Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
MIT2 25F13 EquationSheet
Hochgeladen von
Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MIT2 25F13 EquationSheet
Hochgeladen von
Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Boundary Layer Equations ( !
(x) << x )
Reynolds Transport Theorem Bcv = "cv !dV = "cv #b dV The Equations of
Fluid Mechanics
dBsys d
# "v "v & "p "2 v
! % vx x + v y x ( = ) + 2x
Form A:
dt
= " !dV + "CS (#b) ( v $ vc ) % n dA
dt cv Gareth H. McKinley
$ "x "y ' "x "y
dBsys !" December 2006
"p " !vx !v y % Form B: =#
% dV + ( ( &b)v ' n dA
0=! $# !x + !y '& = 0 dt $ !t CS
"y cv
Young-Laplace Equation
Cauchy Momentum Equation Continuity
(
Free Surface Flows; p ! "# $2 h $x 2 ) !
Dv
= "#p + # $ % + !g
1 D!
= " (# $ v )
# 1
!p = " % + (
1 &
$ R1 R2 '
!h !Q" h Dt ! Dt
+ = 0 where Q! = " vx! dy
!t !x 0
!h $ " gh sin # ' !h " g cos # ! * 3 !h -
2 Newtonian Constitutive Equation
+&
!t %
) =
( !x
,h
3 !x + !x .
/ {
! = "v + ("v)t = #! } Incompressible Flow
!"v = 0
Quasi-Fully Developed Flow (Lubrication approximation) Navier-Stokes Equation for isothermal flow Hydrostatics
h L << 1 , ReL ( h L ) << 1 , h (!" ) << 1 )
2 2 of an incompressible Newtonian fluid !p = "(g # a)
"p
Dv % "v (
#p #2 v ! = ! & + v #$ v ) = +$p + $ 2 v + !g
0!" + 2x + $ gx 0! + # gy Dt ' "t *
#x #y "y
Across streamlines
Inviscid fluid Re ! ! (outward pointing normal n)
Very viscous fluid (Stokes Flow; Re ! 0 ) (Euler Equation)
0 = !"p + " 2 v + #g !p " v 2
!
Dv
= "#p + !g =
Dt !n R
Steady Irrotational Flow ( ! = 0 )
Unsteady Bernoulli Equation along a streamline
Velocity potential v = !"
! =0 2 2
# !v " dr + # dp
(! " v) = ! # = 0 ( ) + ( (2 & (1 ) = 0
2 ! =0
2 v 2 & 2 v1 + %
1 2
% 1 2
$ !t $ '
1 1
Kutta-Zhukowski Theorem Steady Bernoulli Equation along a streamline for
! = $ " # dA = !
$ v # ds an inviscid flow of an incompressible fluid
L = !V" D=0 ( )
2 v 2 ! 2 v1 +
1 2 1 2 1
"
( p2 ! p1 ) + g ( z2 ! z1 ) = 0
MIT OpenCourseWare
http://ocw.mit.edu
2.25 Advanced Fluid Mechanics
Fall 2013
For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- PICP Manual 3rd Edition PDFDokument62 SeitenPICP Manual 3rd Edition PDFanmolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stat Mech Mcquarrie ch3-5 SolnsDokument20 SeitenStat Mech Mcquarrie ch3-5 Solnsmalicepk80% (5)
- Optis - Ow - LM - Ug - 2014 SP1 PDFDokument251 SeitenOptis - Ow - LM - Ug - 2014 SP1 PDFRaghavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cd300m Parts BreakdownDokument10 SeitenCd300m Parts BreakdownAmanda FitzgeraldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemd CheatsheetDokument1 SeiteSystemd Cheatsheetzaffa11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transport Phenomena in Biological Systems 2nd Edition Truskey Solutions ManualDokument14 SeitenTransport Phenomena in Biological Systems 2nd Edition Truskey Solutions ManualRobertMaddoxpdiym100% (16)
- Freno Motor ISMDokument6 SeitenFreno Motor ISMFabiiam Kiimtero100% (2)
- VSL Technical Report - PT ExternalDokument36 SeitenVSL Technical Report - PT ExternalTran Nguyen KhiemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structured Text CheatsheetDokument1 SeiteStructured Text CheatsheetMauricio Rodriguez0% (1)
- Gapura Company Profile - 17mar17Dokument43 SeitenGapura Company Profile - 17mar17als izmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ahmad Mustaqiem CVDokument4 SeitenAhmad Mustaqiem CVAhmad MustaqiemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Eqs FinalDokument1 SeiteFluid Eqs FinaladifogelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potential Stream Function V VDokument2 SeitenPotential Stream Function V VJorge EstebanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiche - Equations Cable Coaxial - 1pDokument1 SeiteFiche - Equations Cable Coaxial - 1pzakariiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dwnload Full Transport Phenomena in Biological Systems 2nd Edition Truskey Solutions Manual PDFDokument36 SeitenDwnload Full Transport Phenomena in Biological Systems 2nd Edition Truskey Solutions Manual PDFjoseph8gfth100% (8)
- Formula Sheet + Charts Must Be Returned A3er The ExamDokument19 SeitenFormula Sheet + Charts Must Be Returned A3er The ExamRaphael ErfeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capture D'écran . 2022-10-16 À 17.57.03Dokument39 SeitenCapture D'écran . 2022-10-16 À 17.57.03Nabil SôùlTãnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potential Flow Theory: 2.016 HydrodynamicsDokument2 SeitenPotential Flow Theory: 2.016 HydrodynamicsJorge EstebanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP WireDrawingDokument29 SeitenMP WireDrawingMadhusudhan ModemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Math Prelim 09Dokument19 Seiten2 Math Prelim 09Denis GithinjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rudder DesignDokument66 SeitenRudder DesignHrithin TNoch keine Bewertungen
