Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sodium
Hochgeladen von
tuffie850 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
32 Ansichten1 SeiteHYPONATREMIA causes causes HYPERNATERMIA Elevated blood pressure (hypertension) Elevated pulse (tachycardia) Elevated temperature Elevated respiratory rate, possible dyspnea increased body weight Bounding peripheral pulses Moist mucous membranes Moist respiratory secretions Crackles in lungs on auscultation Fever Edema (may pit) Dry skin Thirst Weakness Restlessness / agitation Disorient
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenHYPONATREMIA causes causes HYPERNATERMIA Elevated blood pressure (hypertension) Elevated pulse (tachycardia) Elevated temperature Elevated respiratory rate, possible dyspnea increased body weight Bounding peripheral pulses Moist mucous membranes Moist respiratory secretions Crackles in lungs on auscultation Fever Edema (may pit) Dry skin Thirst Weakness Restlessness / agitation Disorient
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
32 Ansichten1 SeiteSodium
Hochgeladen von
tuffie85HYPONATREMIA causes causes HYPERNATERMIA Elevated blood pressure (hypertension) Elevated pulse (tachycardia) Elevated temperature Elevated respiratory rate, possible dyspnea increased body weight Bounding peripheral pulses Moist mucous membranes Moist respiratory secretions Crackles in lungs on auscultation Fever Edema (may pit) Dry skin Thirst Weakness Restlessness / agitation Disorient
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
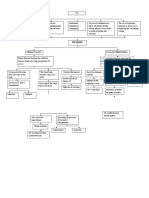
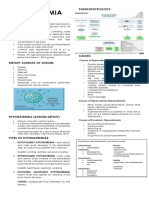
SODIUM (NA+)
NORMAL/PANIC HYPERNATREMIA CAUSES OF HYPONATREMIA CAUSES OF
VALUE HYPERNATREMIA HYPONATREMIA
OTHER
INFORMATION
Normal adult: Elevated blood pressure Increased sodium intake: Increased pulse (tachycardia) Decreased sodium intake:
135-145 mEq/liter (hypertension) Excessive dietary intake of sodium Weak, thready peripheral Insufficient dietary intake
(135-145 Elevated pulse (tachycardia) or water pulses Deficient sodium in IV fluids
mmol/liter) Elevated temperature Excessive saline in IV therapy Flat neck veins N/G feeding with inadequate
Normal urine sodium: Elevated respiratory rate, Excessive infusion of isotonic IV Increased respiratory rate fluid
27-287 mEq/24 possible dyspnea solutions Decreased blood pressure Increased sodium loss:
hrs Increased body weight Decreased sodium loss: (hypotension) Addison's disease
(27-287 mmol/24 Bounding peripheral pulses Cushing's syndrome Decreased body weight Fever
hrs) Moist mucous membranes Hyperaldosteronism Thick, slurred speech Diarrhea
Panic (critical) values: Moist respiratory secretions Decreased water output due to Anorexia Vomiting
below120 Crackles in lungs on auscultation renal disease Nausea/Vomiting/abdominal Excessive use of diuretics
mEq/liter Fever Excessive body water loss: cramps Chronic renal insufficiency
above 160 mEq/liter Edema (may pit) Excessive sweating Oliguria Nephrotic syndrome
Dry skin Extensive burns Anuria Excessive body water gains:
Thirst Dehydration Lethargy/Malaise Excessive oral intake
Weakness Diabetes insipidus Headache Excessive IV water intake
Restlessness/agitation Osmotic diuresis Confusion CHF
Disorientation Other causes of increased water: Muscular twitching SIADH (Syndrome of
Delusions Azotemia Seizures inappropriate secretion of
Hallucinations Heart failure Coma ADH)
Lethargic when undisturbed Pulmonary edema Respiratory arrest Osmotic dilution
Irritable when stimulated Lactic acidosis Third-space losses of sodium:
Muscle irritability Long term administration of Ascites
Diminished or absent DTRs adrenocortidal hormones Peripheral edema
High pitched cry in infants Pleural effusion
Seizures Ileus or mechanical bowel
Coma (due to swelling of brain obstruction
cells) Hidden fluid in body cavities
Respiratory arrest due to
increased osmotic pressure
Sodium (Na+)
- MOST abundant cation (+) in the extracellular space
- the major ion of body water balance
- promotes neuromuscular function
- reflects the balance between dietary sodium intake and renal excretion
