Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sound and Light
Hochgeladen von
GurdevBainesCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sound and Light
Hochgeladen von
GurdevBainesCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
8L
Summary Sheets
Sound and hearing
Sound vibrations and waves
Sound is a form of energy. Sounds are made when things vibrate. The vibrations
are passed on by particles in solids, liquids or gases. Sound needs a substance to pass
on the vibrations, so it can travel through solids, liquids and gases but not through a
vacuum.
8
L
The speed of sound is faster through solids than liquids, and slowest through gases.
This is because the particles are very close together in solids and so the energy is more
likely to be passed from one particle to the next. The sound travels in all directions
because the particles move in all directions unless something stops them.
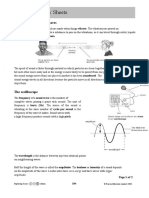
Sound waves can be shown
on an oscilloscope.
The frequency of a wave is the number of vibrations each second. The unit for
frequency is hertz (Hz). If you listen to a sound with a frequency of 100 Hz, one
hundred waves reach your ear every second. High pitched sounds have a high
frequency, and low pitched sounds have a low frequency.
The distance between the waves is called the wavelength. It can be measured
between any point on a wave and the same point of the next wave. It is often more
convenient to measure it between the top of one wave and the next.
amplitude
The thick line
shows one wave.
Half the height of the wave is called the amplitude. The loudness of a sound depends
on the amplitude. Louder notes have more energy and the wave has a bigger amplitude.
Page 1 of 2
Exploring Science for QCA
Copymaster File 8
540
Pearson Education Limited 2002
8L
Summary Sheets (continued)
Hearing and the ear
Sound waves travel through the air and into the ear. They cause the eardrum to
vibrate. The vibrations are passed on to the cochlea in the inner ear, where they are
changed to electrical signals called impulses. A nerve takes this message to the brain.
When the message reaches the brain we hear the sound.
ear canal
ear bones
auditory nerve
8
L
cochlea
eardrum
Sound can damage the ears if it is too loud or goes on for too long. Loud sounds can
damage the eardrum or the cochlea. Unpleasant sound is often called noise.
We can measure how loud a sound is by using a sound intensity meter. This is an
instrument which measures the loudness of a sound in decibels (dB). The threshold
of hearing is the quietest sound we can hear and we say this is 0 dB.
Soft materials can absorb sound. Soft materials are used in soundproofing and for
making ear protectors. Double glazed windows and soft materials like curtains help to
reduce sound levels.
Sound and light
One major difference between light and sound energy is that light can travel
through space (a vacuum) but sound cannot.
Light also travels much faster than sound. It is nearly a million times faster. Light
travels at 300 million metres per second (or 300 000 km/s) and sound travels at about
330 metres per second.
Both light waves and sound waves can be reflected. We hear a reflected sound wave
as an echo.
Exploring Science for QCA
Copymaster File 8
541
Pearson Education Limited 2002
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 747-400 and - 8Dokument24 Seiten747-400 and - 8GurdevBaines100% (5)
- Nursing Practice Skills: Adult Intensive Care Unit PatientsDokument10 SeitenNursing Practice Skills: Adult Intensive Care Unit PatientsMona Doria67% (3)
- 8F and 8G Homework Booklet Sept & Oct 20 12Dokument20 Seiten8F and 8G Homework Booklet Sept & Oct 20 12Mostafa100% (1)
- Summary Sheets: SolutionsDokument2 SeitenSummary Sheets: Solutions박찬우Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exploring Science 8 Sample PagesDokument8 SeitenExploring Science 8 Sample PagesFozia Ghulam Mustafa Fozia Ghulam MustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABS Rules For Cable SizingDokument2 SeitenABS Rules For Cable SizingMohammed JassimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Answer 1 11 2 12 3 13 4 14 5 15 6 16 7 17 8 18 9 19 10 20Dokument4 SeitenAnswer Answer 1 11 2 12 3 13 4 14 5 15 6 16 7 17 8 18 9 19 10 20Liana Jalil100% (1)
- Study Note 767sDokument39 SeitenStudy Note 767sGurdevBaines100% (4)
- A 320 Fault Verification GuideDokument36 SeitenA 320 Fault Verification GuideMiklós Meixner100% (5)
- Vocal TractDokument16 SeitenVocal TractniroelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A Activity Pack Worksheets PDFDokument44 Seiten9A Activity Pack Worksheets PDFJESUS EDUARDO CARBONO NIEBLESNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9J Gravity and Space Multiple Choice TestDokument3 Seiten9J Gravity and Space Multiple Choice Testapi-3698146100% (2)
- S934 - Instruction ManualDokument36 SeitenS934 - Instruction ManualTony MarascaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7G Particles Test 2004Dokument2 Seiten7G Particles Test 2004api-36981460% (1)
