Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Heui Cat
Hochgeladen von
Vago Si BeerOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Heui Cat
Hochgeladen von
Vago Si BeerCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
Cerrar SIS
Pantalla anterior
Producto: TRUCK ENGINE
Modelo: 3126 TRUCK ENGINE 7LZ
Configuracin: 3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP
Localizacin y Solucin de Problemas
3100 HEUI DIESEL TRUCK ENGINE
Nmero de medio -SENR6566-03 Fecha de publicacin -01/01/1998 Fecha de actualizacin -28/11/2007
SENR65660003
P-1.0 3100 HEUI Electronic System Overview
System Operation
The 3100 HEUI Diesel Truck Engines use a Hydraulic Electronic Unit Injector fuel system. The injection
pump, fuel lines and nozzles required for fuel injection in mechanical Caterpillar engines have been replaced
with a hydraulic electronic unit injector in each cylinder. Some mechanical drive components, cam lobes,
lifter, push rod, and rocker arms required for fuel injection in mechanical or Electronic Unit Injector
Caterpillar engines have been replaced with a high pressure oil system.
A solenoid on each injector controls the amount of fuel delivered by the injector. A gear-driven axial piston
pump raises the normal engine operating oil pressure to injector actuation pressure levels required by the
injectors. An Electronic Control Module (ECM) sends a signal to the injection actuation pressure control
valve to control injection pressure, and another signal to each injector solenoid to inject fuel.
Electronic Controls
The 3100 HEUI Diesel Truck Engines electronic system consists of the Electronic Control Module (ECM),
Engine Sensors, Injection Actuation Pressure Control Valve, and Vehicle Interface. The ECM is the
computer which controls the 3100 HEUI engine. The Personality Module in the ECM contains the software
which controls how the ECM behaves (the personality module stores the operating maps that define power
rating, torque curves, rpm, etc).
Engine Governor
The Electronic Control system on the 3100 HEUI engine serve as the engine governor. The Electronic
Control system determines when and how much fuel to deliver to the cylinders, as well as injection pressure
based on the actual and desired conditions at any given time during starting and operation.
Basic Governor
The basic governor operation considers the desired and actual conditions, and then takes action to best
accommodate the desired conditions.
The desired conditions are typically the position of the accelerator pedal, desired vehicle speed when in
cruise control, or desired engine rpm when in PTO control. The actual conditions are based on current
VCADS Pro 1(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
operating conditions such as coolant temperature, load conditions, etc.
Timing Considerations
Once the ECM has determined how much fuel is required, it must next determine when to inject the fuel.
Injection timing is determined by the ECM after considering input from the coolant temperature sensor,
intake manifold air temperature sensor, and boost pressure sensor.
VCADS Pro 2(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
The ECM knows the cylinder position for timing because of the signal from the Engine Speed/Timing
Sensors. The ECM adjusts timing for best engine performance, fuel economy and white smoke control.
Actual and Desired Timing cannot be viewed with an Electronic Service Tool.
The ECM knows where top center on cylinder #1 is from the signal provided by the engine Speed/Timing
Sensors. The ECM decides when injection should occur relative to top center and provides the signal to the
injector at the desired time.
Fuel Injection
The ECM controls the amount of fuel injected by varying signals to the injectors. The injectors will pump
fuel only if the injector solenoid is energized. The ECM sends a high voltage signal to energize the solenoid.
The energized solenoid lifts the poppet off its seat, closing the oil path to drain and opening the inlet for the
high pressure oil. The high pressure oil enters the injector and acts on an intensifier piston, increasing the
pressure and injecting fuel. By controlling the timing and duration of the high voltage signal, the ECM can
control injection timing and the amount of fuel injected.
The ECM also controls the pressure of the fuel injected into the cylinder by controlling the injection
actuation pressure control valve. The injection actuation pressure control valve is a dump valve closely
controlling the output pressure of the high pressure oil pump.
