Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
UNIT 14 Time and Timetables Teaching Notes: Historical Background and Introduction
Hochgeladen von
mkhawarbashirOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
UNIT 14 Time and Timetables Teaching Notes: Historical Background and Introduction
Hochgeladen von
mkhawarbashirCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MEP: Demonstration Project Teacher Support Y7B
UNIT 14 Time and Timetables Teaching Notes
Historical Background and Introduction
The two basic periods on which our system of timekeeping depends are
year
day
WINTER
These are determined by two distinct motions:
a year is the time of one revolution of the earth
about the sun; a day is the time taken for the
earth to revolve once about its axis.
Sun
The two motions are independent and, SPRING AUTUMN
unfortunately for timekeepers, the number of
days is a year is Earth
365.242195...
Another complication is the month. The lunar
SUMMER
cycle, that is, the time of revolution of the moon
about the earth, is
29.53059... days,
so that 1 year 12.36813... lunar months! A year of 12 lunar months is too short, and 13 is
far too long, hence the strange system that we now have with the year divided into twelve
months mostly containing 30 or 31 days, but with the complication of the 'leap' year (see
Activity 14.1).
In fact, with 7 days in a week (from the religious division of time, i.e. "for in six days the
Lord made Heaven and Earth ... and rested the seventh day"),
29.530588 days in a lunar month
365.242195 days in a year
we have a system with incompatible numbers.
The shortest cycle which contains a whole number of years and whole number of lunar
months is 19 years. Note that
29.530588 235 6939.688 days in 235 lunar months
and 365.242195 19 6939.602 days in 19 years
i.e. 0.086 day difference 2.06 hours
Income Tax Year
The following information explaining the origin of the dates of the income tax year might be
of interest to you (although probably not to your pupils).
Until 1752 the legal year had run from Lady Day to Lady Day (25 March) and despite
calendar changes, the Treasury just went on balancing annual accounts at yearly intervals.
Since the calendar had omitted 3-13 September 1752 (see Activity 14.1, Notes and Solutions),
March 1753 was only 354 days after 25 March 1752. In order to include 365 days of income
and expenditure in his annual accounts the Chancellor of the Exchequer did not have them
The Gatsby Charitable Foundation
MEP: Demonstration Project Teacher Support Y7B
ready until 365 days after 25 March 1752, that is, on 6 April 1753. Thus, he added 25-31 March
and 1-5 April, 1753, to make up for those days dropped out the previous September, and we have
just gone on like this, being taxed on incomes earned during the year beginning 6 April and
finishing 5 April.
Routes Standard Academic Express
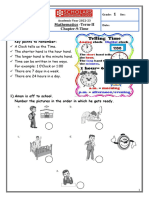
14.1 Telling the Time
14.2 12- and 24- hour Clocks
14.3 Units of Time
14.4 Timetables
14.5 Time Problems in Context ()
Language
Half an hour, quarter of an hour, etc.
'a.m.', 'p.m.'
24-hour clock
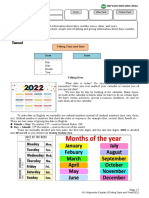
Months
Leap year
() denotes extension work for these pupils
Misconceptions
Misunderstanding of 24-hour clock time, e.g. pupils often find it difficult to understand that 0012 is 12
minutes past midnight.
All 24-hour clock times have 4 digits, e.g. 0730, not 730.