- Basic Pancakes Recipe - Martha StewartDokument37 SeitenBasic Pancakes Recipe - Martha Stewartkrishna kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Sheets: Compounds and MixturesDokument2 SeitenSummary Sheets: Compounds and MixturesVictor Barber SanchisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Projects Organisation: Material Specification For 316/316L and 6mo Austenitic Stainless SteelDokument33 SeitenGlobal Projects Organisation: Material Specification For 316/316L and 6mo Austenitic Stainless SteelThiyagarajan JayaramenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force Field Questions: Name Ghadeer Hussain Al-Khayat Class Date 1Dokument2 SeitenForce Field Questions: Name Ghadeer Hussain Al-Khayat Class Date 1ghadeer alkhayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8k Light End of Unit Test PDFDokument3 Seiten8k Light End of Unit Test PDFGurdevBainesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 767Dokument9 Seiten767GurdevBainesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food and Digestion - EUTDokument4 SeitenFood and Digestion - EUTLakshmi GanapathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reactions Practice TestDokument3 SeitenChemical Reactions Practice TestShemy RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDokument2 SeitenQuick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionazharNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9J AnsDokument1 Seite9J AnscalebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Pack &student Book Answers - 8Dokument86 SeitenActivity Pack &student Book Answers - 8Eliana FalahatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 747Dokument12 Seiten747GurdevBaines100% (3)
- 747Dokument12 Seiten747GurdevBaines100% (3)
- 7E7F SATs Question BookletDokument28 Seiten7E7F SATs Question BookletangeltwinkleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel ImbalanceDokument7 SeitenFuel ImbalanceGurdevBaines100% (1)
- 8f Summary SheetsDokument3 Seiten8f Summary SheetsBeedu AvengersNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Root: B SeedDokument11 SeitenA Root: B SeedAhmed HamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseVon EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseNoch keine Bewertungen
- RespiratoryDokument5 SeitenRespiratoryKrisdiansah PurnawidjajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KS3 LightDokument107 SeitenKS3 LightRenee DisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8e Mark SchemeDokument6 Seiten8e Mark SchemeLamis AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8b Test PDFDokument5 Seiten8b Test PDFngarmpisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 6 2nd Periodical Test With TOS Answer Keys MATH 1 PDFDokument6 SeitenGrade 6 2nd Periodical Test With TOS Answer Keys MATH 1 PDFmafeh caranogNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8g Summary SheetsDokument3 Seiten8g Summary SheetszunairaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure and Moments MarkschemeDokument1 SeitePressure and Moments Markscheme박찬우Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dokumen - Tips - End of Unit Test Physicslocker Exploring Science8h End of Unit Test 8 H NameDokument4 SeitenDokumen - Tips - End of Unit Test Physicslocker Exploring Science8h End of Unit Test 8 H Nameumi100% (1)
- 7B Reproduction Test 2004Dokument2 Seiten7B Reproduction Test 2004api-3698146100% (3)
- 9A QuizDokument31 Seiten9A Quizcaleb100% (1)
- 7J Electricity Test 2004Dokument3 Seiten7J Electricity Test 2004api-3698146100% (2)
- KS3 Sci / 8A 8E 8I Test MC AnswersDokument8 SeitenKS3 Sci / 8A 8E 8I Test MC AnswersPaul BurgessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 8 Science Paper Inset Days PDFDokument56 SeitenYear 8 Science Paper Inset Days PDFA.K MonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 EmarkDokument1 Seite8 Emarkleelakdd108Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual de Despiece Honda Beat 100Dokument84 SeitenManual de Despiece Honda Beat 100jorgeeu8833% (3)
- 8J Summary SheetDokument2 Seiten8J Summary Sheet박찬우Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Schem Es: Quick Quiz Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC LevelsDokument1 SeiteMark Schem Es: Quick Quiz Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC LevelsSumathi Ganasen100% (1)
- Science 9dDokument4 SeitenScience 9dno100100% (1)
- WST Macros Add-In FeaturesDokument1 SeiteWST Macros Add-In FeaturesTrader CatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 KtestDokument3 Seiten9 Ktest박찬우100% (2)
- 8ca - Aerobic Respiration: Word SheetsDokument3 Seiten8ca - Aerobic Respiration: Word SheetsOanaEmmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure and Moments Unit TestDokument3 SeitenPressure and Moments Unit Test박찬우Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Sheets: Sound Vibrations and WavesDokument2 SeitenSummary Sheets: Sound Vibrations and Waves박찬우Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8C Summary SheetDokument2 Seiten8C Summary Sheet박찬우100% (2)
- 8F QPDokument7 Seiten8F QPsureshthevanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESWS - Teacher Guide 2014Dokument32 SeitenESWS - Teacher Guide 2014Vikrant ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combustion and Oxidation: Summary SheetsDokument2 SeitenCombustion and Oxidation: Summary Sheetsanna russuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burning Fuels: I CanDokument5 SeitenBurning Fuels: I CanAddy The human100% (1)
