Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Gilbert
Hochgeladen von
John BermundoCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Gilbert
Hochgeladen von
John BermundoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Blink
This example shows the simplest thing you can do with an Arduino or
Genuino to see physical output: it blinks an LED.
Hardware Required
Arduino or Genuino Board
LED
220 ohm resistor
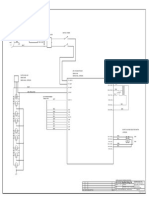
Circuit
To build the circuit, connect one end of the resistor to Arduino pin 13.
Connect the long leg of the LED (the positive leg, called the anode) to the
other end of the resistor. Connect the short leg of the LED (the negative leg,
called the cathode) to the Arduino GND, as shown in the diagram and the
schematic below.
Most Arduino boards already have an LED attached to pin 13 on the board
itself. If you run this example with no hardware attached, you should see that
LED blink.
The value of the resistor in series with the LED may be of a different value
than 220 ohm; the LED will lit up also with values up to 1K ohm.
Schematic
Code
After you build the circuit plug your Arduino or Genuino board into your
computer, start the Arduino Software (IDE) and enter the code below. You
may also load it from the menu File/Examples/01.Basics/Blink . The first thing
you do is to initialize pin 13 as an output pin with the line
pinMode(13, OUTPUT);
In the main loop, you turn the LED on with the line:
digitalWrite(13, HIGH);
This supplies 5 volts to pin 13. That creates a voltage difference across the
pins of the LED, and lights it up. Then you turn it off with the line:
digitalWrite(13, LOW);
That takes pin 13 back to 0 volts, and turns the LED off. In between the on
and the off, you want enough time for a person to see the change, so the
delay() commands tell the board to do nothing for 1000 milliseconds, or one
second. When you use the delay() command, nothing else happens for that
amount of time. Once you've understood the basic examples, check out the
BlinkWithoutDelay example to learn how to create a delay while doing other
things.
Once you've understood this example, check out the DigitalReadSerial
example to learn how read a switch connected to the board.
/*
Blink
Turns on an LED on for one second, then off for one second,
repeatedly.
Most Arduinos have an on-board LED you can control. On the Uno
and
Leonardo, it is attached to digital pin 13. If you're unsure
what
pin the on-board LED is connected to on your Arduino model,
check
the documentation at http://www.arduino.cc
This example code is in the public domain.
modified 8 May 2014
by Scott Fitzgerald
*/
// the setup function runs once when you press reset or power
the board
void setup() {
// initialize digital pin 13 as an output.
pinMode(13, OUTPUT);
}
// the loop function runs over and over again forever
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH);
// turn the LED on (HIGH is the
voltage level)
delay(1000);
// wait for a second
digitalWrite(13, LOW);
// turn the LED off by making the
voltage LOW
delay(1000);
// wait for a second
}
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Electronic Measurements A Practical Approach (Farzin Asadi, Kei Eguchi) - CompressedDokument172 SeitenElectronic Measurements A Practical Approach (Farzin Asadi, Kei Eguchi) - CompressedManafu GregorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Design ProjectDokument12 SeitenElectrical Design ProjectClyde Anthony G. BalgosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering ManagementDokument213 SeitenEngineering ManagementDarnell H. de Luna93% (15)
- MSD6886 US Service Manual V1.0 2019-7-11-6Dokument105 SeitenMSD6886 US Service Manual V1.0 2019-7-11-6Tena y EstebanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH Formulas PDFDokument33 SeitenMATH Formulas PDFAnonymous 0Mduljho100% (3)
- Math Iecep (Kung Nakakuha Ka Nito, Maswerter Ka)Dokument4 SeitenMath Iecep (Kung Nakakuha Ka Nito, Maswerter Ka)davidmeanne100% (5)
- GENERAL ENGINEERING Handbook-of-Formulae - And-Constants PDFDokument43 SeitenGENERAL ENGINEERING Handbook-of-Formulae - And-Constants PDFhasib_07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of System Noise Temperature and Noise PowerDokument13 SeitenCalculation of System Noise Temperature and Noise PowerSaptarshi GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCH VsdSpeedstar2000 UmDokument93 SeitenSCH VsdSpeedstar2000 Umyasser_nasef5399Noch keine Bewertungen
- Full Page PictureDokument1 SeiteFull Page PictureJohn BermundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comp Fundamentals - Midterm ProjectDokument2 SeitenComp Fundamentals - Midterm ProjectJohn BermundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDokument2 SeitenCJohn BermundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2Dokument2 Seiten2John Bermundo100% (1)
