Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pain and Inflammation Med Charts
Hochgeladen von
surviving nursing schoolOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pain and Inflammation Med Charts
Hochgeladen von
surviving nursing schoolCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pain and Inflammation Med Charts
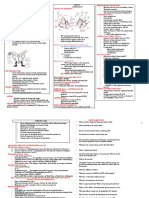
Name Nonsteroidal Antinflammatory Drugs
Mechanism inhibition of cyclooxygenase, results in decrease in platelet aggregation,
of Action inflammation, fever, pain
Therapeutic inflammation, mild analgesia, fever, dysmenorrhea, inhibition of platelet
Uses aggregation (protection against stroke, MI)
Side Effects/ GI upset, damage to gastric mucosa, renal dysfunction, increased risk of
Precautions MI and stroke(for non ASA NSAIDS), Salicylism risk for ASA(tinnitus,
sweating, HA, respiratory aklaosis)
Interactions increased risk of bleeding with other anticoagulants, glucocorticoids,
alcohol. Ibuprofen decreases antiplatelet effects of ASA
Nursing/Pati take NSAIDS with food to decrease gastric discomfort, notify provider if
ent teaching symptoms of salicylism occurs, concurrent use with opioids allow for lower
dosages of opioids
Common ASA, Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Indomethacin (Indocin), Ketorolac (Toradol),
Drugs Meloxicam (Mobic), Colecoxib (Celebrex)
Name Acetaminophen
Mechanism slows production of protaglandins in CNS
of Action
Therapeutic analgesic, antipyretic
Uses
Side Effects/ acute toxicity results in liver damage (early symptoms include nausea,
Precautions vomiting, diarrhea, sweating, abdominal discomfort)
Interactions alcohol increases risk of liver damage, slows metabolism of warfarin
Nursing/Pati do not exceed 4 mg/ day, acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) is antidote for
ent teaching overdose
Common tylenol
Drugs
Name Opioid Agonist
Mechanism act on mu and kappa receptors, produces analgesia, respiratory
of Action depression, euphoria, sedation, decreased GI motility
Therapeutic moderate to severe pain
Uses
Side Effects/ respiratory depression, constipation, orthostatic hypotension, urinary
Precautions retention, cough suppression, sedation, emesis
Interactions CNS depressants have additive depression action. Anticholinergics,
antihistamines, tricyclic antidepressants have additive anticholinergic
effects. MAOIs may cause hyperpyrexic coma.
Nursing/Pati overdose triad: coma, repiratory depression, pinpoint pupils. Administer
ent teaching very slowly, over 4 to 5 minutes. Narcan is antidote. Do not administer
more than 600 mg/24 hour period for meperidine (Demerol).
Common morphine, Fentanyl (Sublimaze, Duragesic), Meperidine (Demoerol),
Drugs Methadone (Dolophine), Codeine/oxycodone (OxyContin)
Name Agonist - antagonist opioids
Mechanism antagonists act on mu and kappa receptors, lower potential for abuse, less
of Action respiratory depression, and less analgesic effect compared to pure opioid
agonists
Therapeutic moderate to sever pain, treament of opioid dependence, adjunct to
Uses balanced anesthesia,,
Side Effects/ sedation, respiratory depression, dizziness, increased intracranial
Precautions pressure, HA, increased cardiac workload. abstinence syndrome (for those
who are dependant on opioids)
Interactions additive CNS depression with other CNS depressants, opioid agonists may
antagonize and reduce analgesic effects (do not use concurrently)
Nursing/Pati caution when undisclosed opioid use is suspected. Again, opioid agonist
ent teaching and opioid agonist antagonist should not be used together. Naloxone
(narcan) is antidote
Common butorphanol (Stadol), hydrochloride (Nubain), Buprenorphine
Drugs hydrochloride (Buprenex)
Adjuvant Medications for Pain: used with a primary pain medication,
usually an opioid agonist in order to reduce opioid dosage to reduce side
effects.
