Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Nodal Analysis
Hochgeladen von
Joyprakash LairenlakpamOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nodal Analysis
Hochgeladen von
Joyprakash LairenlakpamCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory
Nodal Analysis
North-Eastern Hill University
06.09.2016 joIp_rkas, ECE, NEHU, Shillong - 793 022
Nodal Analysis
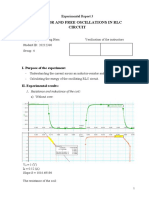
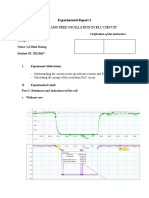
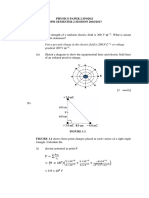
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
2 k
10 k
0.4ix ix
5 mA 5 k 20 k
Fig. 1: A circuit where ix is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 1 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
2 k
10 k
1 2 3
0.4ix ix
5 mA 5 k 20 k
0
Fig. 1: A circuit where ix is to be calculated.
Nodes have been identified in the given circuit
with node numbers, 1, 2 and 3, having node
voltages, v1 , v2 and v3 respectively while the
bottom node is marked 0 as the reference node.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 1 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
2 k
10 k
1 2 3
0.4ix ix
5 mA 5 k 20 k
0
Fig. 1: A circuit where ix is to be calculated.
Nodes have been identified in the given circuit
with node numbers, 1, 2 and 3, having node
voltages, v1 , v2 and v3 respectively while the
bottom node is marked 0 as the reference node.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 1 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
2 k
Applying KCL at node 1, we have
v1 v3
5 103 + + 0.4ix = 0
10 k 2 103
1 2 3 v2 v3
10 + v1 v3 + 0.08(v2 v3 ) = 0 ix =
10 103
0.4ix ix
v1 + 0.08v2 1.08v3 = 10 (1)
5 mA 5 k 20 k
0
Fig. 1: A circuit where ix is to be calculated.
Nodes have been identified in the given circuit
with node numbers, 1, 2 and 3, having node
voltages, v1 , v2 and v3 respectively while the
bottom node is marked 0 as the reference node.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 1 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
2 k
Applying KCL at node 1, we have
v1 v3
5 103 + + 0.4ix = 0
10 k 2 103
1 2 3 v2 v3
10 + v1 v3 + 0.08(v2 v3 ) = 0 ix =
10 103
0.4ix ix
v1 + 0.08v2 1.08v3 = 10 (1)
5 mA 5 k 20 k And KCL at node 2 gives us
v2
0.4ix + + ix = 0
5 103
v2 v2 v3
+ 0.6 =0
0 5 103 10 103
2.6v2 0.6v3 = 0 (2)
Fig. 1: A circuit where ix is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 1 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
2 k
Applying KCL at node 1, we have
v1 v3
5 103 + + 0.4ix = 0
10 k 2 103
1 2 3 v2 v3
10 + v1 v3 + 0.08(v2 v3 ) = 0 ix =
10 103
0.4ix ix
v1 + 0.08v2 1.08v3 = 10 (1)
5 mA 5 k 20 k And KCL at node 2 gives us
v2
0.4ix + + ix = 0
5 103
v2 v2 v3
+ 0.6 =0
0 5 103 10 103
2.6v2 0.6v3 = 0 (2)
Fig. 1: A circuit where ix is to be calculated.
And also KCL at node 3 yields
v3 v1 v3 v2 v3
+ + =0
2 103 10 103 20 103
10(v3 v1 ) + 2(v3 v2 ) + v3 = 0
10v1 2v2 + 13v3 = 0 (3)
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 1 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
2 k
Applying KCL at node 1, we have
v1 v3
5 103 + + 0.4ix = 0
10 k 2 103
1 2 3 v2 v3
10 + v1 v3 + 0.08(v2 v3 ) = 0 ix =
10 103
0.4ix ix
v1 + 0.08v2 1.08v3 = 10 (1)
5 mA 5 k 20 k And KCL at node 2 gives us
v2
0.4ix + + ix = 0
5 103
v2 v2 v3
+ 0.6 =0
0 5 103 10 103
2.6v2 0.6v3 = 0 (2)
Fig. 1: A circuit where ix is to be calculated.
And also KCL at node 3 yields
Writing Eqs. (1), (2) and (3) in matrix form, we get v3 v1 v3 v2 v3
+ + =0
1 0.08 -1.08 v1 10 2 103 10 103 20 103
0 2.6 -0.6 v2 = 0
10(v3 v1 ) + 2(v3 v2 ) + v3 = 0
-10 -2 13 v3 0 10v1 2v2 + 13v3 = 0 (3)
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 1 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
2 k
Solving the matrix for v2 and v3 using Cramers rule,
1 10 -1.08
10 k
1 2 3 0 0 -0.6
-10 0 13 60
ix v2 = = = 12 V
0.4ix 1 0.08 -1.08 5
0 2.6 -0.6
5 mA 5 k 20 k
-10 -2 13
0
Fig. 1: A circuit where ix is to be calculated.
Writing Eqs. (1), (2) and (3) in matrix form, we get
1 0.08 -1.08 v1 10
0 2.6 -0.6 v2 = 0
-10 -2 13 v3 0
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 1 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
2 k
Solving the matrix for v2 and v3 using Cramers rule,
1 10 -1.08
10 k
1 2 3 0 0 -0.6
-10 0 13 60
ix v2 = = = 12 V
0.4ix 1 0.08 -1.08
5
0 2.6 -0.6
5 mA 5 k 20 k
-10 -2 13
and,
1 0.08 10
0 2.6 0
0 -10 -2 0 260
v3 = = = 52 V
Fig. 1: A circuit where ix is to be calculated. 1 0.08 -1.08
5
0 2.6 -0.6
Writing Eqs. (1), (2) and (3) in matrix form, we get
-10 -2 13
1 0.08 -1.08 v1 10
0 2.6 -0.6 v2 = 0
-10 -2 13 v3 0
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 1 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
2 k
Solving the matrix for v2 and v3 using Cramers rule,
1 10 -1.08
10 k
1 2 3 0 0 -0.6
-10 0 13 60
ix v2 = = = 12 V
0.4ix 1 0.08 -1.08
5
0 2.6 -0.6
5 mA 5 k 20 k
-10 -2 13
and,
1 0.08 10
0 2.6 0
0 -10 -2 0 260
v3 = = = 52 V
Fig. 1: A circuit where ix is to be calculated. 1 0.08 -1.08
5
0 2.6 -0.6
Writing Eqs. (1), (2) and (3) in matrix form, we get
-10 -2 13
1 0.08 -1.08 v1 10 Hence,
0 2.6 -0.6 v2 = 0
v2 v3 12 52
-10 -2 13 v3 0 ix = = = 4 mA
10 103 10 103
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 1 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
10 k
0.4ix ix
5 mA 5 k 20 k
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
10 k
1 2 3
0.4ix ix
5 mA 5 k 20 k
4
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated.