The Personality Module inside the ECM sets certain limits on the amount of fuel that can be injected. FRC
VCADS Pro 3(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
Fuel Pos is a limit based on boost pressure to control the air/fuel ratio for emissions control. When the ECM
senses a higher boost pressure (more air into cylinder), it increases the FRC Fuel Pos limit (allows more fuel
into cylinder).
Rated Fuel Pos is a limit based on the power rating of the engine and rpm. It is similar to the rack stops and
torque spring on a mechanically governed engine. It provides power and torque curves for a specific engine
family and rating. All of these limits are determined at the factory in the Personality Module and cannot be
changed in the field. Injection timing depends on engine rpm, load and other operating factors.
Injection Actuation Pressure System
The ECM controls fuel injection by controlling oil. The pressure of the oil in the high pressure oil manifold
is controlled by the ECM through control of the injection actuation pressure control valve. The injection
actuation pressure control valve (dump valve) controls the high pressure pump outlet pressure by dumping
excess flow back to the oil sump.
The ECM monitors the pressure in the high pressure manifold through the injection actuation pressure
sensor. The injection actuation pressure sensor is located in the top of the manifold on the left side of the
engine. The injection actuation pressure sensor signal (Inj Act Pr) is compared by the ECM to the desired
injection actuation pressure (Des Inj Act Pr). The ECM determines the Des Inj Act Pr based on several
inputs and changes the position of the injection actuation pressure control valve (Inj Act Output) to adjust
the oil pressure in the high pressure manifold.
High pressure oil is routed from the pump to the high pressure manifold through a steel tube. From the
VCADS Pro 4(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
manifold the oil is routed to each injector through short jumper tubes. All injectors have a constant supply of
oil while the engine is running. Cutting out an injector disables the electrical signal to the injector solenoid,
but does not interrupt the oil flow to the injector.
Customer Parameters Affect on Engine Governing
A unique feature of Electronic Engines is Customer Specified Parameters. These parameters allow the truck
owner to instruct the ECM how to fine tune the engine operation to accommodate the typical usage of the
vehicle, and to match the power train of the vehicle.
Many of the Customer Parameters provide additional restrictions on the "Required Action" the ECM will
take in response to the drivers' input.
Some parameters are intended to notify the driver of potential engine damage (Engine Monitoring
Parameters). Some parameters enhance fuel economy (Vehicle Speed, Cruise Control, Engine/Gear Limits
and Idle Shutdown Parameters). Other parameters are provided to enhance the engine installation or provide
engine operation information to the truck owner.
Engine Monitoring
Caterpillar provides a factory installed Engine Monitoring system. The Caterpillar Engine Monitoring
system monitors engine coolant temperature. The coolant temperature sensor is standard on all engines.
Caterpillar Engine Monitoring can be programmed to three different modes (OFF, WARNING, or
DERATE) through a Customer Parameter. The Coolant Temperature Sensor will operate in the Engine
Monitoring Mode selected.
NOTE: Excessive Coolant Temperature will not shut down the engine.
Caterpillar Engine Monitoring OFF Operation
If Caterpillar Engine Monitoring is programmed to OFF, the control system ignores the coolant temperature
sensor if conditions are exceeded which could cause the ECM to take Engine Monitoring action.
The engine still uses the Coolant Temperature sensor for normal engine operation, such as for Cold Mode
operation.
Caterpillar Engine Monitoring WARNING Operation
If the system is programmed to WARNING, the ECM causes the Check Engine Lamp to Flash (because of
the Active Diagnostic Code) to indicate a problem has been detected by the Engine Monitoring System. The
diagnostic code is logged. No further ECM or engine action occurs if the ECM is programmed to
WARNING.
Caterpillar Engine Monitoring DERATE Operation
VCADS Pro 5(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
Figure 1 - Engine Monitoring Coolant Temperature Graph
Figure 2 - Engine Monitoring Coolant Temperature Graph
Figure 3 - Engine Monitoring Coolant Temperature Graph
VCADS Pro 6(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
If the system is programmed to DERATE, the ECM begins by flashing the Check Engine Lamp to indicate a
problem has been detected by the Engine Monitoring System. The diagnostic code is logged. The ECM
limits the maximum vehicle speed and reduces available power as shown below.