NSAIDS treats inflammation.
side effects: bone marrow suppresion, GI distress
Tricyclic treats depression, neuropathic pain such as cramping/aching/burning.
antidepress (amitriptyline (Elavil))
ants side effects: orthostatic hypotension, sedation, anticholinergic effects
Anticonvuls neuropathic pain (carbamazepine (Tegretol), gabapentin (Neurontin))
ants side effects: bone marrow suprresion, GI distress
CNS analgesia, decrease sedation. (methylphenidate (Ritalin))
stimulants side effects: weight loss, insomnia
Antihistami decrease anxiety, prevent insomnia and relieve nausea (hydroxyzine
nes (Vistaril))
Bisphospho manage hypercalcemia and bone pain (etidronate (Didronel))
nates side effects: flu like symptoms, venous irritation, renal failure
glucocortico decrease pain from intracranial pressure and spinal cord compression.
ids (dexamethason (Didronel))
side effects: adrenal insufficiency, osteoporosis, hypokalemia, glucose
intolerance, peptic ulcer disease
Name Migraine Meds
Mechanism prevent inflammation and dilation of the intracranial blood vessels,
of Action relieving migraine pain
Therapeutic stopping acute migraine attacks, prevention of chronic migrains
Uses
Side Effects/ depends on type (pg 473)
Precautions
Interactions depends on type
Nursing/Pati avoid trigger factors that cause stress (alcohol, fatigue, tyramine
ent teaching containing foods (aged cheese))
Common Ergot alkaloids: ergotamine (Ergostat)
Drugs Serotonin receptor agonist: sumatriptan (Imitrex)
Beta Blockers: propranolol (Inderal)
Anticonvulsants: divalproex (Depakote)
Tricyclic antidepressants: anitriptyline (Elavil)
Calcium channel blockers: verapamil (Calan)
Estrogens: Estraderm
Ergot alkaloids: Cafergot
Name Local Anesthetics
Mechanism decrease pain by blocking conduction of pain impulses in a specific area
of Action
Therapeutic dental procedures, minor surgical procedures, labor and delivery, regional
Uses anesthesia, skin and mucous membrane disorders, minor procedures (IV
insertion, injection, wart removal)
Side Effects/ CNS excitation (seizures, followed by respiratory depression, leading to
Precautions unconsciousness), hypotension, can prolong labor
Interactions additive hypotensive effects with parenteral administration
Nursing/ vasoconstrictors (epinephrine) often used in combination with local
Patient anesthetic to stop the spread. topical cream applied one hour before
teaching procedure.
Common lidocaine (Xylocaine), tetracain (Pontocaine), procain (Novocain)
Drugs
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Von EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- NCLEX Review: Pharmacology Charlene Natale, BSN, RNDokument43 SeitenNCLEX Review: Pharmacology Charlene Natale, BSN, RNMenly Susada100% (1)
- Drug Suffixes Cheat Sheet Sorted AlphabeticallyDokument3 SeitenDrug Suffixes Cheat Sheet Sorted Alphabeticallystudynote155Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Classification TemplateDokument1 SeiteDrug Classification Templatehovismj100% (1)
- Pharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDokument18 SeitenPharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsPadmavathy Naidu Chokkapu100% (2)
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Dokument48 SeitenNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medications and assessmentsDokument225 SeitenMedications and assessmentsJessica 'Baker' IsaacsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psycho PharmaDokument8 SeitenPsycho PharmaMark JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEDokument3 SeitenPharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEMitu Miressa تNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anxiety Disorders Treatment OptionsDokument5 SeitenAnxiety Disorders Treatment OptionsJohn HolmesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Medical Suffixes Cheat SheetDokument1 SeitePharmacology Medical Suffixes Cheat SheetPattyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug CardsDokument4 SeitenDrug CardsBrittany Lynn MyersNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 Essential Drugs1Dokument8 Seiten100 Essential Drugs1Sudip DevadasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student medication interactionsDokument26 SeitenStudent medication interactionsLila DanielsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs WorksheetDokument16 SeitenDrugs Worksheetninja-2001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Family Names of DrugsDokument1 SeiteFamily Names of DrugsangelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Mathematics For AnesthetistsDokument18 SeitenClinical Mathematics For AnesthetistsAlex Kireva100% (1)