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
10 k
1 2 3
0.4ix ix
5 mA 5 k 20 k
4
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated.
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
10 k
1 2 3
1 2 3
0.4ix ix
5 mA 5 k 20 k
4 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
10 k
1 2 3
1 2 3
0.4ix ix
5 mA 5 k 20 k
4 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
10 k
1 2 3
1 2 3
0.4ix ix
5 mA 5 k 20 k
4 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
10 k
1 2 3
1 2 3
0.4ix ix
5 mA 5 k 20 k
4 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
10 k
1 2 3
1 2 3
0.4ix ix
5 mA 5 k 20 k
4 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
10 k
1 2 3
1 2 3
0.4ix ix
5 mA 5 k 20 k
4 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
3 Assign branch voltages with polarity.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
+ vz
10 k
1 2 3
1 2 3
0.4ix ix
+
5 mA 5 k 20 k +
vx
vy
4 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
3 Assign branch voltages with polarity.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
+ vz
10 k
1 2 3
1 2 3
0.4ix ix
+
5 mA 5 k 20 k +
vx
vy
4 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
3 Assign branch voltages with polarity.
4 Apply KCL at appropriate node(s).
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
Here in nodal analysis using graph theory,
10 k you will see that you dont need that many
1 2 3
ix
number of equations as that of unknown
0.4ix
variables!
5 mA 5 k 20 k
4
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated.
+ vz
1 2 3
+
+
vx
vy
4
Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
Lets apply KCL at nodes of the selected tree:
10 k
1 2 3
0.4ix ix
5 mA 5 k 20 k
4
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated.
+ vz
1 2 3
+
+
vx
vy
4
Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
Lets apply KCL at nodes of the selected tree:
1 2
10 k
3 vx
Node 2: 0.4ix + + ix = 0
ix
5 103
0.4ix
vx vx vy vx vy
+ 0.6 = 0 ix =
5 mA 5 k 20 k 5 103 10 103 10 103
2.6vx 0.6vy = 0 (4)
vx vy
4 Node 4: 5 103 + + =0
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated. 5 103 20 103
+ vz 100 4vx vy = 0
vy = 100 4vx (5)
1 2 3
+
+
vx
vy
4
Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
Lets apply KCL at nodes of the selected tree:
1 2
10 k
3 vx
Node 2: 0.4ix + + ix = 0
ix
5 103
0.4ix
vx vx vy vx vy
+ 0.6 = 0 ix =
5 mA 5 k 20 k 5 103 10 103 10 103
2.6vx 0.6vy = 0 (4)
vx vy
4 Node 4: 5 103 + + =0
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated. 5 103 20 103
+ vz 100 4vx vy = 0
vy = 100 4vx (5)
1 2 3
Using Eq. (5) in Eq. (4), we have
+ 60
vx
+ 2.6vx 60 + 2.4vx = 0 vx = = 12 V
vy
5
4
Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
Lets apply KCL at nodes of the selected tree:
1 2
10 k
3 vx
Node 2: 0.4ix + + ix = 0
ix
5 103
0.4ix
vx vx vy vx vy
+ 0.6 = 0 ix =
5 mA 5 k 20 k 5 103 10 103 10 103
2.6vx 0.6vy = 0 (4)
vx vy
4 Node 4: 5 103 + + =0
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated. 5 103 20 103
+ vz 100 4vx vy = 0
vy = 100 4vx (5)
1 2 3
Using Eq. (5) in Eq. (4), we have
+ 60
vx
+ 2.6vx 60 + 2.4vx = 0 vx = = 12 V
vy
5
Substituting the value of vx in Eq. (5), we get
vy = 100 4 12 vy = 52 V
4
Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method: Using graph theory
Example - 1: Find ix in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2 k
Lets apply KCL at nodes of the selected tree:
1 2
10 k
3 vx
Node 2: 0.4ix + + ix = 0
ix
5 103
0.4ix
vx vx vy vx vy
+ 0.6 = 0 ix =
5 mA 5 k 20 k 5 103 10 103 10 103
2.6vx 0.6vy = 0 (4)
vx vy
4 Node 4: 5 103 + + =0
Fig. 2: A circuit where ix is to be calculated. 5 103 20 103
+ vz 100 4vx vy = 0
vy = 100 4vx (5)
1 2 3
Using Eq. (5) in Eq. (4), we have
+ 60
vx
+ 2.6vx 60 + 2.4vx = 0 vx = = 12 V
vy
5
Substituting the value of vx in Eq. (5), we get
vy = 100 4 12 vy = 52 V
4 Therefore, vx vy 12 52
ix = = = 4 mA
Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2 10 103 10 103
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 2 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 1.
8 15
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 3 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 1.
8 15
Step - 1: Identify nodes!
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 3 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 1.
8 15
0
Step - 2: Select a reference node and
+ vx
label it as 0 (not necessarily 0 but it is
+
100 V 4 vx /14 a practice to do so)!
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 3 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 1.
8 15
0
Step - 2: Select a reference node and
+ vx
label it as 0 (not necessarily 0 but it is
+
100 V 4 vx /14 a practice to do so)! Normally, a node
having maximum number of branches
connected to it has been chosen as a
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. reference node to simplify
computation!!
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 3 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 1.
8 15
1 2 0
Step - 3: Label other nodes too! Either
+ vx
node number 2 or 3 would have been a
+
100 V 4 vx /14 better option for the reference node
actually!
3
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 3 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 1.
8 15
1 2 0
Step - 4: Check at which node(s), KCL
+ vx
can be applied! We see that we can
+
100 V 4 vx /14 apply KCL at
- Node 2 but not on 1 and 3
3
because of 100 V source. OR
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. - The supernode formed by
combining nodes 1 and 3.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 3 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 1.
