Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ISO 9001 What Are The Changes - Arun Sinha
Hochgeladen von
EXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCEOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ISO 9001 What Are The Changes - Arun Sinha
Hochgeladen von
EXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCECopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ISO 9001:2015
WHAT ARE THE CHANGES?
Overview
ISO 9001:2015 has now been released and is a major revision to the previous edition issued in
2008. This revision introduces many new concepts, terminology and current thinking, drawing on
the collective resources of many other Standards that have been developed over the past decade of
quality management, users and national bodies.
All management system Standards of the future will have the same high level structure, identical core
text, as well as common terms and definitions. While the high level structure cannot be changed, sub
clauses and discipline-specific text have been added.
The Standard ISO 9001:2015
ISO 9001:2015 Section 1: Scope
The scope sets out the intended outcomes of the management system. The outcomes are industry
specific and should be aligned with the context of the organisation (clause 4).
ISO 9001:2015 Section 2: Normative references
Provides details of the reference Standard, ISO 9000:2015.
ISO 9001:2015 Section 3: Terms and definitions
Identifies terms and definitions applicable to the Standard that can be found in ISO 9000:2015.
ISO 9001:2015 Section 4: Context of the organisation
Section 4 consists of four clauses:
4.1 Understanding the organisation and its context
4.2 Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties
4.3 Determining the scope of the managements system
4.4 Quality management system and its processes.
As the flagstone of a management system, Section 4 determines why the organisation is here. As
part of the answer to this question, the organisation needs to identify internal and external issues that
can impact on its intended outcomes, as well as all interested parties and their requirements. It also
needs to document its scope and set the boundaries of the management system all in line with the
business objectives.
1 Version 2.0 www.saiglobal.com
ISO 9001:2015 Section 5: Leadership
Section 5 comprises three clauses:
5.1 Leadership and commitment
5.2 Policy
5.3 Organisational roles, responsibilities and authorities.
The new high level structure places particular emphasis on leadership, not just management as
set out in previous Standards. This means top management now has greater accountability and
involvement in the organisations management system. They need to integrate the requirements of
the management system into the organisations core business processes, ensure the management
system achieves its intended outcomes and allocate the necessary resources. Top management
is also responsible for communicating the importance of the management system and heighted
employee awareness and involvement.
Top management now has greater accountability and involvement
in the organisations management system.
Section 6: Planning
Section 6 includes three clauses:
6.1 Actions to address risks and opportunities
6.2 Quality objectives and planning to achieve them
6.3 Planning of changes.
Section 6 brings risk-based thinking to the forefront. Once the organisation has highlighted risks and
opportunities in Section 4, it needs to stipulate how these will be addressed through planning. The
planning phase looks at what, who, how and when these risks must be addressed. This proactive
approach replaces preventive action and reduces the need for corrective actions later.
Particular focus is also placed on the objectives of the management system and updated when
needed. Quality objectives shall:
Be consistent with the quality policy,
Be measurable,
Take into account applicable requirements,
Be monitored,
Be communicated, and
Be updated as appropriate.
2 Version 2.0 www.saiglobal.com
When planning how to achieve its quality objectives the organisation shall determine:
What will be done,
What resources will be required,
Who will be responsible,
When it will be completed, and
How the results will be evaluated.
Section 7: Support
Section 7 consists of five clauses:
7.1 Resources
7.2 Competence
7.3 Awareness
7.4 Communication
7.5 Documented information.
After addressing the context, commitment and planning, organisations will have to look at the support
needed to meet their goals and objectives. This includes resources, targeted internal and external
communications, as well as documented information that replaces previously used terms such as
documents, documentation and records.
7.3 Awareness - Persons doing work under the organisations control shall be aware of:
The quality policy,
Their contribution to the effectiveness of the quality management system, including the
benefits of improved quality performance, and
The implications of not conforming to the quality management system requirements.
7.4 Communication - The organisation shall determine the need for internal and external
communications relevant to the quality management system including:
On what it will communicate,
When to communicate, and
With whom to communicate.
Section 8: Operation
Section 8 has many clauses:
8.1 Operational planning and control
8.2 Requirements for products and services
8.3 Design and development of products and services
8.4 Control of externally provided processes, products and services
3 Version 2.0 www.saiglobal.com
8.5 Production and service provision
8.6 Release of products and services
8.7 Control of nonconforming outputs.
The bulk of the management system operation requirements are within this section. Clause 8
addresses both in-house and outsourced processes, while the overall process management includes
adequate criteria to control these processes, as well as ways to manage planned and unintended
change. The organisation shall plan, implement and control the processes needed to meet
requirements, and to implement the actions determined in 6.1, by:
Establishing criteria for the processes,
Implementing control of the processes in accordance with the criteria,
Keeping documented information to the extent necessary to have confidence that the
processes have been carried out as planned.
