Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Exp - 7 Surface Tension
Hochgeladen von
Mohamed Fardin KhanOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Exp - 7 Surface Tension
Hochgeladen von
Mohamed Fardin KhanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SURFACE TENSION
Aim: To determine the surface tension of water capillary rise method.
Apparatus: Travelling microscope, retort stand, capillary tube, beaker etc.
Principle:
Capillarity i.e., The rise and fall of a liquid in a capillary tube when a capillary tube is dipped in a
liquid. The liquid raises in a capillary tube untill its weight is
balanced by the upward force of surface tension.
Theory:
When a clean capillary tube is placed vertically with its lower
end under water, there will be rise of water into the tube due to
surface tension acting tangentially at every point all along the line of
contact.
If 'h' is the height of the water column in the tube
measured upto the bottom of the meniscus and 'r' is the radius of the
capillary tube. When the liquid is in equilibrium ,
r
2 r T cos = r 2 h dg
3
where d is the density of water and
is the angle of contact of water with glass (for pure
water and glass =0 0 )
r
h drg
T = surface tension of water = 3
2
Description:
A capillary tube AB is clamped vertically to a retort stand. It's lower end is dipped in a
beaker of water. One or two drops of red ink is added to water. So that the level of water in the
tube can be clearly seen. The rise in level of water can be measured using a travelling
microscope M. A pin CDE bent twice is fixed to the tube by means of rubber bands.
Procedure:
Determination of 'h':
The length of one division on main scale and total no.of vernier scale divisions on verniar sclae
are noted to calculate the least count of travelling microscope.The microscope is focused on the meniscus.
And see that horizontal cross wires was just tangential to the meniscus.The reading R1 is noted. The water
beaker was removed with care and by adjusting the height of the microscope. The horizontal cross wire
appears to just touch the tip of the bent pin. The second reading R2 was noted. The capillary ascent of
liquid in tube is
h=(R1-R2) cm
Determination of 'r':
The capillary tube is clamped horizontally. The microscope is focussed on
one end of the capillary tube. Then two concentric circles are observed. The
microscope is moved until the vertical cross wire is tangential to the inner circle
on the left side and microscope reading R3 is noted. The microscope is moved so
that the vertical cross wire is again tangential to the inner circle on the right side.
And reading 'R4' is noted. The difference between R3 and R4 is equal to the horizontal diameter of the
capillary bore similary the vertical diameter of the bore is measured. The average diameter of the
capillary bore and the radius of the bore (r) are calculated. From the given equation the surface tansion of
the water is determined.
R 4 R 3
The radius of the tube r = cm
2
r
h drg
T= 3 dyne.cm-1
2
where d is density of water.
Observations:
The length of 1 division on the main scale = 0.05 cm
Total number of divisions on the vernier = N = 50
1M.S.D. 0.05
Least count of the microscope, L.C.= = =0.001 cm
N 50
The average radius of the capillary tube r = ................................... cm
Density of water at room temperature d=...................................... gm/cc
Average ascent of water in the tube, h = ................................... cm
Surface tension of water, T = ................................. dyne.cm-1
Table for determination heigh(h) :
S.NO. Reading of the bottom of the meniscus Reading of the bottom of the meniscus in Height of the
in capillary tube beaker capillary rise(h)
=
MSR b=V.C x L.C Total reading MSR a b=V.C x L.C Total reading
R1 R2 cm
a R1 = a+b (cm) R2 =a+b (cm)
Height of rise of liquid in capilllary tube is = ........cm
Table for determination diameter(d):
S.No. Reading on the left edge Reading on the right edge Diameter (d) =
R4 R3 cm
MSR b=V.C x L.C Total reading R3 MSR a b=V.C x L.C Total reading R4
a = a+b (cm) =a+b (cm)
Diameter of capillary tube bore is = ......... cm
Radius of capillary tube bore is(r) = d/2 = ........ cm
Precautions:
(1) The bore of the capillary tube should be perfectly clean.
(2) The bore of the tube should be uniform.
(3) The tube should be clamped vertically.
(4) Readings should be taken without parallax error.
(5) The horizontal position of the microscope should not be disturbed during the experiment.