- Drug Names - Stems, Prefixes, Roots and Suffixes - NCLEX MasteryDokument5 SeitenDrug Names - Stems, Prefixes, Roots and Suffixes - NCLEX MasteryMarcel YoungNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1000 Drug CardsDokument33 Seiten1000 Drug CardsJelly Bean100% (1)
- Labs Electrolyte ChartDokument1 SeiteLabs Electrolyte ChartmdcmepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartDokument5 SeitenNeuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartMonica J Ortiz Pereira100% (1)
- Drug CardsDokument11 SeitenDrug CardsLizShermanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Printable Drug Template CardDokument2 SeitenPrintable Drug Template CardJennifer LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicDokument28 SeitenA-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicMahmoud Ahmed MahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug CardsDokument3 SeitenDrug CardsDave HillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 200 Drug Study Reference RLPDokument31 SeitenTop 200 Drug Study Reference RLPYathrika YathrikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS: Types, Mechanisms and Side EffectsDokument21 SeitenANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS: Types, Mechanisms and Side EffectsKashis SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, InteractionsDokument6 SeitenHmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, Interactionswaste78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mnemonic S 2Dokument9 SeitenMnemonic S 2Anj Shrestha100% (2)
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology OutlineDokument11 SeitenCardiovascular Pharmacology OutlineLhay de OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Template Drug Card1Dokument1 SeiteTemplate Drug Card1Kay TaylorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sulfonamides, Tetracyclines, and Penicillins ComparisonDokument20 SeitenSulfonamides, Tetracyclines, and Penicillins ComparisonKeying Chen100% (1)
- Drug SuffixesDokument3 SeitenDrug SuffixesjeromeasuncionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Med BundleDokument36 SeitenMed Bundlejamie sealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Clear and Simple A Guide To Drug Classifications and Dosage Calculations 2nd Edition Watkins Solutions ManualDokument4 SeitenPharmacology Clear and Simple A Guide To Drug Classifications and Dosage Calculations 2nd Edition Watkins Solutions ManualJamesJoFrancis100% (1)
- Medication Classes Cheat SheetDokument2 SeitenMedication Classes Cheat SheetJoax Wayne SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Final Study GuideDokument28 SeitenPharmacology Final Study GuideAnthony Palladeno100% (1)
- Vitamin K IV antidote for warfarin bleedingDokument10 SeitenVitamin K IV antidote for warfarin bleedingQueennitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labs 1.19 ABG AnalysisDokument1 SeiteLabs 1.19 ABG AnalysisMonica GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care Drug Reference SheetDokument12 SeitenCritical Care Drug Reference SheetYanina CoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- OB Drug ChartsDokument2 SeitenOB Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lang 10 EditionDokument235 SeitenLang 10 Editionraju niraulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test InformationDokument5 SeitenTest InformationCatalina BorquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agents Causing Coma or SeizuresDokument3 SeitenAgents Causing Coma or SeizuresShaira Aquino VerzosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharm 1.11 Insulin Cheat SheetDokument1 SeitePharm 1.11 Insulin Cheat SheetSanobar Charania100% (1)
- Cardiac MedicationsDokument8 SeitenCardiac Medicationsangeline totaram100% (2)
