Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Drug Study - Lactulose (Duphalac, Lilac)
Hochgeladen von
AgronaSlaughterOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Drug Study - Lactulose (Duphalac, Lilac)
Hochgeladen von
AgronaSlaughterCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
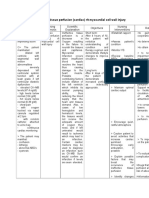
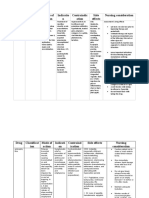
Drug Study: Lactulose
(Duphalac, Lilac)
Classification: Laxative
Action: Causes an influx of fluid in the intestinal
tract by increasing the osmotic pressure within
the intestinal lumen. Bacterial metabolism of the
drug to lactate and other acids which are only
partially absorbed in the distal ileum and colon
augments the osmotic effect of lactulose. The
distention of the colon due to increased fluid
enhances intestinal motility and secretion.
These result to the passage of soft stools.
Decrease in the lumenal pH (due to bacterial
metabolism) further increase motility and
secretion. Lactulose also lowers intestinal absorption of ammonia
presumably due to increased utilization of ammonia by intestinal bacteria.
Indication: Constipation, salmonellosis. Treatment of hepatic
encephalopathy.
Adverse Reactions: Abdominal discomfort associated with flatulence and
intestinal cramps. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea on prolonged used.
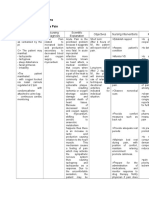
Nursing Considerations
Assessment
Assess patients condition before therapy and reassess regularly
thereafter to monitor drugs effectiveness. Identify cause of constipation:
Assess lifestyle in relation to fluids, bulk and exercise
For patient with hepatic encephalopathy, regularly assess mental
condition (clearing of confusion, lethargy, restlessness, irritability) and
ammonia level (30-70 mg/100 mL).
Monitor for possible adverse GI reaction: nausea,
vomiting, abdominal cramps, belching, diarrhea, flatulence and distension.
Monitor fluid and electrolyte status: urine output, input-output ratio to
identify fluid loss, hypokalemia and hypernatremia.
Monitor for increased glucose levels in diabetic patients.
Assess patients and familys knowledge of drug therapy.
Nursing Diagnoses
Constipation related to underlying condition
Diarrhea related to adverse drug reaction
Fluid and electrolyte imbalance related to adverse GI reaction
Knowledge-deficit related to drug therapy
Noncompliance
Planning
Oral route
o
Give with full glass of fruit juice, water, milk to increase
palatability of oral form; increase fluids by 2 L/day; do not give with
other laxatives; if diarrhea occurs, reduce dosage.
Rectal route
o
Administer retention enema by diluting 300 mL of lactulose/700
mL of water or 0.9% NaCl; administer by rectal balloon catheter; retain
for 30-60 minutes; repeat if evacuated too quickly.
Implementation
Advice patient to dilute drug with juice or water or take with food to
improve taste
Teach patient that normal bowel movements do not always occur daily
and that adequate fluid consumption is necessary
Inform patient of possible adverse effects and the need to notify
physician immediately if these occurs. Remind patient not to use in
presence of abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
Instruct patient to notify physician if constipation is unrelieved or
symptoms of electrolyte imbalance occur; muscle cramps, pain, weakness,
dizziness and excessive thirst
Inform patient that bowel tone may be lost if used as laxative for long
term therapy. Do not give at bedtime because it may interfere with sleep.
Inform patient that diarrhea may indicate over dosage.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- SenokotDokument1 SeiteSenokotKatie McPeek100% (1)
- Psych-K Practical ApplicationsDokument10 SeitenPsych-K Practical Applicationsdeluca4482% (17)
- Drug StudyDokument40 SeitenDrug Studyapi-374468390% (61)
- What Is Permanent Make-Up?: First in Looks That LastDokument4 SeitenWhat Is Permanent Make-Up?: First in Looks That LastNatural Enhancement0% (1)
- Lactulose (Constulose, Enulose, Enerlac, Cholac, Constilac)Dokument4 SeitenLactulose (Constulose, Enulose, Enerlac, Cholac, Constilac)AgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atorvastatin 0Dokument7 SeitenAtorvastatin 0AgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes MellitusDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Diabetes MellitusAgronaSlaughter67% (6)
- Imbalanced Nutrition - Less Than Body Requirements 02Dokument7 SeitenImbalanced Nutrition - Less Than Body Requirements 02AgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avapro (Irbesartan)Dokument2 SeitenAvapro (Irbesartan)ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Intolerance Related To ImmobilizationDokument3 SeitenActivity Intolerance Related To ImmobilizationAgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Coronary Syndrome NCP 02Dokument6 SeitenAcute Coronary Syndrome NCP 02AgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- CloxacillinDokument1 SeiteCloxacillinYzracle Bermejo FlorentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study MetforminDokument3 SeitenDrug Study MetforminAgronaSlaughter0% (1)
- Lactulose Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenLactulose Drug StudyAgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lactulose Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenLactulose Drug StudyAgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sanofi-Aventis, Deepak Tripathi, ITS GhaziabadDokument69 SeitenSanofi-Aventis, Deepak Tripathi, ITS Ghaziabadmaildeepak23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gentlelase Service Manual PDFDokument381 SeitenGentlelase Service Manual PDFsivan ebdo100% (1)
