Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Psych Student Notes
Hochgeladen von
Jack BangcoyoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Psych Student Notes
Hochgeladen von
Jack BangcoyoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
3.
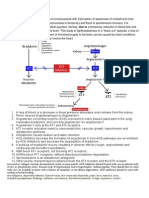
Medications for CHF
Medication
ACE Inhibitors
Angiotensin
Receptor
Blocker
Vasodilators
Aldosterone
Receptor
Antagonist
Action
It act in the lungs to prevent ACE
from converting angiotensin I to
angiotensin
II,
a
powerful
vasoconstrictor and stimulator of
aldosterone release. This action
leads to a decrease in blood
pressure
and
in
aldosterone
secretion, with a resultant slight
increase in serum potassium and a
loss of serum sodium and fluid.
Rationale
ACE inhibitors is used to decreases the peripheral
vascular resistance, thereby, decreasing BP, as
well as reducing the peripheral edema by
decreasing water and sodium retention. It also
helps by reducing the cardiac increased workload
due to increased peripheral resistance.s
It selectively bind with
the Same action with ACE inhibitors
angiotensin II receptors in vascular
smooth muscle and in the adrenal
cortex to block vasoconstriction and
the release of aldosterone. These
actions block the blood pressure
raising effects of the renin
angiotensin system and lower blood
pressure.
The vasodilators act directly on It is used to decrease BP and cardiac muscle
vascular smooth muscle to cause workload by relaxing the smooth muscles.
muscle relaxation, leading to
vasodilation and drop in blood
pressure. They do not block the
reflex tachycardia that occurs when
blood pressure drops.
It acts by antagonizing the reception Same reason with ACE and ARB.
of Aldosterone, thereby, inhibiting
the action of aldosterone.
4. Diet Recommendation
- Sodium Restricted Diet
-Low Sodium Diet
-Low watery food intake
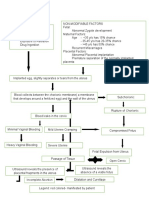
Cues
Nursing
Scientific basis
Objectives
Insufficient
General :
Intervention
Rationale
Evaluation
Diagnosis
Subjective
akong
kapoy
lawas
as
verbalized by the patient
Activity
Intolerance
r/t
physiological
or
After 2 days of holistic
Imbalance
psychological
nursing care, the pt will
between Oxygen
energy to endure
be able to reach OLOF.
Objective-
supply
or
Specific
Pallor
demand;
required
or
After 8 hrs of nurse-pt
(anemia)
desired activities.
interaction, the pt will be
1.
able to :
importance
Skin
Conjunctiva
Nail Beds
Lips
Oral Mucosa
and
complete
Hypoventilation
1.
occurs
when
alveolar
demonstrate
or
the
of
1.
For the client and
significant
others
adhere
Oxygen Therapy
the therapy.
verbalize a decrease in
2.
2. To discern treatment
activity intolerance.
related factors.
ventilation
is
2. demonstrate CRT of
inadequate
to
<3seconds.
meet the oxygen
Discuss
Note
treatment
related factor from disease
factor.
3.
Administer
O2
therapy as ordered
3. To relieve hypoxia
by
delivering
oxygen
at
demand of the
concentrations greater than
body
ambient air
or
eliminate
(21%).
sufficient carbon
4. Monitor V/S and
4. To determine adverse
dioxide.
cognitive
signs,
effect of Oxygen therapy; to
alveolar
watching
for
immediately condemn the
ventilation
changes
As
decreases,
body
in
blood
the
pressure, heart, and
retains
respiratory rate; note
line.
carbon dioxide
skin
pallor
and
cyanosis.
5.
5.
To determine adverse
Monitor
effect of Oxygen therapy; to
Nurses
physiologic signs of
immediately condemn the
Guide12th
rejection to Oxygen
line.
edition
Doenges,
Source :
Moorhouse, Murr
therapy.
6. Take precautions
6.
To
on Oxygen tank care
safety
promote
Oxygen
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone SystemDokument24 SeitenTargeting the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone SystemAriel OlshevskyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHARMA ScriptDokument5 SeitenPHARMA Scriptjlamadrid267Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Acting On Cardiovascular System-FinalsDokument125 SeitenDrugs Acting On Cardiovascular System-FinalsPrincess C. SultanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACE InhibitorsDokument8 SeitenACE InhibitorsJohn HillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diuretic: 3. Calcium Channel BlockersDokument3 SeitenDiuretic: 3. Calcium Channel BlockersAniRafikaBullatzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Failure New SlidesDokument41 SeitenHeart Failure New SlidesjawadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers An OverviewDokument7 SeitenAngiotensin II Receptor Blockers An OverviewAmit KhairnarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan HF FinalDokument10 SeitenNursing Care Plan HF FinalCristina L. JaysonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Cardiovascular DrugsDokument120 SeitenPharmacology Cardiovascular DrugsDareRaymond100% (1)
- Arbs vs. Ace Inhibitors Nursing NclexDokument10 SeitenArbs vs. Ace Inhibitors Nursing NclexSameerQadumiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 antihypertensionSDSDokument7 SeitenLecture 1 antihypertensionSDSSara AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inhibitors of AngiotensinDokument37 SeitenInhibitors of AngiotensinBoyu GrtrNoch keine Bewertungen
- QA NotesDokument6 SeitenQA NotesGayleNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUR3111 Nursing Care Plan Copy 1Dokument19 SeitenNUR3111 Nursing Care Plan Copy 1liNoch keine Bewertungen
- CARDIAC-MEDICATION-LECTUREDokument23 SeitenCARDIAC-MEDICATION-LECTUREilikeedsheeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Drugs (Group-7)Dokument46 SeitenCardiovascular Drugs (Group-7)2042 Shoaib AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVS (HF, HTN) PharmacologyDokument99 SeitenCVS (HF, HTN) PharmacologyCherenet TomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARBs (Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers) NCLEXDokument15 SeitenARBs (Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers) NCLEXSameerQadumi100% (1)
- Drug Presentation On Anti-Hypertensive: All India Institute of Medical and Science New Delhi 2021-2022Dokument12 SeitenDrug Presentation On Anti-Hypertensive: All India Institute of Medical and Science New Delhi 2021-2022Priya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Class: Department: Roll No.: Subject: Course Code: Cr. HR.: Submitted To: Date of SubmissionDokument10 SeitenName: Class: Department: Roll No.: Subject: Course Code: Cr. HR.: Submitted To: Date of SubmissionAnoosha FarooquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obat ACE Inhibitors: Cara Kerja dan Efek SampingDokument3 SeitenObat ACE Inhibitors: Cara Kerja dan Efek SampingMuharram RanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17 Cardiovascular DrugsDokument35 SeitenChapter 17 Cardiovascular Drugsaisyahasrii_Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10 and 11 Treatment of Hypertension and AnginaDokument10 Seiten10 and 11 Treatment of Hypertension and AnginaBrandon AviciiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beyond ACEI and BBDokument18 SeitenBeyond ACEI and BBMaria CamilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ten PharmaDokument4 SeitenTen PharmaChrisciela MatienzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Drugs Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument70 SeitenCardiovascular Drugs Nursing ResponsibilitiesRayne Bonifacio100% (2)
- RAASDokument5 SeitenRAASJamaica VillonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Affecting Renin-Angiotensin System (RASDokument19 SeitenDrugs Affecting Renin-Angiotensin System (RASvinita SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inotropes in Critical Care UnitDokument48 SeitenInotropes in Critical Care UnitKelvin Christopher Ker100% (1)
- Antihypertensive & Antianginal DrugsDokument5 SeitenAntihypertensive & Antianginal Drugsdomememe1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Number 1Dokument5 SeitenCase Study Number 1Kevin Kyle RizarriNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReninDokument4 SeitenReninSarah AndrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treating Heart Failure: Current Guidelines for Pharmacological ManagementDokument11 SeitenTreating Heart Failure: Current Guidelines for Pharmacological ManagementKareem SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angiotensin II Angiotensin IIDokument5 SeitenAngiotensin II Angiotensin IIJia En YeohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacotherapy of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)Dokument163 SeitenPharmacotherapy of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)Aditya rathoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11A Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemDokument85 Seiten11A Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemJaps De la CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Physiology Regulation Arterial Blood PressureDokument5 SeitenReview Physiology Regulation Arterial Blood PressureRae OkonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHF PBLDokument3 SeitenCHF PBLqtiefyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isyncope: Partial or Complete Loss