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDokument23 SeitenFluids and ElectrolytesJonah MaasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids and Electrolytes (Concentration and Composition Changes)Dokument6 SeitenFluids and Electrolytes (Concentration and Composition Changes)Kristin SaberonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sodium Imbalances (Hyponatremia Vs Hypernatremia)Dokument17 SeitenSodium Imbalances (Hyponatremia Vs Hypernatremia)Angel FiloteoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sodium Imbalances Main Cation & Primary Determinant of ECF Osmolality (Na+ Is ECF) : p.325Dokument3 SeitenSodium Imbalances Main Cation & Primary Determinant of ECF Osmolality (Na+ Is ECF) : p.325lmonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids and Renal DisorderDokument139 SeitenFluids and Renal DisorderLhara MañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Billy L. Perpetua, Man RN: Fluids, Electrolytes andDokument96 SeitenMark Billy L. Perpetua, Man RN: Fluids, Electrolytes andMaica LectanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDLec and FluidsEABB CompiledDokument12 SeitenCDLec and FluidsEABB CompiledJuana ToriomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolyte Imbalances Causes: Signs & Symptoms:: Physical Exam: Lab FindingsDokument4 SeitenElectrolyte Imbalances Causes: Signs & Symptoms:: Physical Exam: Lab Findingsworleyb83Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolyte AbnormalitiesDokument74 SeitenElectrolyte Abnormalitiesbluecrush1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Main Fluid and ElectrolyteDokument133 SeitenMain Fluid and ElectrolyteMaria Charis Anne IndananNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 FXN: Vasoconstriction of Vessels 3 FXN: Blood Pressure Regulation (Increases BP)Dokument7 Seiten2 FXN: Vasoconstriction of Vessels 3 FXN: Blood Pressure Regulation (Increases BP)rise wiiinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3A - BOLDIOS Electrolytes Tabular ComparisonDokument20 Seiten3A - BOLDIOS Electrolytes Tabular ComparisonPsyche Valerie BoldiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared By: Mark Joseph V. Liwanag, RN, MSNDokument136 SeitenPrepared By: Mark Joseph V. Liwanag, RN, MSNjosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypervolemia Lab TestDokument1 SeiteHypervolemia Lab TestAdelin MeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis and Management of Common Electrolyte DisordersDokument42 SeitenDiagnosis and Management of Common Electrolyte DisorderspandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disturbances of Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDokument3 SeitenDisturbances of Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceJezel B. AnadonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Volume ExcessDokument34 SeitenFluid Volume ExcessajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Diagnoses Data BaseDokument34 SeitenNursing Diagnoses Data BaseEnyew TaddieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blok 24 Skenario 1 - Analisa Gas Darah Akibat Ketidakseimbangan ElektrolitDokument15 SeitenBlok 24 Skenario 1 - Analisa Gas Darah Akibat Ketidakseimbangan ElektrolitGogmaFirmansyahSiraitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Philippine Nursing Board TopicsDokument16 SeitenCommon Philippine Nursing Board TopicsLyrae SiriusNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 112-Mod4Dokument2 SeitenNCM 112-Mod4Samantha BolanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antidotes - and - Poisoning (Clinical Chemistry)Dokument2 SeitenAntidotes - and - Poisoning (Clinical Chemistry)Mae AnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolyte Abnormalities in The Hospitalized PatientDokument70 SeitenElectrolyte Abnormalities in The Hospitalized PatientClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Electrolyte Balances and ImbalanceDokument157 SeitenFluid Electrolyte Balances and ImbalanceManisha Shakya0% (1)
- Diabetes Insipidus and SIADH Reference Sheet: Normal Lab Values Siadh DIDokument13 SeitenDiabetes Insipidus and SIADH Reference Sheet: Normal Lab Values Siadh DIJohn TusselNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water & Electrolyte BalanceDokument27 SeitenWater & Electrolyte Balanceanisa rachmitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dialysis Hypotension Is The Result of AnDokument4 SeitenDialysis Hypotension Is The Result of AnCathy ManicadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolyte Disorders: Crisbert I. Cualteros, MD S.page - TLDokument45 SeitenElectrolyte Disorders: Crisbert I. Cualteros, MD S.page - TLm_arianne268932Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Gland OSCE ExaminationDokument13 SeitenThyroid Gland OSCE ExaminationkylieverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyponatremia: Overload of Fluid With Congestive HeartDokument10 SeitenHyponatremia: Overload of Fluid With Congestive HeartKyla Shain GallegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentasi SyokDokument30 SeitenPresentasi SyokPradnya PrabestiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Dokument46 SeitenFluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Gabrielle Frances FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sodium CompatibleDokument2 SeitenSodium CompatiblesherikeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- OTM 101 Nursing MnemonicsDokument2 SeitenOTM 101 Nursing MnemonicsMarlena Nicole100% (6)
