Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
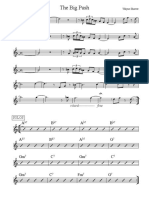
Song
Hochgeladen von
Andrey AndreevCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Song
Hochgeladen von
Andrey AndreevCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
A song, most broadly, is a single (and often standalone) work of music that is t
ypically intended to be sung by the human voice with distinct and fixed pitches
and patterns using sound and silence and a variety of forms that often include t
he repetition of sections. Written words created specifically for music or for w
hich music is specifically created, are called lyrics. If a pre-existing poem is
set to composed music in classical music it is an art song. Songs that are sung
on repeated pitches without distinct contours and patterns that rise and fall a
re called chants. Songs in a simple style that are learned informally are often
referred to as folk songs. Songs that are composed for professional singers who
sell their recordings or live shows to the mass market are called popular songs.
These songs, which have broad appeal, are often composed by professional songwr
iters, composers and lyricists. Art songs are composed by trained classical comp
osers for concert or recital performances. Songs are performed live and recorded
on audio or video (or in some, cases, a song may be performed live and simultan
eously recorded). Songs may also appear in plays, musical theatre, stage shows o
f any form, and within operas.
A song may be for a solo singer, a lead singer supported by background singers,
a duet, trio, or larger ensemble involving more voices singing in harmony, altho
ugh the term is generally not used for large classical music vocal forms includi
ng opera and oratorio, which use terms such as aria and recitative instead.[1] S
ongs with more than one voice to a part singing in polyphony or harmony are cons
idered choral works. Songs can be broadly divided into many different forms, dep
ending on the criteria used.
Songs may be written for one or more singers to sing without instrumental accomp
animent or they may be written for performance with instrumental accompaniment.
The accompaniment used for a song depends on the genre of music and, in classica
l styles, the instructions of the composer as set out in the musical score. Song
s may be accompanied by a single accompanist playing piano or guitar, by a small
ensemble (e.g., a jazz quartet, a basso continuo group (in the case of Baroque
music), a rock or pop band or a rhythm section) or even a big band (for a jazz s
ong) or orchestra (for a classical aria). One division is between "art songs", "
pop songs" and traditional music which includes "folk songs" and early blues son
gs. Other common methods of classification are by purpose (sacred vs secular), b
y style (dance, ballad, Lied, etc.), or by time of origin (Renaissance, Contempo
rary, etc.). Songs may be learned and passed on "by ear" (as in traditional folk
songs); from a recording or lead sheet (in jazz and pop) or from detailed music
notation (in classical music). While the term "song" usually refers to a sung m
elody, the term is also used in some instrumental music in which the composer wi
shes the performer to play in a singing style (e.g., Mendelssohn's Songs Without
Words for solo piano.)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Boquillas EquivalenciasDokument4 SeitenBoquillas EquivalenciasAri Palmieri100% (1)
- Joseph Hartmann: About The ArtistDokument3 SeitenJoseph Hartmann: About The ArtistgiulianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalog of Rare Old Violins Violas and Violoncellos 1000738211Dokument99 SeitenCatalog of Rare Old Violins Violas and Violoncellos 1000738211luitoviolin100% (1)
- 40 HighSchoolCadetsDokument84 Seiten40 HighSchoolCadetsMareina Harris100% (1)
- Post of Nakatani Gong Orchestra Followed The Master Plan Post 1 (First Intro About Artist Biography)Dokument5 SeitenPost of Nakatani Gong Orchestra Followed The Master Plan Post 1 (First Intro About Artist Biography)anh sy tranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Jazz Scales You Should KnowDokument122 Seiten10 Jazz Scales You Should Knowjamespco_119633823Noch keine Bewertungen
- 06 SoE BK 1 Alto SaxophoneDokument52 Seiten06 SoE BK 1 Alto SaxophoneRicardo Martínez LópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anthem - KamelotDokument13 SeitenAnthem - KamelotErik CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suburbia - PartiturDokument44 SeitenSuburbia - PartiturChris BehrNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIG PUSH TRPT (I) Copy 2 PDFDokument1 SeiteBIG PUSH TRPT (I) Copy 2 PDFMike OlmosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lady of Shalott ScriptDokument3 SeitenLady of Shalott ScriptSamko PutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jingle Bells, HallelujahDokument48 SeitenJingle Bells, Hallelujahyouth scout mouvementNoch keine Bewertungen
- UB9 Bertoglio PDFDokument26 SeitenUB9 Bertoglio PDFaarrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cycle Des QuintesDokument24 SeitenCycle Des QuintesHenri DeltourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Langston Hughes - Slave On The BlockDokument4 SeitenLangston Hughes - Slave On The Blockathpapoulis1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modernism in Music and Erik Satie's ParadeDokument18 SeitenModernism in Music and Erik Satie's ParadeAnami0Noch keine Bewertungen
- La boheme-AZNAVOURDokument3 SeitenLa boheme-AZNAVOURCsc CorsicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MR BojangDokument3 SeitenMR Bojangkuifje143Noch keine Bewertungen
- In The Mood - GuitarDokument2 SeitenIn The Mood - GuitarAndrés MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arsm (Associate of The Royal Schools of Music) : September 2020Dokument27 SeitenArsm (Associate of The Royal Schools of Music) : September 2020hasworoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why-Not-Michel-Camilo-TROMBONE 1Dokument3 SeitenWhy-Not-Michel-Camilo-TROMBONE 1Gab DRUMMERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mozart S Oboe Concerto - Bernhard PaumgartnerDokument5 SeitenMozart S Oboe Concerto - Bernhard PaumgartnerEmil Loyal100% (1)
- A Handbook To Twentieth-Century Musical SketchesDokument11 SeitenA Handbook To Twentieth-Century Musical Sketchesbalintk100% (1)
- James Snead, "On Repetition in Black Culture"Dokument11 SeitenJames Snead, "On Repetition in Black Culture"Michael Litwack50% (2)
- Greg PhillinganesDokument3 SeitenGreg PhillinganesivanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poniżej Zestaw Grup Rockowych Z Albumami W Plikach PDFDokument24 SeitenPoniżej Zestaw Grup Rockowych Z Albumami W Plikach PDFHendiHurtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Output: Defining and Developing The Music Sector in Northern IrelandDokument92 SeitenOutput: Defining and Developing The Music Sector in Northern IrelandGenerator NINoch keine Bewertungen
- BACH - Toccata and Fugue in D Minor BWV 565 PDFDokument15 SeitenBACH - Toccata and Fugue in D Minor BWV 565 PDFAntonio ArnaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ornette Solos AnalysisDokument154 SeitenOrnette Solos AnalysisJoão RoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evening in ParisDokument1 SeiteEvening in ParisJan v.KlewitzNoch keine Bewertungen