- 전력 4장Dokument25 Seiten전력 4장이승혁Noch keine Bewertungen
- Potential Lines: Spherical Coordinates (r, θ, ϕ)Dokument2 SeitenPotential Lines: Spherical Coordinates (r, θ, ϕ)Jorge EstebanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diy Acrylicbutterfly LampDokument28 SeitenDiy Acrylicbutterfly LampElan ChezhianNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Derivative Part 1 (Handout With Solutions)Dokument10 SeitenThe Derivative Part 1 (Handout With Solutions)Jay GaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.62 Physical Chemistry Ii: Mit OpencoursewareDokument7 Seiten5.62 Physical Chemistry Ii: Mit OpencoursewareDiana UrizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample For Solution Manual Convective Heat and Mass Transfer 2nd Edition by GhiaasiaanDokument43 SeitenSample For Solution Manual Convective Heat and Mass Transfer 2nd Edition by Ghiaasiaanاحمد الدلالNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fractional Calculus: Basic Theory and Applications: (Part I)Dokument23 SeitenFractional Calculus: Basic Theory and Applications: (Part I)Oscar Mtz FtsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Propagation of Uncertainty in Dynamic Systems: Uncertain Linear, Time-Varying (LTV) Dynamic Model"Dokument13 SeitenPropagation of Uncertainty in Dynamic Systems: Uncertain Linear, Time-Varying (LTV) Dynamic Model"tariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06Dokument6 Seiten06gildas assoumou allogoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Stats Reference SheetDokument7 SeitenAP Stats Reference SheetRamenKing12Noch keine Bewertungen
- ACE 15 Lab Exercise 1Dokument5 SeitenACE 15 Lab Exercise 1Darnell HendersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- מתכונת 1 - בלי פתרוןDokument4 Seitenמתכונת 1 - בלי פתרוןNoya DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
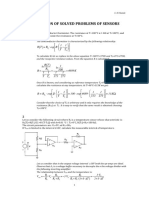
- Solved ProblemsDokument16 SeitenSolved ProblemsB ShreeruthraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math136 w23 WA3 SolnDokument8 SeitenMath136 w23 WA3 Solnyasin pakzatNoch keine Bewertungen
- P361 Lecture2 Vector Differential Integral OperatorsDokument28 SeitenP361 Lecture2 Vector Differential Integral OperatorsPatrick SibandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rev 2 Com ADokument4 SeitenRev 2 Com AThaviksha BulathsinhalaNoch keine Bewertungen
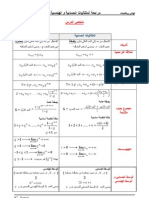
- Alhndsa Alfdhaiia Mlkhs Aldrs 3Dokument2 SeitenAlhndsa Alfdhaiia Mlkhs Aldrs 3rayan mrabtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ملخص مركز في رياضياتDokument39 Seitenملخص مركز في رياضياتHakika ZakariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02Dokument15 Seiten02Franc ChedjouNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.4 TM - Graphical MethodDokument14 Seiten2.4 TM - Graphical MethodFernando Intriago VélizNoch keine Bewertungen
- AME 3253 Aerodynamics Practice v03.0Dokument3 SeitenAME 3253 Aerodynamics Practice v03.0jfishryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN Rexroth变量斜轴柱塞马达A6VEDokument12 SeitenCN Rexroth变量斜轴柱塞马达A6VEcunvip163.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metodo Dirichlet Potencial ConstanteDokument4 SeitenMetodo Dirichlet Potencial ConstanteSantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 12 Formula SheetDokument1 SeiteMath 12 Formula Sheetcanuckskick71% (17)
- Résumé Suites Arith-GeomDokument1 SeiteRésumé Suites Arith-GeomcherazerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial2 Concept and Exercises of Electrostatics 0219Dokument16 SeitenTutorial2 Concept and Exercises of Electrostatics 0219Rakib Al MahdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. P. Calculus Ab Prep Sheet: Graphing CalculatorsDokument15 SeitenA. P. Calculus Ab Prep Sheet: Graphing CalculatorsrheoguqNoch keine Bewertungen
- FormulasDokument2 SeitenFormulaspradeep250946Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ece 2005 Soln 2Dokument7 SeitenEce 2005 Soln 2api-25903748Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integration by PartsDokument3 SeitenIntegration by PartsOliverSpurgeon0% (1)