- Syndrome of Inappropriate AdhDokument5 SeitenSyndrome of Inappropriate AdhCarloRafaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.7 WOC of Intra DyalisisDokument2 Seiten2.7 WOC of Intra Dyalisisvictor zhefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABGs ManifestationsDokument3 SeitenABGs ManifestationsAnmari OnespinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PotassiumDokument2 SeitenPotassiumtuffie85Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCM112 RSHF LSHF DD SDDokument3 SeitenNCM112 RSHF LSHF DD SDKryffa DegayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid ImbalancesDokument43 SeitenFluid ImbalancesHarold DiasanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids & Electrolytes Imbalance KMUDokument37 SeitenFluids & Electrolytes Imbalance KMUSHAFIQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyper Hyponatremia LERMADokument8 SeitenHyper Hyponatremia LERMAJINYVEV APARICINoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Chemistry 2 LAB MT305 Rlh3: ElectrolytesDokument2 SeitenClinical Chemistry 2 LAB MT305 Rlh3: ElectrolytesEmiaj Francinne Mendoza100% (1)
- Diagnostic Approach:: Renal Losses Extrarenal LossesDokument2 SeitenDiagnostic Approach:: Renal Losses Extrarenal LossesPatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids Electrolytes Visual NotesDokument8 SeitenFluids Electrolytes Visual NotesVin Lorenzo CampbellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids & Electrolytes (Review)Dokument2 SeitenFluids & Electrolytes (Review)Chaina MacaspacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patho DiagramDokument1 SeitePatho Diagrampaupaulala100% (2)
- The Pathophysiology ofDokument2 SeitenThe Pathophysiology ofMelanie Moises JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- จมน้ำdrowningถถDokument21 Seitenจมน้ำdrowningถถRungtip RuangnaparatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid-Base Disorders: Respiratory Acidosis Respiratory AlkalosisDokument3 SeitenAcid-Base Disorders: Respiratory Acidosis Respiratory AlkalosisLia DicksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Base BalanceDokument4 SeitenAcid Base BalanceHenric CasimiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary: Congenital Disease 2. Finnish Nephrotic Syndrome (Inherited) 3. Nephrotic Syndrome Minimal Change (The Most Common Type)Dokument6 SeitenPrimary: Congenital Disease 2. Finnish Nephrotic Syndrome (Inherited) 3. Nephrotic Syndrome Minimal Change (The Most Common Type)Cici Novelia ManurungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary: Congenital Disease 2. Finnish Nephrotic Syndrome (Inherited) 3. Nephrotic Syndrome Minimal Change (The Most Common Type)Dokument6 SeitenPrimary: Congenital Disease 2. Finnish Nephrotic Syndrome (Inherited) 3. Nephrotic Syndrome Minimal Change (The Most Common Type)Cici Novelia ManurungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study & NCPDokument15 SeitenDrug Study & NCPStephanie Mae Amoylen OdchigueNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYPONATREMIA Final HandoutsDokument2 SeitenHYPONATREMIA Final HandoutsSahata BOHARINoch keine Bewertungen
- Eelectrolyte DisordersDokument14 SeitenEelectrolyte DisordersarianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Electrolyte Imbalance n132 160210135651Dokument100 SeitenFluid Electrolyte Imbalance n132 160210135651Shahan FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectrolytesDokument60 SeitenElectrolytesnmukila2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperthyroid Is MDokument13 SeitenHyperthyroid Is MMario Rodriguez GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
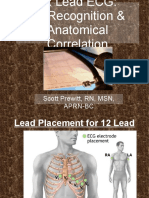
- Basic Dysrhythmias: Scott Prewitt, RN, MSN, APRN-BCDokument42 SeitenBasic Dysrhythmias: Scott Prewitt, RN, MSN, APRN-BCtuffie85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scott Prewitt, RN, MSN, Aprn-BcDokument21 SeitenScott Prewitt, RN, MSN, Aprn-Bctuffie85Noch keine Bewertungen
- 07 Endocrine SystemDokument3 Seiten07 Endocrine Systemtuffie85Noch keine Bewertungen
- PotassiumDokument2 SeitenPotassiumtuffie85Noch keine Bewertungen
- MagnesiumDokument2 SeitenMagnesiumtuffie85Noch keine Bewertungen