The organisation shall control planned changes and review the consequences of unintended changes,
taking action to mitigate any adverse effects, as necessary.
Section 9: Performance evaluation
Section 9 is formed of three clauses:
9.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation
9.2 Internal audit
9.3 Management review.
The organisation shall control planned changes and review the
consequences of unintended changes, taking action to mitigate any
adverse effects.
Here organisations need to determine what, how and when things are to be monitored, measured,
analysed and evaluated. The organisation shall determine:
What needs to be monitored and measured,
The methods for monitoring, measurement analysis and evaluation, as applicable, to ensure
valid results,
When the monitoring and measuring shall be performed,
When the results from monitoring and measurement shall be analysed and evaluated.
An internal audit is also part of this process to ensure the management system conforms to the
requirements of the organisation as well as the Standard, and is successfully implemented and
maintained.
4 Version 2.0 www.saiglobal.com
The final step, management review, looks at whether the management system is suitable, adequate
and effective.
Section 10: Improvement
Section 10 looks at ways to address nonconformities and corrective action, as well as strategies for
improvement on a continual basis. In an ever-changing business world, not everything always goes
according to plan. It includes the following clauses:
10.1 General
10.2 Nonconformity and corrective action
10.3 Continual improvement.
For 10.2 Nonconformity and correction action - When nonconformity occurs, the organisation shall:
React to the nonconformity, and as applicable take action to control and correct it, and
Deal with the consequences.
Evaluate the need for action to eliminate the causes of the nonconformity, in order that it does
not recur or occur elsewhere, by:
Reviewing the nonconformity
Determining the causes of the nonconformity,
Determining if similar nonconformities exist, or could potentially occur,
Implement any action needed,
Review the effectiveness of any action taken,
Make changes to the quality management system, if necessary.
Corrective actions shall be appropriate to the effects of the nonconformities encountered.
For 10.3 Continual improvement - The organisation shall continually improve the suitability, adequacy,
and effectiveness of the quality management system by:
Considering the outputs of analysis and evaluation,
The outputs from management review, to confirm if there are areas of underperformance or
opportunities that shall be addressed as part of continual improvement.
5 Version 2.0 www.saiglobal.com
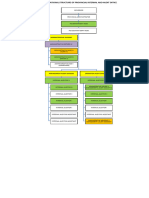
CORRELATION MATRIX
ISO 9001:2008 ISO 9001:2015
4. Quality management system 4. Context of the organisation
4.1 General requirements 4.4 Quality management system and its processes
4.2 Documentation requirements 7.5 Documented information
4.2.1 General 7.5.1 General
4.2.2 Quality manual 4.3 Determining the scope of the quality management
system
4.4 Quality management system and its Processes
7.5.1 General
4.2.3 Control of documents 7.5.2 Creating and updating
7.5.3 Control of documented Information
4.2.4 Control of records 7.5.2 Creating and updating
7.5.3 ontrol of documented Information
5. Management responsibility 5. Leadership
5.1 Management commitment 5.1 Leadership and commitment
5.1.1 General
5.2 Customer focus 5.1.2 Customer focus
5.3 Quality policy 5.2 Policy
5.4 Planning 6 Planning
5.4.1 Quality objectives 6.2 Quality objectives and planning to achieve them
5.4.2 Quality management system planning 6 Planning
6.1 Actions to address risks and opportunities
6.3 Planning of changes
5.5 Responsibility, authority and communication 5 Leadership
5.5.1 Responsibility and authority 5.3 Organisational roles, responsibilities and
authorities
5.5.2 Management representative Title removed
5.3 Organisational roles, responsibilities and