This derating of usual engine performance is provided to influence the drivers' attention so action can be
taken to avoid engine damage. The three graphs above show the temperature derate trip points for the 3100
engines, and a rating for special applications.
Other ECM Performance Functions
The ECM also provides enhanced control of the engine for vehicle functions such as engine exhaust braking.
The illustration on page 13 shows many of the OEM systems the ECM can monitor to provide enhanced
vehicle performance, fuel economy and driver convenience.
Self-Diagnostics
The 3100 HEUI electronic system has some ability to diagnose itself. When a problem is detected, a
diagnostic code is generated and the Check Engine/Service Engine Soon lamp is turned ON. In most cases,
the code is also stored in permanent memory (Logged) in the ECM.
When diagnostic codes occur, they are called Active. They indicate a problem of some kind currently exists.
They should always be serviced first. If a truck has an Active Code, find the code in the front of this manual
and proceed to the indicated page to diagnose the cause.
Diagnostic codes stored in memory are Logged. Since the problem may have been temporary or may have
been repaired since the time it was logged, logged codes do not necessarily mean something needs to be
repaired. They are instead meant to be an indicator of probable causes for intermittent problems.
Some of the codes require passwords to clear. Codes not requiring passwords to clear are automatically
deleted from memory after 50 ECM operating hours.
Diagnostic Codes Effect on Engine Performance
This manual contains a table listing all of the PID-FMI Diagnostic codes, along with the page number
where details regarding the cause, performance affect, and troubleshooting of the code can be located.
The table on "PA-12: Possible Performance Effect of Active Diagnostic Codes" on page 46 lists all 3100
HEUI Diagnostic Codes, and whether each code may or may not affect engine performance.
The discussion on Engine Monitoring mentions the Check Engine Lamp flashes when a specific condition
exists. When the ECM detects the engine problem, it generates an Active Diagnostic Code and also Logs the
code to indicate when, and if appropriate, how many times the problem occurs. There are two types of
Diagnostic Codes, Fault Codes and Event Codes.
Diagnostic Fault Codes are provided to indicate an electrical or electronic problem has been detected by the
ECM. In some cases the engine performance can be affected when the condition causing the code exists.
More frequently, however, the driver cannot detect any difference in the engine performance.
If the driver indicates a performance problem occurs whenever the Check Engine Lamp is flashing, one of
the Diagnostic Codes may be the cause of the problem, and should be corrected.
VCADS Pro 7(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
If the driver does not indicate a problem with the engine performance and a Diagnostic Code is logged by the
ECM, it indicates the ECM detected an abnormal condition, but it did not affect performance.
If this is the case, unless there are several occurrences of the specific diagnostic code in a very short period
of time, or the ECM is indicating the problem exists at the present time, there is most likely nothing wrong
with the electronic system.
Diagnostic Event Codes are provided to indicate operational problem has been detected in the engine (or
truck) by the ECM. This usually does not indicate an electronic malfunction. Event codes typically are not an
indication of an electronic system problem.
Lifetime Totals Stored In The ECM
The ECM maintains engine total data for the following parameters.
Engine Hours is engine running hours (it does not include time when the ECM is powered ON without the
engine running).
Distance data requires a vehicle speed sensor connected to the ECM (the same sensor used for ECM vehicle
speed).
PTO Hours and PTO Fuel are logged when engine rpm is set using the Cruise Control switches and the
engine is operating under some load, or when the Dedicated PTO On/Off Switch is ON and vehicle speed is
within range of the Idle/PTO Vehicle Speed Limit Parameter.
Idle Hours and Idle Fuel can include time when the engine speed is set using the Cruise switches and the
vehicle speed is within range of the Idle/PTO Vehicle Speed Limit Parameter, but the engine is not operating
under load.
