Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Reviewer 1st Exam
Hochgeladen von
aefCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Reviewer 1st Exam
Hochgeladen von
aefCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1ST EXAM REVIEWER GEOL 11
Jaya F. Salazar
2013-12433
1. What is the difference between petrology and petroleum geology?
Petrology deals with the origin, composition and formation of rocks. Petroleum geology refers
to the application of geology for exploration of hydrocarbons.
2. Can you make yourself a mineral at home? Why/why not?
No, minerals are naturally occuring, has a definite chemical composition and are formed as a
result of geological processes under a variety of conditions.
3. What is the Mohs Scale of Hardness? What are different common objects (and their
corresponding hardness) used in determing relative hardness of minerals?
The Mohs Scale of Hardness is a scale for classifying minerals based on their hardness. 2.5
Fingernail, 3.5 Copper coin, 5 Steel nail, 5-6 Glass, 7 Streak Plate.
4. If all expenses are covered for airfare and everything else youll need for a trip abroad, where
would you go to take a sample of lava (considering factors like safety and ease of access)?
Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii since its non-explosive and has zero volcano explosivity index.
5. Differentiate the inner from outer planets.
The terrestrial planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars contain high temperature minerals.
They have rocky composition, largely silicate rocks and metals. The Jovian planets, Jupiter,
Saturn, Uranus and Neptune contain lower temperature materials. They lack solid surfaces in
gaseous or liquid form. Theyre composed of mostly light elements.
6. Is the Earth as old as the universe? Explain your answer.
No, the formation of the universe is believed to have been caused by the Big Bang, while the
Earth is believed to be an offshoot of the formation of the universe, therefore making the
universe older than the Earth.
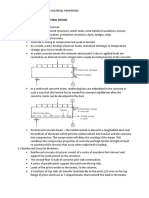
7. Imagine that you are to dissect the earth similar to how you dissect a frog in zoology class,
draw how it would look like, label its parts, and describe each of its parts.
Crust- it is made up of the oceanic crust
and continental crust. Outermost layer.
Mantle- it extends to a depth of ~2900km
and is composed of the upper mantle
Mantle
and the mesosphere.
Core- iron rich sphere with small amounts
of nickel and other elements. Divided into
Inner core
inner and outer core.
Outer
8. What is the difference between lava and
magma? Describe magmas components
and
Crust
how it is formed.
1ST EXAM REVIEWER GEOL 11
Magma (intrusive) is molten material which may contain suspended crystals and dissolved
volatiles. It is formed due to the melting of upper mantle or lower crust. Lava (extrusive) is hot
fluid molten rock that flows along the land surface.
9. How does magma composition diversify and, consequently, result in the formation of different
types of igneous rocks?
Magma is classified based on the chemical composition: Felsic, Intermediate, Mafic and
Ultramafic. Basically, the silica content is a factor in the formation of extrusive or intrusive
rocks.
10. Why is there a distinction between a continuous and a discontinuous series in Bowens
reactions series diagram?
There is a distinction since minerals can either react discontinuously to form new minerals
with different crystal structures, or react continuously to form new minerals with almost the
same structures.
11. Relate the following magma properties: silica content, viscosity, temperature, and density.
Explain the relationships among these.
Magma is classified according to silica content, viscosity and temperature. The properties of
magma are viscosity and density. As temperature and density increases, viscosity and silica
content decreases.
12. State the different types of volcanic landforms and associate these with the general
composition of magma/lava responsible for their formation.
Shield volcano-made up of succesive lava flows
Cinder cone- made up of pyroclastic material
Composite or strato-volcano- tephra and lava flows
13. In a cooling magma body, what affects the resultant texture of an igneous rock?
The composition and the different cooling temperatures of the minerals affects the texture.
14. What composition of magma results in the most explosive volcanic eruptions? What are the
usual types of materials ejected during such volcanic eruptions?
Felsic, acidic or silicic magma, which has the most silica content, results in the most explosive
volcanic eruptions. Large volumes of ash and blocks are usually ejected.