Challenging Questions
The following question is more challenging than others in the same section:
Section Question No. Page
Practice Book Y7B 14.3 11 29
The Gatsby Charitable Foundation
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 01 How To Erect A HoroscopeDokument25 SeitenChapter 01 How To Erect A HoroscopeColin WagonerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics DLP SK Year 5 Part 2Dokument140 SeitenMathematics DLP SK Year 5 Part 2Abdul Hafiz100% (1)
- ViewpdfDokument8 SeitenViewpdfAnant DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 The Calendar: Pre-Reading TaskDokument174 SeitenUnit 1 The Calendar: Pre-Reading TaskmemeNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Text Grade 10Dokument97 SeitenEnglish Text Grade 10Mann Mark TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument32 SeitenUntitledBussari Abdul-Rahman AlabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Term MathDokument12 SeitenFinal Term MathAngelica AngelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 X 1 X 1 X 1 y Xy (X+y) Total Work To Be Done Work Done in One DayDokument3 Seiten1 X 1 X 1 X 1 y Xy (X+y) Total Work To Be Done Work Done in One DaySaurav TripathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W1Dokument4 SeitenDLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W1Arriane Sumile JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1) Time and CalendarDokument2 Seiten1) Time and Calendarshofiya nrzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan GR 4 Mathematics TimeDokument18 SeitenLesson Plan GR 4 Mathematics TimeTshiovhe DakaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 6Dokument9 SeitenLab 6nilimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in MathematicsDokument5 SeitenLesson Plan in MathematicsAlyana Joy AribanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sam Up Naka 155Dokument16 SeitenSam Up Naka 155Guarachandar ChandNoch keine Bewertungen
- LeaP Math G5 Week 7 Q3Dokument4 SeitenLeaP Math G5 Week 7 Q3archie monreal75% (4)
- 2019 20 Calendar at A Glance Approved 121318 EngDokument1 Seite2019 20 Calendar at A Glance Approved 121318 Engapi-291535968Noch keine Bewertungen
- 16-Voyage Planing and TimeDokument44 Seiten16-Voyage Planing and TimeErnestoDom100% (1)
- 06 GN TIME TIME CONVERSIONS Apparent TimeDokument27 Seiten06 GN TIME TIME CONVERSIONS Apparent TimemartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calendar Until 2019. No ProblemDokument6 SeitenCalendar Until 2019. No ProblemhardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clocks:: Cheat Sheets - Clocks and CalendarsDokument8 SeitenClocks:: Cheat Sheets - Clocks and CalendarsMeghna ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 7 TimeZone Students Copy CompressedDokument87 SeitenScience 7 TimeZone Students Copy Compressedstarrynx1Noch keine Bewertungen
- My Class Agenda by SlidesgoDokument44 SeitenMy Class Agenda by SlidesgoNURUL NADIA BT MUHAMADNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 5-Q3-Week 7Dokument14 SeitenMath 5-Q3-Week 7Johnpaulo BernardinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W1Dokument4 SeitenDLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W1shyfly21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mms4 Textbook Unit4 MeasurementDokument50 SeitenMms4 Textbook Unit4 MeasurementDelfinBijuNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Mathematics 3 q4 w1Dokument4 SeitenDLL Mathematics 3 q4 w1Ariane AsuncionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math3 LP Q4 Wk1 Day1-5-QA-doneDokument12 SeitenMath3 LP Q4 Wk1 Day1-5-QA-doneJanice Saure Ajoc100% (1)
- Four Pillars Easy FormulasDokument11 SeitenFour Pillars Easy FormulasAdriana-Gabriela Prelipcean100% (3)
- Math5 - Q3 - Week7 (28pages) - M7-RegionDokument28 SeitenMath5 - Q3 - Week7 (28pages) - M7-RegionCastro, Brick's M.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Converting Days, Weeks, Months and YearsDokument7 SeitenConverting Days, Weeks, Months and YearsJaysan Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSE TP By: SudhanshuDokument15 SeitenCSE TP By: SudhanshuSudhanshu MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDokument4 SeitenGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridaySheilaMarB.EstebanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cheat Sheets - Clocks and CalendarsDokument8 SeitenCheat Sheets - Clocks and CalendarsDileep Kumar MotukuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Question To Aptitude Test: Manoj Kumar Rout BiitmDokument35 SeitenModel Question To Aptitude Test: Manoj Kumar Rout BiitmBikash Kumar DashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sis g1 Math CH 9 Worksheet 2022 23Dokument4 SeitenSis g1 Math CH 9 Worksheet 2022 23ak dNoch keine Bewertungen
