Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Nursing Care Plan For MI
Hochgeladen von
louie roderosOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nursing Care Plan For MI
Hochgeladen von
louie roderosCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
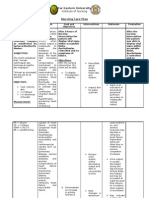
NURSING CARE PLAN
Decreased Cardiac Output related to altered heart rate and rhythm 2o MI
ASSESSMENT NURSING PLANNING NURSING ACTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
Subjective Cues: Decreased STG: Assessed for and document At the end of 8-hour
N/A Cardiac Output At the end of 30-min Nursing the ff: Nursing
related to altered Interventions, the client will o Mental Status Cerebral perfusion is Interventions, the
Objective Cues: heart rate and be able to: directly r/t cardiac output goal was partially
Generalized rhythm 2o MI Demonstrate and aortic perfusion met as evidenced
paleness hemodynamic stability pressure and is by:
noted (blood pressure and influenced by hypoxia
Irregular cardiac output) by 20% and electrolyte and acid- PR = 50s
rhythm of 30% as revealed in the base variation Cardiac monitoring
pulse noted cardiac monitor revealed
o Blood Pressure Hypotension r/t disturbance
LTG: hypoperfusion, vagal
At the end of 8-hour Nursing stimulation,
Interventions, the client will dysrhythmias, or
PR = 50s be able to: ventricular dysfunction
Demonstrate may occur
hemodynamic stability
(Blood pressure and o Heart Sounds
Bradycardia may be
cardiac output) by 31%-
present because of vagal
80% as revealed in the
stimulation or conduction
cardiac monitor
disturbances r/t area of
Manifest absence of
MI
angina
o Urine Output
Urine output
<0.5mL/kg/hrmay reflect
reduced renal perfusion
and glomerular filtration
as a result of reduced
cardiac output
o Peripheral Perfusion Decreased may indicate
a decreased cardiac
output
Kept client on bed in Semi- Facilitate oxygenation
fowlers and administered
O2
Angina indicates
myocardial ischemia,
Monitored and assessed
which may decrease
angina for type, severity
cardiac ouput
and duration
To facilitate increase in
myocardial contractility
thus increasing cardiac
Administered beta-blockers ouput
and inotropin agents as
ordered
- Monitor cardiac rate, rythm
& conduction (report any
change)
- Observe vital signs, ECG,
urine output, skin temp &
colour
- Administer prophylactic anti-
arrhythmic & other drugs as
ordered
- Administer IV fluids
- Promote physical & mental
rest & comfort
- Monitor laboratorium result
- Keep anti-dysrhythmic drugs
& defibrillator ready
Acute (Chest) Pain r/t myocardial ischemia resulting from coronary artery occlusion with loss/restriction of blood flow to an area of the myocardium and necrosis of
the myocardium.
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVAULATION
Subjective: Acute (Chest) STG:
The client reports Pain r/t Within 1 hour of nursing INDEPENDENT: After nursing intervention,
of chest pain myocardial interventions, the client will assess characteristics of pain is indication of MI. the client had still had
ischemia have improved comfort in chest pain, including location, assisting the client in chest pain:
resulting from chest, as evidenced by: duration, quality, intensity, quantifying pain may Still displays tension,
Objective: coronary artery States a decrease in the presence of radiation, differentiate pre-existing and Still requires analgesia
Restlessness occlusion with rating of the chest pain. precipitating and alleviating current pain patterns as well or nitroglycerin.
Facial loss/restriction of Is able to rest, displays factors, and as associated as identify complications.
grimacing blood flow to an reduced tension, and symptoms, have client rate
Fatigue area of the sleeps comfortably. pain on a scale of 1-10 and Goal unmet
myocardium and Requires decrease document findings in nurses
Peripheral
necrosis of the analgesia or nitroglycerin. notes.
cyanosis
myocardium.