- Disorders of The Nervous SystemDokument5 SeitenDisorders of The Nervous SystemAgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Coronary Syndrome NCP 03Dokument6 SeitenAcute Coronary Syndrome NCP 03AgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kalium Durule Brand Name: Potassium ChlorideDokument3 SeitenKalium Durule Brand Name: Potassium ChlorideRon Christian100% (1)
- Name of Drugs Kaligen 8Dokument2 SeitenName of Drugs Kaligen 8mellany100% (1)
- LactuloseDokument2 SeitenLactuloseDiane Kate Tobias Magno100% (1)
- Bactroban (Mupirocin)Dokument1 SeiteBactroban (Mupirocin)ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Imbalanced Nutrition - Less Than Body Requirements 01Dokument6 SeitenImbalanced Nutrition - Less Than Body Requirements 01AgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition in Pediatrics PDFDokument1.121 SeitenNutrition in Pediatrics PDFPutri Wulan Sukmawati100% (5)
- Nursing Responsibility Adverse Effects Machanism of Action Drug NameDokument2 SeitenNursing Responsibility Adverse Effects Machanism of Action Drug NameSalwa ZeinNoch keine Bewertungen
- LactuloseDokument1 SeiteLactulosex483xD100% (3)
- Drug Study MetforminDokument3 SeitenDrug Study MetforminAgronaSlaughter86% (7)
- 107 Reaction PaperDokument1 Seite107 Reaction PaperKL Ea100% (1)
- Impaired Physical MobilityDokument11 SeitenImpaired Physical MobilityAgronaSlaughter100% (1)
- Co AmoxiclavDokument1 SeiteCo AmoxiclavGrace DonatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Coronary Syndrome NCP 01Dokument5 SeitenAcute Coronary Syndrome NCP 01AgronaSlaughter0% (1)
- D5WDokument1 SeiteD5WBreena Reubee EstilloreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Vit B ComplexDokument2 SeitenDrug Study Vit B Complexbekbekk cabahugNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG LactuloseDokument1 SeiteDRUG LactuloseJona Phie Domingo MonteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- MetronidazoleDokument2 SeitenMetronidazoleJm RomancapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug AnalysisDokument18 SeitenDrug AnalysisArt Christian RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study LosartanDokument2 SeitenDrug Study LosartanIris BalinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Stugeron and Kalium DuruleDokument1 SeiteDrug Study Stugeron and Kalium DuruleawesomedawnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearse Tablet InsertDokument2 SeitenBearse Tablet InsertLeonard ByunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postop Drug2Dokument3 SeitenPostop Drug2zbestgurlNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpironolactoneDokument2 SeitenSpironolactoneKatrina PonceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cephalexin (Keflex)Dokument1 SeiteCephalexin (Keflex)ENoch keine Bewertungen
- DolcetDokument2 SeitenDolcetmarc_hansen_1312Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aminoleban Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteAminoleban Drug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Sennosides (Senokot)Dokument1 SeiteSennosides (Senokot)E100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug StudyLorina Lynne ApelacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- OxytocinDokument1 SeiteOxytocinJoi Danielle Tabares IsturisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioNoch keine Bewertungen
- TergecefDokument2 SeitenTergecefianecunar100% (3)
- Generic Name:: ClassificationsDokument4 SeitenGeneric Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cefazolin Sodium AncefDokument1 SeiteCefazolin Sodium AncefKristi WrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRug StudyDokument6 SeitenDRug StudyRochell Torres ArtatesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mu CostaDokument7 SeitenMu Costayvoniemaebruno0% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteDrug StudycliffordbuenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stugeron® TabletsDokument3 SeitenStugeron® TabletsmahgadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeDokument2 SeitenSenna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeTempoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZonisamideDokument2 SeitenZonisamideRo-anne AkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Therabloc DrugDokument2 SeitenTherabloc DrugMsOrangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study LevofloxacinDokument2 SeitenDrug Study LevofloxacinDannah BulliandayNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChlorphenamineDokument1 SeiteChlorphenaminereinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG STUDY - Docx Grand CaseDokument10 SeitenDRUG STUDY - Docx Grand CaseAntonette PereyraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ivf StudyDokument2 SeitenIvf StudyDanePepitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Database - Potassium CitrateDokument2 SeitenDrug Database - Potassium CitrateReg LagartejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsDokument4 SeitenDrug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Ciprofloxacin QuinosynDokument10 SeitenDrug Study Ciprofloxacin QuinosynNelle ReyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formoterol Gonzaga.Dokument2 SeitenFormoterol Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study ProglinDokument2 SeitenDrug Study ProglinChris Denver BancaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- AldactoneDokument2 SeitenAldactoneianecunarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic Name: Classification: IndicationDokument2 SeitenGeneric Name: Classification: IndicationKristine YoungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mefenamic AcidDokument3 SeitenMefenamic AcidAngelica Cassandra VillenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Pletal: Pharmacologic Class: Pharmacokinetics General Indications Contraindications BeforeDokument2 SeitenGeneric Name: Brand