8 15
1 2 0
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
3
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
Applying KCL on node 2, we have
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 3 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 1.
8 15
1 2 0
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
3
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
Applying KCL on node 2, we have
v2 v1 v2 v2 v3
+ + =0
8 15 4
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 3 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 1.
8 15
1 2 0
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
3
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
Applying KCL on node 2, we have
v2 v1 v2 v2 v3
+ + =0
8 15 4
15(v2 v1 ) + 8v2 + 30(v2 v3 ) = 0
15v1 + 53v2 30v3 = 0 (1)
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 3 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 1.
8 15
1 2 0
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
3
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
Applying KCL on node 2, we have
v2 v1 v2 v2 v3
+ + =0
8 15 4
15(v2 v1 ) + 8v2 + 30(v2 v3 ) = 0
15v1 + 53v2 30v3 = 0 (1)
At terminals of 100 V source, we see that
v1 v3 = 100 (2)
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 3 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 1.
8 15
1 2 0 At node 0(dependent source!), we know
+ vx
v2 0 vx
+ =0
15 14
+ vx /14
100 V 4
3
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
Applying KCL on node 2, we have
v2 v1 v2 v2 v3
+ + =0
8 15 4
15(v2 v1 ) + 8v2 + 30(v2 v3 ) = 0
15v1 + 53v2 30v3 = 0 (1)
At terminals of 100 V source, we see that
v1 v3 = 100 (2)
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 3 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 1.
8 15
1 2 0 At node 0, we know
+ vx
v2 0 vx
+ =0
15 14
+ vx /14
100 V 4 14v2 + 15vx = 0
14v2 + 15(v1 v2 ) = 0
15v1 v2 = 0 (3)
3
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
Applying KCL on node 2, we have
v2 v1 v2 v2 v3
+ + =0
8 15 4
15(v2 v1 ) + 8v2 + 30(v2 v3 ) = 0
15v1 + 53v2 30v3 = 0 (1)
At terminals of 100 V source, we see that
v1 v3 = 100 (2)
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 3 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 1.
8 15
1 2 0 At node 0, we know
+ vx
v2 0 vx
+ =0
15 14
+ vx /14
100 V 4 14v2 + 15vx = 0
14v2 + 15(v1 v2 ) = 0
15v1 v2 = 0 (3)
3
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Using Eqs. (2) and (3) in Eq. (1), we have
15v1 + 53 15v1 30 (v1 100) = 0
Applying KCL on node 2, we have
3000
v2 v1 v2 v2 v3 v1 = = 4 V
+ + =0 750
8 15 4
15(v2 v1 ) + 8v2 + 30(v2 v3 ) = 0 Thus, from Eq. (3),
15v1 + 53v2 30v3 = 0 (1) v2 = 15 4 = 60 V
At terminals of 100 V source, we see that
v1 v3 = 100 (2)
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 3 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 1.
8 15
1 2 0 At node 0, we know
+ vx
v2 0 vx
+ =0
15 14
+ vx /14
100 V 4 14v2 + 15vx = 0
14v2 + 15(v1 v2 ) = 0
15v1 v2 = 0 (3)
3
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Using Eqs. (2) and (3) in Eq. (1), we have
15v1 + 53 15v1 30 (v1 100) = 0
Applying KCL on node 2, we have
3000
v2 v1 v2 v2 v3 v1 = = 4 V
+ + =0 750
8 15 4
15(v2 v1 ) + 8v2 + 30(v2 v3 ) = 0 Thus, from Eq. (3),
15v1 + 53v2 30v3 = 0 (1) v2 = 15 4 = 60 V
At terminals of 100 V source, we see that
v1 v3 = 100 (2) Therefore, vx = v1 v2 = 4 (60) = 56 V
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 3 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 2.
8 15
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 4 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 2.
8 15
Here: this time, bottom node is chosen
+ vx
as reference node!
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 4 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 2.
8 15
1 2 3
Here: this time, bottom node is chosen
+ vx
as reference node! By doing this, we
+
100 V 4 vx /14 know v1 = 100 V . That means, we
now need to find only v2 to get the
value of vx !!
0
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 4 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 2.
8 15
1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
Applying KCL on node 2, we have
v2 v1 v2 v2 v3
+ + =0
8 4 15
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 4 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 2.
8 15
1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
Current flowing from
node 2 to node 3 which
vx
0 equals to 14
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
Applying KCL on node 2, we have
v2 v1 v2 v2 v3
+ + =0
8 4 15
v1 = 100 V as node 0
being reference node!
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 4 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 2.
8 15
1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
Applying KCL on node 2, we have
v2 v1 v2 v2 v3
+ + =0
8 4 15
v2 100 v2 vx
+ = 0Adjuster (4)
8 4 14
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 4 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 2.
8 15
1 2 3 From control-voltage variable branch,
+ vx
vx = v1 v2 = 100 v2
+ v2 = 100 vx (5)
100 V 4 vx /14
0
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
Applying KCL on node 2, we have
v2 v1 v2 v2 v3
+ + =0
8 4 15
v2 100 v2 vx
+ = 0Adjuster (4)
8 4 14
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 4 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 2.
8 15
1 2 3 From control-voltage variable branch,
+ vx
vx = v1 v2 = 100 v2
+ v2 = 100 vx (5)
100 V 4 vx /14
Using Eqs. (5) in Eq. (4), we have
0 100 vx 100 100 vx vx
+ =0
8 4 14
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
7vx + 1400 14vx 4vx = 0
Applying KCL on node 2, we have 1400
vx = = 56 V
v2 v1 v2 v2 v3 25
+ + =0
8 4 15
v2 100 v2 vx
+ = 0Adjuster (4)
8 4 14
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 4 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0 0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 4: Graph of Fig. 3
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0 0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 4: Graph of Fig. 3
While forming a tree, we must
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0 0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 4: Graph of Fig. 3
1 2 3
While forming a tree, we must
Place all voltage sources in the tree and all current
sources in the co-tree.
0
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0 0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 4: Graph of Fig. 3
1 2 3
While forming a tree, we must
Place all voltage sources in the tree and all current
sources in the co-tree.
Place all control-voltage branches of
voltage-controlled dependent sources in the tree if
possible without forming any loop.