Result:
The surface tension of water is T = ......................................... dyne.cm-1
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- M303, Fluid MEchanics FM - M III P.P. Binu & Sunand CDokument21 SeitenM303, Fluid MEchanics FM - M III P.P. Binu & Sunand CPremjith SugunanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC Chapter 01Dokument39 SeitenEC Chapter 01Muhammad qamar100% (1)
- ANNUITIESDokument23 SeitenANNUITIESJonalyn Bautista-CanlasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thanh Huyen - Week 5 - Final Test AnswerDokument3 SeitenThanh Huyen - Week 5 - Final Test AnswerNguyễn Sapphire Thanh HuyềnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab Fundamental 17Dokument4 SeitenMatlab Fundamental 17duc anhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering HydrologyDokument24 SeitenEngineering HydrologyPrince Vince100% (1)
- Advanced PHP ManualDokument246 SeitenAdvanced PHP Manualkennedy onuzulikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH.2 InterestDokument41 SeitenCH.2 InterestJenalyn MacarilayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Basic Microscopy and Animal Cell StructureDokument4 Seiten01 Basic Microscopy and Animal Cell StructureAntoni Andreu MartijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Management Central TendencyDokument33 SeitenData Management Central TendencyAnn Kristel EstebanNoch keine Bewertungen
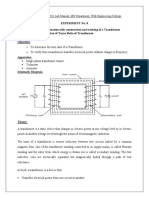
- Experiment No: 8 A) Familiarization With Construction and Working of A Transformer B) Verification of Turns Ratio of TransformerDokument3 SeitenExperiment No: 8 A) Familiarization With Construction and Working of A Transformer B) Verification of Turns Ratio of TransformerSaad AliKhan0% (1)
- NUmerical SolutionsDokument76 SeitenNUmerical SolutionsLiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 2 FMDokument5 SeitenExp 2 FMNur AsiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absorption of Beta Particles & Beta End Point Decay Energy ObjectiveDokument3 SeitenAbsorption of Beta Particles & Beta End Point Decay Energy ObjectiveMridhul MohananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Math2.1Dokument15 SeitenReport Math2.1Anonymous qOUo59FCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Course: Yr. & Sec: Section: Time: Room: Instructor:: I. ObjectivesDokument6 SeitenName: Course: Yr. & Sec: Section: Time: Room: Instructor:: I. Objectiveskeempee meeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Maxima and Minima 1Dokument7 SeitenApplication of Maxima and Minima 1Sam StrannerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impedance Bridge CircuitDokument5 SeitenImpedance Bridge CircuitJOHN LLOYD PEREZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics: Engr. Cheryll C. MalibiranDokument29 SeitenFluid Mechanics: Engr. Cheryll C. MalibiranYedda M IlaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCA Practical ExercisesDokument13 SeitenMCA Practical ExercisessujathalaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture5 1Dokument52 SeitenLecture5 1Han ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Construction Kit Lab: Part 1: Ohm's LawDokument13 SeitenCircuit Construction Kit Lab: Part 1: Ohm's LawRAFIQANoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 2 Plane Surveying PDFDokument7 SeitenMODULE 2 Plane Surveying PDFJexther Pascua NazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ SomDokument4 SeitenMCQ Somddeepak123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Physics PDFDokument20 SeitenModern Physics PDFPrathm MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 5 and 6Dokument9 SeitenWorksheet 5 and 6husan hashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - Fundamentals of Fluid FlowDokument7 SeitenModule 1 - Fundamentals of Fluid FlowClifford T NethercottNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 3 - Hydrostatic Forces On Plane and Curved SurfacesDokument5 SeitenLab 3 - Hydrostatic Forces On Plane and Curved SurfacesAlyssa Suzanne TafallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 8 Series and Parallel Circuits Physics LabDokument7 SeitenExperiment 8 Series and Parallel Circuits Physics LabGrace UrbanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thevenin's and Norton's TheoremDokument3 SeitenThevenin's and Norton's TheoremDozdi80% (5)
- Lab 13 - RC and RL CircuitsDokument4 SeitenLab 13 - RC and RL CircuitsMuhammad AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exact Differential EqauationDokument16 SeitenExact Differential Eqauationmei krismahariyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03-01 Lecture Notes Compilation - Vectors and ScalarsDokument6 Seiten03-01 Lecture Notes Compilation - Vectors and ScalarsElaine BarrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- WS#2 Time Value of Money 1 - Introducing The FactorsDokument8 SeitenWS#2 Time Value of Money 1 - Introducing The FactorsPatricia DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 1 5b Ohms Law WorksheetDokument5 Seiten3 1 5b Ohms Law Worksheetapi-291536660100% (1)
- Electric Current, Resistance and ResistivityDokument8 SeitenElectric Current, Resistance and ResistivityPavan BoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIM CEE 108 Week 1-3 PDFDokument28 SeitenSIM CEE 108 Week 1-3 PDFIah Belleza MedelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors Scalars PPTDokument14 SeitenVectors Scalars PPTDaniel LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 6890Dokument3 SeitenActivity 6890Raymond Gicalde RementillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential EquationsDokument19 SeitenDifferential EquationsDinah Jane MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Chapter 2 - Force VectorDokument20 Seiten02 Chapter 2 - Force VectorShaun KerouacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Note About ForceDokument6 SeitenLesson Note About Forcemark joseph cometaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genchem Module - Final 2019Dokument66 SeitenGenchem Module - Final 2019Jason SamudraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2Dokument31 SeitenLecture 2Edwin KhundiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Chart and PseudocodesDokument42 SeitenFlow Chart and PseudocodesMAHER ALNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surveying Prob SetDokument2 SeitenSurveying Prob SetErika Tolentino0% (3)