15. Group together the terms that are synonymous:
Intrusive and plutonic
Volcanic and extrusive
Basaltic and malfic and basic
Andesitic and intermediate
Felsic, silicic, granitic, acidic
Ultramafic and ultrabasic
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- MDC Buildplus Inc.: SF SalazarDokument5 SeitenMDC Buildplus Inc.: SF SalazaraefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Vendor Current Challenges (During Pandemic)Dokument1 SeiteVendor Current Challenges (During Pandemic)aefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banner InfographicsDokument20 SeitenBanner InfographicsasdadasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Name of Project: Pilot Testing Location: Ametta Place, Pasig City Item Description Unit Qty Materials I II III Pilot TestingDokument2 SeitenName of Project: Pilot Testing Location: Ametta Place, Pasig City Item Description Unit Qty Materials I II III Pilot TestingaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Your Great Subtitle: Element 02 Element 01Dokument69 SeitenYour Great Subtitle: Element 02 Element 01aefNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Inspection and Test Plan 2 PDF FreeDokument3 SeitenInspection and Test Plan 2 PDF FreeaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- 36 Surveying Vertical Curve SolutionsDokument2 Seiten36 Surveying Vertical Curve SolutionsaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Pipe Preparation CUTTING PDFDokument23 SeitenPipe Preparation CUTTING PDFchineduNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Materials ApprovalDokument2 SeitenMaterials ApprovalaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- M3 - U6 - Pipe Threading and TestingDokument25 SeitenM3 - U6 - Pipe Threading and TestingAfonso BuenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- FATDokument39 SeitenFATRoshan ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Introduction To Structural DesignDokument4 SeitenIntroduction To Structural DesignaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials ApprovalDokument2 SeitenMaterials ApprovalaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Employee Clearance CertificateDokument1 SeiteEmployee Clearance CertificateaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- ASTM C136 C136M 14 Standard Test Method For Sieve Analysis of Fine and Coarse AggregatesDokument5 SeitenASTM C136 C136M 14 Standard Test Method For Sieve Analysis of Fine and Coarse AggregatesJEAN ANTHONY CHICALLA MAMANI100% (11)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- RFA - Valves and FHCDokument2 SeitenRFA - Valves and FHCaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Materials ApprovalDokument2 SeitenMaterials ApprovalaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kitchen Facilities Eating Facilities Airline Operations: Departure or Arrival Lounge With 3 GatesDokument1 SeiteKitchen Facilities Eating Facilities Airline Operations: Departure or Arrival Lounge With 3 GatesaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vol. 34 No. 4, October 2015, Pp. University of Nigeria, Nsukka, ISSN: 0331-8443Dokument7 SeitenVol. 34 No. 4, October 2015, Pp. University of Nigeria, Nsukka, ISSN: 0331-8443aefNoch keine Bewertungen
- KjfkjeDokument24 SeitenKjfkjeaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lafayette College Department of Civil and Environmental EngineeringDokument3 SeitenLafayette College Department of Civil and Environmental EngineeringaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Formwork Systems: Group 1: Albino Gumiran Negapatan Salazar SerranoDokument55 SeitenFormwork Systems: Group 1: Albino Gumiran Negapatan Salazar SerranoaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating Population Growth Rate and Doubling TimeDokument12 SeitenCalculating Population Growth Rate and Doubling TimefdsfNoch keine Bewertungen
- AefDokument2 SeitenAefaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Lesson1 2Dokument36 SeitenLesson1 2JulianBudiPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 12 Combined Axial and Bending PDFDokument24 SeitenChap 12 Combined Axial and Bending PDFaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lateral-Torsional Buckling of BeamsDokument47 SeitenLateral-Torsional Buckling of BeamsaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generally, Sand Is Not Used in Mortar To Increase Its Strength. Rather It Is Mainly Used As An Inert Material To Increase The Volume of Mortar For The EconomyDokument2 SeitenGenerally, Sand Is Not Used in Mortar To Increase Its Strength. Rather It Is Mainly Used As An Inert Material To Increase The Volume of Mortar For The EconomyaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Compression Members: 6.2 Euler Elastic BucklingDokument31 SeitenCompression Members: 6.2 Euler Elastic BucklingaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compression Members: 6.2 Euler Elastic BucklingDokument31 SeitenCompression Members: 6.2 Euler Elastic BucklingaefNoch keine Bewertungen
