Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
OCR Chemistry A Level Y2 Glossary
Hochgeladen von
ifratsubhaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
OCR Chemistry A Level Y2 Glossary
Hochgeladen von
ifratsubhaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Year 2 Glossary
OCR Chemistry A
Glossary
A
acid a species that releases H+ ions in aqueous solution.
acid dissociation constant Ka the equilibrium constant that shows the extent of
[H+(aq)][A (aq)]
dissociation of a weak acid. For a weak acid HA(aq), Ka = .
[HA(aq)]
acidbase pair a pair of two species that transform into each other by gain or loss
of a proton.
activation energy the minimum energy required to start a reaction by the
breaking of bonds.
actual yield the amount of product obtained from a reaction.
addition polymerisation formation of a very long molecular chain, by repeated
addition reactions of many unsaturated alkene molecules (monomers).
addition reaction a reaction in which a reactant is added to an unsaturated
molecule to make a one saturated molecule.
adsorption the process that occurs when a gas or liquid or solute is held to the
surface of a solid.
alicyclic containing carbon atoms joined together in a ring that is not aromatic.
aliphatic containing carbon atoms joined together in straight or branched chains.
alkali a type of base that dissolves in water forming hydroxide ions, OH(aq) ions.
alkanes the hydrocarbon homologous series with single carbon-to-carbon bonds
and the general formula: CnH2n+2.
alkenes the hydrocarbon homologous series with at one double carbon-to-carbon
bonds and the general formula: CnH2n.
alkyl group a side chain formed by removing a hydrogen atom removed from an
alkane parent chain, for example, CH3, C2H5; any alkyl group is often shown
as R.
alkynes the hydrocarbon homologous series with one triple carbon-to-carbon
bonds and the general formula: CnH2n2.
amount of substance the quantity whose unit of the mole, used as a means of
counting any species such as atoms, ions and molecules.
anhydrous containing no water molecules.
anion a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons.
aromatic containing one or more benzene rings.
Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original
Year 2 Glossary
OCR Chemistry A
atom economy (sum of molar masses of desired products)/(sum of molar masses
of all products) ~100%.
atomic (proton) number the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
atomic orbital a region around the nucleus that can hold up to two electrons, with
opposite spins.
average bond enthalpy the average enthalpy change that takes place when
breaking by homolytic fission 1mol of a given type of bond in the molecules of a
gaseous species.
Avogadro constant NA the number of atoms per mole of the carbon-12 isotope.
(6.02 1023mol1).
B
base a compound that neutralises an acid to form a salt.
binary compound a compound containing two elements only.
bond angle the angle between two bonds at an atom.
bond dissociation enthalpy the enthalpy change that takes place when breaking
by homolytic fission 1mol of a given bond in the molecules of a gaseous species.
bonded pair a pair of electrons shared between two atoms to make a covalent
bond.
BrnstedLowry acid a species that is a proton, H+, donor.
BrnstedLowry base a species that is a proton, H+, acceptor.
buffer solution a system that minimises pH changes on addition of small
amounts of an acid or a base.
C
carbocation an ion that contains a positively charged carbon atom.
catalyst a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being
used up in the process; a catalyst provide an alternative route for the reaction with
lower activation energy.
cation a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons.
chain reaction a reaction in which the propagation steps release new radicals
that continue the reaction.
chemical shift a scale, in ppm, that compares the frequency of an NMR
absorption with the frequency of the reference TMS at = 0ppm.
chiral carbon a carbon atom attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms.
Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original
Year 2 Glossary
OCR Chemistry A
chromatogram a visible record showing the result of separation of the
components of a mixture by chromatography.
cistrans isomerism a special type of E/Z isomerism in which there are two
non-hydrogen groups and two hydrogen atoms around the C=C double bond: the
cis isomer (Z isomer) has H atoms on each carbon on the same side; the trans
isomer (E isomer) has H atoms on each carbon on different sides.
closed system a system isolated from its surroundings.
collision theory two reacting particles must collide for a reaction to occur, and
must be in the correct orientation and have sufficient energy to overcome the
activation energy of the reaction.
complex ion a transition metal ion bonded to ligands by coordinate bonds (dative
covalent bonds).
concentration the amount of solute, in moles, dissolved in 1dm3 (1000cm3) of
solution.
condensation reaction a reaction in which two small molecules react together to
form a larger molecule with elimination of a small molecule such as water.
conjugate acid a species that releases a proton to form a conjugate base.
conjugate base a species that accepts a proton to form a conjugate acid.
coordinate bond a shared pair of electrons in which the bonded pair has been
provided by one of the bonding atoms only; also called a dative covalent bond.
coordination number the total number of coordinate bonds formed between a
central metal ion and ligands.
covalent bond the strong electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of
electrons and the nuclei of the bonded atoms.