Maintenance Indicator Data
The ECM records the Lifetime Data Totals when a maintenance reset occurs for three levels of maintenance
- PM1, PM2, and Coolant Flush/Fill. The previous maintenance point is used by the ECM to calculate when
the next maintenance is due.
The Maintenance Indicator feature is programmable to hours or distance. The PM1 maintenance is
programmable to OFF, Automatic-Distance, Automatic-Hours, Manual-Distance, or Manual-Hours.
If PM1 is programmed to Automatic (Distance or Hours), the ECM calculates the next maintenance due by
considering the vehicle operation history from the previous maintenance interval. If the vehicle has a history
of poor fuel economy, the maintenance indicator will occur sooner than a vehicle with better fuel economy.
The ECM also uses the Engine Oil Capacity, with a larger capacity providing a longer maintenance interval.
Engine Oil Capacity is programmed in quarts. If the PM1 Maintenance Indicator is programmed to Manual,
the owner can program in their own specific maintenance mileage or time interval. PM2 and Coolant
Flush/Fill intervals are determined by the factory.
CAT ID
The Caterpillar Driver Information Display (CAT ID) is available to provide operating information to the
driver about the engine such as engine rpm, coolant temperature, boost pressure, etc, as well as engine
VCADS Pro 8(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
diagnostic codes with the PID-FMI and a brief text description.
CAT ID will also allow changing/resetting of certain operating parameters if the ECM is programmed to
access these parameters as well as PM1 Reset and Theft Deterrent.
The Theft Deterrent feature allows the driver to input a four character password to shut the engine down
and/or prevent the engine from restarting until the four character password is successfully entered.
NOTE: For CAT ID to function properly an AUG96 or later Personality Module is required in the ECM.
The CAT ID must also have the EEPROM chip capable of supporting communication with 3100 HEUI
engines, software version 1.3 or later. The version number is displayed initially on powerup of CAT ID.
Programmable Parameters
Certain parameters that affect 3100 HEUI Diesel Truck Engine operation may be changed with electronic
service tools. The parameters are stored in the ECM, and are protected from unauthorized changes by
passwords. These parameters are either "System Configuration Parameters" or "Customer Parameters".
System Configuration Parameters are set at the factory and affect emissions or power ratings within a
family of engines. Factory Passwords must be obtained and used to change System Configuration
Parameters.
Customer Parameters are variable and can be used to affect cruise control, vehicle speed limits,
progressive shifting, rpm/power ratings within the limits set by the factory, Caterpillar Engine Monitoring,
and PTO operation. Customer Passwords are necessary to change Customer Specified Parameters.
Some parameters may affect engine operation in ways a driver does not expect. Without adequate training,
these parameters may lead to power or performance complaints, even when the engine is performing to
specification.
Read section "P-2.0 Programming Parameters" on page 24 for more details.
Passwords
"System Configuration Parameters" are protected by Factory Passwords. Factory passwords are calculated
on a computer system available only to Caterpillar dealers. Since factory passwords contain alphabetic
characters, only an ECAP or Caterpillar Electronic Technician may change System Configuration
Parameters. System Configuration Parameters affect power family or emissions.
"Customer Parameters" are protected by Customer Passwords. The customer passwords are programmed
by the customer.
See section "P-2.0 Programming Parameters" on page 24, for more details when passwords are needed and
how to obtain them.
