Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Foto Torax: Electrocardiography. The Typical Finding On Electrocardiography
Hochgeladen von
andi reskifais0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten2 Seitenbb
Originaltitel
Chest Radiography
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenbb
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten2 SeitenFoto Torax: Electrocardiography. The Typical Finding On Electrocardiography
Hochgeladen von
andi reskifaisbb
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
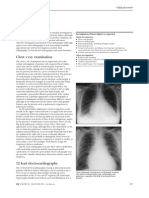
Chest Radiography.
Cardiac size is often normal in
patients with AS, with rounding of the LV border and apex
due to the LV hypertrophy. Aortic valve and aortic root
calcification are best appreciated in the lateral projections
on fluoroscopy. They are rarely detected on anteroposterior
or posteroanterior projections. The proximal ascending
aorta may be dilated, particularly in patients with bicuspid
valves. Cardiomegaly is a late feature in patients with
AS. In patients with heart failure, the heart is enlarged,
with congestion of pulmonary vasculature. In cases of advanced
heart failure, the right atrium and right ventricle
may also be enlarged.
Foto torax ukuran jantung normal, kalsifikasi aorta dapat dideteksi pada pemeriksaan
lateral.aorta proksimal mengalami dilatasi. Kardiomegali ditemukan pada fase akhir. Kalo
disertai dgn gagal jantung maka bisa ditemukan corakan bronkovaskular.
Electrocardiography. The typical finding on electrocardiography
(ECG) in patients with AS is LV hypertrophy,
often with secondary repolarization abnormalities.
This is found in 85% of patients with severe AS. However,
its absence does not preclude AS. Left atrial enlargement
and conduction abnormalities are also common, including
left and right bundle branch block. This may be due to extension
of the calcification into the surrounding conduction
system. The axis may be shifted leftward or rightward.
Atrial fibrillation can also develop, particularly in older patients
and those with hypertension. A sample ECG from a
patient with AS is shown in
elektrokardiogram bisa ditemukan hipertrofi ventrikel kiri dengan ditandai oleh repolarisasi
yang abnormal, karena adanya klsifikasi di katup yang memblok berkas his. Aksis bergeser ke
kanan atau ke kiri.
Echocardiography. Echocardiography is the imaging
modality of choice to help diagnose and estimate the severity
of AS. Two-dimensional echocardiography demonstrates
the morphology of the aortic valve and can often
delineate if it is trileaflet or bicuspid.
Cardiac Catheterization. Because of the accuracy of
echocardiographic assessment of the severity of AS, cardiac
catheterization is currently used most often to identify
the presence of associated coronary artery disease (CAD)
rather than to define hemodynamic abnormalities. However,
invasive hemodynamic measurements are helpful in
patients in whom the noninvasive tests are inconclusive
or provide discrepant results regarding the severity of AS.
Coronary arteriography is recommended before surgical
AVR in all patients at risk of CAD. Coronary angiography
is indicated in patients with chest pain, objective evidence
of ischemia, LV systolic dysfunction, and a history of CAD
or coronary risk factors, including older age. This procedure
should also be performed preoperatively in younger
patients who will be undergoing the Ross procedure if the
origin of the coronary arteries cannot be identified by noninvasive
imaging.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Plain English Part 2Dokument18 SeitenPlain English Part 2ابو ريمNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cryptogenic StrokeDokument52 SeitenCryptogenic Strokemrabhilekh100% (1)
- Ethical Conflicts in Psychology PDF DownloadDokument2 SeitenEthical Conflicts in Psychology PDF DownloadAvory0% (2)
- Sanskrit Subhashit CollectionDokument110 SeitenSanskrit Subhashit Collectionavinash312590% (72)
- Mathematics - Mathematics of Magic - A Study in Probability, Statistics, Strategy and Game Theory XDokument32 SeitenMathematics - Mathematics of Magic - A Study in Probability, Statistics, Strategy and Game Theory XHarish HandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aortic Stenosis AmendillaDokument31 SeitenAortic Stenosis AmendillaVadim BursacovschiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vascular Board Questions NumberedDokument60 SeitenVascular Board Questions NumberedAudrey Schlembach100% (6)
- Non-Invasive Cardiac ImagingDokument9 SeitenNon-Invasive Cardiac Imagingoddone_outNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aortic StenosisDokument20 SeitenAortic Stenosisvasarhely imolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCP Vol 2 PDF (2022 Edition)Dokument548 SeitenGCP Vol 2 PDF (2022 Edition)Sergio AlvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Right Ventricular Myocardial InfarctionDokument43 SeitenRight Ventricular Myocardial Infarctionrudresh m g0% (2)