- BulkanoDokument17 SeitenBulkanoKirby MalibiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-03 - PPt-05 - Sclassification of Igneous RocksDokument34 SeitenUnit-03 - PPt-05 - Sclassification of Igneous RocksShivam SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geo-Classes Regular Test Series: M.M. 25 M.T. 20 Minutes Obtained MarksDokument6 SeitenGeo-Classes Regular Test Series: M.M. 25 M.T. 20 Minutes Obtained MarksVikram DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitin R Karmalkar: About MeDokument9 SeitenNitin R Karmalkar: About MeMPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Volcanogenic SedimentsDokument3 SeitenClassification of Volcanogenic Sedimentshugoluis_hNoch keine Bewertungen
- SITREP NUMBER 82 As of 4 February 2020 1700HDokument105 SeitenSITREP NUMBER 82 As of 4 February 2020 1700HEdison ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Temporal Evolution of Chemical and Physical Properties of Magmatic SystemsDokument15 SeitenThe Temporal Evolution of Chemical and Physical Properties of Magmatic SystemsSergio Paucar MoreyraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth'S Materials and Processes: Marilyn P. MifuelDokument57 SeitenEarth'S Materials and Processes: Marilyn P. MifuelSheyah Villanueva100% (1)
- Geochemical Plots of Igneous Rocks - 2009Dokument5 SeitenGeochemical Plots of Igneous Rocks - 2009Patricia Del Carmen Guevara VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Types of Earthquakes: - Group 2Dokument30 SeitenTypes of Earthquakes: - Group 2Joan PecundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Older GranitesDokument5 SeitenOlder GranitesNkem Okonkwo50% (2)
- Volcano Lesson PlanDokument17 SeitenVolcano Lesson PlanApril Rose AyubanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Domos Volcanicos y Mineralizacion de Oro en El DisDokument21 SeitenDomos Volcanicos y Mineralizacion de Oro en El DisfacflNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hawaiian Hot SpotsDokument8 SeitenHawaiian Hot SpotsshoaibnadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Igneous Petrology 1Dokument97 SeitenIgneous Petrology 1Kamal SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Reviewer: Lesson 1Dokument2 SeitenScience Reviewer: Lesson 1AMIEL MOIRA BERNARDONoch keine Bewertungen
- Continentalization of An Intraoceanic Arc As Exemplified by The Jurassic Bonanza Arc of Vancouver Island, CanadaDokument13 SeitenContinentalization of An Intraoceanic Arc As Exemplified by The Jurassic Bonanza Arc of Vancouver Island, CanadaAgustin CardonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7-Core Subject-Science 11-Earth - Life Science-Q1-Module 7Dokument22 Seiten7-Core Subject-Science 11-Earth - Life Science-Q1-Module 7DonabelEscotaEspaño100% (2)
- Introduction To Volcanoes and Their TypesDokument2 SeitenIntroduction To Volcanoes and Their TypesJohn Renz CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petrogenesa Batuan Metamorf Pada Blok Kemum Daerah Wariori Indah, Distrik Masni, Kabupaten Manokwari, Provinsi Papua BaratDokument7 SeitenPetrogenesa Batuan Metamorf Pada Blok Kemum Daerah Wariori Indah, Distrik Masni, Kabupaten Manokwari, Provinsi Papua BaratMeriana GM HarahapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supervolcanoe S: Type of Volcanoes Picture and DetailsDokument2 SeitenSupervolcanoe S: Type of Volcanoes Picture and DetailsPhilip AmelingNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGNTU EContent 296373693601 M.SC Geology 2 DR - vikramPratapSingh Stratigraphy 1Dokument21 SeitenIGNTU EContent 296373693601 M.SC Geology 2 DR - vikramPratapSingh Stratigraphy 1Monu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanic Eruption LPDokument17 SeitenVolcanic Eruption LPLV BENDANANoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4 PetrologyDokument5 SeitenLab 4 PetrologyKachel Joy S. SarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Igneous Rocks LabDokument7 SeitenIgneous Rocks LabMelissa HibbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology and Geochemistry of High-Grade Mercury MineralizationDokument12 SeitenGeology and Geochemistry of High-Grade Mercury MineralizationHeri GeologistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life in PompeiiDokument4 SeitenLife in PompeiiOatna GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EARTH SCIENCE Quarter 1 AnswersDokument26 SeitenEARTH SCIENCE Quarter 1 AnswersJongseong ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. Magma Mixing:: Magmatic DifferentiationDokument5 SeitenA. Magma Mixing:: Magmatic DifferentiationAnkit YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL 16Dokument2 SeitenDLL 16Marjorie BrondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessVon EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincVon EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (137)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersVon EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseVon EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (69)