D
dative covalent a shared pair of electrons in which the bonded pair has been
provided by one of the bonding atoms only; also called a coordinate bond.
dehydration an elimination reaction in which water is removed from a saturated
molecule to make an unsaturated molecule.
delocalised electrons electrons that are shared between more than two atoms.
desorption release of an adsorbed substance from a surface.
dipole a separation in electrical charge so that one atom of a polar covalent bond,
or one end of a polar molecule, has a small positive charge + and the other has a
small negative charge .
Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original
Year 2 Glossary
OCR Chemistry A
displacement reaction a reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a
less reactive element from an aqueous solution of its ions.
displayed formula a formula showing the relative positioning of all the atoms in a
molecule and the bonds between them.
disproportionation a redox reaction in which the same element is both oxidised
and reduced.
dynamic equilibrium the equilibrium that exists in a closed system when the rate
of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction and
concentrations do not change.
E
E/Z isomerism a type of stereoisomerism in which different groups attached to
each carbon of a C=C double bond may be arranged differently in space because
of the restricted rotation of the C=C bond.
electron configuration a shorthand representation that shows how electrons
occupy sub-shells in an atom.
electronegativity a measure of the attraction of a bonded atom for the pair of
electrons in a covalent bond.
electrophile an atom (or group of atoms) which is attracted to an electron-rich
centre or atom, where it accepts a pair of electrons to form a new covalent bond.
electrophilic addition an addition reaction in which the first step is attack by an
electrophile on a region of high electron density.
electrophilic substitution a type of substitution reaction in which an electrophile
is attracted to an electron-rich centre or atom, where it accepts a pair of electrons
to form a new covalent bond.
elimination reaction the removal of a molecule from a saturated molecule to
make an unsaturated molecule.
empirical formula the formula that shows the simplest whole-number ratio of
atoms of each element present in a compound.
enantiomers stereoisomers that are nonsuperimposable mirror images of each
other; also called optical isomers.
end point the point in a titration where the indicator changes colour; the end point
indicates when the reaction is just complete.
endothermic reaction a reaction in which the enthalpy of the products is greater
than the enthalpy of the reactants, resulting in heat being taken in from the
Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original
Year 2 Glossary
OCR Chemistry A
surroundings (H is positive).
enthalpy H the heat content that is stored in a chemical system.
enthalpy change H the difference between the enthalpy of the products and the
enthalpy of the reactants.
enthalpy cycle a diagram showing alternative routes between reactants and
products which allows the indirect determination of an enthalpy change from other
known enthalpy changes using Hesss law.
enthalpy profile diagram a diagram for a reaction to compares the enthalpy of
the reactants with the enthalpy of the products.
entropy the used for the dispersal of energy and disorder within the chemicals
making up the chemical system.
equilibrium constant Kc a measure of the position of equilibrium; the magnitude
of an equilibrium constant indicates whether there are more reactants or more
products in an equilibrium system.
equivalence point the point in a titration at which the volume of one solution has
reacted exactly with the volume of the second solution.
esterification a reaction in which a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol to form
an ester and water.
exothermic reaction a reaction in which the enthalpy of the products is smaller
than the enthalpy of the reactants, resulting in heat loss to the surroundings (H is
negative).
F
fingerprint region an area of an infrared spectrum below 1500cm1 that gives a
characteristic pattern for different compounds.
first electron affinity the enthalpy change that takes place when one electron is
added to each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous
1 ions.
first ionisation energy the energy required to remove one electron from each
atom in one mole of gaseous atoms of an element to form one mole of gaseous
1+ ions.
fractional distillation the separation of components in a liquid mixture by their
different boiling points into fractions with different compositions.
fragment ions ions formed from the breakdown of the molecular ion in a mass
spectrometer.
Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original
Year 2 Glossary
OCR Chemistry A
fragmentation the process in mass spectrometry that causes a positive ion to
spilt into smaller pieces, one of which is a positive fragment ion.
free energy change G the balance between enthalpy, entropy and temperature
for a process given by G = H TS. A process is feasible when G < 0.
functional group the part of the organic molecule responsible for its chemical
reactions.
G
general formula the simplest algebraic formula of a member of a homologous
series. For example, the general formula of the alkanes is CnH2n+2.
