Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Modulation
Hochgeladen von
alokesh19820 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten3 SeitenOriginaltitel
Modulation.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten3 SeitenModulation
Hochgeladen von
alokesh1982Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
Modulation
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
For other uses, see Modulation (disambiguation).
Passband modulation
Analog modulation
AM
FM
PM
QAM
SM
SSB
Digital modulation
ASK
APSK
CPM
FSK
MFSK
MSK
OOK
PPM
PSK
QAM
SC-FDE
TCM
Spread spectrum
CSS
DSSS
FHSS
THSS
See also
Capacity-approaching codes
Demodulation
Line coding
Modem
AnM
PoM
PAM
PCM
PWM
M
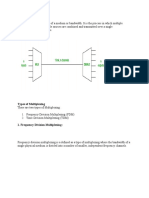
OFDM
FDM
Multiplex techniques
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more
properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal that
typically contains information to be transmitted.
In telecommunications, modulation is the process of conveying a message signal, for example a
digital bit stream or an analog audio signal, inside another signal that can be physically
transmitted. Modulation of a sine waveform transforms a baseband message signal into a
passband signal.
A modulator is a device that performs modulation. A demodulator (sometimes detector or
demod) is a device that performs demodulation, the inverse of modulation. A modem (from
modulatordemodulator) can perform both operations.
The aim of analog modulation is to transfer an analog baseband (or lowpass) signal, for
example an audio signal or TV signal, over an analog bandpass channel at a different frequency,
for example over a limited radio frequency band or a cable TV network channel.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Learn Amateur Radio Electronics on Your SmartphoneVon EverandLearn Amateur Radio Electronics on Your SmartphoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileVon EverandAmateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessVon EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- ModulationDokument41 SeitenModulationNimma Avanthi100% (1)
- Wavelength Division Multiplexing: A Practical Engineering GuideVon EverandWavelength Division Multiplexing: A Practical Engineering GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- ModulationDokument26 SeitenModulationRahul SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Analog Modulation MethodsDokument7 Seiten1 Analog Modulation MethodszeynepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Electrical Engineering: EE323-Communication Systems IIDokument15 SeitenDepartment of Electrical Engineering: EE323-Communication Systems IIAyad A. ABDULKAFINoch keine Bewertungen
- Dulation Is The Process of Varying One or More Properties of A High Frequency PeriodicDokument10 SeitenDulation Is The Process of Varying One or More Properties of A High Frequency PeriodicnikhiljainbemechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project PDF FinalDokument21 SeitenProject PDF FinalramratanecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument9 SeitenChapter 2Bangash KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term Paper of Ele-102: TopicDokument12 SeitenTerm Paper of Ele-102: Topicshailesh singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modulacion-Demodulacion-Medios de Transmision y NormatividadDokument5 SeitenModulacion-Demodulacion-Medios de Transmision y NormatividadOziel RivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On Modulation (Class 12)Dokument14 SeitenProject Report On Modulation (Class 12)Shivam Tripathi100% (9)
- Presented by Lipika Sahu Roll No-Pc12IST018 Bscist 2 YearDokument14 SeitenPresented by Lipika Sahu Roll No-Pc12IST018 Bscist 2 YearSuneeta SethyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modulation: Modulation Is The Process of Varying One Waveform in Relation ToDokument7 SeitenModulation: Modulation Is The Process of Varying One Waveform in Relation ToNitesh HotwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Low-Frequency Message Signal (Top) May Be Carried by An AM or FM Radio WaveDokument3 SeitenA Low-Frequency Message Signal (Top) May Be Carried by An AM or FM Radio Wavebasha007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modulation/Demodulation: Asst. Prof. Chaiporn Jaikaeo, PH.DDokument19 SeitenModulation/Demodulation: Asst. Prof. Chaiporn Jaikaeo, PH.DDorian GreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Am/fdm and Am/tdmDokument22 SeitenAm/fdm and Am/tdmHere's meNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is Multiplexing? ExplainedDokument26 SeitenWhat is Multiplexing? ExplainedSammar AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokument4 SeitenNew Microsoft Office Word Documentganeshpillutla4163Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modulation and CodingDokument87 SeitenModulation and CodingKENNETH EBIONoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Communications-Notes PDFDokument110 SeitenAnalog Communications-Notes PDFjyothimunjam100% (1)
- Analog Communications: BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4)Dokument88 SeitenAnalog Communications: BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4)Sagar Babu NandigamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Report Modulation: Arshdeep Singh 100905012 EIC-1Dokument24 SeitenAssignment Report Modulation: Arshdeep Singh 100905012 EIC-1Arshdeep Singh MalhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE2009 Communications Modulation and Demodulation TechniquesDokument77 SeitenEEE2009 Communications Modulation and Demodulation TechniquesShrikant ChamlateNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE2009 Communications Modulation and Demodulation TechniquesDokument77 SeitenEEE2009 Communications Modulation and Demodulation TechniquesArun MoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2Dokument31 SeitenLecture 2taif.mossa88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modulation: Analog Modulation Methods Digital Modulation MethodsDokument8 SeitenModulation: Analog Modulation Methods Digital Modulation Methodsmazen ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Modulation TechDokument63 SeitenDigital Modulation Techgaurav_juneja_4Noch keine Bewertungen
- DSLAMDokument45 SeitenDSLAMPaulpandi MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 NewDokument18 SeitenChapter 3 NewCicie_RawkstarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elza 2 CommDokument153 SeitenElza 2 CommlegasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC CheatsheetDokument2 SeitenDC CheatsheetRashi SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Modulation Works to Transmit Information SignalsDokument8 SeitenHow Modulation Works to Transmit Information SignalsMubashir AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Modulation Techniques / MultiplexingDokument3 SeitenDigital Modulation Techniques / MultiplexingYzza Veah Esquivel100% (2)