of Consciousness With Interruption of Awareness of Oneself and OnesDokument4 SeitenIsyncope: Partial or Complete Loss of Consciousness With Interruption of Awareness of Oneself and OnesLimLichynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care Nursing Guide to Shock and Multi-Organ DysfunctionDokument63 SeitenCritical Care Nursing Guide to Shock and Multi-Organ DysfunctiontikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACE INHIBITORS & ARBsDokument31 SeitenACE INHIBITORS & ARBsMaria khurshidNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAS 4 Drugs For HypertensionDokument28 SeitenLAS 4 Drugs For HypertensionMuhammad Haroon RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition and Vasoactive Substances in The Critically Ill PatientDokument7 SeitenNutrition and Vasoactive Substances in The Critically Ill PatientTupperware NeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Drugs - IODokument18 SeitenCardiovascular Drugs - IOJoël N PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Considerations in Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor TherapyDokument8 SeitenRenal Considerations in Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor TherapyCondurache Ilie-AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- L7 heart failure practice essayDokument2 SeitenL7 heart failure practice essaymoshlingmomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genxraver Girl Interrupted Usmle Step 2 Notes PDFDokument259 SeitenGenxraver Girl Interrupted Usmle Step 2 Notes PDFughbuzzoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Drugs HypertensionDokument5 SeitenCardiac Drugs HypertensionEciOwnsMeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs For Congestive Heart FailureDokument46 SeitenDrugs For Congestive Heart Failuresultan khabeeb100% (1)
- CardiologyDokument20 SeitenCardiologycnnc21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acei and ArbDokument6 SeitenAcei and ArbNurulrezki AtikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology RAASDokument3 SeitenPhysiology RAASAulia Mahya FaradisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology - A Summary of Common ConditionsDokument50 SeitenPharmacology - A Summary of Common ConditionsJeremy YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs for Hypertension 2023 (1)Dokument19 SeitenDrugs for Hypertension 2023 (1)aguilarjanicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10-11 Treatment of HypertensionDokument11 Seiten10-11 Treatment of HypertensionHanif GandohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihypertensive Drugs: HypertensionDokument8 SeitenAntihypertensive Drugs: Hypertensionalmastar officeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesVon EverandNursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Diabetes: Oxidative Stress and Dietary AntioxidantsVon EverandDiabetes: Oxidative Stress and Dietary AntioxidantsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Artery Stenosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandRenal Artery Stenosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating PolyneuropathyDokument1 SeiteChronic Inflammatory Demyelinating PolyneuropathyJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPPDokument3 SeitenPPPJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disease Info TobeprintedDokument15 SeitenDisease Info TobeprintedJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDokument84 SeitenTraumatic Brain InjuryJack Bangcoyo100% (2)
- Fast Facts On Traumatic Brain InjuryDokument15 SeitenFast Facts On Traumatic Brain InjuryJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DXDokument18 SeitenDXJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory ExamsDokument17 SeitenLaboratory ExamsJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CidpDokument72 SeitenCidpJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory ExamsDokument17 SeitenLaboratory ExamsJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Part Findings and Diagnostic TestsDokument3 SeitenBody Part Findings and Diagnostic TestsAlex SilvanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTRODUCTIONDokument9 SeitenINTRODUCTIONJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental StatusDokument3 SeitenMental StatusJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory ExamsDokument17 SeitenLaboratory ExamsJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level of DeveDokument44 SeitenLevel of DeveJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profileand XrayDokument1 SeiteProfileand XrayJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Part Findings and Diagnostic TestsDokument3 SeitenBody Part Findings and Diagnostic TestsAlex SilvanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TbiDokument8 SeitenTbiJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tibia Fracture Final PPPDokument3 SeitenTibia Fracture Final PPPJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAYDokument108 SeitenSAYJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical AssessmentDokument23 SeitenPhysical AssessmentJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- VasectomyDokument2 SeitenVasectomyJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tibia fracture risk factors in 61-year-old maleDokument1 SeiteTibia fracture risk factors in 61-year-old maleJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level of Growth and Development 3.3.1 Normal Development of A Young Adult (Potter and Perry)Dokument59 SeitenLevel of Growth and Development 3.3.1 Normal Development of A Young Adult (Potter and Perry)Jack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Teaching Plan for Traumatic Brain InjuryDokument7 SeitenHealth Teaching Plan for Traumatic Brain InjuryJack Bangcoyo100% (1)