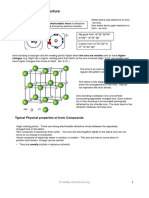
giant covalent lattice a three-dimensional structure of atoms, bonded together by
strong covalent bonds.
giant ionic lattice a three-dimensional structure of oppositely charged ions,
bonded together by strong ionic bonds.
giant metallic lattice a three-dimensional structure of positive ions and
delocalised electrons, bonded together by strong metallic bonds.
group a vertical column in the periodic table. Elements in a group have similar
chemical properties and their atoms have the same number of outer shell
electrons.
H
half-life the time taken for the concentration of a reactant to decrease by half.
Hesss Law if a reaction can take place by more than one route and the initial and
final conditions are the same, the total enthalpy change is the same for each
route.
heterogeneous catalysis a reaction in which the catalyst has a different physical
state from the reactants; frequently reactants are gases whilst the catalyst is a
solid.
heterogeneous equilibrium an equilibrium in which the species making up the
reactants and products have different physical states.
heterolytic fission the breaking of a covalent bond with both of the bonded
electrons going to each atom, forming a cation (positive ion) and an anion
(negative ion).
homogeneous catalysis a reaction in which the catalyst and reactants are in the
same physical state, which is most frequently the aqueous or gaseous state.
Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original
Year 2 Glossary
OCR Chemistry A
homogeneous equilibrium an equilibrium in which all the species making up the
reactants and products have the same physical state.
homologous series a series of organic compounds with the same functional
group but with each successive member differing by CH2.
homolytic fission the breaking of a covalent bond with one of the bonded
electrons going to each atom, forming two radicals.
hydrated a crystalline compound containing water molecules.
hydrocarbon a compound of hydrogen and carbon only.
hydrogen bond a strong dipole-dipole attraction between an electron-deficient
hydrogen atom of NH, OH or HF on one molecule and a lone pair of electrons
on a highly electronegative atom containing N, O or F on a different molecule.
hydrolysis a reaction with water that breaks a chemical compound into two
compounds, the H and OH in a water molecule becomes incorporated into the two
compounds.
I
induced dipoledipole interaction attractive forces between induced dipoles in
different molecules also called London Forces.
infrared spectroscopy an instrumentation method of analysis that identifies
bonds from absorption of the infrared radiation of different wavelengths.
initial rate of reaction the change in concentration of a reactant or product per
unit time at the start of the reaction: t = 0.
initiation the first stage in a radical reaction in which radicals starts when a
covalent bond is broken by homolytic fission of a covalent bond.
intermediate a species formed during a reaction that reacts further and is not
present in the final products.
intermolecular force an attractive force between molecules. Intermolecular
forces can be London forces, permanent dipole-dipole interactions or hydrogen
bonding.
ion a positively or negatively charged atom or a (covalently bonded) group of
atoms (a polyatomic ion), where the number of electrons is different from the
number of protons.
ionic bonding the electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions.
ionic product of water Kw the product of the ions formed in the partial
dissociation of water, given by Kw = [H+(aq)] [OH(aq)].
Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original
Year 2 Glossary
OCR Chemistry A
isotopes atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons and
different masses.
L
lattice enthalpy the enthalpy change that accompanies the formation of one mole
of an ionic compound from its gaseous ions under standard conditions.
Le Chateliers principle when a system in dynamic equilibrium is subjected to a
external change, the system readjusts itself to minimise the effect of the change
and to restore equilibrium.
ligand a molecule or ion that can donate a pair of electrons to the transition metal
ion.
ligand substitution a reaction in which one or more ligands in a complex ion are
replaced by different ligands.
limiting reagent the reactant that is not in excess, which will be used up first and
stop the reaction.
lone pair an outer shell pair of electrons that is not involved in chemical bonding.
M
mass number the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
also known as nucleon number.
metallic bond the electrostatic attraction between positive metal ions and
delocalised electrons.
mobile phase the phase that moves in chromatography.
molar gas volume Vm the volume per mole of gas molecules at a stated
temperature and pressure.
molar mass M the mass per mole of a substance, in units of gmol1.
mole the amount of any substance containing as many elementary particles as
there are carbon atoms in exactly 12g of the carbon-12 isotope, that is,
6.02 1023 particles.
molecular formula a formula that shows the number and type of atoms of each
element present in a molecule.
molecular ion the positive ion formed in mass spectrometry when a molecule
loses an electron.
molecule the smallest part of a covalent compound that can exist while retaining
its chemical identity, consisting of two or more atoms covalently bonded together.
Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original
Year 2 Glossary
OCR Chemistry A
monomer a small molecule that combines with many other monomers to form a
polymer.
N
neutralisation a chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react together to
produce a salt.
nomenclature a system of naming compounds.
non-polar with no charge separation across a bond or in a molecule.
nucleophile an atom (or group of atoms) which is attracted to an electron-
deficient centre or atom, where it donates a pair of electrons to form a new
covalent bond.
nucleophilic substitution a reaction in which a nucleophile is attracted to an
electron-deficient carbon atom, and replaces an atom or group of atoms on the
carbon atom.
O
optical isomers stereoisomers that are nonsuperimposable mirror images of
each other; also called enantiomers.
order the power to which the concentration of a reactant is raised in the rate
equation.
overall order the sum of the individual orders of reactants in the rate equation:
m + n.
oxidation loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation number.
oxidation number a measure of the number of electrons that an atom uses to
bond with atoms of another element. Oxidation numbers are derived form a set of
rules.
oxidation state the oxidation number.
oxidising agent a reagent that oxidises (takes electrons from) another species.
P
-bond a bond formed by the sideways overlap of two p-orbitals, with the electron
density above and the plane of the bonding atoms.
partial dissociation the splitting of some of a species in solution into aqueous
ions.
Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original
Year 2 Glossary
OCR Chemistry A
Pauling electronegativity value a value assigned as a measure of the relative
attraction of a bonded atom for the pair of electrons in a covalent bond.
actual amount, in mol, of product
percentage yield % yield = 100.
theoretical amount, in mol, of product
period a horizontal row of elements in the periodic table. Elements show trend in
properties across a period.
periodicity a repeating trend in properties of the elements across each period of
the periodic table.
permanent dipole a small charge difference that does not change across a bond,
with + and partial changes on the bonded atoms: the result of the bonded
atoms having different electrongativities.
permanant dipoledipole interaction an attractive force between permanent
dipoles in neighbouring polar molecules.
pH the expression, pH = log[H+(aq)].
polar (molecule) with + and charges at different ends of the molecule.
polar covalent bond a bond with a permanent dipole, having + and partial
changes on the bonded atoms.
polar molecule a molecule with an overall dipole, having taken into account any
dipoles across bonds and the shape of the molecule.
polyatomic ion an ion containing more than one atom.
polymer an large molecule formed from many thousands of repeat units of
smaller molecules known as monomers.
position of equilibrium the relative quantities of reactants and products,
indicating the extent of a reversible reaction at equilibrium.
precipitation reaction the formation of a solid from a solution during a chemical
reaction. Precipitates are often formed when two aqueous solutions are mixed
together.
primary on a carbon atom at the end of a chain.
primary alcohol an alcohol in which the OH group is attached to a carbon atom
that is attached to two or three hydrogen atoms.
principal quantum number n a number representing the relative overall energy
of each orbital, which increases with distance from the nucleus. The sets of
orbitals with the same n-value are referred to as electron shells or energy levels.
propagation the steps that continue a free radical reaction, in which a radical
reacts with a reactant molecule to form a new molecule and another radical,
Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original
Year 2 Glossary
OCR Chemistry A
causing a chain reaction.
proton number the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom; also known as
atomic number.
R
radical a species with an unpaired electron.
rate constant k the constant that links the rate of reaction with the concentrations
of the reactants raised to the powers of their orders in the rate equation.
rate equation for a reaction: A + B C with orders m for A and n for B, the rate
equation is given by: rate = k[A]m[B]n.
rate of reaction the change in concentration of a reactant or a product in a given
time.
rate-determining step the slowest step in the reaction mechanism of a multi-step
reaction.
reaction mechanism the sequence of bond breaking and bond-forming steps that
shows the path taken by electrons during a reaction.
redox reaction a reaction involving reduction and oxidation.
reducing agent a reagent that reduces (adds electron to) another species.
reduction gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation number.
reflux the continual boiling and condensing of a reaction mixture back to the
original container to ensure that the reaction takes place without the contents of
the flask boiling dry.
relative atomic mass Ar the weighted mean mass of an atom of an element
compared with one-twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
relative formula mass the weighted mean mass of the formula unit of a
compound compared with one-twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
relative isotopic mass the mass of an atom of an isotope compared with
one-twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
relative molecular mass Mr the weighted mean mass of a molecule of a
compound compared with one-twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
repeat unit a specific arrangement of atoms that occurs in the structure over and
over again. Repeat units are included in brackets outside of which is the symbol n.
retention time in gas chromatography. The time for a component to pass from the
column inlet to the detector.
reversible reaction a reaction that takes place in both forward and reverse
Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original
Year 2 Glossary
OCR Chemistry A
directions.
distance moved by component
Rf value Rf = .
distance moved by solvent
-bond a bond formed by the overlap of one orbital from each bonding atom,
consisting of two electrons and with the electron density centred around a line
directly between the nuclei of the two atoms.