- End of Unit Test: Name ClassDokument4 SeitenEnd of Unit Test: Name ClassMr Lava. مستر لافاNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8e Combustion Scheme of LearningDokument4 Seiten8e Combustion Scheme of LearningJude HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Quiz: Copymaster File 9Dokument2 SeitenQuick Quiz: Copymaster File 9ReenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 8 - Food and Digestion and Respiration Mark SchemeDokument4 SeitenYear 8 - Food and Digestion and Respiration Mark SchemerickyNoch keine Bewertungen
- End of Unit Test: Name ClassDokument4 SeitenEnd of Unit Test: Name ClassSandyDavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Main Words and Terms Used in Unit 7JDokument2 SeitenThe Main Words and Terms Used in Unit 7JJohn OsborneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7j Quick Quiz PDFDokument3 Seiten7j Quick Quiz PDF10 D Maanya GeraNoch keine Bewertungen
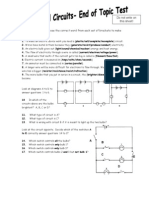
- Year 7 Energy Resources and Electrical Circuits-2Dokument11 SeitenYear 7 Energy Resources and Electrical Circuits-2PhysicsF3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Quiz: 9ba 9BbDokument2 SeitenQuick Quiz: 9ba 9BbOneth RajapakseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDokument2 SeitenQuick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionOneth RajapakseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme (Results) June 2011: International GCSE Information and Communication Technology Paper 02Dokument22 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) June 2011: International GCSE Information and Communication Technology Paper 02Sawrab100% (1)
- Magnetism Unit TestDokument5 SeitenMagnetism Unit Testrebbieg100% (2)
- Summary Sheets: Carbohydrate Protein Vitamins Minerals Fibre Constipation) WaterDokument2 SeitenSummary Sheets: Carbohydrate Protein Vitamins Minerals Fibre Constipation) WaterHelenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9DC Plants Photosynthesis and Plants For Food Multiple Choice TestDokument2 Seiten9DC Plants Photosynthesis and Plants For Food Multiple Choice Testapi-3698146100% (1)
- Summary Sheets For Unit 7JDokument2 SeitenSummary Sheets For Unit 7JJohn Osborne100% (1)
- Year 7 Energy Resources and Electrical Circuits Mark SchemeDokument6 SeitenYear 7 Energy Resources and Electrical Circuits Mark SchemePhysicsF3100% (1)
- 8 LsoundDokument2 Seiten8 LsoundTamara Martínez LiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C5 10aDokument6 SeitenC5 10aGurdevBainesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal New Growth - NCM 103 - or CaseDokument19 SeitenRenal New Growth - NCM 103 - or CasePat EnriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infant of A Diabetic MotherDokument17 SeitenInfant of A Diabetic MotherLovina Falendini AndriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimizing With eGaN FETsDokument6 SeitenOptimizing With eGaN FETskhsniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- bNSG9000 Datasheet 2Dokument3 SeitenbNSG9000 Datasheet 2RobertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dense Ball PackingDokument334 SeitenDense Ball PackingLucas RibeiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lake Superior RoadmapDokument2 SeitenLake Superior RoadmapWDIV/ClickOnDetroitNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCNHS - Diagnostic-test-G8-cookery 7&8Dokument2 SeitenTCNHS - Diagnostic-test-G8-cookery 7&8Elna Grace Dicon-Ybañez100% (4)
- Ap Art and Design Drawing Sustained Investigation Samples 2019 2020 PDFDokument102 SeitenAp Art and Design Drawing Sustained Investigation Samples 2019 2020 PDFDominic SandersNoch keine Bewertungen
- p14.6 - D.C. Motor - Igcse AidDokument2 Seitenp14.6 - D.C. Motor - Igcse Aidrandom channelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crimin Q and A Set 1Dokument6 SeitenCrimin Q and A Set 1Marc angelo RegnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Risk Assessment in The Construction of High-Rise BuildingsDokument5 SeitenA Study On Risk Assessment in The Construction of High-Rise BuildingsMohamedSaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hibon - SN Ingersoll Rand BlowerDokument7 SeitenHibon - SN Ingersoll Rand BlowermarquezsiemNoch keine Bewertungen
- VisakhapatnamDokument27 SeitenVisakhapatnamCherukupalli Gopala KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquid SizingDokument38 SeitenLiquid SizingChetan ChuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo Smartline Transmitter Family Ferrum Energy 变送器Dokument12 SeitenCatalogo Smartline Transmitter Family Ferrum Energy 变送器peng chaowenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slidex StrepDokument9 SeitenSlidex StrepLizeth Daniela RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Netrunner AllCardsDokument154 SeitenNetrunner AllCardsIvo PantaleaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- At Your Service: Affordable LandscapingDokument1 SeiteAt Your Service: Affordable LandscapingDamaris HigginsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accesorios Del Lamborghini VenenoDokument31 SeitenAccesorios Del Lamborghini VenenoVicente Gil PalopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Danas Si Moja I BozijaDokument1 SeiteDanas Si Moja I BozijaMoj DikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEVISER S7200 - ManualDokument326 SeitenDEVISER S7200 - ManualNicolas Maldonado BenitezNoch keine Bewertungen