- Introduction To Modulation and DemodulationDokument77 SeitenIntroduction To Modulation and DemodulationPulak MandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Engineering Pulse Modulation GuideDokument13 SeitenDigital Engineering Pulse Modulation Guidealexlorenzo9mmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Modulation and DemodulationDokument77 SeitenIntroduction To Modulation and Demodulationkavish malakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Modulation TechniquesDokument3 SeitenDigital Modulation TechniquesrohitpowariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modulation of Digital Data Student ReportDokument9 SeitenModulation of Digital Data Student Reportالبياتي محمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Communication-Prabhakar KapulaDokument105 SeitenAnalog Communication-Prabhakar KapulaDavid ReevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Communication-Prabhakar KapulaDokument105 SeitenAnalog Communication-Prabhakar KapulaSanJeev Dani PeDrosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On Performance of Digital Modulation TechniquesDokument8 SeitenProject Report On Performance of Digital Modulation Techniqueseshet chafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-I: Introduction To Communication SystemDokument107 SeitenUnit-I: Introduction To Communication SystemSivaKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication System IntroductionDokument65 SeitenCommunication System IntroductionMylavarapu SriprithamNoch keine Bewertungen
- مروان الناجي (analog)Dokument5 Seitenمروان الناجي (analog)مروان الحاسيNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 5 Digital CommunicationDokument14 SeitenUNIT 5 Digital CommunicationSunithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT2004 - Introduction To Data Communication & NetworksDokument73 SeitenIT2004 - Introduction To Data Communication & NetworksRamya AththanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modulation and TransmissionDokument168 SeitenModulation and TransmissionayadmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital TransmissionDokument12 SeitenDigital TransmissionOrlando BangayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modulation and DemodulationDokument2 SeitenModulation and Demodulationnezar AbdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comm. Sys. Lect. 10Dokument21 SeitenComm. Sys. Lect. 10sulllNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks Assignment 1Dokument5 SeitenComputer Networks Assignment 1kishan30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amplitude Modulation1Dokument44 SeitenAmplitude Modulation1Dilbagh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formalism of Quantum MechanicsDokument2 SeitenFormalism of Quantum Mechanicsalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formulation of Quantum MechanicsDokument1 SeiteFormulation of Quantum Mechanicsalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- History of Quantum PhysicsDokument1 SeiteHistory of Quantum Physicsalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digital ModulationDokument1 SeiteDigital Modulationalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum Mechanics: The Discrete Nature of Energy at the Atomic ScaleDokument1 SeiteQuantum Mechanics: The Discrete Nature of Energy at the Atomic Scalealokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modulation Types and Techniques ExplainedDokument3 SeitenModulation Types and Techniques Explainedalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Foundations of Quantum MechanicsDokument1 SeiteThe Foundations of Quantum Mechanicsalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Particle DualityDokument1 SeiteWave Particle Dualityalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Brief History of Quantum Mechanics Development and ApplicationsDokument1 SeiteBrief History of Quantum Mechanics Development and Applicationsalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Max Planck's Quantum Theory and Planck's ConstantDokument1 SeiteMax Planck's Quantum Theory and Planck's Constantalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum MechanicsDokument1 SeiteQuantum Mechanicsalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum mechanics theory explainedDokument1 SeiteQuantum mechanics theory explainedalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Region of Convergence Example 2: Inverse Z-TransformDokument1 SeiteRegion of Convergence Example 2: Inverse Z-Transformalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Region of ConvergenceDokument1 SeiteRegion of Convergencealokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitor FilterDokument2 SeitenCapacitor Filteralokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inverse Z TransformDokument1 SeiteInverse Z Transformalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rabindranath TagoreDokument1 SeiteRabindranath Tagorealokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Basic Idea of the Z-Transform for Solving Linear Difference EquationsDokument1 SeiteThe Basic Idea of the Z-Transform for Solving Linear Difference Equationsalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rabindranath TagoreDokument1 SeiteRabindranath Tagorealokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carrier ConcentrationsDokument1 SeiteCarrier Concentrationsalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- FetDokument1 SeiteFetalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Absorption and Extinction Coefficient TheoryDokument2 SeitenAbsorption and Extinction Coefficient Theoryalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- d1q3 and d1q2Dokument1 Seited1q3 and d1q2alokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- OpticalDokument2 SeitenOpticalalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- D2Q4Dokument1 SeiteD2Q4alokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- BoltzmannDokument1 SeiteBoltzmannalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Silicon, (Si) :the Most Common Semiconductor, Atomic Number 14Dokument1 SeiteSilicon, (Si) :the Most Common Semiconductor, Atomic Number 14alokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- One DimensionalDokument1 SeiteOne Dimensionalalokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- LatticeDokument1 SeiteLatticealokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen