Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Er NCP
Hochgeladen von
Mjhay Montemayor0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
48 Ansichten3 SeitenAnxiety related to hospitalization
Decreased cardiac output
Originaltitel
ER NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenAnxiety related to hospitalization
Decreased cardiac output
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
48 Ansichten3 SeitenEr NCP
Hochgeladen von
Mjhay MontemayorAnxiety related to hospitalization
Decreased cardiac output
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
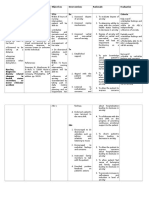
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF OBJECTIVES NURSING RATIONALE EVALUA
THE PROBLEM INTERVENTIONS TION
Subjective: Normally, there is STO: within 2 Diagnostic Fully met:
Magpapacheck- significant increase in hours of 1.) Assessed vital signs (BP, 1.) To determine the Patients
up lang sana ako, blood pressure among nursing HR) effectiveness of BP:
kaso nahilo at pregnant women interventions, intervention. 130/90,
tumaas BP ko during their course of client will have 2.) Assessed peripheral 2.) To identify possible absence of
pregnancy period. BP of less than extremities presence edema, dizziness
It is a response of the or equal to varicosities or swelling. and
Objective: body to the increase in 130/90mmHg, tingling
Vital signs: blood volume. absence of Therapeutic sensation
BP: However, it becomes dizziness and 1.) Administered 1.) To reduce blood fluid on both
150/100mmHg fatal if not monitored tingling magnesium sulfate via volume by means of hands.
CR: 102 bpm regularly. sensation on solu-set increasing urine output.
SpO2: 94% both hands 2.) To meet oxygen demand
RR: 20 cpm Due to the increased 2.) Given low flow oxygen by the increased heart
blood pressure, there (1-2 lpm) via nasal rate.
cannula 3.) To allow full lung
No signs of edema is a decreased cardiac
3.) Positioned to semi- expansion and allows
on extremities due to increase in
fowlers. more air to enter the
Not distended heart rate resulting to
lungs
jugular vein inadequate blood
No signs of pumped by the heart.
4.) Provided warm blanket 4.) To provide warmth.
paleness
Capillary refill and Decreased cardiac
skin turgor less output is defined as Educative
1.) Taught deep breathing 1.) To reduce stimuli and
than 1 second inadequate blood
exercises produce calming effect
With pulse grade pumped by the heart
reducing BP
of +2 to meet the metabolic
2.) Emphasized importance 2.) Lessens physical stress
With tingling demands of the body.
of adequate rest and and tension that affect
sensation on both
limit strenuous activities increase in blood
hands pressure
Not in respiratory References
distress. Doenges, M., 3.) To increase venous
3.) Instructed to ambulate
Moorhouse, M., & return.
feet regularly
Nursing Murr, A. (2009).
Diagnosis Nurse's pocket guide. 4.) Instructed to report
Decreased cardiac Philadelphia: Davis dizziness and difficulty 4.) To provide proper
output related to Company. in breathing. medical and nursing
increased heart management as needed.
rate.
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF OBJECTIVE NURSING RATIONALE EVALUAT
THE PROBLEM S INTERVENTIONS ION
Subjective: It is normal for a STO: after 30 Diagnostic Fully met:
Kinakabahan kasi person to get anxious mins of 1.) Assessed stressors 1.) To determine Patient was
ako lagi kapag during clinical nursing contributing to anxiety appropriate able to
nagpapacheck-up consultation or check- intervention interventions and relax as
up. In the case of our patient will be evaluate degree of manifested
patient, she gets in a relaxed Therapeutic anxiety by calm
Objective: anxious every time she state as 1.) Use presence, touch 1.) Being supportive and face, able
Observed to goes for a check-up, manifested by (with permission), approachable promotes to interact
holding and reason was the result calm face and verbalization, and communication clearly,
rubbing both may not desirable or non-shaky demeanor to remind understand
hands. not as she expected as hands with patients that they are s the
Noted to be texting claimed by the stable vital not alone and to situation ,
her son to come see patient. signs 2.) Diverted patient 2.) Talking or otherwise non-shaky
her as soon as BP: =< attention. expressing feelings hands, and
possible 130/90mmHg sometimes reduces vital signs
Shaky hands And CR: < 100 anxiety. of BP:
Vital signs: References: bpm Educative 130/90mm
BP: 150/100mmHg 1.) Encourage expression or 1.) Talking about anxiety- Hg, CR:
CR: 102 bpm Doenges, M., clarification of needs, producing situations and <100 bpm
SpO2: 94% Moorhouse, M., & concerns, unknowns, anxious feeling can help the
RR: 20 cpm Murr, A. (2009). and questions about patient perceive the situation
Nurse's pocket guide. hospitalization. realistically and recognize
Philadelphia: Davis factors leading
Company.