3100 HEUI Sensor and Connector Locations
VCADS Pro 9(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
VCADS Pro 10(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
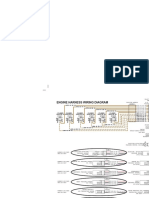
3100 HEUI Engine Harness Wiring Diagram - 3126
3100 HEUI Vehicle Harness Wiring Diagram - 3126
VCADS Pro 11(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
3100 HEUI Engine Harness Wiring Diagram - 3116
VCADS Pro 12(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
3100 HEUI Vehicle Harness Wiring Diagram - 3116
VCADS Pro 13(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
3100 HEUI Component Diagram
VCADS Pro 14(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
Electrical Connectors and Functions
VCADS Pro 15(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
Electrical Connectors and Functions
VCADS Pro 16(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
VCADS Pro 17(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
Service Tools
The Caterpillar Electronic Service Tools for the 3100 HEUI Electronic Control system are designed to help
the service technician analyze and locate faults or problems within the system. It is required to perform some
sensor calibrations electronically, and to read or change engine parameters. The Electronic Control Analyzer
Programmer (ECAP) tool has small plug-in modules, called Service Program Modules (SPM), to adapt the
basic tool to the specific Caterpillar electronic control application. Caterpillar Electronic Technician (ET)
requires a personal computer with the ET software installed and either a Caterpillar Communication Adapter
or MPSI Pro-Link with Caterpillar Cartridge to translate from the Vehicle ATA Data Link to the computer
RS-232 port.
Either the ECAP or ET communicates with the 3100 HEUI Electronic Control Module to read Diagnostic
Codes, to read the various sensor output signals such as engine rpm, or boost pressure, and controls
electronic calibration of the 3100 HEUI sensors through the ECM.
The ECAP (requires PWM adapter to measure at the sensor) can measure Pulse Width Modulated (PWM)
signals, such as the signal produced by the Throttle Position Sensor.
There are several adapter cables, breakout T cables, probes, etc, that are used with the service tools in order
to access measurements of signals. A heavy duty multimeter is suitable for making the necessary
measurements, a multimeter that is capable of measuring Duty Cycle may also be required. Other Special
Tools include those needed to measure pressure or temperature.
3100 HEUI Service Tools
VCADS Pro 18(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
VCADS Pro 19(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
VCADS Pro 20(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
VCADS Pro 21(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
Optional 3100 HEUI Service Tools
VCADS Pro 22(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
VCADS Pro 23(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
VCADS Pro 24(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
VCADS Pro 25(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
Thu Sep 29 13:42:23 CDT 2011
Copyright 1993 - 2008 Caterpillar Inc.
VCADS Pro 26(27)
3126 Truck Engine 7LZ00001-UP(SEBP2797 - 07) - Estructura del docum... 29/09/2011 01:44:05 p.m.
Todos los derechos reservados.
Red privada para licenciados del SIS.
VCADS Pro 27(27)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fuel System C15 & C18Dokument10 SeitenFuel System C15 & C18Moshé Abelardo Peláez Figueroa100% (2)
- Mot 3412 HeuiDokument28 SeitenMot 3412 HeuiMamadou DiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C15 Fuel System OperationDokument7 SeitenC15 Fuel System OperationTaka100% (1)
- CAT Fuel System C-15 C-16 C-18 Truck W1a 0001-Up PDFDokument10 SeitenCAT Fuel System C-15 C-16 C-18 Truck W1a 0001-Up PDFvimagapiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heui Fuel System c9 EngineDokument25 SeitenHeui Fuel System c9 Enginebabaisandip91% (53)