- Cool Fire Manual 45M620N2UK 01 PDFDokument198 SeitenCool Fire Manual 45M620N2UK 01 PDFPaun MihaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vieworks DR Panel BrochureDokument8 SeitenVieworks DR Panel Brochuretito goodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Pathology: Professor Mircea BuruianDokument174 SeitenCardiovascular Pathology: Professor Mircea BuruianDiana PopoviciNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Great Muslim Scientist - Imam Jaffer Sadiq (ADokument78 SeitenThe Great Muslim Scientist - Imam Jaffer Sadiq (ASalman Book Centre100% (2)
- Aortic Stenosis:: Updates in Diagnosis & ManagementDokument48 SeitenAortic Stenosis:: Updates in Diagnosis & ManagementCuca PcelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastroesophagea L of Reflux Disease (GERD)Dokument34 SeitenGastroesophagea L of Reflux Disease (GERD)Alyda Choirunnissa SudiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart BlockDokument10 SeitenHeart BlockEköw Santiago JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guideline - Research ProposalDokument38 SeitenGuideline - Research ProposalRASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic of The Philippines Division of Bohol Department of Education Region VII, Central VisayasDokument6 SeitenRepublic of The Philippines Division of Bohol Department of Education Region VII, Central VisayasJOHN MC RAE RACINESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lvot o IiDokument179 SeitenLvot o Iimona300Noch keine Bewertungen
- EP001 LifeCoachSchoolTranscriptDokument13 SeitenEP001 LifeCoachSchoolTranscriptVan GuedesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 160kW SOFT STARTER - TAP HOLE 1Dokument20 Seiten160kW SOFT STARTER - TAP HOLE 1Ankit Uttam0% (1)
- Project Chalk CorrectionDokument85 SeitenProject Chalk CorrectionEmeka Nicholas Ibekwe100% (6)
- ABC 5 Investigation-BMJ 2000Dokument4 SeitenABC 5 Investigation-BMJ 2000fidos618Noch keine Bewertungen
- TUGAS Ventricular Septal DefectDokument8 SeitenTUGAS Ventricular Septal DefectMohammad NafisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDokument22 SeitenCongenital Heart DiseaseDiosa MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anomalous CoronaryDokument9 SeitenAnomalous Coronaryndang01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Board Review: Vikram Chhokar MD University of Tennessee Division of CardiologyDokument79 SeitenBoard Review: Vikram Chhokar MD University of Tennessee Division of CardiologyFernando SalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estenosis AórticaDokument11 SeitenEstenosis AórticaFamilia Morales JuradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bahan Refrat Anes!!!!Dokument6 SeitenBahan Refrat Anes!!!!Ajeng Oktri DewantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Congenital DiseaseDokument27 SeitenCardiac Congenital Diseasenovitafitri123Noch keine Bewertungen
- 53 Coronary Artery AnomaliesDokument5 Seiten53 Coronary Artery AnomaliesVictor PazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitral Regurgitation Etiology and Pathophysiology: Physical ExaminationsDokument11 SeitenMitral Regurgitation Etiology and Pathophysiology: Physical ExaminationsDelmy SanjayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract Avrtcad2vd MuhammadakhiruddinDokument2 SeitenAbstract Avrtcad2vd MuhammadakhiruddinNanank Akhiruddin SyamsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertensive Heart DiseaseDokument10 SeitenHypertensive Heart DiseaseAyu Indriyani MunggaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symptoms, Diagnosis, TreatmentDokument17 SeitenSymptoms, Diagnosis, TreatmentatanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecg 7 Der y AvrDokument9 SeitenEcg 7 Der y AvrElmer MoscosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Koarktacija Aorte Pri Odraslih Bolnikih: Coarctation of The Aorta in Adult PatientsDokument8 SeitenKoarktacija Aorte Pri Odraslih Bolnikih: Coarctation of The Aorta in Adult Patientssecpol658Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Scenerio: DR Sourath Munir Malkani Fcps-Ii TraineDokument31 SeitenCase Scenerio: DR Sourath Munir Malkani Fcps-Ii TraineSoonh ChannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine: DR: Jawad 9-Oct-06 Lec: - 3Dokument3 SeitenMedicine: DR: Jawad 9-Oct-06 Lec: - 3api-3829364Noch keine Bewertungen