Weak pulse
LTG: obtain history of previous this provides information that
Cold and cardiac pain and familial may help to differentiate
The client will have an
clammy skin history of cardiac problems. current pain from previous
improved feeling of control
Palpitations problems and complications.
as evidenced by verbalizing
Shortness of a sense of control over
breath present situation and future
Pain scale of outcomes within 2 days of assess respirations, BP and respirations may be
10/10 nursing interventions. heart rate with each episodes increased as a result of pain
Levines sign of chest pain. and associate anxiety.
maintain bedrest during pain, to reduce oxygen
with position of comfort, consumption and demand,
maintain relaxing to reduce competing stimuli
environment to promote and reduces anxiety.
calmness.
prepare for the administration pain control is a priority, as it
of medications, and monitor indicates ischemia.
response to drug therapy.
Notify physician if pain does
not abate.
instruct patient/family in to promote knowledge with
medication effects, side- therapeutic regimen and to
effects and contraindications alleviate fear of unknown.
contraindications
DEPENDENT:
obtain a 12-lead ECG on ECG and stat ECGs record
admission, then each time changes that can give
chest pain recurs for evidence of further cardiac
evidence of further infarction damage and location of MI.
as prescribed.
administer analgesics as analgesics may be used to
ordered reduce pain and reduce the
workload on the heart.
administer beta-blockers as to block sympathetic
ordered. stimulation, reduce heart
rate and lowers myocardial
demand.
administer calcium-channel to increase coronary blood
blockers as ordered. flow and collateral circulation
which can decrease pain
due to ischemia.
Impaired tissue perfusion related to hypovolemia secondary to decreased cardiac output ; decreased hemoglobin concentration in blood secondary tp
chronic anemia
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INRTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
SUBJECTIVE; Impaired tissue INDEPENDENT: After nursing intervention:
N/A perfusion related STG:
to hypovolemia Monitor neurological status; New onset of these -the client still displays
OBJECTIVE: secondary to Demonstrates adequate do a neurological examination neurological symptoms can pale, cold, clammy skin
decreased cardiac tissue perfusion as signify a stroke. If caused by -still with weal peripheral
Hematuria output ; decreased evidenced by palpable a thrombus and the client pulses
Edema hemoglobin peripheral pulses, warm and receives treatment within 3 -decreased gcs score
weak or absent concentration in dry skin, adequate urinary hours, a stroke can often be
pulses blood secondary output, and the absence of reversed.
skin color pale tp chronic anemia respiratory distress
on elevation, Note skin color and feel Skin pallor or mottling, cool
color does not temperature of the skin. or cold skin temperature, or
return on an absent pulse can signal
lowering the leg arterial obstruction, which is
Speech an emergency that requires
abnormalities immediate intervention.
extremity
weakness Check capillary refill. Nail beds usually return to a
altered mental pinkish color within 3
status seconds after nail bed
changes in compression (Dykes, 1993).
motor response
chest pain Monitor peripheral pulses. If These are symptoms of
dyspnea new onset of loss of pulses arterial obstruction that can
with bluish, purple, or black result in loss of a limb if not
areas and extreme pain, immediately reversed.
notify physician immediately.