- Injection Actuation PressureDokument20 SeitenInjection Actuation Pressureabdelrhmangbr8682% (11)
- CAT C13 2007 Service Bulletin (Cooling Sys, DPF, and Diagnostic Trouble Codes)Dokument34 SeitenCAT C13 2007 Service Bulletin (Cooling Sys, DPF, and Diagnostic Trouble Codes)Jonathan Carlson100% (4)
- HEUI Systems Operation 3126Dokument25 SeitenHEUI Systems Operation 3126विशाल पुडासैनी89% (9)
- Cat C7Dokument8 SeitenCat C7jhonathan hernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- C13 TDC InstallDokument4 SeitenC13 TDC InstallEwgeny100% (1)
- C7 and C9 HEUI Engine Rail Cleaning ProcedureDokument16 SeitenC7 and C9 HEUI Engine Rail Cleaning Procedureahmed100% (5)
- C7 ACERT 205bkWDokument5 SeitenC7 ACERT 205bkWsheronNoch keine Bewertungen
- REHS3819-02 Procedure For Troubleshooting and Cleaning The Oil Rail System For The HEUIDokument8 SeitenREHS3819-02 Procedure For Troubleshooting and Cleaning The Oil Rail System For The HEUImoises100% (2)
- C9 Heui Pump Replace PIPDokument5 SeitenC9 Heui Pump Replace PIPharikrishnanpd33270% (1)
- C15-Testing & AdjDokument113 SeitenC15-Testing & AdjJefMoreno100% (30)
- C-11, C-13, C-15 TS Manual 2006 PDFDokument420 SeitenC-11, C-13, C-15 TS Manual 2006 PDFjuan eduardo rodriguez100% (2)
- C9 Injection Actuation Pressure TestDokument18 SeitenC9 Injection Actuation Pressure Testharikrishnanpd3327100% (1)
- Caterpillar 3126Dokument0 SeitenCaterpillar 3126manuel12515100% (22)
- Engine Valve Lash - Inspect/Adjust: SMCS - 1102-025Dokument5 SeitenEngine Valve Lash - Inspect/Adjust: SMCS - 1102-025Bassie100% (2)
- Calculating Cylinder Liner Projection For G3500Dokument7 SeitenCalculating Cylinder Liner Projection For G3500NimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Engine Safety Caterpillar c7 c9 On Highway Truck EnginesDokument27 SeitenManual Engine Safety Caterpillar c7 c9 On Highway Truck EnginesCiprian Andreescu100% (2)
- Cat C15-C18 Brake SystemDokument8 SeitenCat C15-C18 Brake Systemhenry lavieraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT C9 ACERT Engine PDFDokument4 SeitenCAT C9 ACERT Engine PDFettoscar100% (1)
- Engine Pressure Sensor Open or Short PDFDokument14 SeitenEngine Pressure Sensor Open or Short PDFNydRomG100% (2)
- Acert Technology For C7 and C9 On-Highway Engines Introduction To Mechanical ChangesDokument40 SeitenAcert Technology For C7 and C9 On-Highway Engines Introduction To Mechanical ChangesGallego Carlos100% (1)
- Cat C7 .Dokument4 SeitenCat C7 .dionymackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service 3126Dokument18 SeitenService 3126jrrodrigueza293% (15)
- 980c Especificaciones InglesDokument19 Seiten980c Especificaciones InglesEdgar TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acert Technology For Off-Highway C15 Engines: Caterpillar ConfidentialDokument62 SeitenAcert Technology For Off-Highway C15 Engines: Caterpillar ConfidentialMilorad ZelenovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- C7Dokument72 SeitenC7victorhernandezrega94% (35)
- Motor CAT C9Dokument4 SeitenMotor CAT C9avictoras100% (2)
- C15 Electronic Unit Injector Adjustment 8453341Dokument2 SeitenC15 Electronic Unit Injector Adjustment 8453341anon_84596428586% (14)
- Engine Speed - Test SMCS-1907-038 - I02637941Dokument9 SeitenEngine Speed - Test SMCS-1907-038 - I02637941EstoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tractores d9r D10r-HeuiDokument49 SeitenTractores d9r D10r-HeuiRodrigo Chacca100% (1)
- Caterpillar C7 Operação Dos SistemasDokument7 SeitenCaterpillar C7 Operação Dos SistemasNahoj AdacnomNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Operation Testing and Adjustin C10 y C12Dokument96 SeitenSystem Operation Testing and Adjustin C10 y C12Zamir Andres Sencio100% (1)
- c9 Machine Acert 2Dokument56 Seitenc9 Machine Acert 2Gustavo Portos100% (4)
- Sensor Electrical Connectors C15 PDFDokument4 SeitenSensor Electrical Connectors C15 PDFHerrera Salazar Visnu100% (1)
- c13 Cat Engine Brochure PDFDokument6 Seitenc13 Cat Engine Brochure PDFJosè Manuel Coronado Saucedo100% (1)