authorities
5.5.3 Internal communication 7.4 Communication
5.6 Management review 9.3 Management review
5.6.1 General 9.3.1 General
5.6.2 Review input 9.3.2 Management review inputs
5.6.3 Review output 9.3.3 Management review outputs
6 Resource management 7.1 Resources
6.1 Provision of resources 7.1.1 General
7.1.2 People
6.2 Human resources Title removed
7.2 Competence
6.2.1 General 7.2 Competence
6.2.2 Competence, training and awareness 7.2 Competence
7.3 Awareness
6 Version 2.0 www.saiglobal.com
ISO 9001:2008 ISO 9001:2015
6.3 Infrastructure 7.1.3 Infrastructure
6.4 Work environment 7.1.4 Environment for the operation of processes
7 Product realisation 8 Operation
7.1 Planning of product realisation 8.1 Operational planning and control
7.2 Customer-related processes 8.2 Requirements for products and services
7.2.1 Determination of requirements related to the 8.2.2 Determining the requirements related to
product products and services
7.2.2 Review of requirements related to the product 8.2.3 Review of requirements related to the products
and services
7.2.3 Customer communication 8.2.1 Customer communication
7.3 Design and development 8.5 Production and service provision
7.3.1 Design and development planning 8.3 Design and development of products and
services
8.3.1 General
8.3.2 Design and development planning
7.3.2 Design and development inputs 8.3.3 Design and development Inputs
7.3.3 Design and development outputs 8.3.5 Design and development outputs
7.3.4 Design and development review 8.3.4 Design and development controls
7.3.5 Design and development verification 8.3.4 Design and development controls
7.3.6 Design and development validation 8.3.4 Design and development controls
7.3.7 Control of design and development changes 8.3.6 Design and development changes
7.4 Purchasing 8.4 Control of externally provided processes,
products and services
7.4.1 Purchasing process 8.4.1 General
8.4.2 Type and extent of control
7.4.2 Purchasing information 8.4.3 Information for external providers
7.4.3 Verification of purchased product 8.6 Release of products and services
7.5 Production and service provision 8.5 Production and service provision
7.5.1 Control of production and service provision 8.5.1 Control of production and service provision
8.5.5 Post-delivery activities
7.5.2 Validation of processes for production and 8.5.1 Control of production and service provision
service provision
7.5.3 Identification and traceability 8.5.2 Identification and traceability
7.5.4 Customer property 8.5.3 Property belonging to customers or external
providers
7.5.5 Preservation of product 8.5.4 Preservation
7.6 Control of monitoring and measuring equipment 7.1.5 Monitoring and measuring resources
8 Improvement 8 Performance evaluation
8.0 Measurement, analysis and improvement 9.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysis and
evaluation
8.1 General 9.1.1 General
7 Version 2.0 www.saiglobal.com
ISO 9001:2008 ISO 9001:2015
8.2 Monitoring and measurement 9.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysis and
evaluation
8.2.1 Customer satisfaction 9.1.2 Customer satisfaction
8.2.2 Internal audit 9.2 Internal audit
8.2.3 Monitoring and measurement of processes 9.1.1 General
8.2.4 Monitoring and measurement of product 8.6 Release of products and services
8.3 Control of nonconforming product 8.7 Control of nonconforming outputs
8.4 Analysis of data 9.1.3 Analysis and evaluation
8.5 Improvement 10 Improvement
8.5.1 Continual improvement 10.1 General
10.3 Continual Improvement
8.5.2 Corrective action 10.2 Nonconformity and corrective action
8.5.3 Preventive action Clause removed
6.1 Actions to address risks and opportunities
The information contained in these pages is provided by way of indicative guidance only and SAI Global Limited does not represent
that it is accurate or complete or suitable for any particular specific purposes. The onus remains with users to satisfy themselves of their
requirements and needs for their own particular circumstances.