- 1Dokument3 Seiten1John BermundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12Dokument3 Seiten12John BermundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument1 SeiteUntitledJohn BermundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResearchDokument1 SeiteResearchJohn BermundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EU Fines Airlines $1.11 Billion in Cartel Case: by Alessandro Torello Updated Nov. 9, 2010 4:26 P.M. ETDokument2 SeitenEU Fines Airlines $1.11 Billion in Cartel Case: by Alessandro Torello Updated Nov. 9, 2010 4:26 P.M. ETJohn BermundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TIE BreakerDokument8 SeitenTIE BreakerJohn BermundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burglar Alarm System Using Arduino, Motion Sensor and GSM Module Through TextingDokument2 SeitenBurglar Alarm System Using Arduino, Motion Sensor and GSM Module Through TextingJohn BermundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReadmeDokument2 SeitenReadmeJonh AlmeidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AmpoyDokument2 SeitenAmpoyJohn BermundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planner DraftDokument1 SeitePlanner DraftJohn BermundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AvastDokument1 SeiteAvastJohn BermundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- mbr20100ct PDFDokument2 Seitenmbr20100ct PDFMonica XiomaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asus ZenFone Max ZC550KL - Schematic DiagarmDokument154 SeitenAsus ZenFone Max ZC550KL - Schematic Diagarmhardiantara.dt0% (1)
- Communication Systems (ELE 3103) RCS (MAKE UP) 2017Dokument2 SeitenCommunication Systems (ELE 3103) RCS (MAKE UP) 2017devangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wattio Mobilemanual Gate EsDokument17 SeitenWattio Mobilemanual Gate EsalienstrikesNoch keine Bewertungen
- TamagawaDokument35 SeitenTamagawadfu5346Noch keine Bewertungen
- As2 As4 Adlee ManualDokument77 SeitenAs2 As4 Adlee Manualr7abouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coship SD Mpeg 4 ManualDokument8 SeitenCoship SD Mpeg 4 ManualpravnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Furman AR1215 Power Conditioning (120vac)Dokument18 SeitenFurman AR1215 Power Conditioning (120vac)Bob FarlowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Rover With Secure Communication Through LI-FIDokument2 SeitenAdvanced Rover With Secure Communication Through LI-FIPrerith.MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Fiber Technology: SciencedirectDokument7 SeitenOptical Fiber Technology: SciencedirectsamiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 - CEC342 - Common Types of Analog and Mixed - Signal Circuits - Applications of Mixed-Signal CircuitsDokument6 Seiten1.1 - CEC342 - Common Types of Analog and Mixed - Signal Circuits - Applications of Mixed-Signal CircuitsSriram Sundar SubramanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex 2200 PDFDokument2 SeitenEx 2200 PDFLindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Examples Using The ToolboxDokument23 SeitenDesign Examples Using The Toolboxrajeevjain09Noch keine Bewertungen
- 36101-g60 SannexesDokument492 Seiten36101-g60 SannexesmbegulekNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACER ACER Aspire V5-531pDokument103 SeitenACER ACER Aspire V5-531pRicardo OlivaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pan Vs VanDokument1 SeitePan Vs VanFahad AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of 3D Integrated Circuits: Vachan Kumar Azad NaeemiDokument3 SeitenAn Overview of 3D Integrated Circuits: Vachan Kumar Azad NaeemiMeghanand KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EziweighDokument4 SeitenEziweighBerney RyxlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- IRS ProductsDokument12 SeitenIRS ProductsGianluca BacchiegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCB Layout Recommendations For Bga PackagesDokument83 SeitenPCB Layout Recommendations For Bga PackagesLê Đình TiếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear PotentiometerDokument3 SeitenLinear PotentiometerProdip KhanikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mxa710 Spec Sheet Letter enDokument2 SeitenMxa710 Spec Sheet Letter enBobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Devices Engineering UniversityDokument5 SeitenAnalog Devices Engineering UniversityjeevarajanmkNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7-439D-6AW-R Campana PDFDokument2 Seiten7-439D-6AW-R Campana PDFAndres Rodriguez ArevaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet Sensor UltrasonikDokument5 SeitenDatasheet Sensor UltrasonikHairul AminNoch keine Bewertungen