DEPENDENT
Blood transfusion therapy -to correct hemoglobin and
hematocrit levels; improve
oxygenation
To increase circulating blood
Hydration with fluid volume volume
replacement
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Atrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesVon EverandAtrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Decreased Cardiac OutputDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Decreased Cardiac OutputJames Czar FontanillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shaira May B. Luzadas BS Nursing Level 2-A Clinical Instructor: Mrs. Michelle AngDokument3 SeitenShaira May B. Luzadas BS Nursing Level 2-A Clinical Instructor: Mrs. Michelle AngZoe Jisel LuzadasNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaDokument2 SeitenNURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaAce Dioso Tubasco100% (1)
- NCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalDokument13 SeitenNCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jas AssignmentDokument3 SeitenJas AssignmentjasperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jas AssignmentDokument3 SeitenJas AssignmentjasperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 NCP Chronic Heart FailureDokument5 Seiten2 NCP Chronic Heart FailureLovely CacapitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afib NCPDokument3 SeitenAfib NCPGen RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reduced Cardiac Output Nursing InterventionsDokument4 SeitenReduced Cardiac Output Nursing InterventionsEllee HadesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reduced Cardiac Output Nursing InterventionsDokument4 SeitenReduced Cardiac Output Nursing InterventionsEllee HadesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAD NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputDokument3 SeitenCAD NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputLeizel Apolonio100% (3)
- Icu 4Dokument7 SeitenIcu 4GemilleDaphneAndradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 2 Cardiac Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenActivity 2 Cardiac Drug StudyKlai ArriolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputDokument2 SeitenNURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputRy Pablo83% (41)
- Myocardial Infarction: Definition, Pathophysiology, Types, Assessment, ManagementDokument8 SeitenMyocardial Infarction: Definition, Pathophysiology, Types, Assessment, ManagementOdai AL KarkiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materi To Kardio 03 JanuariDokument50 SeitenMateri To Kardio 03 JanuariMamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing responsibilities for cardiac stimulant DobutamineDokument2 SeitenNursing responsibilities for cardiac stimulant DobutamineCyril Joy N. FernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Syncope: Causes, Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument44 SeitenUnderstanding Syncope: Causes, Diagnosis and TreatmentSap ModulesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypovolemic Shock: Dr. Sherwin BuluranDokument8 SeitenHypovolemic Shock: Dr. Sherwin BuluranChristian UretaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Er FinalsDokument63 SeitenEr FinalsNaren RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Cardio 3Dokument50 SeitenMCQ Cardio 3Dian ParamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument7 SeitenDrug StudyCassie ValderramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jake Yvan Dizon Case Study, Chapter 49, Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersDokument8 SeitenJake Yvan Dizon Case Study, Chapter 49, Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersJake Yvan DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- KGD 1 VivianDokument101 SeitenKGD 1 VivianVivian SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis&Manajemen ShockDokument8 SeitenDiagnosis&Manajemen ShockHJKIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipd - KardiologiDokument116 SeitenIpd - KardiologiWynda MuljonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute & Chronic Heart Failure: Dr. Nurkhalis, SPJP, FihaDokument98 SeitenAcute & Chronic Heart Failure: Dr. Nurkhalis, SPJP, FihablackcatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Pressure-For StudentsDokument79 SeitenBlood Pressure-For StudentsAshok Kumar P100% (1)
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output: Nursing DiagnosisDokument4 SeitenRisk For Decreased Cardiac Output: Nursing DiagnosisRiska RamadaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Exercise TableDokument16 SeitenCardiac Exercise TablePreet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiogenic Shock Hemodynamic ParametersDokument31 SeitenCardiogenic Shock Hemodynamic ParameterscantikarevieraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDokument9 SeitenDecreased Cardiac OutputRae AnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 118 ReviewerDokument14 SeitenNCM 118 ReviewerMarceil MortelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Institute of Nursing: Far Eastern UniversityDokument3 SeitenInstitute of Nursing: Far Eastern UniversityaleccespirituNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 5Dokument4 SeitenActivity 5AngieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On Children With Cardiac DisordersDokument3 SeitenCase Study On Children With Cardiac DisordersAlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stages of ShockDokument1 SeiteStages of ShockronaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacotherapy of Heart FailureDokument17 SeitenPharmacotherapy of Heart FailurelisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systolic Dysfunction:: Types of Heart FailureDokument13 SeitenSystolic Dysfunction:: Types of Heart FailureElisabeth F. OjhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vehicular Accident (VA) Manifesting Hypovolemic Shock NCPDokument6 SeitenVehicular Accident (VA) Manifesting Hypovolemic Shock NCPCHRISTIE MONTANONoch keine Bewertungen