0
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0 0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 4: Graph of Fig. 3
1 2 3
While forming a tree, we must
Place all voltage sources in the tree and all current
sources in the co-tree.
Place all control-voltage branches of
voltage-controlled dependent sources in the tree if
possible without forming any loop.
0
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0 0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 4: Graph of Fig. 3
1 2 3
While forming a tree, we must
Place all voltage sources in the tree and all current
sources in the co-tree.
Place all control-voltage branches of
voltage-controlled dependent sources in the tree if
possible without forming any loop.
0
Complete the tree with the inclusion of node 3!
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0 0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 4: Graph of Fig. 3
1 2 3 Now, we assign (branch) voltages on twigs! From Fig. 3,
0
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0 0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 4: Graph of Fig. 3
1 + vx 2 3 Now, we assign (branch) voltages on twigs! From Fig. 3,
Place the voltage source (value with proper
+ polarity), 100 V , and the controlled-voltage, vx , on
respective twigs.
100 V
0
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0 0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 4: Graph of Fig. 3
1 + vx 2 + vy 3 Now, we assign (branch) voltages on twigs! From Fig. 3,
Place the voltage source (value with proper
+ polarity), 100 V , and the controlled-voltage, vx , on
respective twigs.
100 V
We now assign a new voltage variable, vy , on the
third tree branch/third twig.
0
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0 0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 4: Graph of Fig. 3
1 + vx 2 + vy 3 Now, we assign (branch) voltages on twigs! From Fig. 3,
Place the voltage source (value with proper
+ polarity), 100 V , and the controlled-voltage, vx , on
respective twigs.
100 V
We now assign a new voltage variable, vy , on the
third tree branch/third twig.
0 We therefore have two unknowns, vx , and vy , and
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree. we need to obtain two equations in terms of them.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0 0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 4: Graph of Fig. 3
1 + vx 2 + vy 3 Lets start analysis!
There are four nodes, but the presence of the
+ voltage source, 100 V , causes two of them to form
a single supernode.
100 V
0 Supernode!
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 1 2 3
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0 0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 4: Graph of Fig. 3
1 + vx 2 + vy 3 Lets start analysis!
There are four nodes, but the presence of the
+ voltage source, 100 V , causes two of them to form
a single supernode.
100 V
Kirchhoffs current law may be applied at any two
of the three nodes including supernodes.
0
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 Lets apply KCL at nodes: 2 and 3!
+ vx
+ vx /14
100 V 4
0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
1 + vx 2 + vy 3
+
100 V
0
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 Lets apply KCL at nodes: 2 and 3!
+ vx vx vx + 100 vy
2: + + =0
+ vx /14 8 4 15
100 V 4
15vx 30vx + 3000 + 8vy = 0
45vx 8vy = 3000 (6)
0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
1 + vx 2 + vy 3
+
100 V
0
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 Lets apply KCL at nodes: 2 and 3!
+ vx vx vx + 100 vy
2: + + =0
+ vx /14 8 4 15
100 V 4
15vx 30vx + 3000 + 8vy = 0
45vx 8vy = 3000 (6)
0 vy vx
3: =0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. 15 14
15
1 + vx 2 + vy 3 vy = vx (7)
14
15vx 30vx + 300 + 8vy = 0
+
100 V
0
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3 Lets apply KCL at nodes: 2 and 3!
+ vx vx vx + 100 vy
2: + + =0
+ vx /14 8 4 15
100 V 4
15vx 30vx + 3000 + 8vy = 0
45vx 8vy = 3000 (6)
0 vy vx
3: =0
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. 15 14
15
1 + vx 2 + vy 3 vy = vx (7)
14
15vx 30vx + 300 + 8vy = 0
Using Eqs. (7) in (6), we have
+ 15
45vx 8 vx = 3000
100 V 14
45 7vx + 4 15vx = 3000 7
0 21000
vx = = 56 V
375
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3
What if we apply KCL at Supernode !
+ vx - Simplest of all at least for this circuit!
+ At supernode,
100 V 4 vx /14 vx 100 + vx vx
+ + =0
8 4 14
7vx 1400 + 14vx + 4vx = 0
0
1400
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. vx = = 56 V
25
1 + vx 2 + vy 3 Because of the nature of this circuit, in this case,
we dont need any other equation to find vx as
KCL at supernode itself is suffice to get the value.
+
100 V
0
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3
What if we apply KCL at Supernode !
+ vx - Simplest of all at least for this circuit!
+ At supernode,
100 V 4 vx /14 vx 100 + vx vx
+ + =0
8 4 14
7vx 1400 + 14vx + 4vx = 0
0
1400
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. vx = = 56 V
25
1 + vx 2 + vy 3 Because of the nature of this circuit, in this case,
we dont need any other equation to find vx as
KCL at supernode itself is suffice to get the value.
+
100 V Summary of Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
0
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3
What if we apply KCL at Supernode !
+ vx - Simplest of all at least for this circuit!
+ At supernode,
100 V 4 vx /14 vx 100 + vx vx
+ + =0
8 4 14
7vx 1400 + 14vx + 4vx = 0
0
1400
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. vx = = 56 V
25
1 + vx 2 + vy 3 Because of the nature of this circuit, in this case,
we dont need any other equation to find vx as
KCL at supernode itself is suffice to get the value.
+
100 V Summary of Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
0
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3
What if we apply KCL at Supernode !
+ vx - Simplest of all at least for this circuit!
+ At supernode,
100 V 4 vx /14 vx 100 + vx vx
+ + =0
8 4 14
7vx 1400 + 14vx + 4vx = 0
0
1400
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. vx = = 56 V
25
1 + vx 2 + vy 3 Because of the nature of this circuit, in this case,
we dont need any other equation to find vx as
KCL at supernode itself is suffice to get the value.
+
100 V Summary of Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
0
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3
What if we apply KCL at Supernode !
+ vx - Simplest of all at least for this circuit!
+ At supernode,
100 V 4 vx /14 vx 100 + vx vx
+ + =0
8 4 14
7vx 1400 + 14vx + 4vx = 0
0
1400
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. vx = = 56 V
25
1 + vx 2 + vy 3 Because of the nature of this circuit, in this case,
we dont need any other equation to find vx as
KCL at supernode itself is suffice to get the value.
