Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Malaria Comparison p1-2 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Ranjit Kumar ShahOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Malaria Comparison p1-2 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Ranjit Kumar ShahCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
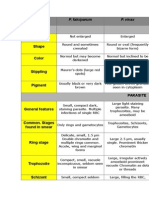
Comparison of the Plasmodium Species
Which Cause Human Malaria
Plasmodium Stages found Appearance of Erythrocyte
species in blood (RBC) Appearance of Parasite
normal; multiple infection of RBC more delicate cytoplasm; 1-2 small chromatin
Ring common than in other species dots; occasional appliqu (accoll) forms
P. falciparum
normal; rarely, Maurers clefts seldom seen in peripheral blood; compact
Trophozoite (under certain staining conditions) cytoplasm; dark pigment
seldom seen in peripheral blood; mature
normal; rarely, Maurers clefts
Schizont = 8-24 small merozoites; dark pigment,
(under certain staining conditions) clumped in one mass
crescent or sausage shape; chromatin in a
Gametocyte distorted by parasite single mass (macrogametocyte) or diffuse
(microgametocyte); dark pigment mass
normal to 1-1/4 X, round; occasionally fine large cytoplasm with occasional
Ring Schffners dots; multiple infection of RBC pseudopods; large chromatin dot
not uncommon
enlarged 1-1/22 X; may be distorted; fine large ameboid cytoplasm; large chromatin;
Trophozoite Schffners dots fine, yellowish-brown pigment
P. vivax
large, may almost fill RBC; mature = 12-24
enlarged 1-1/22 X; may be distorted; fine
Schizont merozoites; yellowish-brown, coalesced
Schffners dots pigment
round to oval; compact; may almost fill
enlarged 1-1/22 X; may be distorted; fine RBC; chromatin compact, eccentric
Gametocyte Schffners dots (macrogametocyte) or diffuse (micro-
gametocyte); scattered brown pigment
normal to 1-1/4 X, round to oval; occasionally
Ring Schffners dots; occasionally fimbriated; sturdy cytoplasm; large chromatin
multiple infection of RBC not uncommon
normal to 1-1/4 X; round to oval; some compact with large chromatin;
Trophozoite fimbriated; Schffners dots dark-brown pigment
P. ovale
mature = 6-14 merozoites with large
normal to 1-1/4 X; round to oval; some
Schizont nuclei, clustered around mass of
fimbriated; Schffners dots dark-brown pigment
round to oval; compact; may almost fill
normal to 1-1/4 X; round to oval; some RBC; chromatin compact, eccentric
Gametocyte fimbriated; Schffners dots (macrogametocyte) or more diffuse (micro-
gametocyte); scattered brown pigment
Ring normal to 3/4 X sturdy cytoplasm; large chromatin
compact cytoplasm; large chromatin;
normal to 3/4 X; rarely, Ziemanns stippling
Trophozoite occasional band forms; coarse, dark-brown
P. malariae
(under certain staining conditions) pigment
mature = 6-12 merozoites with large
normal to 3/4 X; rarely, Ziemanns stippling
Schizont nuclei, clustered around mass of coarse,
(under certain staining conditions) dark-brown pigment; occasional rosettes
round to oval; compact; may almost fill
normal to 3/4 X; rarely, Ziemanns stippling RBC; chromatin compact, eccentric
Gametocyte (under certain staining conditions) (macrogametocyte) or more diffuse (micro-
gametocyte); scattered brown pigment
Keypoints for Plasmodium Species
Which Cause Human Malaria
Infected RBCs
Size Shape Schffners Dots
<N, N: PM Crescent: PF (gametocytes) PV, PO
N: PF Ameboid: PV
>N: PO Fimbriation: PO
> >N: PV Elongated: PO
Parasites Found In Circulating Blood
Rings Trophozoites Schizonts (mature) Gametocytes
Rings only Ameboid: PV 6-12 nuclei: PM Crescent: PF
(gametocytes): PF
Compact: PO 6-14 nuclei: PO Round: PV
Numerous: PF PM PO
PF (rarely seen) 12-24: PV PM
Multiply infected 8-24: PF (rarely seen)
RBCs: PF Band form: PM
Rosettes: PM
Accessory
chromatin dots: PF
Delicate: PF
Certain morphologic key characteristics of the infected erythrocytes and parasites Legend
can be used to orient the diagnosis towards one of the four Plasmodium species
