Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Viton Selecting The Correct Type
Hochgeladen von
Hary PrasetyoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Viton Selecting The Correct Type
Hochgeladen von
Hary PrasetyoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Selecting the Correct Type of Viton
Types of Viton / FKM Polymers and some of their Important Characteristics
The designations (i.e. A, B, GF, and GLT) were established by DuPont Dow Elastomers many years ago and have become
standard reference points. Other fluorocarbon polymer suppliers may use different designations.
A or E type The most common elastomers in the FKM product line. They generally have 66% fluorine content and are
supplied to the most common aerospace specifications. These grades are considered general purpose FKMs. They exhibit low
compression set, but are not resistant to flex fuels with high levels of alcohol or MBTE.
B type These have increased fluorine content and offer better fluid resistance to acids and flex fuels than the A or E types.
They generally have 67% fluorine content and are commonly used in applications where resistance to flex fuels containing
alcohol or MTBE in required.
GF or F type These have further increases in fluorine content to provide better fuel and solvent resistance. They generally
have 70% fluorine content and are used in flex fuel and agricultural applications where a variety of very aggressive chemicals
are routinely used.
GLT type These have been developed to improve the low temperature flexibility compared with A or E types. The low
temperature flexibility normally reaches 40 F. They generally have 65% fluorine content and are not suitable for flex fuels or
aggressive solvents.
GFLT type Developed to balance fluid resistance with improved low temperature flexibility. They generally have 68% fluorine
content and are rated to 35 F. These materials are suitable for flex fuel applications.
Viton Extreme This is sometimes referred to as ETP. These materials generally have 73.5% fluorine, and offer improved
resistance to aggressive solvents.
Differences in Fluids Resistance and Low Temperature
Family and Type of Viton Fluoroelastomer
A B F GB GF GLT GFLT ETP
Environment
Cure System
Bisphenol Peroxide
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons, process fluids, chemicals 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Aromatic hydrocarbons (toluene, etc.), process fluids, chemicals 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 1
Automotive and Aviation Fuels (pure hydrocarbons - no alcohol) 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Automotive fuels containing legal levels (5-15%) of alcohols and
2 1 1 1 1 2 1 1
ethers (methanol, ethanol, MTBE, TAME)
Automotive/methanol fuels blends up to 100% methanol (flex fuels) NR 2 1 2 1 NR 1 1
Engine Lubricating Oils (SE-SF grades) 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Engine Lubricating Oils (SG-SH grades) 3 2 2 1 1 1 1 1
Acid (HSO, HNO) hot water and steam 3 2 2 1 1 1 1 1
Strong base, high pH, caustic, amines NR NR NR NR NR NR NR 1-2
Low molecular weight carbonyls - 100% concentration
NR NR NR NR NR NR NR 1-2
(MTBE, MEK, MIBK, etc)
Temperature of retraction (TR-10) -17C -14C -7C -15C -6C -30C -24C -11C
1 = excellent, minimal volume swell 2 = Very Good, small volume swell
3 Good, moderate volume swell NR = Not Recommended, excessive volume swell or change in physical properties
Unit 2 & 2A Solingen House, T: +44 (0) 1670 840529
Remscheid Way F: +44 (0) 1670 840644
Jubilee Industrial Estate, Ashington E: sales@easternseals.co.uk
Northumberland, NE63 8UJ, UK W: www.easternseals.co.uk
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Applied Economics 2Dokument8 SeitenApplied Economics 2Sayra HidalgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Man and Historical ActionDokument4 SeitenMan and Historical Actionmama.sb415Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- ChatGpt PDFDokument19 SeitenChatGpt PDFsanx2014100% (1)
- Literatura Tecnica 3Dokument10 SeitenLiteratura Tecnica 3Christian PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Comparison Between CompetitorsDokument2 SeitenComparison Between Competitorsritesh singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Global Divides: The North and The South: National University Sports AcademyDokument32 SeitenGlobal Divides: The North and The South: National University Sports AcademyYassi CurtisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Aleutia Solar Container ClassroomDokument67 SeitenAleutia Solar Container ClassroomaleutiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- 2022 WR Extended VersionDokument71 Seiten2022 WR Extended Versionpavankawade63Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Physics Education Thesis TopicsDokument4 SeitenPhysics Education Thesis TopicsPaperWriterServicesCanada100% (2)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Subject Manual Tle 7-8Dokument11 SeitenSubject Manual Tle 7-8Rhayan Dela Cruz DaquizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- IMCI Chart BookletDokument43 SeitenIMCI Chart Bookletmysticeyes_17100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- MultiLoadII Mobile Quick Start PDFDokument10 SeitenMultiLoadII Mobile Quick Start PDFAndrés ColmenaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- PresentationDokument27 SeitenPresentationMenuka WatankachhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Illustrating An Experiment, Outcome, Sample Space and EventDokument9 SeitenIllustrating An Experiment, Outcome, Sample Space and EventMarielle MunarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scholastica: Mock 1Dokument14 SeitenScholastica: Mock 1Fatema KhatunNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- QSP 04bDokument35 SeitenQSP 04bakrastogi94843Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 140322224412 Phpapp02Dokument26 SeitenQuiz 140322224412 Phpapp02Muhammad Mubeen Iqbal PuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 2Dokument5 SeitenCase Study 2api-247285537100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Genetics Icar1Dokument18 SeitenGenetics Icar1elanthamizhmaranNoch keine Bewertungen
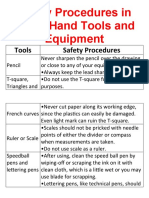
- Safety Procedures in Using Hand Tools and EquipmentDokument12 SeitenSafety Procedures in Using Hand Tools and EquipmentJan IcejimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- SLA in PEGA How To Configue Service Level Agreement - HKRDokument7 SeitenSLA in PEGA How To Configue Service Level Agreement - HKRsridhar varmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SweetenersDokument23 SeitenSweetenersNur AfifahNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSA Poster Project WorkbookDokument38 SeitenPSA Poster Project WorkbookwalliamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pg2022 ResultDokument86 SeitenPg2022 ResultkapilNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- 20-Admission of PatientDokument3 Seiten20-Admission of Patientakositabon100% (1)
- Jakub - BaZi CalculatorDokument3 SeitenJakub - BaZi Calculatorpedro restinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- postedcontentadminuploadsFAQs20for20Organization PDFDokument10 SeitenpostedcontentadminuploadsFAQs20for20Organization PDFMohd Adil AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workbook Group TheoryDokument62 SeitenWorkbook Group TheoryLi NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Anatomy of the pulp cavity กย 2562-1Dokument84 SeitenAnatomy of the pulp cavity กย 2562-1IlincaVasilescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- BrochureDokument3 SeitenBrochureapi-400730798Noch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)