2.) Taught deep breathing 2.) Promotes relaxation
Nursing exercises and provided
Diagnosis calm environment
Anxiety related to
3.) Familiarize patient with 3.) Awareness of the
hospitalization
the environment and environment promotes
new experiences or comfort and may
people as needed. decrease anxiety
experienced by the
patient. Anxiety may
intensify to a panic level
if patient feels threatened
and unable to control
environmental stimuli.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- New Text DocumentDokument1 SeiteNew Text DocumentMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Specs SampleDokument14 SeitenSpecs SampleAThaddeusAntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Building Permit RequirementsDokument6 SeitenA Building Permit RequirementsMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- A Building Permit RequirementsDokument6 SeitenA Building Permit RequirementsMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Valuing Urban Open Space Using The TravelDokument14 SeitenValuing Urban Open Space Using The TravelMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Flores de Mayo: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument7 SeitenFlores de Mayo: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- DengueDokument16 SeitenDengueMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- 710702Dokument7 Seiten710702Mjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Abstract 1st Batch EbscoDokument4 SeitenAbstract 1st Batch EbscoMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Acute Pain NCPDokument3 SeitenAcute Pain NCPMjhay Montemayor100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Calcium, Hypercalcemia, HypocalcemiaDokument2 SeitenCalcium, Hypercalcemia, HypocalcemiaMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- ED SegmentationDokument8 SeitenED SegmentationMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Urban Heat Island EffectDokument8 SeitenUrban Heat Island EffectMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Regions of The PhilippinesDokument2 SeitenRegions of The PhilippinesMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- NCPDokument1 SeiteNCPMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- School Catechism Sample LEtterDokument4 SeitenSchool Catechism Sample LEtterMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippines History ReportDokument5 SeitenPhilippines History ReportMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDokument8 SeitenHemodynamic MonitoringMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippines History ReportDokument5 SeitenPhilippines History ReportMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Excess and DeficitDokument3 SeitenFluid Excess and DeficitMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Sign and Symproms of Psychiatric PatientDokument1 SeiteSign and Symproms of Psychiatric PatientMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extracellular and Intracellular FluidsDokument5 SeitenExtracellular and Intracellular FluidsMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Operational Use of CultureDokument2 SeitenThe Operational Use of CultureMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Statistics FinalDokument10 SeitenStatistics FinalMjhay MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profession Lesson PlaDokument8 SeitenProfession Lesson PlaSoumya KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saudi Nursing Licensure Examination Blueprint: (To Be Applied in January 2019)Dokument3 SeitenSaudi Nursing Licensure Examination Blueprint: (To Be Applied in January 2019)Baebee LouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taking Charge of Nursing PracticeDokument59 SeitenTaking Charge of Nursing PracticeMeia JaycelNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Inpatient Violence and Aggression: A Literature ReviewDokument196 SeitenInpatient Violence and Aggression: A Literature ReviewEdward Arthur IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barron - Essential - Words - For - IELTS-trang-294-369-đã NénDokument76 SeitenBarron - Essential - Words - For - IELTS-trang-294-369-đã NénHứa Hiểu Vân100% (1)
- Assignment 815 Article Challenges of Nursing StudentsDokument12 SeitenAssignment 815 Article Challenges of Nursing StudentsabdirahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patient Experience: A Critical Indicator of Healthcare PerformanceDokument14 SeitenPatient Experience: A Critical Indicator of Healthcare PerformanceMarvy MarthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power and PoliticsDokument16 SeitenPower and PoliticsARUN JOSE (08156864174)100% (1)
- Chronic DiseaseDokument13 SeitenChronic DiseaseDanielle MadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stakeholder Engagement Plan Guide and TemplateDokument3 SeitenStakeholder Engagement Plan Guide and TemplateDan RadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam in MS1 Cope 2nd ExamDokument5 SeitenExam in MS1 Cope 2nd ExamIbrahim RegachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflective Portfolio As Evaluation and Self-Assessment Instrument in The Teaching Process Learning: Experience ReportDokument8 SeitenReflective Portfolio As Evaluation and Self-Assessment Instrument in The Teaching Process Learning: Experience ReportIJAERS JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portfolio ReflectionDokument2 SeitenPortfolio Reflectionapi-317257113Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psych Videbeck 19Dokument1 SeitePsych Videbeck 19aum311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- SEA 58 Hand Off Comms 9 6 17 FINAL PDFDokument6 SeitenSEA 58 Hand Off Comms 9 6 17 FINAL PDFCharley CMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maycee Ruiz: (602) - 501-1491 - Mayceer@email - Arizona.eduDokument2 SeitenMaycee Ruiz: (602) - 501-1491 - Mayceer@email - Arizona.eduapi-534220527Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing ShortageDokument26 SeitenNursing Shortageapi-240927368Noch keine Bewertungen
- GEO-NSS-UM Belum PDFDokument271 SeitenGEO-NSS-UM Belum PDFsukma wirabuanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sekotlong RJ 2014Dokument83 SeitenSekotlong RJ 2014Osotua 1Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 111 Nursing Research Reviewer PrelimsDokument8 SeitenNCM 111 Nursing Research Reviewer PrelimsKIRSTEN CHAVEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- G2 NCM 101 - HygieneDokument42 SeitenG2 NCM 101 - HygieneItzayana SyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Health ResumeDokument6 SeitenMental Health Resumeafjwdudgyodbef100% (2)
- Unit 1 (C) Nursing ProcessDokument43 SeitenUnit 1 (C) Nursing ProcessSumaira NoreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAMHS MSDS Application 2023Dokument1 SeiteSAMHS MSDS Application 2023Lihle MakhungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Betz Rebecca ResumeDokument2 SeitenBetz Rebecca Resumeapi-316054946Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bahasa Inggris Bu YuliDokument8 SeitenBahasa Inggris Bu YuliNova FitriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fariha HameedDokument6 SeitenFariha HameedSHAFIQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exempt Non Exempt 09Dokument24 SeitenExempt Non Exempt 09Tara Greskoviak100% (1)
- Neonaticide and NursingDokument6 SeitenNeonaticide and Nursingapi-471591880Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical TeachingDokument48 SeitenClinical TeachingAmy Roc100% (2)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- The Stoic Mindset: Living the Ten Principles of StoicismVon EverandThe Stoic Mindset: Living the Ten Principles of StoicismBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Summary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesVon EverandSummary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1635)
- Becoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonVon EverandBecoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1478)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: The Infographics EditionVon EverandThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: The Infographics EditionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2475)
- The Motive: Why So Many Leaders Abdicate Their Most Important ResponsibilitiesVon EverandThe Motive: Why So Many Leaders Abdicate Their Most Important ResponsibilitiesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (224)