+
100 V Summary of Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
0 3 Assign branch voltages.
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 2: Use nodal analysis to find the value of vx in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
8 15
1 2 3
What if we apply KCL at Supernode !
+ vx - Simplest of all at least for this circuit!
+ At supernode,
100 V 4 vx /14 vx 100 + vx vx
+ + =0
8 4 14
7vx 1400 + 14vx + 4vx = 0
0
1400
Fig. 3: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. vx = = 56 V
25
1 + vx 2 + vy 3 Because of the nature of this circuit, in this case,
we dont need any other equation to find vx as
KCL at supernode itself is suffice to get the value.
+
100 V Summary of Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
0 3 Assign branch voltages.
4 Apply KCL at appropriate node(s).
Fig. 5: Selecting an appropriate tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 5 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V
+
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
5
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 6 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
Steps for nodal analysis:
::::::::::::::::::::::
2A
30 V
+
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
5
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 6 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
Steps for nodal analysis:
::::::::::::::::::::::
2A
30 V Count number of nodes. Select one of the
node as reference node (node 0) and label
+
the rest!
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
5
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 6 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
Steps for nodal analysis:
::::::::::::::::::::::
2A
30 V Count number of nodes. Select one of the
1 0
node as reference node (node 0) and label
+
the rest!
+
+ Best candidate for reference node for this
1A 4 vx 6vx circuit: Top right node or Bottom left
3A node! Reduces unknown node variables!!
2 3
5
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 6 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
Steps for nodal analysis:
::::::::::::::::::::::
2A
30 V Count number of nodes. Select one of the
1 0
node as reference node (node 0) and label
+
the rest!
+
+ Best candidate for reference node for this
1A 4 vx 6vx circuit: Top right node or Bottom left
3A node! Reduces unknown node variables!!
Look out for voltage source(s) and nodes
2 3
5 they are connected to!
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 6 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
Steps for nodal analysis:
::::::::::::::::::::::
2A
30 V Count number of nodes. Select one of the
1 0
node as reference node (node 0) and label
+
the rest!
+
+ Best candidate for reference node for this
1A 4 vx 6vx circuit: Top right node or Bottom left
3A node! Reduces unknown node variables!!
Look out for voltage source(s) and nodes
2 3
5 they are connected to!
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 6 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
Steps for nodal analysis:
::::::::::::::::::::::
2A
30 V Count number of nodes. Select one of the
1 0
node as reference node (node 0) and label
+
the rest!
+
+ Best candidate for reference node for this
1A 4 vx 6vx circuit: Top right node or Bottom left
3A node! Reduces unknown node variables!!
Look out for voltage source(s) and nodes
2 3
5 they are connected to!
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Apply KCL at either
Node 2 (bottom left) when top right node
is a reference node! OR
Supernode! Supernode (formed by combining top left,
top right, and bottom right nodes)!
Reference node here is bottom left node!!
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 6 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
When top right node is selected for the refer-
2A
30 V ence node, we have
1 0
+
v1 = 30 V
+
+ v3 = 6vx
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A vx = v1 v2 = 30 v2 v2 = 30 vx
2 3
5
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 6 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
When top right node is selected for the refer-
2A
30 V ence node, we have
1 0
+
v1 = 30 V
+
+ v3 = 6vx
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A vx = v1 v2 = 30 v2 v2 = 30 vx
Applying KCL at node 2:
2 3
5
v2 v1 v2 v3
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. 1+ +3+ =0
4 5
vx 30 vx (6vx )
+2+ =0
4 5
5vx + 40 + 120 + 20vx = 0
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 6 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
When top right node is selected for the refer-
2A
30 V ence node, we have
1 0
+
v1 = 30 V
+
+ v3 = 6vx
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A vx = v1 v2 = 30 v2 v2 = 30 vx
Applying KCL at node 2:
2 3
5
v2 v1 v2 v3
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. 1+ +3+ =0
4 5
vx 30 vx (6vx )
+2+ =0
160 4 5
vx = = 10.6667 V 5vx + 40 + 120 + 20vx = 0
15
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 6 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1: Using supernode idea
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V
+
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
5
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 7 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1: Using supernode idea
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
Supernode method:
::::::::::::::::::
2A
30 V
+
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
5
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 7 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1: Using supernode idea
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
Supernode method:
::::::::::::::::::
2A
30 V Combine the top left, the top right and the
bottom right nodes to form a supernode as
+
voltage sources are connected to them!
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
5
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
Supernode!
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 7 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1: Using supernode idea
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
Supernode method:
::::::::::::::::::
2A
30 V Combine the top left, the top right and the
bottom right nodes to form a supernode as
+
voltage sources are connected to them!
+
+ Out of 4 nodes after forming supernode,
1A 4 vx 6vx only bottom left node is left and is named
3A as the reference node!!
5
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 7 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1: Using supernode idea
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
Supernode method:
::::::::::::::::::
2A
30 V Combine the top left, the top right and the
1 2
bottom right nodes to form a supernode as
+
voltage sources are connected to them!
+
+ Out of 4 nodes after forming supernode,
1A 4 vx 6vx only bottom left node is left and is named
3A as the reference node!!
0 3
5
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 7 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1: Using supernode idea
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
Supernode method:
::::::::::::::::::
2A
30 V Combine the top left, the top right and the
1 2
bottom right nodes to form a supernode as
+
voltage sources are connected to them!
+
+ Out of 4 nodes after forming supernode,
1A 4 vx 6vx only bottom left node is left and is named
3A as the reference node!!
We now can apply KCL at supernode!!!
0 3
5
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 7 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1: Using supernode idea
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
From the circuit, we have
2A
30 V v1 = vx
1 2
+
v1 v2 = 30 V v2 = vx 30
+
+ v2 v3 = 6vx v3 = 5vx 30
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
0 3
5
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 7 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 1: Using supernode idea
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 1 using nodal analysis.
From the circuit, we have
2A
30 V v1 = vx
1 2
+
v1 v2 = 30 V v2 = vx 30
+
+ v2 v3 = 6vx v3 = 5vx 30
1A 4 vx 6vx
Applying KCL at supernode:
3A v1 v3
1+ 3+ +22=0
4 5
0
5
3 vx 5vx 30
2+ =0
Fig. 1: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. 4 5
5vx 40 20vx 120 = 0
160
vx = = 10.6667 V
15
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 7 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V
+
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
5
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V
1 2
+
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V
1 2
+
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V
1 2
1 2
+
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5 3 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V
1 2
1 2
+
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5 3 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
Branches corresponding 1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
to current sources on the
co-tree!