- Cylinder Head: 3406E Marine EngineDokument3 SeitenCylinder Head: 3406E Marine Enginemartinskaf100% (2)
- Qsb6.7 Tech Pkg-18sep13Dokument44 SeitenQsb6.7 Tech Pkg-18sep13Usman Shah100% (3)
- CAT Programming ManualDokument258 SeitenCAT Programming ManualAnggraini Sari100% (2)
- Heui PDFDokument56 SeitenHeui PDFGerman Ramos German Ramos100% (5)
- Testing and Adjunting Steering 950FDokument10 SeitenTesting and Adjunting Steering 950FEsteban MunaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor 3126 HEUIDokument128 SeitenMotor 3126 HEUITiago Soares100% (2)
- 980b Wheel Loader HydraDokument13 Seiten980b Wheel Loader HydraChrissz Noxd0% (1)
- C7 Serv1824Dokument31 SeitenC7 Serv1824Marcus VeniciusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat Service Training Acert TechnologyDokument62 SeitenCat Service Training Acert TechnologyNasser Ayoub90% (10)
- 3114, 3116 and 3126 Testing and Adjusting Fuel System - Prime PDFDokument2 Seiten3114, 3116 and 3126 Testing and Adjusting Fuel System - Prime PDFCharly Brown80% (5)
- Jake BrackDokument6 SeitenJake BrackDaniel DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- C15 Electronic Control SystemDokument5 SeitenC15 Electronic Control SystemTakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WDM D9R PTDokument2 SeitenWDM D9R PTRendy PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel System: Systems OperationDokument7 SeitenFuel System: Systems OperationbejoythomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel System: Systems OperationDokument11 SeitenFuel System: Systems OperationNy Romero100% (2)
- Sistema de Combustible c15Dokument10 SeitenSistema de Combustible c15Elmer Tintaya MamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel System: Shutdown SIS Previous ScreenDokument9 SeitenFuel System: Shutdown SIS Previous Screenjames foxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel System C27Dokument7 SeitenFuel System C27insano008Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Information - System Operation: Pantalla AnteriorDokument4 SeitenGeneral Information - System Operation: Pantalla AnteriorGustavo PereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- c15 and c18 Engines For Caterpillar Built Engines Fuel SystemDokument10 Seitenc15 and c18 Engines For Caterpillar Built Engines Fuel SystemDiegoD'AmbrosioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Common Rail Injection Electronic Components ExplainedVon EverandDiesel Common Rail Injection Electronic Components ExplainedBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (7)
- Hino Motors W06D-TI Workshop Manual PDFDokument236 SeitenHino Motors W06D-TI Workshop Manual PDFVago Si BeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Howo Trucks Fault Codes List - Table of Diagnostic Flashing Codes For Faults of The Fuel Pump System of Common Rail Diesel Engine PDFDokument15 SeitenHowo Trucks Fault Codes List - Table of Diagnostic Flashing Codes For Faults of The Fuel Pump System of Common Rail Diesel Engine PDFLuciana Silveira80% (5)
- Howo Trucks Fault Codes List - Table of Diagnostic Flashing Codes For Faults of The Fuel Pump System of Common Rail Diesel Engine PDFDokument15 SeitenHowo Trucks Fault Codes List - Table of Diagnostic Flashing Codes For Faults of The Fuel Pump System of Common Rail Diesel Engine PDFLuciana Silveira80% (5)
- Electronic Unit Injector - Adjust: SMCS - 1290-025Dokument2 SeitenElectronic Unit Injector - Adjust: SMCS - 1290-025Vago Si BeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Man Engine Brake (English)Dokument8 SeitenMan Engine Brake (English)W MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- PV776-20 020418Dokument14 SeitenPV776-20 020418Vago Si Beer100% (3)
- Mack ES T310 Service ManualDokument206 SeitenMack ES T310 Service ManualVago Si Beer100% (6)