Name: Pletal: Pharmacologic Class: Pharmacokinetics General Indications Contraindications Beforeart_mutantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenSodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyShaira Suzane SabidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic Name: Metoclopramide Brand Name: Reglan and Metozolv ODTDokument2 SeitenGeneric Name: Metoclopramide Brand Name: Reglan and Metozolv ODTJohn Paolo Tamayo OrioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study SARAHDokument2 SeitenDrug Study SARAHirene Joy DigaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ketorolac Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenKetorolac Drug StudyRic VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cebu Normal University: Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenCebu Normal University: Drug StudyGwen Marie Taboada100% (1)
- DRUG StudyDokument2 SeitenDRUG StudyKC IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugsDokument2 SeitenDrugsKC IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- LactuloseDokument1 SeiteLactuloseMsOrangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic NameDokument3 SeitenGeneric NameKimsha ConcepcionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atorvastatin Side Effects 01Dokument7 SeitenAtorvastatin Side Effects 01AgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atorvastatin Side Effects 01Dokument7 SeitenAtorvastatin Side Effects 01AgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metformin (Met For Min)Dokument16 SeitenMetformin (Met For Min)AgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metformin, Glucophage, Glucophage XR, Glumetza, Fortamet, RiometDokument5 SeitenMetformin, Glucophage, Glucophage XR, Glumetza, Fortamet, RiometAgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metformin - Oral, GlucophageDokument6 SeitenMetformin - Oral, GlucophageAgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Origin of 'Inaugurate': What Does 'Inaugurate' Have To Do With Interpreting Omens?Dokument2 SeitenThe Origin of 'Inaugurate': What Does 'Inaugurate' Have To Do With Interpreting Omens?AgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bible Printables - Creation Coloring Pages - Bible Creation Day 6Dokument4 SeitenBible Printables - Creation Coloring Pages - Bible Creation Day 6AgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heredity: Genetic MutationsDokument2 SeitenHeredity: Genetic MutationsAgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wishi NG You The Best Hey Hump H!: ! I'm Happy Birthda Y!Dokument2 SeitenWishi NG You The Best Hey Hump H!: ! I'm Happy Birthda Y!AgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature Complain's: By: Flore Mae MasuayDokument2 SeitenNature Complain's: By: Flore Mae MasuayAgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- White Paper On Medical Device (Issue 1)Dokument4 SeitenWhite Paper On Medical Device (Issue 1)Rishabh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application For Transfer in General ISMDokument2 SeitenApplication For Transfer in General ISMThasreen sNoch keine Bewertungen
- In-Patient Pharmacy Dispensing PersonnelDokument3 SeitenIn-Patient Pharmacy Dispensing Personneljanr123456Noch keine Bewertungen
- DR - Harish DurejaDokument26 SeitenDR - Harish Durejaarpita_949242356Noch keine Bewertungen
- MudrasDokument8 SeitenMudrasKishore CheralaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ureño 2019 D-MerDokument8 SeitenUreño 2019 D-MerCarolina GómezNoch keine Bewertungen
- S11 XylitolDokument4 SeitenS11 XylitolJholanda Ninggar BahtriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DkaDokument32 SeitenDkanatheNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABHA Final PaperDokument8 SeitenABHA Final PaperVishva SavaliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Amsterdam Preoperative Anxiety and Information.2Dokument7 SeitenThe Amsterdam Preoperative Anxiety and Information.2Jose Rafael Villafan BernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Study Resource WasDokument3 SeitenThis Study Resource WasCarlito AglipayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course NotesDokument125 SeitenCourse Notesfuji_reihNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Rid The Body of CandidaDokument2 SeitenHow To Rid The Body of Candidaradio53fingerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaesthetic Management of Obstetric: HaemorrhageDokument52 SeitenAnaesthetic Management of Obstetric: Haemorrhagerevathidadam55555Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report of Mangalore VisitDokument6 SeitenReport of Mangalore VisitAmal DominicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Culture Recomendation in PicuDokument11 SeitenBlood Culture Recomendation in PicuJack Eugene LiowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nejme 2305752Dokument2 SeitenNejme 23057525fqkqkcdhtNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Abstract Presenters ISMPNP-2024 EMAILDokument7 SeitenList of Abstract Presenters ISMPNP-2024 EMAILasadalijanjua.0003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hizon, DrugsDokument4 SeitenHizon, DrugsDan HizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- R 141bDokument8 SeitenR 141bLUISALBERTO06011985Noch keine Bewertungen
- G.R. No. 132319. May 12, 2000Dokument2 SeitenG.R. No. 132319. May 12, 2000Chua RoxyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aki VS CKDDokument2 SeitenAki VS CKDKevin TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seizure Updated ILAE ClassificationDokument12 SeitenSeizure Updated ILAE ClassificationNasheei RadjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clark IndigestionDokument50 SeitenClark IndigestionRaveendra MungaraNoch keine Bewertungen