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V
1 2
1 2
+
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5 3 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V
1 2
1 2
+
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5 3 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V
1 2
1 2
+
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5 3 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
Does inclusion of this 1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
control-voltage branch
create any loop?
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V
1 2
1 2
+
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5 3 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
This branch must be on
co-tree!
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V
1 2
1 2
+
+
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5 3 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
3 Assign branch voltages with polarity.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V
1 2 + 30 V
1 2
+
+
+ + +
1A 4 vx 6vx
vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5 3 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
3 Assign branch voltages with polarity.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V
1 2 + 30 V
1 2
+
+
+ + +
1A 4 vx 6vx
vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5 3 4
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Fig. 3: Graph of Fig. 2
Steps! Nodal Analysis using Graph theory:
1 Draw a graph!
2 Select a tree.
3 Assign branch voltages with polarity.
4 Apply KCL at appropriate node(s).
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V Observation for KCL at nodes:
1 2
+
Four nodes: 1, 2, 3, and 4.
+
No KCL at nodes to which voltage sources are connected
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
1 + 30 V 2
+ +
vx 6vx
3 4
Fig. 3: Appropriate tree of Fig. 2
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V Observation for KCL at nodes:
1 2
+
Four nodes: //
1,////
2, 3, and //
4.
+
No KCL at nodes to which voltage sources are connected.
+
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
KCL can be applied at node 3!
3 4
5
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. Nodal analysis using graph theory, you will see that you dont need
that many number of equations as that of unknown node voltages!
Its all about branch voltages when we use graph theory in nodal
analysis!!
1 + 30 V 2
+ +
vx 6vx
3 4
Fig. 3: Appropriate tree of Fig. 2
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V Applying KCL at node 3 of the selected tree:
1 2
vx vx + 30 + 6vx
+
+ Node 3: 1+ +3+ =0
+ 4 5
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
1 + 30 V 2
+ +
vx 6vx
3 4
Fig. 3: Appropriate tree of Fig. 2
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V Applying KCL at node 3 of the selected tree:
1 2
vx vx + 30 + 6vx
+
+ Node 3: 1+ +3+ =0
+ 4 5
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
Twig voltage between nodes 3 and 1
Twig resistance
1 + 30 V 2
+ +
vx 6vx
3 4
Fig. 3: Appropriate tree of Fig. 2
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V Applying KCL at node 3 of the selected tree:
1 2
vx vx + 30 + 6vx
+
+ Node 3: 1+ +3+ =0
+ 4 5
1A 4 vx 6vx
3A
3 4
5
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated.
Twig voltage between nodes 3 and 1
Twig resistance
1 + 30 V 2
+ +
vx 6vx
Link voltage between nodes 3 and 4 = Sum of twig voltages between them
Link resistance
3 4
Fig. 3: Appropriate tree of Fig. 2
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Nodal Analysis
Alternative Method - 2/3: Using graph theory
Example - 3: Find the value of vx in the circuit of Fig. 2 using nodal analysis.
2A
30 V Applying KCL at node 3 of the selected tree:
1 2
vx vx + 30 + 6vx
+
+ Node 3: 1+ +3+ =0
+ 4 5
1A 4 vx 6vx
vx 30 + 5vx
3A +2+ =0
4 5
3
5
4 5vx + 40 + 120 + 20vx = 0
Fig. 2: A circuit where vx is to be calculated. 160
vx = = 10.6667 V
15
1 + 30 V 2
+ +
vx 6vx
3 4
Fig. 3: Appropriate tree of Fig. 2
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 8 / 10
Text Books & References
W.H. Hayt, J.E. Kemmerly, S.M. Durbin
Engineering Circuit Analysis, 8/e.
MH, 2012.
M. E. Van Valkenburg
Network Analysis, 3/e.
PHI, 2005.
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 9 / 10
Khublei Shibun!
Thank You!
Any Question?
AeL. je. siHh/L. J. Singh(nehu/NEHU) EE - 304 Electrical Network Theory 06.09.2016 10 / 10
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Final Exam SolutionsDokument4 SeitenFinal Exam Solutionsdredg0661Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 ENADokument4 SeitenAssignment 1 ENATalha MazharNoch keine Bewertungen
- thí nghiệm lý 2 03Dokument5 Seitenthí nghiệm lý 2 03Hoang Anh PhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 47498827FinalExamSolutionsDokument3 Seiten47498827FinalExamSolutionsMahdi WashahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid 2020 SDokument11 SeitenMid 2020 Samedpv56Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bee Report1Dokument5 SeitenBee Report1Rajeev kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGG 325 - Electric Circuits and Systems Midterm ExaminationDokument9 SeitenENGG 325 - Electric Circuits and Systems Midterm ExaminationTaha EtemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report 3Dokument5 SeitenReport 3Kiệt Như LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 2meshandnodeanalysis-Jameel23oct23Dokument30 SeitenCH 2meshandnodeanalysis-Jameel23oct23Gorin GorinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument15 SeitenChapter 2Abd Alkader Alwer100% (1)
- DC-Lab Report 05Dokument9 SeitenDC-Lab Report 05Shahriar Ahsan JohaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report 3Dokument4 SeitenReport 3namNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mesh Analysis and Nodal Analysis: Mapúa UniversityDokument9 SeitenMesh Analysis and Nodal Analysis: Mapúa UniversityRick AlvientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic PhysicsDokument14 SeitenAtomic PhysicssmeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2 GRADE 12 Lesson 1 Electric Charge, Force and FieldsDokument8 SeitenPhysics 2 GRADE 12 Lesson 1 Electric Charge, Force and FieldsAryhen Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thevenin Theorem 2Dokument18 SeitenThevenin Theorem 2monkeydluffyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elec9713-11 Tutorial 2 Solutions PDFDokument6 SeitenElec9713-11 Tutorial 2 Solutions PDFRajeev ValunjkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4: Power Flow: Prof. Tom Overbye Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M UniversityDokument45 SeitenLecture 4: Power Flow: Prof. Tom Overbye Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M UniversityManuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power System Analysis: Newton-Raphson Power FlowDokument44 SeitenPower System Analysis: Newton-Raphson Power FlowPenny87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatics PDFDokument17 