that infect humans, as shown above.These characteristics are by no means absolute, PF: P. falciparum
however.The final diagnosis should be based on the combined findings for the various
characteristics: what is the most probable species, based on the available findings. PV: P. vivax
PO: P. ovale
PM: P. malariae
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- RBC InclusionsDokument6 SeitenRBC Inclusionsjingx5100% (1)
- Morphological Characteristics of Malaria ParasitesDokument71 SeitenMorphological Characteristics of Malaria Parasitesed100% (6)
- SEM2 MALARIA Plasmodium Falciparum 2013Dokument23 SeitenSEM2 MALARIA Plasmodium Falciparum 2013odysseyfairy2739Noch keine Bewertungen
- Para MidtermsDokument126 SeitenPara Midtermshezekiah hezNoch keine Bewertungen
- MalariaDokument5 SeitenMalariaRina KhazarenNoch keine Bewertungen
- MalariaDokument30 SeitenMalariaderilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Praktikum Blok 3.2-Plasmodium Malariae-Dini23112016Dokument21 SeitenPraktikum Blok 3.2-Plasmodium Malariae-Dini23112016Ddn RmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasmodium Malariae: Laboratory Diagnosis of MalariaDokument4 SeitenPlasmodium Malariae: Laboratory Diagnosis of MalariaKals SpartanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malaria TableDokument1 SeiteMalaria TableJessie PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 6: Malarial Parasites: Parasitology LaboratoryDokument2 SeitenExercise 6: Malarial Parasites: Parasitology LaboratorySigfred Tarnate AoasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Diagnosis of Malaria ParasiteDokument101 SeitenDifferential Diagnosis of Malaria ParasiteSohaib Omer Salih100% (1)
- Malaria (Table of Characteristics)Dokument1 SeiteMalaria (Table of Characteristics)Noelle Grace Ulep BaromanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sporozoa and CoccidiaDokument155 SeitenSporozoa and CoccidiaJosue Luis VillarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staining TechniquesDokument62 SeitenStaining Techniques1x CzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 6 - الملارياDokument5 SeitenLecture 6 - الملارياAhmed Qassim MadhloomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Praktikum MalariaDokument22 SeitenPraktikum MalariaGeniaaldafitriaasgen100% (1)
- Gambar Plasmodium OvaleDokument4 SeitenGambar Plasmodium OvaleRonalda BudyantaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- MalariaDokument23 SeitenMalariafiras frs100% (1)
- Plasmodium Ovale: Laboratory Diagnosis of MalariaDokument4 SeitenPlasmodium Ovale: Laboratory Diagnosis of MalariaFitrah QolbinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FalciparumDokument4 SeitenFalciparumDandun Dannie-DunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pfalciparum Benchaidv2Dokument4 SeitenPfalciparum Benchaidv2kim hanbinhanbyulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical - Parasitology Zero 1Dokument13 SeitenClinical - Parasitology Zero 1Chirag EducationNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Handout The Malarial ParasitesDokument4 Seiten3rd Handout The Malarial ParasitesPatrica Willyn B. DiosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malaria: EtiologyDokument10 SeitenMalaria: EtiologyAlayza Joy GasmenNoch keine Bewertungen
- MalariaDokument25 SeitenMalariaYelai CarveroNoch keine Bewertungen
- By Fawad Khan Marwat Khalid Shakeel BabarDokument26 SeitenBy Fawad Khan Marwat Khalid Shakeel BabarksbabarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MalariaDokument3 SeitenMalariaAnonymous 75TDy2yNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Apicomplexa Malaria-1Dokument48 SeitenUnit 4 Apicomplexa Malaria-1Denise MichelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- المحاضرة 11 و 12 مادة الطفيلياتDokument18 Seitenالمحاضرة 11 و 12 مادة الطفيلياتdyabw6430Noch keine Bewertungen