- CalciumDokument2 SeitenCalciumtuffie85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 18 Heart and Peripheral Vascular SystemDokument11 SeitenChapter 18 Heart and Peripheral Vascular Systemtuffie85100% (2)
- Unit 2 PharmacologyDokument9 SeitenUnit 2 Pharmacologytuffie85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bedside Nursing Process NotesDokument5 SeitenBedside Nursing Process NoteskiaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assertiveness FinlandDokument2 SeitenAssertiveness FinlandDivyanshi ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Citibank Vs Hon ChuaDokument12 SeitenCitibank Vs Hon ChuaJA BedrioNoch keine Bewertungen
- DentinogenesisDokument32 SeitenDentinogenesisNajeeb UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deutz Common RailDokument20 SeitenDeutz Common RailAminadav100% (3)
- How To Format Your Business ProposalDokument2 SeitenHow To Format Your Business Proposalwilly sergeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study GingerDokument2 SeitenCase Study Gingersohagdas0% (1)
- Stdy RCD PDFDokument204 SeitenStdy RCD PDFBol McSafeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kami Export - Tools in Studying Environmental ScienceDokument63 SeitenKami Export - Tools in Studying Environmental ScienceBenBhadzAidaniOmboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Franieboy Ponce, BSIT-1, - DAY 2 ACTIVITYDokument2 SeitenFranieboy Ponce, BSIT-1, - DAY 2 ACTIVITYFrancisco PonceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Women in IslamDokument22 SeitenWomen in Islamsayed Tamir janNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Country Ranking Alevel 2023Dokument225 SeitenMath Country Ranking Alevel 2023Lutaaya Paul BamutaliraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planificare 3 FairylandDokument6 SeitenPlanificare 3 FairylandBulf Adela MihaelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jao Vs Court of Appeals G.R. No. 128314 May 29, 2002Dokument3 SeitenJao Vs Court of Appeals G.R. No. 128314 May 29, 2002Ma Gabriellen Quijada-TabuñagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Café Management System Full and Final ReportDokument18 SeitenCafé Management System Full and Final ReportMuhammad Xalman Xhaw100% (3)
- CBDCs For Dummies Everything You Need ToDokument18 SeitenCBDCs For Dummies Everything You Need Tolati.training7Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Normal Distribution and Sampling Distributions: PSYC 545Dokument38 SeitenThe Normal Distribution and Sampling Distributions: PSYC 545Bogdan TanasoiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian School Bousher Final Term End Exam (T2) : Academic Session - 2021-22 Grade: 7Dokument7 SeitenIndian School Bousher Final Term End Exam (T2) : Academic Session - 2021-22 Grade: 7Shresthik VenkateshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glint 360 Design GuideDokument2 SeitenGlint 360 Design GuidebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profix SS: Product InformationDokument4 SeitenProfix SS: Product InformationRiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Employee Benefit Psak 24 (Guide)Dokument21 SeitenPost Employee Benefit Psak 24 (Guide)AlvianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiananmen1989(六四事件)Dokument55 SeitenTiananmen1989(六四事件)qianzhonghua100% (3)
- Geotagging ManualDokument93 SeitenGeotagging ManualAlthea AcasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pr1 m4 Identifying The Inquiry and Stating The ProblemDokument61 SeitenPr1 m4 Identifying The Inquiry and Stating The ProblemaachecheutautautaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT3 Liste PDFDokument2 SeitenPT3 Liste PDFSiti KamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- STAG-4 QBOX, QNEXT, STAG-300 QMAX - Manual - Ver1 - 7 - 8 (30-09-2016) - EN PDFDokument63 SeitenSTAG-4 QBOX, QNEXT, STAG-300 QMAX - Manual - Ver1 - 7 - 8 (30-09-2016) - EN PDFIonut Dacian MihalachiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSG 9 Tienganh 2019Dokument7 SeitenHSG 9 Tienganh 2019Bảo HoàngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingrid Gross ResumeDokument3 SeitenIngrid Gross Resumeapi-438486704Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lifetime Prediction of Fiber Optic Cable MaterialsDokument10 SeitenLifetime Prediction of Fiber Optic Cable Materialsabinadi123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Floating PonttonDokument9 SeitenFloating PonttonToniNoch keine Bewertungen
- R. K. NarayanDokument9 SeitenR. K. NarayanCutypie Dipali SinghNoch keine Bewertungen