- SoftDokument6 SeitenSoftJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast Facts On Traumatic Brain InjuryDokument15 SeitenFast Facts On Traumatic Brain InjuryJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDokument77 SeitenTraumatic Brain InjuryJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frontpagez XZDokument6 SeitenFrontpagez XZJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movie ReviewDokument1 SeiteMovie ReviewJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinecod Forte Tablet: Each Film Coated Sustained Release Tablet Contains ButamirateDokument10 SeitenSinecod Forte Tablet: Each Film Coated Sustained Release Tablet Contains ButamirateJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Hypertensive DrugsDokument113 SeitenAnti Hypertensive DrugsRobert DowneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone System: Pathophysiological Role and Pharmacologic InhibitionDokument12 SeitenThe Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone System: Pathophysiological Role and Pharmacologic Inhibitionfatimah hasibuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Proposal Form FINALDokument5 SeitenResearch Proposal Form FINALJohn Felix AgdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food MicrobiologyDokument7 SeitenFood MicrobiologyJuan Jose Escobar P.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amlodipine BesylateDokument2 SeitenAmlodipine BesylateGLen CaniedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amlodipine ReadingDokument12 SeitenAmlodipine Readingines pachecoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANS, RAAS, and ADH Heart RegulatorsDokument2 SeitenANS, RAAS, and ADH Heart RegulatorsParis ParisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Drug Information: RamiprilDokument1 SeiteKey Drug Information: Ramiprilamaliea234Noch keine Bewertungen
- CARDIODokument11 SeitenCARDIOJenica SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews: Ganiyu Oboh, Ayokunle O. AdemosunDokument5 SeitenDiabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews: Ganiyu Oboh, Ayokunle O. AdemosunDian Ayu ChotimahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angiotensin Receptor BlockersDokument6 SeitenAngiotensin Receptor BlockersMohammad Arafat SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- APPENDIX A B GlossaryDokument15 SeitenAPPENDIX A B GlossaryaddiramonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Captopril Drug Study PDFDokument5 SeitenCaptopril Drug Study PDFRenz TalladorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apostolidis Et Al 2015Dokument31 SeitenApostolidis Et Al 2015movilather coperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angiotensin Ii Receptor Blockers (ARBS) : Danielle Trisha L. MallariDokument7 SeitenAngiotensin Ii Receptor Blockers (ARBS) : Danielle Trisha L. MallariTrisha MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- MoexiprilDokument23 SeitenMoexiprilYeyenJaejoongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Heart Failure. Case Study ExplanationDokument6 SeitenCongestive Heart Failure. Case Study ExplanationOkenabirhie100% (1)
- Covid PGXDokument13 SeitenCovid PGXDyahsekarayupudak wangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypertensionDokument36 SeitenHypertensionRECEPTION AND DIAGNOSTIC CENTER RDC MEDICAL SECTIONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Care HFDokument14 SeitenVirtual Care HFTom BiusoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Esperanza Cabral ModuleDokument54 SeitenDr. Esperanza Cabral ModuleNazarine TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Drugs: Dr. April Dawn R. LuceroDokument122 SeitenCardiovascular Drugs: Dr. April Dawn R. LuceroRjDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology: Ana Sharmaine S. Uera, MD DR PJGMRMC Anesthesiology Department 1st Year ResidentDokument68 SeitenCardiovascular Pharmacology: Ana Sharmaine S. Uera, MD DR PJGMRMC Anesthesiology Department 1st Year ResidentLalay CabanagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Separation and Quantification of Octahydro-1h-Indole-2-Carboxilic Acid and Its Three Isomers by HPLC Using Refractive Index DetectorDokument6 SeitenSeparation and Quantification of Octahydro-1h-Indole-2-Carboxilic Acid and Its Three Isomers by HPLC Using Refractive Index DetectorSanthi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental Care For Patients With Heart Failure: An UpdateDokument9 SeitenDental Care For Patients With Heart Failure: An UpdateGustavo A OrtegonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes - 2022: 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk ManagementDokument31 SeitenStandards of Medical Care in Diabetes - 2022: 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk ManagementAdina SimionNoch keine Bewertungen
- CilazaprilDokument24 SeitenCilazaprilMarcelle GuimarãesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Pressure Drugs ReviewDokument54 SeitenBlood Pressure Drugs ReviewJeremy VivitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihypertensive Drugs: Re Jackson BSC MB CHB Frca and MC Bellamy MB BS MA FRCA FRCP (Edin) FficmDokument6 SeitenAntihypertensive Drugs: Re Jackson BSC MB CHB Frca and MC Bellamy MB BS MA FRCA FRCP (Edin) FficmDwie SeptivianieNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHRONIC HEART FAILURE SYMPTOMS AND DIAGNOSISDokument10 SeitenCHRONIC HEART FAILURE SYMPTOMS AND DIAGNOSISYudha GanesaNoch keine Bewertungen