in vehicles.
(i) Name the catalyst used.
[1 mark]
(ii) State the type of catalysis which takes place in the catalytic converter.
[1 mark]
(iii) Write two equations of reactions involved in the catalytic converter. [2 marks]
(c) Suggest two other ways to decrease air pollution from internal combustion of engines of
vehicles.
[2 marks]
Section C [30 marks]
Answer two questions only in this section.
18.(a) What is meant by stereoisomerism?
[2 marks]
(b) An amount of 0.01 mole of a hydrocarbon is burnt in excess oxygen. The products of the
combustion are passed through anhydrous calcium chloride and then through potassium
hydroxide solution. The masses of anhydrous calcium chloride and potassium hydroxide solution
increase by 0.72 g and 1.76 g respectively.
[7 marks]
(i) Determine the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon.
(ii) Draw the structural formulae of all the isomers of the hydrocarbon.
[4 marks]
(iii)If one of the isomers shows stereoisomerism, draw and name the stereoisomer.
[2 marks]
19. (a) (i) What is meant by electrophile?
[1 mark]
(ii) Give an example of addition reaction involving bromine, and describe the mechanism
involved.
[4 marks]
(b)Cracking is very important in the petroleum industry. There are two main cracking
processes. When 3,4-dimethylheptane undergoes a catalytic cracking reaction, a possible
reaction is as follows:
CH3 CH3
l
l
Catalyst
CH3CH2-CH-CH-CH2CH2CH3
X + CH3CH2CH3
Compound X shows geometrical isomerism. On vigorous oxidation, X forms compounds Y and
Z with the molecular formulae C4H8O and C2H4O2 respectively.
(i) State the catalyst used for this reaction.
[1 mark]
(ii)Write the structural formulae of compounds X, Y and Z. Give a suitable reagent which
can be used for the oxidation of X.
[4 marks]
(iii)3,4-dimethylheptane is used as a fuel. Write the structural formula of its isomer with
a higher octane number. Explain your answers.
[2 marks]
(iv)State two important uses of cracking reaction in the petroleum industry.[2 marks]
(v)Name another main cracking process.
[1 mark]
20. (a)Polychlorinated methanes are useful solvents. Dichloromethane is a component of many
paint-stripping solvents.
(i) State the condition used to produce dichloromethane.
[1 mark]
(ii) Name the mechanism of the reaction involved.
[1 mark]
(iii)Write the mechanism of the reaction.
[3 marks]
(iv) Can the chloroform formed from dichloromethane? Explain it.
[2 marks]
(b) Cycloalkanes and alkenes have the same general formulae. The structural formula of a
cycloalkane is shown below.
H3C
CH3
(i) State the types of isomerism shown by the cycloalkane above.
[2 marks]
(ii) Write the structural formula of an alkene, C7H14, that exhibits the isomerism in (i) and
draw all of its isomers.
[3 marks]
(iii) Suggest a chemical test to distinguish cycloalkane from the alkene in (ii). State the
observation and write the reaction equation involved.
[3 marks]
Prepared by,
Approved by,
--------------------------(Gan Lui Nam)
Chemistry Teacher
------------------------------(Pn Hjh Hashimah Binti Salleh)
Form Six Senior Assistant
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- K WentworthDokument195 SeitenK WentworthThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candidate'S Performance ReportDokument7 SeitenCandidate'S Performance ReportThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KKXXDokument4 SeitenKKXXThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guru Kelas: PN Thilagavathy Sethuramah Kelas: 6 Atas SC Epsilon Dan DeltaDokument2 SeitenGuru Kelas: PN Thilagavathy Sethuramah Kelas: 6 Atas SC Epsilon Dan DeltaThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinopsis SekolahDokument2 SeitenSinopsis SekolahThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemDokument10 SeitenChemThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- T4Dokument18 SeitenT4ThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Chew 1Dokument7 SeitenExam Chew 1ThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Group TEDokument6 SeitenNotes Group TEThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QUIZ 6 ThermochemistryDokument1 SeiteQUIZ 6 ThermochemistryThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RevisionDokument2 SeitenRevisionThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 BH Didik 3 Apr PDFDokument17 Seiten12 BH Didik 3 Apr PDFFAZARINoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Excel 1 2017 Term 2Dokument2 SeitenAnswer Excel 1 2017 Term 2ThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1 ThermochemDokument1 SeiteExercise 1 ThermochemThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Chew 1Dokument7 SeitenExam Chew 1ThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attendance List For Extra Class: U 6 SC ZetaDokument1 SeiteAttendance List For Extra Class: U 6 SC ZetaThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- K WentworthDokument195 SeitenK WentworthThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NameDokument1 SeiteNameThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemDokument10 SeitenChemThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemDokument1 SeiteChemThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Both The Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces ProvidedDokument5 SeitenAnswer Both The Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces ProvidedThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Confidential : (Malacca High School Estd.1826)Dokument9 SeitenConfidential : (Malacca High School Estd.1826)ThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 6186105941197324304 PDFDokument56 Seiten5 6186105941197324304 PDFThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Okeke, ODokument132 SeitenOkeke, OThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple MachinesDokument14 SeitenSimple MachinesThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Exercise 3 - Hess' LawDokument2 Seiten2.1 Exercise 3 - Hess' LawHorro8480100% (1)