- Fractional Calculus: Basic Theory and Applications: (Part III)Dokument18 SeitenFractional Calculus: Basic Theory and Applications: (Part III)Danyal SharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integral TableDokument4 SeitenIntegral TableGemmaCollV35Noch keine Bewertungen
- Overview Aerodynamics 2017Dokument10 SeitenOverview Aerodynamics 2017marcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra P 09 Ex 2007 IIIDokument2 SeitenAlgebra P 09 Ex 2007 IIIJean IngaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barrasi1 (TechnoElectroDokument70 SeitenBarrasi1 (TechnoElectroAli PadaryamNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAP 2 Sol-ManDokument27 SeitenCHAP 2 Sol-ManAdriel BayNoch keine Bewertungen
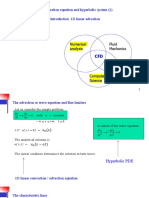
- The Advection Equation and Hyperbolic System (1) Introduction: 1D Linear AdvectionDokument17 SeitenThe Advection Equation and Hyperbolic System (1) Introduction: 1D Linear Advection刘伟轩Noch keine Bewertungen
- A B C A B C A B C A B C BC A B A C Ac B C A B Ab C: Identidades Trigonométricas Fórmulas de DerivaciónDokument2 SeitenA B C A B C A B C A B C BC A B A C Ac B C A B Ab C: Identidades Trigonométricas Fórmulas de DerivaciónGael Garcia VazquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SummaryDokument3 SeitenSummaryapi-3807270Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hamiltonian Dynamics and Neural NetworksDokument13 SeitenHamiltonian Dynamics and Neural NetworksRavi SankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet Pile NewDokument32 SeitenSheet Pile Newyadi suryadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - SolutionDokument27 SeitenChapter 2 - SolutionJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fall+2009 Midterm Opkst Mth101Dokument8 SeitenFall+2009 Midterm Opkst Mth101aftab_javed0000Noch keine Bewertungen
- From: Powered by ©Dokument15 SeitenFrom: Powered by ©Zaheer SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 2Dokument7 Seiten01 2haythem.mejri.proNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loi de Kirchhoff Cours 02Dokument7 SeitenLoi de Kirchhoff Cours 02Bertin BakariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Productivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionVon EverandProductivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tecnologías Emergentes para Disposicion de RelavesDokument16 SeitenTecnologías Emergentes para Disposicion de RelavesMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- McCabe - ThieleDokument6 SeitenMcCabe - ThieleMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector GradienteDokument6 SeitenVector GradienteMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pep IiDokument10 SeitenPep IiMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector GradienteDokument6 SeitenVector GradienteMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Please Both Print and Sign Your NameDokument6 SeitenPlease Both Print and Sign Your NameMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2001 Exam 3 SolDokument7 Seiten2001 Exam 3 SolMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
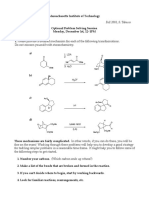
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Dokument4 SeitenMassachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- October 8, 2003 Prof. Timothy F. Jamison: Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Dokument1 SeiteOctober 8, 2003 Prof. Timothy F. Jamison: Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry Sample ExamDokument7 SeitenOrganic Chemistry Sample ExamHeol SobaNoch keine Bewertungen
- October 10, 2003 Prof. Timothy F. Jamison: 14 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Dokument2 SeitenOctober 10, 2003 Prof. Timothy F. Jamison: 14 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Dokument1 SeiteMassachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Dokument10 SeitenMassachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Dokument4 SeitenMassachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prob Solving SesDokument1 SeiteProb Solving SesMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Dokument10 SeitenMassachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outline & Study Guide For Unit VIII. Radicals: 5.13: Organic Chemistry II Fall 2003Dokument2 SeitenOutline & Study Guide For Unit VIII. Radicals: 5.13: Organic Chemistry II Fall 2003Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 StudyjhhhhhhhhhhhhhkjhDokument2 SeitenUnit 3 StudyjhhhhhhhhhhhhhkjhMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outline & Study Guide For Unit VI. Enols & Enolates: 5.13: Organic Chemistry II Fall 2003Dokument2 