S
salt the product of a reaction in which the H ions from the acid are replaced by
metal or ammonium ions.
saturated containing single bonds only.
saturated hydrocarbon a hydrocarbon with single bonds only.
second electron affinity the enthalpy change that takes place when one electron
is added to each ion in one mole of gaseous 1 ions to form one mole of gaseous
2 ions.
second ionisation energy the energy required to remove one electron from each
ion in one mole of gaseous 1+ ions of an element to form one mole of gaseous
2+ ions.
secondary on a carbon atom to which two carbon chains are attached.
secondary alcohol an alcohol in which the OH group is attached to a carbon
atom that is attached to two carbon chains and one hydrogen atom.
shell a group of atomic orbitals with the same principal quantum number, n. Also
known as a main energy level.
shielding effect the repulsion between electrons in different inner shells.
Shielding reduces the net attractive force between the positive nucleus on the
outer shell electrons.
simple molecular lattice a three-dimensional structure of molecules, bonded
together by weak intermolecular forces.
skeletal formula a simplified organic formula, with hydrogen atoms removed from
alkyl chains, leaving just a carbon skeleton and associated functional groups.
specific heat capacity c the energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of a
substance by 1C.
spectator ions ions that are present but take no part in a chemical reaction.
spin-spin coupling in an NMR spectrum, the interaction between spin states of
non-equivalent nuclei that results in the splitting of a signal.
Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original
Year 2 Glossary
OCR Chemistry A
standard conditions a pressure of 100kPa, a stated temperature, usually 298K
(25C) and a concentration of 1moldm3 (for reactions with aqueous solutions).
standard electrode potential E the e.m.f. of a half-cell compared with a
standard hydrogen half-cell, measured at 298K with solution concentrations of
1moldm3 and a gas pressure of 100kPa.
standard enthalpy change of atomisation the enthalpy change that takes place
when one mole of gaseous atoms forms from the element in its standard state.
standard enthalpy change of combustion cH the enthalpy change that takes
place when one mole of a substance reacts completely with oxygen under
standard conditions, all reactants and products being in their standard states.
standard enthalpy change of formation fH the enthalpy change that takes
place when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements in
their standard states under standard conditions.
standard enthalpy change of hydration the enthalpy change that takes place
when one mole of isolated gaseous ions is dissolved in water forming one mole of
aqueous ions under standard conditions.
standard enthalpy change of neutralisation neutH the enthalpy change that
accompanies the reaction of an acid by a base to form one mole of H2O(l), under
standard conditions, with all reactants and products in their standard states.
standard enthalpy change of reaction rH the enthalpy change that
accompanies a reaction in the molar quantities expressed in a chemical equation
under standard conditions, all reactants and products being in their standard
states.
standard enthalpy change of solution the enthalpy change that takes place
when one mole of a compound is completely dissolved in water under standard
conditions.
standard solution a solution of known concentration.
standard state the physical state of a substance under standard conditions of
100kPa and a stated temperature (usually 298K).
stationary phase the phase that does not moves in chromatography.
stereoisomers compounds with the same structural formula but with a different
arrangement of the atoms in space.
stoichiometry the ratio of the amount, in moles, of each substance in a chemical
equation (essentially the ratio of the balancing numbers).
strong acid an acid that dissociates completely in solution.
structural formula a formula showing the minimal detail for the arrangement of
Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original
Year 2 Glossary
OCR Chemistry A
atoms in a molecule.
structural isomers molecules with the same molecular formula but with different
structural formulae.
sub-shell a group of orbitals of the same type within a shell.
substitution reaction a reaction in which an atom or group of atoms is replaced
with a different atom or group of atoms.
surroundings everything that is not the chemical system.
system the chemicals involved in the reaction.
T
termination the step at the end of a radical substitution when two radicals
combine to form a molecule.
tertiary alcohol an alcohol in which the OH group is attached to a carbon atom
that is attached to three carbon atoms and no hydrogen atoms.
theoretical yield the yield resulting from complete conversion of reactants into
products.
thermal decomposition the breaking up of a chemical substance with heat into at
least two chemical substances.
titre the volume added from the burette when the volume of one solution has
exactly reacted with the other solution.
transition element a d-block element which forms an ion with an incomplete
d-sub-shell.