- Tarea 2. Design - of - Machinery NortonDokument10 SeitenTarea 2. Design - of - Machinery Nortonbisiosote100% (1)
- MODULE 1 Plane Geometry Introduction and Triangles 1Dokument7 SeitenMODULE 1 Plane Geometry Introduction and Triangles 1CyndelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bernoulli ApparatusDokument4 SeitenBernoulli ApparatusDarul Imran Azmi0% (1)
- Problem - 7A PDFDokument9 SeitenProblem - 7A PDFMonicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental NoteDokument80 SeitenFundamental Notefiraol temesgenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5 - BJT As InverterDokument3 SeitenLab 5 - BJT As InverterKamal ChapagainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 03Dokument9 SeitenExp 03Zharlene SasotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Experiment No. 1Dokument9 SeitenLaboratory Experiment No. 1JAMIR ARIOLANoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Differential EquationsDokument6 SeitenIntroduction To Differential EquationsLlona Jeramel MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 8 ...Dokument3 SeitenLab 8 ...shaweeeng 101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment N1Dokument9 SeitenAssignment N1Rania ChNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt 2. To Determine Surface Tension by Rise in Capillary TubeDokument3 SeitenExpt 2. To Determine Surface Tension by Rise in Capillary TubeVenkataraman KrishnaiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment: 1: Aim Apparatus RequiredDokument4 SeitenExperiment: 1: Aim Apparatus RequiredSHUBHANKAR SANGISAPUNoch keine Bewertungen
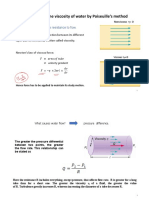
- Determine The Viscosity of Water by Poiseuille S Method: Viscosity Is Defined As The Resistance To FlowDokument21 SeitenDetermine The Viscosity of Water by Poiseuille S Method: Viscosity Is Defined As The Resistance To FlowDeepraj Singh ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Navigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsVon EverandNavigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics Project YsDokument21 SeitenEconomics Project YsYashasvi SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICT & ICT LabDokument22 SeitenICT & ICT LabM Asif 72 2MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sainsbury 2010 PDFDokument13 SeitenSainsbury 2010 PDFronaldNoch keine Bewertungen
- StatisticsDokument2 SeitenStatisticsAnish JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computers & GeosciencesDokument17 SeitenComputers & Geosciencesfrancarlos de la cruz chuquimangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- STA301 Quiz-2 File by Vu Topper RMDokument109 SeitenSTA301 Quiz-2 File by Vu Topper RMTaimur ChaudhryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nama: Fazlun Nisak NIM: 180170127 MK: Kecerdasan Buatan (A2) Tugas PerceptronDokument8 SeitenNama: Fazlun Nisak NIM: 180170127 MK: Kecerdasan Buatan (A2) Tugas PerceptronFazlun NisakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Res2dinvx32 PDFDokument173 SeitenRes2dinvx32 PDFWahyu Sutrisno0% (1)
- Systemmeldungen GBDokument28 SeitenSystemmeldungen GBAhmet0% (1)
- D2 PPT 1 - AbdulDokument25 SeitenD2 PPT 1 - AbdulAshish ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between CURE Clustering and DBSCAN Clustering - GeeksforGeeksDokument3 SeitenDifference Between CURE Clustering and DBSCAN Clustering - GeeksforGeeksRavindra Kumar PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exambank HigherDokument62 SeitenExambank HigherJust WadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Design (Moment and Shear Check) (For Simply Supported)Dokument8 SeitenSteel Design (Moment and Shear Check) (For Simply Supported)aikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Light or Operate An Oven: ProcedureDokument17 SeitenHow To Light or Operate An Oven: ProcedureSHERYL ABUEL100% (1)
- Second Periodical ExamDokument19 SeitenSecond Periodical ExamMaynard Lee Estrada GomintongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid-Semester Paper 09Dokument2 SeitenMid-Semester Paper 09Harsh ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geehy 32 Bit ARM Cortex MCU - 2023 07 13 090801Dokument4 SeitenGeehy 32 Bit ARM Cortex MCU - 2023 07 13 090801palurdo2Noch keine Bewertungen
- CERNCourier2021JanFeb DigitaleditionDokument33 SeitenCERNCourier2021JanFeb DigitaleditionBhakti rautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate: Internal Examiner External ExaminerDokument51 SeitenCertificate: Internal Examiner External ExamineraryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siesta TutorialDokument14 SeitenSiesta TutorialCharles Marcotte GirardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization of AirfoilsDokument9 SeitenOptimization of AirfoilsMD SHAHRIARMAHMUDNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Flyer PROSLIDE 32 B - V5.0 - 2020-03-09 PDFDokument10 SeitenSystem Flyer PROSLIDE 32 B - V5.0 - 2020-03-09 PDFeduardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT - 1 Formula and ProcedureDokument4 SeitenUNIT - 1 Formula and ProcedurevinothNoch keine Bewertungen
- SB Erv Arvu123zea2 03 20Dokument2 SeitenSB Erv Arvu123zea2 03 20Mohammed Tausif AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- UM0384Dokument35 SeitenUM0384Pat 14HS1Noch keine Bewertungen
- S Cubed DatasheetDokument2 SeitenS Cubed DatasheetGulf JobzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.motor Starters - Enclosed VersionsDokument106 Seiten2.motor Starters - Enclosed VersionsRAmesh SrinivasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Midterm Review PacketDokument6 SeitenPhysics Midterm Review PacketJasper SendraNoch keine Bewertungen