- 44 Fire Festivals by Raah SirusDokument7 Seiten44 Fire Festivals by Raah SirusG.n.o.d.e.100% (3)
- Appendix Telling Time and Date PDFDokument3 SeitenAppendix Telling Time and Date PDFSatrio WibowoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calender and Days of The WeekDokument7 SeitenCalender and Days of The WeekKelly RobertsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 13. Schedules - The Simple Present TenseDokument25 SeitenClass 13. Schedules - The Simple Present TenseCamila BurgosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dates and Calendars - Zeller's Rule ShortcutDokument3 SeitenDates and Calendars - Zeller's Rule ShortcutAnonymous qlrjUAIBa9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Astro 1124 Lec 03 F 22Dokument40 SeitenAstro 1124 Lec 03 F 22Maxpain Dell ValleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cot 2 Math 5-Mtepino FinalDokument8 SeitenCot 2 Math 5-Mtepino FinalMitchz Trinos100% (1)
- Session 4 - Date and Time Functions PDFDokument24 SeitenSession 4 - Date and Time Functions PDFNiranjan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4: Measurement: Lesson 1: Time Measure Learning OutcomesDokument15 SeitenChapter 4: Measurement: Lesson 1: Time Measure Learning OutcomesFerdinand MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Basic Steps: Month CodesDokument6 SeitenThe Basic Steps: Month CodesvahnitejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W1Dokument3 SeitenDLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W1Sarah Visperas RogasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mekari Talenta - HR Planner & Calendar 2023 - Google SheetsDokument1 SeiteMekari Talenta - HR Planner & Calendar 2023 - Google SheetsHeru SusantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Final Module On Perpetual CalendarDokument15 Seiten1 Final Module On Perpetual Calendarmilan chaturvedi100% (2)
- Class 5 Fa1 Worksheet 1Dokument6 SeitenClass 5 Fa1 Worksheet 1Kousika VijayakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- G8 - T3, Week 3, Day 3Dokument19 SeitenG8 - T3, Week 3, Day 3Mouza Mubarak Sultan Mohammed Al KhailiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Activity QuestionnaireDokument12 SeitenPhysical Activity QuestionnaireIndah SundariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adobe Scan 3 Apr 2022Dokument16 SeitenAdobe Scan 3 Apr 2022Neha PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W1Dokument4 SeitenDLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W1RENEGIE LOBONoch keine Bewertungen
- 24 3D Object Recognition Based On Image Features A Survey-LibreDokument10 Seiten24 3D Object Recognition Based On Image Features A Survey-LibremkhawarbashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contamination of Vegetables PDFDokument46 SeitenContamination of Vegetables PDFmkhawarbashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Day of Confernce Schdul1Dokument1 Seite2nd Day of Confernce Schdul1mkhawarbashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- DatabaseDokument27 SeitenDatabasemkhawarbashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Computers: October 7, 2013Dokument15 SeitenIntroduction To Computers: October 7, 2013mkhawarbashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Word Assignment 1Dokument5 SeitenWord Assignment 1mkhawarbashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 7 1 Network Flow: 1.1 Dual AlgorithmsDokument5 SeitenWeek 7 1 Network Flow: 1.1 Dual AlgorithmsmkhawarbashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 1 1 193Dokument6 Seiten10 1 1 193mkhawarbashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- BM 13 CH 01Dokument14 SeitenBM 13 CH 01Afsheen Danish NaqviNoch keine Bewertungen
- EstimateDokument1 SeiteEstimatemkhawarbashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Numerology To Improve Your Life.Dokument2 SeitenUsing Numerology To Improve Your Life.advicehero98840% (1)
- Gcse D&T TextileDokument29 SeitenGcse D&T TextileOlusaye OluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pet For Schools Examiner S CommentsDokument7 SeitenPet For Schools Examiner S Commentsbenjo100% (1)
- Skinner, B. F. (1961) The Design of CulturesDokument14 SeitenSkinner, B. F. (1961) The Design of CulturesEdson Oliveira100% (1)
- Writing The Project Report 2Dokument3 SeitenWriting The Project Report 2api-222015490Noch keine Bewertungen
- Feher Lesson Rounding DecimalsDokument3 SeitenFeher Lesson Rounding Decimalsmeganfeher11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Course Outcomes: Object Oriented Programming Through JAVADokument51 SeitenAssessment of Course Outcomes: Object Oriented Programming Through JAVAVeronica ForbesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heartland Horseshoeing School CatalogDokument52 SeitenHeartland Horseshoeing School Catalogjkoehler8439100% (1)
- Assessment 2 PdhpeDokument34 SeitenAssessment 2 Pdhpeapi-379378935Noch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Reasons Why Discussion GuideDokument115 Seiten13 Reasons Why Discussion GuideEC Pisano RiggioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume Eline Van Der BeekDokument1 SeiteResume Eline Van Der BeekEline Van Der BeekNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDU20002: Assignment 3 Template: Student Name: Rumeysa Ongel Student ID: 103011788Dokument8 SeitenEDU20002: Assignment 3 Template: Student Name: Rumeysa Ongel Student ID: 103011788rumeysaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diana Barnett Course Critique n5327 RDokument4 SeitenDiana Barnett Course Critique n5327 Rapi-308950624Noch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative ReportDokument4 SeitenNarrative Reportharold carbonelNoch keine Bewertungen
- A+Measure+of+the+Experience+of+Being+Bullied +An+Initial+Validation+in+Philippine+SchoolsDokument14 SeitenA+Measure+of+the+Experience+of+Being+Bullied +An+Initial+Validation+in+Philippine+SchoolsJuLievee Lentejas100% (1)
- NAAC 10.12.1888888 NewDokument48 SeitenNAAC 10.12.1888888 Newచిమ్ముల సందీప్ రెడ్డిNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Plan Grade 9, EFL in Finland, Two Lessons of 45 Mins Per Week For 8 Weeks Topic 1 Topic 2 SkillsDokument2 SeitenCourse Plan Grade 9, EFL in Finland, Two Lessons of 45 Mins Per Week For 8 Weeks Topic 1 Topic 2 SkillsAnnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RAVEN 18 ItemsDokument7 SeitenRAVEN 18 ItemseastareaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prof Ed 5 Lesson 7 Preparing For Quality Teaching 20231022 003225 0000Dokument17 SeitenProf Ed 5 Lesson 7 Preparing For Quality Teaching 20231022 003225 0000anniejill15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching ResumeDokument4 SeitenTeaching Resumeapi-455245277Noch keine Bewertungen
- UCSP.Q1. Week 1 Observation and Sharing of CultureDokument12 SeitenUCSP.Q1. Week 1 Observation and Sharing of Culturejoel100% (6)
- Factors Associated With Students' Performance in English in The Implementation of Spiral ProgressionDokument26 SeitenFactors Associated With Students' Performance in English in The Implementation of Spiral ProgressionGlobal Research and Development ServicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interrelation Between TEVT and General EducationDokument9 SeitenInterrelation Between TEVT and General EducationLokuliyanaNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigation On Pulse Rate1Dokument8 SeitenInvestigation On Pulse Rate1shiean06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar Sekolah MusikDokument3 SeitenDaftar Sekolah MusikjonesjillyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Puzzles Mega PackDokument42 SeitenMath Puzzles Mega PackAzzaya DashzevegNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outline GA Chap1Dokument4 SeitenOutline GA Chap1RcormierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate Change Liability: Transnational Law and PracticeDokument25 SeitenClimate Change Liability: Transnational Law and PracticeOxfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.ed. Prospectus - 2018Dokument23 SeitenB.ed. Prospectus - 2018Vikram SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Class House RulesDokument12 SeitenOnline Class House RulesIM AM THE ONENoch keine Bewertungen