SeitenElectrostatics PDFcolorado wildernessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 1Faisal IrfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 476 Power System AnalysisDokument35 SeitenECE 476 Power System AnalysisFady MichealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Anuj Engineer SAP ID: 60001170004 Subject: A&M Vlsi IndexDokument47 SeitenName: Anuj Engineer SAP ID: 60001170004 Subject: A&M Vlsi IndexPrasad mohiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2 (Spring 2012) : (Solution)Dokument4 SeitenAssignment 2 (Spring 2012) : (Solution)AmeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- EngineeringDokument7 SeitenEngineeringDevaki sitoulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex 3Dokument5 SeitenEx 3minh hoàng nguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inductor and Free Oscillation in RLC CircuitDokument5 SeitenInductor and Free Oscillation in RLC CircuitNguyễn Đức MạnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inductor and Free Oscillation in RLC CircuitDokument5 SeitenInductor and Free Oscillation in RLC CircuitNguyễn Đức MạnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSA FileDokument4 SeitenPSA File2K21B640 Akagra GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cie-3 III Sem Applied Mathematics-III 20cse31a 20ise31a QP Odd Sem 2021-2022Dokument1 SeiteCie-3 III Sem Applied Mathematics-III 20cse31a 20ise31a QP Odd Sem 2021-2022ShivangNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssignmentDokument6 SeitenAssignmentA7 XmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Btech Ee 3 Sem Electromagnetic Field Theory Kee301 2022Dokument2 SeitenBtech Ee 3 Sem Electromagnetic Field Theory Kee301 2022Priyanshu SuryavanshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study - Material - 2021-22 All Papers 1670660608584Dokument18 SeitenStudy - Material - 2021-22 All Papers 1670660608584lokhandemayank9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Report 3Dokument4 SeitenExperimental Report 3Kiệt Như LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter3 NodalDokument45 SeitenChapter3 Nodalpsychic_jason0071319Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Mesh and Nodal AnalysisDokument27 SeitenChapter 3 Mesh and Nodal Analysisthines raveentraanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELECTRON DIFFRACTION ReportDokument4 SeitenELECTRON DIFFRACTION Reportsohaila gaberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Solutions in Electrical Circuits Using Nodal and Mesh AnalysisDokument4 SeitenComparison of Solutions in Electrical Circuits Using Nodal and Mesh AnalysisAl MahinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Sample PaperDokument51 SeitenPhysics Sample PaperD̥ͦi̥ͦp̥ͦḁͦy̥ͦḁͦn̥ͦ B͜͡a͜͡n͜͡e͜͡r͜͡j͜͡e͜͡e͜͡Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECE530 - Fall2013 - Lect5 (SLAJDOVI 23,24,25)Dokument42 SeitenECE530 - Fall2013 - Lect5 (SLAJDOVI 23,24,25)Alen SuljicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major SolsDokument4 SeitenMajor SolsSumit BahlNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSIGNMENT - V (Numerical Differentiation and Integration + Matrices and System of Linear Equations) Course: MCSC 202Dokument1 SeiteASSIGNMENT - V (Numerical Differentiation and Integration + Matrices and System of Linear Equations) Course: MCSC 202Rojan PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT2Dokument24 SeitenCAT2SANJUCTA CHOUDHURYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capitulo3 Gillat PDFDokument8 SeitenCapitulo3 Gillat PDFluis fernando riojas pecheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers of Sample Paper 5 10 Physics 12Dokument47 SeitenAnswers of Sample Paper 5 10 Physics 12Pankaj SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook Electric Circuits 10Th Edition Nilsson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDokument68 SeitenEbook Electric Circuits 10Th Edition Nilsson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFalexandercampbelldkcnzafgtw100% (10)
- HW2 20220367 신동민-1Dokument7 SeitenHW2 20220367 신동민-1sdongmin488Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Paper 2 Sf026/2 PSPM Semester 2 Session 2016/2017Dokument13 SeitenPhysics Paper 2 Sf026/2 PSPM Semester 2 Session 2016/2017Voon Chen WeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Solutions (Global Edition) : Prob. 8.1Dokument11 SeitenChapter 8 Solutions (Global Edition) : Prob. 8.1성민김Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECS203 2014 CH 10 U4Dokument23 SeitenECS203 2014 CH 10 U4luzmancia0204Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eca-Ese Questions (Dsy Students) Max. Marks 60 Duration 1.30 HRDokument4 SeitenEca-Ese Questions (Dsy Students) Max. Marks 60 Duration 1.30 HRPrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final RP3Dokument4 SeitenFinal RP3Đình TrườngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics of Electronic Devices Problem 1 Diode Application & BJT Prob 1Dokument17 SeitenPhysics of Electronic Devices Problem 1 Diode Application & BJT Prob 1Luật Lê QuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrillsDokument93 SeitenDrillsjulioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21 - ENG - 102869 Practical 02Dokument13 Seiten21 - ENG - 102869 Practical 02Waruna NirmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Problem 2 A 20 F Capacitor Has Energy 10cos 377Dokument5 SeitenChapter 6 Problem 2 A 20 F Capacitor Has Energy 10cos 377Wad ZzupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ion Beams for Materials AnalysisVon EverandIon Beams for Materials AnalysisR. Curtis BirdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionVon EverandAdvanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Odd Semester TTDokument1 SeiteOdd Semester TTJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Framing WorksheetDokument4 SeitenFraming WorksheetQiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MHRD IICs Brochure PDFDokument5 SeitenMHRD IICs Brochure PDFJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The /hoffset Is Now 0.0pt The /oddsidemargin Is Now - 13.04362ptDokument2 SeitenThe /hoffset Is Now 0.0pt The /oddsidemargin Is Now - 13.04362ptJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beamer Bullet Tikz01Dokument1 SeiteBeamer Bullet Tikz01Joyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- RGB Color Codes PDFDokument11 SeitenRGB Color Codes PDFJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beamer BibLaTeXe001Dokument2 SeitenBeamer BibLaTeXe001Joyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Listings PDFDokument61 SeitenListings PDFJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE304 - 20160906 NodalDokument7 SeitenEE304 - 20160906 NodalJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Qrcode Package: Quick Response Code Generation in L TEXDokument5 SeitenThe Qrcode Package: Quick Response Code Generation in L TEXJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nodal