SeitenOutline & Study Guide For Unit VI. Enols & Enolates: 5.13: Organic Chemistry II Fall 2003Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit2 Study GDDokument1 SeiteUnit2 Study GDMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Dokument2 SeitenMassachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- October 8, 2003 Prof. Timothy F. Jamison: Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Dokument1 SeiteOctober 8, 2003 Prof. Timothy F. Jamison: Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec2 HandoutDokument1 SeiteLec2 HandoutMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec6 HandoutDokument3 SeitenLec6 HandoutMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec5 HandoutDokument2 SeitenLec5 HandoutMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- September 12, 2003 Prof. Timothy F. Jamison: Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Dokument3 SeitenSeptember 12, 2003 Prof. Timothy F. Jamison: Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LibrosDokument2 SeitenLibrosMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- InstructionsDokument2 SeitenInstructionsMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LibrosDokument2 SeitenLibrosMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Quiz When Told at 9:00 Am: 2.25 Advanced Fluid Mechanics Fall 2013Dokument9 SeitenOpen Quiz When Told at 9:00 Am: 2.25 Advanced Fluid Mechanics Fall 2013Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Aj 1609Dokument2 SeitenC Aj 1609vhin84Noch keine Bewertungen
- PC Smart Ptsgob8wDokument11 SeitenPC Smart Ptsgob8wJose LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pro.753687 en EU R4Dokument14 SeitenPro.753687 en EU R4Rakshit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embraco Standard Aftermarket Portfolio PDFDokument2 SeitenEmbraco Standard Aftermarket Portfolio PDFJOR4CHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Character Recognition Using MATLAB: J.Sashank Varma, G.V.N.S.Varma, K.Vikranth ReddyDokument5 SeitenOptical Character Recognition Using MATLAB: J.Sashank Varma, G.V.N.S.Varma, K.Vikranth Reddyvikky23791Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fund PoroDokument97 SeitenFund PoroAgustín Ramos LópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Purpose Hydraulic Valves: Float Level Control ValveDokument2 SeitenGeneral Purpose Hydraulic Valves: Float Level Control Valvevelikimag87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus Compendium For PCN Aerospace Sector ExaminationsDokument27 SeitenSyllabus Compendium For PCN Aerospace Sector ExaminationstomcanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weidmuller HazLoc Catalog 2014 LIT1315EDokument12 SeitenWeidmuller HazLoc Catalog 2014 LIT1315Evaseem shaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Position - List - Tank 17 11 2023Dokument8 SeitenPosition - List - Tank 17 11 2023simionalex1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- SEPG and Consulting ProcessDokument20 SeitenSEPG and Consulting ProcesszafzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avx 10k Data Sheet Data Sheets enDokument6 SeitenAvx 10k Data Sheet Data Sheets enAerotia InternationalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geopolymer Reinforced With Bamboo For Sustainable Construction MaterialsDokument7 SeitenGeopolymer Reinforced With Bamboo For Sustainable Construction MaterialsSamyuktha SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- I20 Key Features Technical Specifications: DimensionsDokument4 SeitenI20 Key Features Technical Specifications: Dimensionsvaibhavsaini88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Bounding Volume Hierarchies: Herman J. Haverkort 18 May 2004Dokument9 SeitenIntroduction To Bounding Volume Hierarchies: Herman J. Haverkort 18 May 2004Alessandro MeglioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijesrt: Modelling and Simulation of Solar Photovoltaic Array For Battery Charging Application Using Matlab-SimulinkDokument5 SeitenIjesrt: Modelling and Simulation of Solar Photovoltaic Array For Battery Charging Application Using Matlab-Simulinksrinureddy2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Windows 10 Volume Licensing GuideDokument19 SeitenWindows 10 Volume Licensing GuideVijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Incident ReportDokument10 SeitenSafety Incident ReportMelanie BrittainNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESDR4Dokument4 SeitenESDR4Eddy Skb0% (1)
- Sin EncoderDokument6 SeitenSin Encoderboynew87Noch keine Bewertungen