U
unsaturated containing a multiple carbon-carbon bond.
V
volatility the ease at which a liquid turns into a gas. Volatility increases as boiling
point decreases.
W
water of crystallisation water molecules that are bonded into a crystalline
structure of a compound.
weak acid an acid that dissociates only partially in solution.
Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ASlevel OCR Chemistry DefinitionsDokument6 SeitenASlevel OCR Chemistry Definitionsmeepingoutloud100% (1)
- AQA A Level Chemistry Unit 4 DefinitionsDokument1 SeiteAQA A Level Chemistry Unit 4 DefinitionsMuadh ChatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Alevel AQA Checklist Ready For UseDokument4 SeitenBiology Alevel AQA Checklist Ready For UseM BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of Organic ChemistryDokument4 SeitenFoundations of Organic Chemistryeager18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry A Level 1Dokument14 SeitenChemistry A Level 1Usama TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Notes - Unit 2 Ocr Biology A-LevelDokument26 SeitenRevision Notes - Unit 2 Ocr Biology A-Levelapi-275024237Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry and Energetics Concepts in 40 CharactersDokument2 SeitenOrganic Chemistry and Energetics Concepts in 40 CharactersEugene TayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master Organic Chemistry SubstitutionDokument43 SeitenMaster Organic Chemistry SubstitutionArsalan Khan GhauriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1.1 Arenes Notes OCR A2 ChemistryDokument3 Seiten1.1.1 Arenes Notes OCR A2 ChemistryCharlieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunity and Vaccines As Biology Answers AQA OCR EdexcelDokument3 SeitenImmunity and Vaccines As Biology Answers AQA OCR EdexcelShela HuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Principles of Chemistry II NotesDokument42 SeitenGeneral Principles of Chemistry II NotesTasmiah Hossain80% (5)
- SOLVED CSIR UGC JRF NET CHEMICAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 (PART-BDokument22 SeitenSOLVED CSIR UGC JRF NET CHEMICAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 (PART-BpolamrajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 2 2 Bonding and StructureDokument7 Seiten2 2 2 Bonding and StructureifratsubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AQA A Level Chemistry Unit 5 DefinitionsDokument2 SeitenAQA A Level Chemistry Unit 5 DefinitionsMuadh ChatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-Level-Chemistry Edexcel FACER Sample-Chapter PDFDokument36 SeitenA-Level-Chemistry Edexcel FACER Sample-Chapter PDFahamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buffer SolutionDokument14 SeitenBuffer SolutionSony0% (1)
- Chemistry NEWDokument15 SeitenChemistry NEWhaiduvnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbonyl Condensation ReactionsDokument41 SeitenCarbonyl Condensation ReactionsVladislav PapperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate As Biology Answers OCR AQA EdexcelDokument4 SeitenCarbohydrate As Biology Answers OCR AQA EdexcelbekoNoch keine Bewertungen
- OCR Chemistry NotesDokument10 SeitenOCR Chemistry NotesJack WoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-Level PS Chemistry Revision Information 2016 - 2017Dokument2 SeitenA-Level PS Chemistry Revision Information 2016 - 2017Anusha SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibria A2Dokument48 SeitenEquilibria A2javedkaleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Rate of Reaction AnswersDokument38 SeitenUnit 4 Rate of Reaction Answersareyouthere92Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9780855836320Dokument66 Seiten9780855836320eibsource100% (1)
- Review of A-Level Chemistry Content: David Read & Charles Harrison August 2010Dokument39 SeitenReview of A-Level Chemistry Content: David Read & Charles Harrison August 2010krisnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structures of ProteinsDokument15 SeitenStructures of ProteinsEdward Juanico HerradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocr Chemistry f325 Revision NotesDokument32 SeitenOcr Chemistry f325 Revision Notesravemylove_100% (2)
- OCR Chemistry Exam Question BookletDokument54 SeitenOCR Chemistry Exam Question Bookletkrnc_11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flashcards - CP1 Finding The Molar Volume of A Gas - Edexcel IAL Chemistry A-LevelDokument23 SeitenFlashcards - CP1 Finding The Molar Volume of A Gas - Edexcel IAL Chemistry A-Levelmaya 1D100% (1)
- A2 Organic Reaction SummaryDokument8 SeitenA2 Organic Reaction SummaryJessie Wu100% (1)