- Spanish Ring & Pinion Installation Instructions: Verificación Práctica Del AdusteDokument7 SeitenSpanish Ring & Pinion Installation Instructions: Verificación Práctica Del AdusteVago Si BeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction of Service SystemDokument19 SeitenIntroduction of Service SystemHEMIL ROBERTO RODRIGUEZ HERRERANoch keine Bewertungen
- Knock Module Manual: 1. ContentsDokument7 SeitenKnock Module Manual: 1. ContentsZaita FregaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Manual Index - March 1, 2022: or From BAE atDokument95 SeitenTechnical Manual Index - March 1, 2022: or From BAE atMohand Said ArroudjNoch keine Bewertungen
- D-155 - 3 Cylinder Diesel Engine (01/75 - 12/85) 00 - Complete Machine 14-09 - ManifoldsDokument3 SeitenD-155 - 3 Cylinder Diesel Engine (01/75 - 12/85) 00 - Complete Machine 14-09 - ManifoldsMANUALESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medidas e Torques (D342)Dokument30 SeitenMedidas e Torques (D342)Lucas ApostoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Akk 107331Dokument96 Seiten9 Akk 107331Roger Gustavo Gutierrez HuanquiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bajai Qute SpacifiDokument79 SeitenBajai Qute Spacifimekonenabdisa3Noch keine Bewertungen
- LCV Crde ManualDokument55 SeitenLCV Crde ManualVicky100% (2)
- Kubota v3600 Engine ManualDokument203 SeitenKubota v3600 Engine Manualashielanie94% (16)
- Catalogo de Códigos Do Compressor 3CDCDokument20 SeitenCatalogo de Códigos Do Compressor 3CDCEvandro MatosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inlet and Exhaust Valves DesignDokument67 SeitenInlet and Exhaust Valves DesignmohanpusNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013-'14 TE-II Schedule, Question Bank & Bit BankDokument26 Seiten2013-'14 TE-II Schedule, Question Bank & Bit BankHerbert DeepakNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUOVO PIGNONE Compressor Spares (2010-37)Dokument4 SeitenNUOVO PIGNONE Compressor Spares (2010-37)sianas1706Noch keine Bewertungen
- Megasquirt Instruction 1.6 MiataDokument16 SeitenMegasquirt Instruction 1.6 MiataRyan KorbianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caterpillar Electronic Injectors ListDokument9 SeitenCaterpillar Electronic Injectors ListMarcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Sealing Design For Wankel EnginesDokument5 SeitenDynamic Sealing Design For Wankel EnginesFurqanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine-Mechanical Nissan MuranoDokument151 SeitenEngine-Mechanical Nissan MuranoRogerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08DDECVI47REVDokument4 Seiten08DDECVI47REVHamilton mirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Output Specs and DimensionsDokument3 SeitenPower Output Specs and DimensionsRicardo La CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lombardini 8LD665 EngineDokument39 SeitenLombardini 8LD665 EngineKft. Progép-TechnikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- K20 Engine Control Module X1Dokument4 SeitenK20 Engine Control Module X1Data TécnicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- INE ListDokument8 SeitenINE Listak autopartsNoch keine Bewertungen
- C15 Electronic ComponentDokument4 SeitenC15 Electronic ComponentJhoni Oberton Art TahaldiadjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Fundamentals 2004-2005Dokument568 SeitenAutomotive Fundamentals 2004-2005Adrian Ferrer84% (19)
- Turbocharger ServiceDokument3 SeitenTurbocharger ServiceIoan PascuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6068HF158Dokument2 Seiten6068HF158Nabil Ibrahim100% (1)
- IO 550 ManualDokument850 SeitenIO 550 ManualJimyToasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CR Injector and Nozzle Reference ChartDokument5 SeitenCR Injector and Nozzle Reference ChartЕкатерина КалашниковаNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bendix Compr - PartsDokument14 SeitenBendix Compr - PartsAdal VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation & Maintenance Manual Fire Pump Drive EnginesDokument139 SeitenOperation & Maintenance Manual Fire Pump Drive EnginesMónica GuerraNoch keine Bewertungen