- Left Ventricular Diverticulum in Association With Bicuspid Aortic Valve and Pseudocoarctation: Hitherto Unreported AssociationDokument3 SeitenLeft Ventricular Diverticulum in Association With Bicuspid Aortic Valve and Pseudocoarctation: Hitherto Unreported AssociationIsabella María GantivarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AV - Congenital Heart DiseaseDokument10 SeitenAV - Congenital Heart DiseasebakiralhamdaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Heart Disease in CatsDokument5 SeitenCongenital Heart Disease in Catsmatias66Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crite RiosDokument8 SeitenCrite RiosNilson Morales CordobaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Types of Supraventricular Tachycardia - Diagnosis and Management - AAFPDokument9 SeitenCommon Types of Supraventricular Tachycardia - Diagnosis and Management - AAFPMohamad MostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tetralogy of FallotDokument3 SeitenTetralogy of FallotKamal FauzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) : Presenter Dr. Maimuna Sayeed Resident (Phase A) Paediatric Gastroenterology & NutritionDokument50 SeitenAtrial Septal Defect (ASD) : Presenter Dr. Maimuna Sayeed Resident (Phase A) Paediatric Gastroenterology & NutritionIrving H Torres LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casos Cardiológicos 1Dokument12 SeitenCasos Cardiológicos 1Larissa SeabraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broad Complex TachyDokument8 SeitenBroad Complex TachyarnabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcapa SyndromeDokument38 SeitenAlcapa SyndromeZiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Description and DiscussionDokument3 SeitenCase Description and DiscussionMary Joy PelicanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVD 10 (١) PDFDokument23 SeitenCVD 10 (١) PDFHmhm HmhmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carotid Artery Stenosis ImagingDokument10 SeitenCarotid Artery Stenosis ImagingCristhian RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Correct Answer Is A. The Differential Diagnosis of Chest Pain Is BroadDokument33 SeitenThe Correct Answer Is A. The Differential Diagnosis of Chest Pain Is BroadMitz JuneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acyanotic CHDDokument83 SeitenAcyanotic CHDmrinmayee deshmukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Heart Disease: Kriti Puri, MD Hugh D. Allen, MD Athar M. Qureshi, MDDokument30 SeitenCongenital Heart Disease: Kriti Puri, MD Hugh D. Allen, MD Athar M. Qureshi, MDhari ilman toniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aortic Regurgitation: Gerald MaurerDokument7 SeitenAortic Regurgitation: Gerald MaurerFarlinda AlyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supraventricular TachycardiDokument8 SeitenSupraventricular TachycardiHairunisa 0049Noch keine Bewertungen
- Braunwald: Chronic Coronary Artery DiseaseDokument122 SeitenBraunwald: Chronic Coronary Artery Diseaseusfcards100% (1)
- Congenital Heart Disease EtiologyDokument8 SeitenCongenital Heart Disease EtiologykudzaimuregidubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovasucular Problems in Children: Niranjana Shalini. M.SC (N) Assistant ProfessorDokument79 SeitenCardiovasucular Problems in Children: Niranjana Shalini. M.SC (N) Assistant ProfessorNIRANJANA SHALININoch keine Bewertungen
- PJB Pada Dewasa AASDokument54 SeitenPJB Pada Dewasa AAS1e23e2ewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Cardiac Assessments: Physical Examination, Electrocardiography, and Chest RadiographyDokument7 SeitenBasic Cardiac Assessments: Physical Examination, Electrocardiography, and Chest Radiographyrowd1yNoch keine Bewertungen
- Echo Case Ao RegurgDokument3 SeitenEcho Case Ao Regurgdgina8800Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac LipomDokument4 SeitenCardiac LipomCiprian MarianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revue TRTDokument6 SeitenRevue TRTalex mihneaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VT IndoDokument37 SeitenVT IndotyaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal Aortic AneurysmDokument10 SeitenAbdominal Aortic AneurysmPrince K. TaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah MITRAL STENOSISDokument19 SeitenKuliah MITRAL STENOSISAdi TrisnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDokument10 SeitenCongenital Heart DiseaseIca JustitiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Chest Imaging and Heart FailureDokument57 SeitenBasic Chest Imaging and Heart FailureKiaa auliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decoding Cardiac Electrophysiology: Understanding the Techniques and Defining the JargonVon EverandDecoding Cardiac Electrophysiology: Understanding the Techniques and Defining the JargonAfzal SohaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- BazarDokument2 SeitenBazarandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Program Studi Pendidikan Dokter: Medical Final Test ACADEMIC YEAR 2011/2012Dokument4 SeitenProgram Studi Pendidikan Dokter: Medical Final Test ACADEMIC YEAR 2011/2012andi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHO Indonesia Tuberculosis ProfilDokument2 