8 Version 2.0 www.saiglobal.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- 37 Newborn Baby Quotes To Share The LoveDokument39 Seiten37 Newborn Baby Quotes To Share The LoveEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- Erection Welding Schedule: Revno: Page No. Date Doc No. Prepared Checked (W.T.C) ApprovedDokument1 SeiteErection Welding Schedule: Revno: Page No. Date Doc No. Prepared Checked (W.T.C) ApprovedEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- 103 Sweet New Baby Quotes To Welcome Them Home - Gifts - Com BlogDokument17 Seiten103 Sweet New Baby Quotes To Welcome Them Home - Gifts - Com BlogEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- CPRI-Project On High Temperature ErosionDokument5 SeitenCPRI-Project On High Temperature ErosionEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Science 2 Marks Questions and AnswersDokument6 SeitenSocial Science 2 Marks Questions and AnswersEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- 84 Inspirational Baby Quotes and Sayings - ShutterflyDokument19 Seiten84 Inspirational Baby Quotes and Sayings - ShutterflyEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- Shut DownDokument22 SeitenShut DownEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Drain ValvesDokument2 SeitenThermal Drain ValvesEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Operations: Shaikh Feroz AliDokument15 SeitenEmergency Operations: Shaikh Feroz AliEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- The Boilers ActDokument30 SeitenThe Boilers ActEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance of Governor Oil - Soumik Majumdar & Sanjay DasDokument21 SeitenPerformance of Governor Oil - Soumik Majumdar & Sanjay DasEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- Mill & Mill Rejects WriteupDokument10 SeitenMill & Mill Rejects WriteupEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- Coal Mill Technologies - Brishank SrivastavaDokument34 SeitenCoal Mill Technologies - Brishank SrivastavaEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCE100% (1)
- Empowering Reliability Through Lubrication Program Development (LPD) Udey DhirDokument28 SeitenEmpowering Reliability Through Lubrication Program Development (LPD) Udey DhirEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- 38DL - Plus Specification PDFDokument5 Seiten38DL - Plus Specification PDFEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotor Dynamics of FanDokument4 SeitenRotor Dynamics of FanEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Factory Mutual 2012 Annual ReportDokument68 SeitenFactory Mutual 2012 Annual ReportNguyen03Noch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Audit Report - CBI HOLDINGSDokument11 SeitenInternal Audit Report - CBI HOLDINGSJean Stephany0% (1)
- Aud JudgmentDokument15 SeitenAud JudgmentKurniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit Committee Effectiveness: A Public Sector Case StudyDokument17 SeitenAudit Committee Effectiveness: A Public Sector Case StudyIsmanidarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Domain 2Dokument20 SeitenDomain 2Nagendra KrishnamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allen Thomas KannattuDokument37 SeitenAllen Thomas KannattuSouvik GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Check Report: QA ElementDokument6 SeitenProcess Check Report: QA ElementMayank RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coa Qms ManualDokument241 SeitenCoa Qms ManualEricka Joi OjerioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bridgeloyalty Company Profile - 2019Dokument20 SeitenBridgeloyalty Company Profile - 2019Rohit KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eurolab Handbook Iso Iec 17025 2017Dokument32 SeitenEurolab Handbook Iso Iec 17025 2017Ali ZafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIA Code of EthicsDokument25 SeitenIIA Code of EthicsMaya MagdalenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformation of Organization The Strategy of Change ManagementDokument23 SeitenTransformation of Organization The Strategy of Change ManagementMohamad Nurreza RachmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cma Part 1 Mock Test 3Dokument37 SeitenCma Part 1 Mock Test 3armaghan186% (22)
- KossDokument8 SeitenKossChris WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- GODLOVE MMARI +2551712166612 University of Dar Es Salaam Business School (2013-2016)Dokument21 SeitenGODLOVE MMARI +2551712166612 University of Dar Es Salaam Business School (2013-2016)fausta kidavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - Reviewing Internal Control Over Financial ReportingDokument9 SeitenChapter 8 - Reviewing Internal Control Over Financial ReportingMicah ErguizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Governance Outline 2Dokument36 SeitenCorporate Governance Outline 2emman neriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delliote - Us-Risk-Cyber-Ia-Urgent-Call-To-ActionDokument10 SeitenDelliote - Us-Risk-Cyber-Ia-Urgent-Call-To-Actionjazzbond007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Accenture Compliance Excellence Insurance Industry PDFDokument37 SeitenAccenture Compliance Excellence Insurance Industry PDFsharon omashNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO-TC309 N0262 ISO 37001 Handbook - Draft For CommentDokument121 SeitenISO-TC309 N0262 ISO 37001 Handbook - Draft For CommentRaul PereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- RFP On Internal AuditDokument33 SeitenRFP On Internal AuditCan dien tu Thai Binh DuongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Individual Assignment - 4 Nov 2022Dokument6 SeitenFinal Individual Assignment - 4 Nov 2022Vernice CuffyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mornbfi 1Dokument795 SeitenMornbfi 1cerptzNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnnualDokument122 SeitenAnnualSiddharth ShekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piao Proposed Structure 2023Dokument5 SeitenPiao Proposed Structure 2023me.I.onlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 RevlonDokument7 Seiten20 RevlonJessica Miranda VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slaus 610Dokument9 SeitenSlaus 610Charitha LakmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Misa BSA 33P Chapter 2 AssignmentDokument6 SeitenMisa BSA 33P Chapter 2 AssignmentJulmar MisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluating The Design and Effectiveness of Internal ControlDokument34 SeitenEvaluating The Design and Effectiveness of Internal ControlClene DoconteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan Guidelines: Preparation and UseDokument7 SeitenBusiness Plan Guidelines: Preparation and UseBernard Boris BELOBONoch keine Bewertungen