- AQA Chemistry A-Level Sample-Chapter Book-1Dokument34 SeitenAQA Chemistry A-Level Sample-Chapter Book-1davin gunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Level Chemistry Unit 3B Revision: Reagent TestsDokument1 SeiteA Level Chemistry Unit 3B Revision: Reagent TestsKaruvarakkalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Organic Chemistry ReactionsDokument6 SeitenUnit 4 Organic Chemistry ReactionsRobbing_Hood100% (1)
- Carbonyl Reactions PDFDokument39 SeitenCarbonyl Reactions PDFAtikah RoselyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 Sample QuestionsDokument262 Seiten2013 Sample QuestionsNorhafiza RoslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AQA A Level Chemistry Unit 5 NotesDokument24 SeitenAQA A Level Chemistry Unit 5 NotesMuadh Chati100% (2)
- Sni, Nighbouring GP Participation & E1cbDokument19 SeitenSni, Nighbouring GP Participation & E1cbsaheedvkNoch keine Bewertungen
- H432-01-Periodic Table, Elements and Physical Chemistry/a Level Chemistry A H432 - H432-01 - QS13Dokument5 SeitenH432-01-Periodic Table, Elements and Physical Chemistry/a Level Chemistry A H432 - H432-01 - QS13Altay ShawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry As Level BookDokument10 SeitenChemistry As Level BookTai PanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leah4Sci OrgChem Cheat Sheet PDFDokument32 SeitenLeah4Sci OrgChem Cheat Sheet PDFhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carboxylic Acids and Acid Derivatives Carbonyl PDFDokument124 SeitenCarboxylic Acids and Acid Derivatives Carbonyl PDFrvignesh2809Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mindmap of Alevel - Physical ChemistryDokument23 SeitenMindmap of Alevel - Physical ChemistryEbs Tam100% (1)
- Unit 4 Organic QuestionsDokument65 SeitenUnit 4 Organic Questionsareyouthere92100% (1)
- A2 Chemistry Areas of Difficulty MisconceptionsDokument21 SeitenA2 Chemistry Areas of Difficulty MisconceptionsPyae Phyo AungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry Chapter 15: Aromaticity of BenzeneDokument65 SeitenOrganic Chemistry Chapter 15: Aromaticity of BenzeneShreya PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 Australian Science Olympiad Exam Chemistry ReviewDokument33 Seiten2020 Australian Science Olympiad Exam Chemistry Reviewnavraj singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Level Biology Course ContentDokument3 SeitenA Level Biology Course Contentapi-102850034Noch keine Bewertungen
- MSC Chemistry QuestionsDokument277 SeitenMSC Chemistry QuestionsChemistry MES100% (1)
- GCSE Chemistry Test Prep Review--Exambusters Flash Cards: GCSE Exam Study GuideVon EverandGCSE Chemistry Test Prep Review--Exambusters Flash Cards: GCSE Exam Study GuideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- O Level Chemistry Structured Practice Papers 9Von EverandO Level Chemistry Structured Practice Papers 9Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Chemistry Glossary For A2Dokument21 SeitenChemistry Glossary For A2s_s_i_hassaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Term DefinitionsDokument5 SeitenChemistry Term Definitionsmeepingoutloud100% (1)
- Chemical Engineers DictionaryDokument77 SeitenChemical Engineers DictionaryAnonymous b9fcR5100% (1)
- Fred Redmore - ChemistryDokument12 SeitenFred Redmore - ChemistryMark Anthony SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- DefinitionsDokument7 SeitenDefinitionsLeAndies WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- All A Topic TestsDokument20 SeitenAll A Topic TestsSameer SarnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defining Common Exam Instruction WordsDokument7 SeitenDefining Common Exam Instruction WordsifratsubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PrintDokument18 SeitenPrintifratsubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M1 TextJT New1Dokument119 SeitenM1 TextJT New1ifratsubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology RevisionDokument11 SeitenBiology RevisionifratsubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 2 2 Bonding and StructureDokument7 Seiten2 2 2 Bonding and StructureifratsubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 1 5 RedoxDokument2 Seiten2 1 5 RedoxifratsubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electron Structure ModelsDokument1 SeiteElectron Structure ModelsifratsubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lifestyle, Health & Risk Factors for Cardiovascular DiseaseDokument11 SeitenLifestyle, Health & Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Diseasenimz1992Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 1 3 Amount of SubstanceDokument8 Seiten2 1 3 Amount of SubstanceifratsubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 1 1 2 1 2 Atomic StructureDokument4 Seiten2 1 