- 11. 201909 抗高血压 antihypertensionDokument72 Seiten11. 201909 抗高血压 antihypertensionShanon LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Emergency DrugsDokument6 SeitenDrug Study Emergency DrugsJhessa Curie PitaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Failure New SlidesDokument41 SeitenHeart Failure New SlidesjawadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CT 11 - HPNDokument12 SeitenCT 11 - HPNLycah RotoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 HypertensionDokument95 Seiten6 HypertensionZeleke temechewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiogenic Shock - SWDokument41 SeitenCardiogenic Shock - SWAyu LuthfiyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example of Nursing Diagnosis Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDokument5 SeitenExample of Nursing Diagnosis Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputAndi Faramida HamzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screenshot 2023-03-23 at 11.04.14 PMDokument1 SeiteScreenshot 2023-03-23 at 11.04.14 PMRenad AlharbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Failure Lily ModifiedDokument57 SeitenHeart Failure Lily ModifiedSabila FatimahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 - Cardiovascular Sys - 2012 - Elsevier S Integrated Review Pharmacology SeconDokument27 Seiten8 - Cardiovascular Sys - 2012 - Elsevier S Integrated Review Pharmacology SeconCecilia GrayebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Cardiovascular PhysiologyDokument1 SeiteApplied Cardiovascular Physiologyoperation KDNANoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemDokument12 SeitenDrugs Acting On The Cardiovascular Systemcleahis cruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing and Treating Impending Thyroid StormDokument4 SeitenAssessing and Treating Impending Thyroid StormRenie SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulation of blood pressure: MAP, autoregulation, and baroreflexDokument55 SeitenRegulation of blood pressure: MAP, autoregulation, and baroreflexsultan khabeebNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP KateDor NewDokument6 SeitenNCP KateDor NewSteffi GolezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Acting in CVSDokument63 SeitenDrugs Acting in CVSMeghan Norico Cristuta100% (1)
- Heart Failure and ShockDokument34 SeitenHeart Failure and Shockfrenee aradanasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart BlockDokument26 SeitenHeart BlockMihir Patel86% (7)
- Artigoni2016 PDFDokument6 SeitenArtigoni2016 PDFlouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inter College IntramuralsDokument6 SeitenInter College Intramuralslouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Donning Sterlie GownDokument1 SeiteDonning Sterlie Gownlouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Donning Sterlie GownDokument2 SeitenDonning Sterlie Gownlouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXTENT of COMPLIANCE With The Team Recommendations For AREA IXDokument1 SeiteEXTENT of COMPLIANCE With The Team Recommendations For AREA IXlouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Alumni 2018Dokument3 SeitenList of Alumni 2018louie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Informatics Thesis TitlesDokument1 SeiteInformatics Thesis Titleslouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Informatics Thesis TitlesDokument1 SeiteInformatics Thesis Titleslouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glob J Health SciDokument11 SeitenGlob J Health Scilouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Informatics in South AmericaDokument5 SeitenNursing Informatics in South Americalouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alumni 2018 Officers Per Class Officers As A Batch December 2018 PanunumpaDokument1 SeiteAlumni 2018 Officers Per Class Officers As A Batch December 2018 Panunumpalouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Program: Mr. and Ms. CONDokument4 SeitenProgram: Mr. and Ms. CONlouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Students' Attitudes Toward Computer Use in HealthcareDokument7 SeitenNursing Students' Attitudes Toward Computer Use in Healthcarelouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alumni 2018 Officers Per Class Officers As A Batch December 2018 PanunumpaDokument1 SeiteAlumni 2018 Officers Per Class Officers As A Batch December 2018 Panunumpalouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Child CareDokument23 SeitenChild Carelouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Make An Inventory of Functional Equipment On CHED Minimum RequirementsDokument2 SeitenMake An Inventory of Functional Equipment On CHED Minimum Requirementslouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Outline Nurs 65Dokument5 SeitenCourse Outline Nurs 65louie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Program: Mr. and Ms. CONDokument4 SeitenProgram: Mr. and Ms. CONlouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9Dokument1 Seite9louie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Donning