Analysis TestDokument13 SeitenNodal Analysis TestJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tie Set MatrixDokument88 SeitenTie Set MatrixJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nodal Analysis TestDokument13 SeitenNodal Analysis TestJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTW Guide Table-Figures 9-30-08 PDFDokument17 SeitenHTW Guide Table-Figures 9-30-08 PDFJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incidence Matrix WSDokument119 SeitenIncidence Matrix WSJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong - 793 022Dokument2 SeitenDepartment of Electronics & Communication Engineering North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong - 793 022Joyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joip - Rkas: Ee - 304 Electrical Network TheoryDokument20 SeitenJoip - Rkas: Ee - 304 Electrical Network TheoryJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE304 - 20160912 MeshDokument13 SeitenEE304 - 20160912 MeshJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong - 793 022Dokument1 SeiteDepartment of Electronics & Communication Engineering North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong - 793 022Joyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE304 - 20160822 Inc - MatDokument6 SeitenEE304 - 20160822 Inc - MatJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE304 - 20160912 MeshDokument13 SeitenEE304 - 20160912 MeshJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering North-Eastern Hill University Superposition PrincipleDokument4 SeitenDepartment of Electronics & Communication Engineering North-Eastern Hill University Superposition PrincipleJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE304 - 20160829 Tie-SetDokument5 SeitenEE304 - 20160829 Tie-SetJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- L TEX Is Very SophisticatedDokument1 SeiteL TEX Is Very SophisticatedJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Book CoverDokument22 SeitenE Book CoverJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE304 - 20160819 GRPH ThryDokument8 SeitenEE304 - 20160819 GRPH ThryJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECV917 Lab RPRT (Main) v5Dokument37 SeitenECV917 Lab RPRT (Main) v5Joyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADokument1 SeiteAJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pgfmanual PDFDokument1.161 SeitenPgfmanual PDFJoyprakash LairenlakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1Dokument15 SeitenPresentation 1Ashish SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On Toy WarDokument15 SeitenCase Study On Toy Warneeraj1412Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCH 101 Course Plan - 2021Dokument4 SeitenNCH 101 Course Plan - 2021RamishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4TH Semester B.A., LL.B B.A., LL.B (H)Dokument14 Seiten4TH Semester B.A., LL.B B.A., LL.B (H)BISTIRNA BARUANoch keine Bewertungen
- (Handbook of Exploration Geochemistry 5) KALEVI KAURANNE (Eds.) - Regolith Exploration Geochemistry in Arctic and Temperate Terrains-Elsevier Science (1992) PDFDokument445 Seiten(Handbook of Exploration Geochemistry 5) KALEVI KAURANNE (Eds.) - Regolith Exploration Geochemistry in Arctic and Temperate Terrains-Elsevier Science (1992) PDFSam BasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dde 23Dokument3 SeitenDde 23omboyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Martin Luther King. Answer KeyDokument1 SeiteMartin Luther King. Answer KeyOleg MuhendisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jean Faber and Gilson A. Giraldi - Quantum Models For Artifcial Neural NetworkDokument8 SeitenJean Faber and Gilson A. Giraldi - Quantum Models For Artifcial Neural Networkdcsi3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Purification and Detection of Linamarin From Cassava Root Cortex by HPLCDokument5 SeitenPurification and Detection of Linamarin From Cassava Root Cortex by HPLCJohn Eiver BelalcazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module1 Lesson 1Dokument22 SeitenModule1 Lesson 1ARLENE NORICONoch keine Bewertungen
- The Importance of Instructional MaterialDokument3 SeitenThe Importance of Instructional MaterialJheramae SegoviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Access 1 Nahwu PDFDokument234 SeitenAccess 1 Nahwu PDFAmru-Rizal RazaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Executive ReportDokument51 SeitenExecutive ReportPrecelle Joy YangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government vs. AlburalDokument2 SeitenGovernment vs. Alburalpoppy2890100% (2)
- Project ExtensionDokument27 SeitenProject Extensionrajith rajeevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powerful Hero Dpa Rtsal Protective DeityDokument50 SeitenPowerful Hero Dpa Rtsal Protective DeityjinpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3-PIC IO Port ProgrammingDokument36 SeitenChapter 3-PIC IO Port Programmingouterrace67% (3)
- SU05Dokument114 SeitenSU05saopaulo100% (1)
- Radical Disciple 1Dokument4 SeitenRadical Disciple 1Milton LucasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Ftir Apodization Functions Using Modeled and Measured Spectral DataDokument4 SeitenComparison of Ftir Apodization Functions Using Modeled and Measured Spectral Dataገዛኽኝ ሱፋNoch keine Bewertungen
- Culture Shock Refers To The Feelings of Confusion and Uncertainty That You Experience When You Come Into Contact With A New CultureDokument13 SeitenCulture Shock Refers To The Feelings of Confusion and Uncertainty That You Experience When You Come Into Contact With A New CultureRetno WulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSTLDokument4 SeitenJSTLSanjeeb PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAM386 Tannenberg 1914 Destruction of The Russian Second ArmyDokument97 SeitenCAM386 Tannenberg 1914 Destruction of The Russian Second ArmyCesarPastenSozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture05e Anharmonic Effects 2Dokument15 SeitenLecture05e Anharmonic Effects 2Saeed AzarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University Mid La Union CampusDokument5 SeitenDon Mariano Marcos Memorial State University Mid La Union CampusSam Bernardo100% (2)
- Preliminary Basic Definitions Definition: 1 GraphDokument27 SeitenPreliminary Basic Definitions Definition: 1 GraphramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - Modes of ExtinguishmentDokument19 SeitenChapter 4 - Modes of ExtinguishmentcartyeolNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Automated Machine Vision Based System For Fruit Sorting and GradingDokument6 SeitenAn Automated Machine Vision Based System For Fruit Sorting and GradingMekaTronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing Guide - Baloch, RafayDokument2 SeitenEthical Hacking and Penetration Testing Guide - Baloch, RafayAyush PoptaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examples in C++Dokument39 SeitenExamples in C++ZhvannNoch keine Bewertungen