1 2 1 2 Atomic StructureifratsubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Level Biology Unit 1 EdexcelDokument21 SeitenAs Level Biology Unit 1 EdexcelLaraine ShawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F324 Standard AnswersDokument9 SeitenF324 Standard AnswersifratsubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PL3 PL4 Output Connection - v1.2Dokument5 SeitenPL3 PL4 Output Connection - v1.2Victor GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP44, IP55, and IP65 junction boxes guideDokument5 SeitenIP44, IP55, and IP65 junction boxes guideRUPESH KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multistage Air Bubble Detection and Fluid Analysis For Dialysis MachinesDokument3 SeitenMultistage Air Bubble Detection and Fluid Analysis For Dialysis MachinesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iec60335 2 2 - 09Dokument32 SeitenIec60335 2 2 - 09Geremias dos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANT ATD4516R5 2031 DatasheetDokument4 SeitenANT ATD4516R5 2031 Datasheetangga meas100% (2)
- ML093290420 PDFDokument326 SeitenML093290420 PDFJM CrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valleylab Force FX-C Service ManualDokument230 SeitenValleylab Force FX-C Service Manualbiomedico123100% (5)
- Package Summary: Plastic, Surface-Mounted Package 6 Leads 0.65 MM Pitch 2 MM X 1.25 MM X 0.95 MM BodyDokument5 SeitenPackage Summary: Plastic, Surface-Mounted Package 6 Leads 0.65 MM Pitch 2 MM X 1.25 MM X 0.95 MM BodydneprashNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS Servo Motor ACM604V60-01-2500 enDokument3 SeitenDS Servo Motor ACM604V60-01-2500 enRafael Morais MachadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DX1000Dokument2 SeitenDX1000Juan OsorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- CARA PEMASANGAN RADIO KERETA DALAM 40 HURUFDokument6 SeitenCARA PEMASANGAN RADIO KERETA DALAM 40 HURUFamir akmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4937 DI5 3x8899 2Dokument17 Seiten4937 DI5 3x8899 2CdeKoninghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medidores Magneticos - IFM PDFDokument6 SeitenMedidores Magneticos - IFM PDFEduardo_77Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6500 2320master Clock DatasheetDokument3 Seiten6500 2320master Clock DatasheetGaniza LongNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETIMAT 1N 1p+N B6 6kA Miniature Circuit Breaker DatasheetDokument4 SeitenETIMAT 1N 1p+N B6 6kA Miniature Circuit Breaker DatasheetCuc Gabriel PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protection Station Installation ManualDokument44 SeitenProtection Station Installation ManualJosip SubaricNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuji-Electric Fujitsu Rs9lb Rs12lbDokument16 SeitenFuji-Electric Fujitsu Rs9lb Rs12lbAlain ClementeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3500/60 & /61 Temperature Monitors: Product DatasheetDokument12 Seiten3500/60 & /61 Temperature Monitors: Product Datasheet666plc11Noch keine Bewertungen
- MajorDokument13 SeitenMajordulipala alekya gupthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UPG-07C/UPG-07 CW/UPG-07 DLCW Ultrasonic Thickness Gages: Quick Start GuideDokument8 SeitenUPG-07C/UPG-07 CW/UPG-07 DLCW Ultrasonic Thickness Gages: Quick Start GuideSiles LimberdsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP ManualDokument270 SeitenATP ManualJose Jorge Fontalvo100% (1)
- Vantage: Installation and Operating InstructionsDokument2 SeitenVantage: Installation and Operating InstructionsAngel Quijano ArmengolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analizador de Bateria Bc3000 Concorde Hart9Dokument13 SeitenAnalizador de Bateria Bc3000 Concorde Hart9Roberto CayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perkins 1500Dokument2 SeitenPerkins 1500Andry HikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remote Telemetry For Industrial Gases - DPW900 - ANOVADokument5 SeitenRemote Telemetry For Industrial Gases - DPW900 - ANOVAsunshine dream50% (2)
- Hus VM Block Module Hitachi Thin Image User Guide V 73-03-3xDokument164 SeitenHus VM Block Module Hitachi Thin Image User Guide V 73-03-3xarungarg_itNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sony Hcd-gnz77d Gnz88d Ver-1.3 SCHDokument6 SeitenSony Hcd-gnz77d Gnz88d Ver-1.3 SCHShailesh SanayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- w3css Tutorial2Dokument54 Seitenw3css Tutorial2RajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advance Electrical MachinesDokument14 SeitenAdvance Electrical MachinesSammar AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- NE91 Project - VC4-ReportDokument8 SeitenNE91 Project - VC4-ReportDipak ShahNoch keine Bewertungen