- Malaria: by Kariuki Njaanake, PHDDokument19 SeitenMalaria: by Kariuki Njaanake, PHDodhiambo samwelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology - Helminthic InfectionsDokument25 SeitenMicrobiology - Helminthic InfectionsvaishnaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasmodium ReportDokument43 SeitenPlasmodium ReportGenessa Agustin BuenafeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Plasmodium SPPDokument1 Seite6 Plasmodium SPPKaycee Gretz LorescaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Protozoa: Plasmodium Vivax, P. Ovale, P. Malariae, and P. Falciparum. All Are Transmitted by Female Anopheles SPPDokument23 SeitenThe Protozoa: Plasmodium Vivax, P. Ovale, P. Malariae, and P. Falciparum. All Are Transmitted by Female Anopheles SPPYusril AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- ON Plasmodium Vivax (Malarial Parasite)Dokument10 SeitenON Plasmodium Vivax (Malarial Parasite)Raja Marudut SimatupangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasites PetalsDokument115 SeitenParasites PetalsMcarl MatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atlas MalariaDokument4 SeitenAtlas MalariaLaboratorium Pkm ManjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach Considerations MALARIADokument3 SeitenApproach Considerations MALARIAAnonymous hvOuCjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology PrelimsDokument20 SeitenParasitology PrelimsTIffany KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 ENG Presentation 4 Malaris Species Identification in Thick and Thin Bloodsmear Oct2019Dokument41 Seiten4 ENG Presentation 4 Malaris Species Identification in Thick and Thin Bloodsmear Oct2019Yantek Btklpp ManadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- P. VivaxDokument33 SeitenP. VivaxAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasmodium Vivax: Laboratory Diagnosis of MalariaDokument4 SeitenPlasmodium Vivax: Laboratory Diagnosis of MalariaShaiji ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malaria (Autosaved)Dokument15 SeitenMalaria (Autosaved)sajad abasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Species Host CELL Size Shape: P. Falciparum P. VivaxDokument2 SeitenSpecies Host CELL Size Shape: P. Falciparum P. VivaxFirah RukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemograma Buna 2023 BunaDokument71 SeitenHemograma Buna 2023 BunaMirelDabuleanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merozoites Fills The RBC, 6-16 (Usually 8) : Usually ENLARGED, Often Oval With Fimbrated EdgesDokument1 SeiteMerozoites Fills The RBC, 6-16 (Usually 8) : Usually ENLARGED, Often Oval With Fimbrated EdgesJqsWattpadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key To Identifying Malaria Parasite Stages in Thin Blood FilmsDokument3 SeitenKey To Identifying Malaria Parasite Stages in Thin Blood FilmsRisa RakhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PlasmodiumDokument92 SeitenPlasmodiumnitesh rawat100% (1)
- ParasitologyDokument4 SeitenParasitologyIan ZyrusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasmodium SPP.: Parasitology DeptDokument38 SeitenPlasmodium SPP.: Parasitology DeptDedy SavradinataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protozoa in Blood and TissuesDokument37 SeitenProtozoa in Blood and Tissuesheni arisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasm Odium SDokument9 SeitenPlasm Odium SAnonymous 7zl6IBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasmodium 132, EpiddiagnostikDokument68 SeitenPlasmodium 132, EpiddiagnostikHachi Nini Shop IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Ospe - ParasitologyDokument12 SeitenOspe - ParasitologyDanial MazukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malaria ParasiteDokument22 SeitenMalaria ParasiteAndy Putra HermawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HaemoparasitesDokument82 SeitenHaemoparasitesAshok WiselinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLASMODIUMDokument3 SeitenPLASMODIUMsakalam shipper48Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology NotesDokument16 SeitenMicrobiology NotesZeraNoch keine Bewertungen