- Emergency DrugsDokument9 SeitenEmergency DrugsaldwinngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharm Drug Outline AdrDokument1 SeitePharm Drug Outline AdrCess Lagera YbanezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Cheat Sheet - Generic Drug Stems - NurseslabsDokument12 SeitenPharmacology Cheat Sheet - Generic Drug Stems - NurseslabsKc Mea Paran BorjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug CardDokument1 SeiteDrug CardPaul AlfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseVon EverandNursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Student Pharmacy TechniciansVon EverandPharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Student Pharmacy TechniciansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsVon EverandDimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsVon EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- PN FUNDAMENTALS: Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandPN FUNDAMENTALS: Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatric Nursing ReviewDokument16 SeitenPsychiatric Nursing Reviewɹǝʍdןnos97% (63)
- PREPUMASTERKEY (Repaired)Dokument2.031 SeitenPREPUMASTERKEY (Repaired)surviving nursing schoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesDokument5 SeitenMajor Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancestheglobalnursingNoch keine Bewertungen
- PREPUMASTERKEY (Repaired)Dokument2.031 SeitenPREPUMASTERKEY (Repaired)surviving nursing schoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 Essential Drugs1Dokument8 Seiten100 Essential Drugs1Sudip DevadasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematologic System Drug ChartsDokument2 SeitenHematologic System Drug Chartssurviving nursing schoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perioperative NursingDokument12 SeitenPerioperative Nursingtheglobalnursing100% (12)
- Pain and Inflammation Med ChartsDokument4 SeitenPain and Inflammation Med Chartssurviving nursing school100% (1)
- Therapeutic DietsDokument8 SeitenTherapeutic DietsmArLoN91% (11)
- Musculoskeletal ChartsDokument27 SeitenMusculoskeletal Chartssurviving nursing school100% (3)
- Digestive Domain Guide 1Dokument31 SeitenDigestive Domain Guide 1surviving nursing school100% (1)
- Final Edited Version - Patho Bible 1Dokument139 SeitenFinal Edited Version - Patho Bible 1RosemaryCastro100% (1)
- Cardiac Study GuideDokument11 SeitenCardiac Study Guidesurviving nursing school100% (2)
- Disease Cheat SheetDokument393 SeitenDisease Cheat Sheetsurviving nursing school50% (2)
- ECG StripsDokument5 SeitenECG Stripssurviving nursing school100% (1)
- ATI Bible 1Dokument205 SeitenATI Bible 1surviving nursing school100% (1)
- Vitamin Chart 2Dokument3 SeitenVitamin Chart 2surviving nursing schoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsDokument4 SeitenGastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug Chartssurviving nursing schoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- NeurologicalDokument3 SeitenNeurologicalsurviving nursing school100% (1)
- FE Imbalance HandoutsDokument2 SeitenFE Imbalance HandoutsPrasanth Kurien Mathew100% (2)
- Nina Bacteria Chart Medical School Step 1Dokument11 SeitenNina Bacteria Chart Medical School Step 1M PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid BaseDokument2 SeitenAcid Basesurviving nursing schoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ValuesDokument3 SeitenLab Valuessurviving nursing schoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine NursingDokument2 SeitenEndocrine Nursingsurviving nursing school100% (2)
- ECG Interpretation Guide - Key Components and AbnormalitiesDokument1 SeiteECG Interpretation Guide - Key Components and Abnormalitieshirsi20051879% (24)
- Neurology Domain GuideDokument29 SeitenNeurology Domain Guidesurviving nursing schoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adult III Cardiac Study GuideDokument15 SeitenAdult III Cardiac Study GuideNursingSchoolNotes100% (6)
- Hematologic System Drug ChartsDokument2 SeitenHematologic System Drug Chartssurviving nursing schoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro Study GuideDokument7 SeitenNeuro Study GuideNursingSchoolNotes100% (2)
- Lecture 11 Sedative-Hypnotic and Anti-Anxiety AgentsDokument32 SeitenLecture 11 Sedative-Hypnotic and Anti-Anxiety AgentsHafsa ShakilNoch keine Bewertungen
- OTC Medications Checklist Version 1.5Dokument2 SeitenOTC Medications Checklist Version 1.5Agustin PeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dfe Brochure Osd Def Web-1Dokument6 SeitenDfe Brochure Osd Def Web-1jessica febeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Drug AdministrationDokument34 SeitenPrinciples of Drug AdministrationArlyn Mendenilla100% (1)