Sterlie GownDokument2 SeitenDonning Sterlie Gownlouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st ViolationDokument3 Seiten1st Violationlouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan: 123 J.P Rizal St. Mendez CaviteDokument2 SeitenBusiness Plan: 123 J.P Rizal St. Mendez Cavitelouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gain Electricity While Losing Energy with Treadmill GeneratorsDokument3 SeitenGain Electricity While Losing Energy with Treadmill Generatorslouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- FDAR ChartingDokument2 SeitenFDAR Chartinglouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics HIDokument10 SeitenEthics HIbjnpedronptrpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing TicsDokument12 SeitenNursing Ticsmitsuki_sylphNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Airway ObstructionDokument14 SeitenUpper Airway Obstructionlouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 14Dokument9 SeitenUnit 14louie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- JeromeDokument2 SeitenJeromelouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Describe at Least Two Purposes of ControllingDokument5 SeitenDescribe at Least Two Purposes of Controllinglouie roderosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: ActionDokument22 SeitenGeneric Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: Actionp_dawg100% (14)
- Good Healthy Eating HabitsDokument31 SeitenGood Healthy Eating HabitsjoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- VentilatorDokument17 SeitenVentilatorDongxia WuNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis With Intermittent Neurogenic Claudication: Disease and DiagnosisDokument13 SeitenA Review of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis With Intermittent Neurogenic Claudication: Disease and DiagnosisIhsan KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephrotic SyndromeDokument61 SeitenNephrotic SyndromeRanah Julia Garchitorena AyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opd PMR 13 05 16Dokument1 SeiteOpd PMR 13 05 16Anurag AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Concerns: Sir. Eurich Roi C. Araneta, RRTDokument72 SeitenLegal Concerns: Sir. Eurich Roi C. Araneta, RRTkyuleen05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical NursingDokument7 SeitenSurgical NursingNick BishopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shannonresume 2018 ADokument1 SeiteShannonresume 2018 Aapi-400871779Noch keine Bewertungen
- DR Renaud Portfolio Presentation 2010Dokument91 SeitenDR Renaud Portfolio Presentation 2010NazihCosmeticsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lindsey D. Lawrence: Long Island University - Brooklyn, NYDokument1 SeiteLindsey D. Lawrence: Long Island University - Brooklyn, NYapi-530532762Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Bioavailability of Dietary Calcium PDFDokument18 SeitenThe Bioavailability of Dietary Calcium PDFStev D'BulletNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental ImplantDokument2 SeitenDental ImplantUmair RizwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stewie's Antisocial Personality DisorderDokument4 SeitenStewie's Antisocial Personality Disordercwinters1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Test QUIZDokument9 SeitenMini Test QUIZAbdul RohimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Health Term PaperDokument8 SeitenMental Health Term Paperchememartinez29100% (2)
- Hypnotize This!Dokument342 SeitenHypnotize This!Jack DICK100% (1)
- WC Guideline ProcedureDokument9 SeitenWC Guideline ProcedureVarlam CristaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soapie, Assessment and NCP On PAINDokument7 SeitenSoapie, Assessment and NCP On PAINAna100% (2)
- Evaluascdc Hiv MethodDokument11 SeitenEvaluascdc Hiv MethodmasaruddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equine Internship Program - Equitom Equine HospitalDokument4 SeitenEquine Internship Program - Equitom Equine HospitalYara AssaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abelmoschus Esculentus (L.) : Bioactive Components'Dokument13 SeitenAbelmoschus Esculentus (L.) : Bioactive Components'Andrea MarceloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community Psychiatry Gp5Dokument34 SeitenCommunity Psychiatry Gp5Codillia CheongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebrolysin in Patients With Hemorrhagic StrokeDokument7 SeitenCerebrolysin in Patients With Hemorrhagic StrokeZeynep Emirhan ŞenyüzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 10 Fist AidDokument81 SeitenUnit 10 Fist AidillimooniteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Download Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology 3rd Edition Will Beachey Test BankDokument36 SeitenFull Download Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology 3rd Edition Will Beachey Test Bankeloisabroomheadfxs100% (34)
- Lemongrass Benefits for Mosquito Repellent and Cancer TreatmentDokument3 SeitenLemongrass Benefits for Mosquito Repellent and Cancer TreatmentAji Deonella Tangcangco CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speech and language disorders explainedDokument22 SeitenSpeech and language disorders explainedJaren NadongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pocket Tutor Understanding ABGs and Lung Function TestsDokument170 SeitenPocket Tutor Understanding ABGs and Lung Function Testsdanelv100% (1)
- Cerebral Palsy in ChildrenDokument17 SeitenCerebral Palsy in Childrenapi-320401765Noch keine Bewertungen