- 4.1 Exercise 1Dokument2 Seiten4.1 Exercise 1ridithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Confidential : (Malacca High School Estd.1826)Dokument9 SeitenConfidential : (Malacca High School Estd.1826)ThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic ChemistryDokument193 SeitenOrganic ChemistryThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- INORGANIC Periodic Table 1Dokument26 SeitenINORGANIC Periodic Table 1ThilagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- GIC DevelopmentDokument12 SeitenGIC DevelopmentJinny ShawNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLEC ChemistryDokument6 SeitenSLEC ChemistryPraveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artículo EDTADokument10 SeitenArtículo EDTAALDAIR COSSIO POLONoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap03 CarbonylsDokument10 SeitenChap03 CarbonylsAPLCTNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heavy MetalsDokument101 SeitenHeavy MetalsMoustafa ElsadanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - Valence Bond TheoryDokument32 SeitenChapter 4 - Valence Bond TheorykhadijahhannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- RSC Advances: ReviewDokument14 SeitenRSC Advances: ReviewLuana Alves MachadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2018 QP - Unit 5 Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelDokument28 SeitenJune 2018 QP - Unit 5 Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelThunn NayChi LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- NChO 2016Dokument87 SeitenNChO 2016Stephan ReynoldsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2 - ComplexationDokument48 SeitenTopic 2 - ComplexationLokesh JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICh O33 IN2001 PPDokument133 SeitenICh O33 IN2001 PPLê Hoàng MinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organometallic CatalysisDokument5 SeitenOrganometallic CatalysisMuhammad Hassan ZiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022-Cu (II) Complexes of Flavonoids in Solution Impact of The Cu (II) Ion On The Antioxidant and DNA-intercalating PropertiesDokument12 Seiten2022-Cu (II) Complexes of Flavonoids in Solution Impact of The Cu (II) Ion On The Antioxidant and DNA-intercalating Propertieslas.chemicalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry MHSSDokument24 SeitenChemistry MHSSnavin chhetriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganica Chimica Acta: Research PaperDokument14 SeitenInorganica Chimica Acta: Research PaperRuan ReisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz - Coordination Compounds PDFDokument2 SeitenQuiz - Coordination Compounds PDFAman JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- @iitwale Join JEE 215 Most Important Question With SolutionsDokument191 Seiten@iitwale Join JEE 215 Most Important Question With SolutionsSjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Symmetry and Group Theory - CarterDokument155 SeitenMolecular Symmetry and Group Theory - CarterRafael Pinto Tiradentes100% (2)
- LigPlot Multiple LiganProtein Interaction Diagrams ForDokument9 SeitenLigPlot Multiple LiganProtein Interaction Diagrams ForSuresh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 55 Chemical Equilibrium - A Practical Introduction For The Physical and Life Sciences Springer Us 1975Dokument251 Seiten55 Chemical Equilibrium - A Practical Introduction For The Physical and Life Sciences Springer Us 1975banepostingNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Two-Coordinate Boron Cation Featuring C-B - C Bonding: ArticlesDokument6 SeitenA Two-Coordinate Boron Cation Featuring C-B - C Bonding: ArticlesCarlo ChacaltanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complexation Reactions and Titrations: Che 401: Analytical ChemistryDokument37 SeitenComplexation Reactions and Titrations: Che 401: Analytical ChemistryScrappy WellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Questions of Inorganic Chemistry 90Dokument7 SeitenImportant Questions of Inorganic Chemistry 90Fahad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synt432 PrepCuA4H2ODokument12 SeitenSynt432 PrepCuA4H2OWisi Wasi100% (1)
- Oxygen Transfer Reactions: Catalysis by Rhenium Compounds: James H. EspensonDokument46 SeitenOxygen Transfer Reactions: Catalysis by Rhenium Compounds: James H. Espensongeo angNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Distortion On The D Orbital Energy LevelsDokument7 SeitenEffect of Distortion On The D Orbital Energy LevelsAcikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rhodium Catalyzed Hydroformylation - CH 01Dokument13 SeitenRhodium Catalyzed Hydroformylation - CH 01maildesantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHP 07 AnsDokument28 SeitenCHP 07 AnsMukundkriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/42Dokument24 SeitenCambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/42YasminNoch keine Bewertungen
- D Block (2012 13)Dokument8 SeitenD Block (2012 13)Anonymous 8VJhV1eI2y100% (1)