- Significance of Pharmaceutical Excipients - A Review: January 2011Dokument11 SeitenSignificance of Pharmaceutical Excipients - A Review: January 2011jhon garcesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lacosamide: A Novel Antiepileptic and Anti-Nociceptive Drug On The BlockDokument5 SeitenLacosamide: A Novel Antiepileptic and Anti-Nociceptive Drug On The BlockFarhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncologist: Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents in Renal MedicineDokument6 SeitenNcologist: Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents in Renal MedicineSergio RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Insulin Options for Improved Glycemic ControlDokument30 SeitenCurrent Insulin Options for Improved Glycemic ControlSERGIO LOPEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychotropic Drugs II. Pharmacology. Pharmacotherapy. PharmacyDokument7 SeitenPsychotropic Drugs II. Pharmacology. Pharmacotherapy. PharmacyJorge Medina FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- HuihgyDokument27 SeitenHuihgySanjukta GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- GastrointestinaldrugsDokument30 SeitenGastrointestinaldrugsmayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 150Dokument68 Seiten150Andrei Miguel RoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar PustakaDokument4 SeitenDaftar PustakaMay May DianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Toxicokinetics and ToxicodynamicsDokument70 SeitenPrinciples of Toxicokinetics and Toxicodynamicskiki rawitriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Russian Pharma Market Reaches $1.15 Trillion in 2014Dokument76 SeitenRussian Pharma Market Reaches $1.15 Trillion in 2014Kushal TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dexmedetomidine: (Precedex - Abbott Laboratories)Dokument6 SeitenDexmedetomidine: (Precedex - Abbott Laboratories)battreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Abbreviations Used in Medical PrescriptionsDokument5 SeitenList of Abbreviations Used in Medical PrescriptionsNathan TonthatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Addiction and Rehabilitation TermsDokument4 SeitenDrug Addiction and Rehabilitation TermsYolly Ces SecretariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Work On Post Marketing Surveillance of Pemazyre: For Partial Fulfilment of The Requirement For TheDokument45 SeitenProject Work On Post Marketing Surveillance of Pemazyre: For Partial Fulfilment of The Requirement For ThesalmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharma ManualDokument40 SeitenPharma Manualryan samuel tanedo100% (1)
- IukulyulytDokument25 SeitenIukulyulytRizki D'biskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Astm E3219 Standard Guide For Derivation of Health Based Exposure Limits (Hbels)Dokument10 SeitenIntroduction To The Astm E3219 Standard Guide For Derivation of Health Based Exposure Limits (Hbels)nsk79inNoch keine Bewertungen
- USP34 NF29General NoticesDokument14 SeitenUSP34 NF29General Noticeskelk200Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacy PricingDokument14 SeitenPharmacy Pricingtipay0221Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ezolvin Syrup Patient Information Leaflet PDFDokument1 SeiteEzolvin Syrup Patient Information Leaflet PDFSameer SamouaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LorazepamDokument4 SeitenLorazepamapi-3797941Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Selection and Use of Essential Medicines: WHO Technical Report SeriesDokument881 SeitenThe Selection and Use of Essential Medicines: WHO Technical Report SeriesAngelica NarvaezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Envision: AAMC Faculty Professional Development SeminarDokument3 SeitenEnvision: AAMC Faculty Professional Development SeminarSlusom WebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inventario Inicial WoDokument22 SeitenInventario Inicial WoJulian SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comirnaty Concentrate For Dispersion For Injection: Consumer Medication Information Leaflet (Rimup)Dokument5 SeitenComirnaty Concentrate For Dispersion For Injection: Consumer Medication Information Leaflet (Rimup)SMK Permaisuri Nur Zahirah TerengganuNoch keine Bewertungen