SeitenWHO Indonesia Tuberculosis Profilandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Pre Final TestDokument3 SeitenMedical Pre Final Testandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Program Studi Pendidikan Dokter: Medical Final Test ACADEMIC YEAR 2011/2012Dokument4 SeitenProgram Studi Pendidikan Dokter: Medical Final Test ACADEMIC YEAR 2011/2012andi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Pre Final Test EditDokument2 SeitenMedical Pre Final Test Editandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Egyptian Journal of Chest Diseases and TuberculosisDokument4 SeitenEgyptian Journal of Chest Diseases and Tuberculosisandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konsep PneumoniaDokument47 SeitenKonsep Pneumoniaandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obesity in Australia: Health, Social and Economic Impact of ObesityDokument6 SeitenObesity in Australia: Health, Social and Economic Impact of Obesityandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Features of Tuberculosis and Sarcoidosis: SciencedirectDokument2 SeitenCommon Features of Tuberculosis and Sarcoidosis: Sciencedirectandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Childhood Obesity in LondonDokument8 SeitenChildhood Obesity in Londonandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Childhood Obesity in LondonDokument8 SeitenChildhood Obesity in Londonandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology in System Uro-Genitalia FK Unisa, 13-3-2014Dokument63 SeitenPharmacology in System Uro-Genitalia FK Unisa, 13-3-2014andi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sist UrogenitaliaDokument46 SeitenSist Urogenitaliaandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- BBBDokument68 SeitenBBBandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konsep PneumoniaDokument47 SeitenKonsep Pneumoniaandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ija 17063Dokument8 SeitenIja 17063andi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cor Pulmonale PresentationDokument17 SeitenCor Pulmonale Presentationandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- WONCA Five-Star Doctors: 2013 WinnerDokument1 SeiteWONCA Five-Star Doctors: 2013 Winnerandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mayoclinproc 85 5 013 PDFDokument18 SeitenMayoclinproc 85 5 013 PDFandi reskifaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notice: Premerger Notification Waiting Periods Early TerminationsDokument5 SeitenNotice: Premerger Notification Waiting Periods Early TerminationsJustia.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- STS Module 11Dokument64 SeitenSTS Module 11Desiree GalletoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paul Wade - The Ultimate Isometrics Manual - Building Maximum Strength and Conditioning With Static Training-Dragon Door Publications (2020) - 120-146Dokument27 SeitenPaul Wade - The Ultimate Isometrics Manual - Building Maximum Strength and Conditioning With Static Training-Dragon Door Publications (2020) - 120-146usman azharNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTS2 HMU Indonesia - Training - 09103016Dokument45 SeitenCTS2 HMU Indonesia - Training - 09103016Resort1.7 Mri100% (1)
- European Construction Sector Observatory: Country Profile MaltaDokument40 SeitenEuropean Construction Sector Observatory: Country Profile MaltaRainbootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To HDLDokument28 SeitenIntroduction To HDLBack UpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project ProposalDokument4 SeitenProject Proposaljiaclaire2998100% (1)
- EngHub How To Break HabitsDokument13 SeitenEngHub How To Break HabitsViktoria NovikovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pelayo PathopyhsiologyDokument13 SeitenPelayo PathopyhsiologyE.J. PelayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A 138Dokument1 SeiteA 138pooja g pNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philhis 1blm Group 6 ReportDokument19 SeitenPhilhis 1blm Group 6 Reporttaehyung trashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousDokument3 SeitenPast Simple Vs Past ContinuousNatalia SalinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- X - WORMWOOD EVENT IMMEDIATE - Paranormal - 4chanDokument7 SeitenX - WORMWOOD EVENT IMMEDIATE - Paranormal - 4chanAnonymous dIjB7XD8ZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Supply Chain Management A Balanced Approach 4th Edition Wisner Solutions ManualDokument36 SeitenPrinciples of Supply Chain Management A Balanced Approach 4th Edition Wisner Solutions Manualoutlying.pedantry.85yc100% (28)
- Animal Health ChecklistDokument4 SeitenAnimal Health ChecklistcapsfastNoch keine Bewertungen
- BÀI TẬP LESSON 7. CÂU BỊ ĐỘNG 1Dokument4 SeitenBÀI TẬP LESSON 7. CÂU BỊ ĐỘNG 1Yến Vy TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen