Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
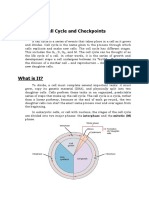
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Hochgeladen von
jayweinx0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
322 Ansichten6 Seiten77777777
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden77777777
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
322 Ansichten6 SeitenCell Cycle Checkpoints
Hochgeladen von
jayweinx77777777
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 6
Cell cycle checkpoints There are a number of checkpoints, but
the three most important ones are:
How cells use checkpoints at the end of G1 phase, end
of G2 phase, and partway through M phase (the spindle The G_11start subscript, 1, end
checkpoint) to regulate the cell cycle.
subscript checkpoint, at the G_11start
subscript, 1, end subscript/S transition.
Introduction The G_22start subscript, 2, end
As cells move through the cell cycle, do
they breeze through from one phase to subscript checkpoint, at the G_22start
the next? If they're cancer cells, the subscript, 2, end subscript/M transition.
answer might be yes. Normal cells, The spindle checkpoint, at the
however, move through the cell cycle in a transition from metaphase to anaphase.
regulated way. They use information
about their own internal state and cues
from the environment around them to
decide whether to proceed with cell
division. This regulation makes sure that
cells don't divide under unfavorable
conditions (for instance, when their DNA
is damaged, or when there isn't room for
more cells in a tissue or organ).
Cell cycle checkpoints
A checkpoint is a stage in the eukaryotic
cell cycle at which at which the cell
examines internal and external cues and
"decides" whether or not to move forward
with division.
The G_11start subscript, 1,
end subscript checkpoint
The G_1 checkpoint is the main
decision point for a cell that is, the
primary point at which it must choose
whether or not to divide. Once the cell
passes the G_1 checkpoint and enters S
phase, it becomes irreversibly committed
Diagram of cell cycle with checkpoints
to division. That is, barring unexpected
marked. G1 checkpoint is near the end of
problems, such as DNA damage or
G1 (close to the G1/S transition). G2
replication errors, a cell that passes the
checkpoint is near the end of G2 (close to
the G2/M transition). Spindle checkpoint is G_1 checkpoint will continue the rest of
partway through M phase, and more the way through the cell cycle and
specifically, at the metaphase/anaphase produce two daughter cells.
transition.
Cell size
Nutrients
Growth factors
DNA damage
At the G_1 checkpoint, a cell checks
whether internal and external conditions
are right for division. Here are some of the
factors a cell might assess:
Size. Is the cell large enough to
divide?
Nutrients. Does the cell have
enough energy reserves or available
nutrients to divide?
Molecular signals. Is the cell
receiving positive cues (such as growth
factors) from neighbors?
The G1 checkpoint. The G1 checkpoint is
DNA integrity. Is any of the DNA
located at the end of G1 phase, before the
transition to S phase. If cells don't pass damaged?
the G1 checkpoint, they may "loop out" of These are not the only factors that can
the cell cycle and into a resting state affect progression through the G_1, and
called G0, from which they may which factors are most important depend
subsequently re-enter G1 under the on the type of cell. For instance, some
appropriate conditions. cells also need mechanical cues (such as
being attached to a supportive network
At the G1 checkpoint, cells decide whether
called the extracellular matrix) in order to
or not to proceed with division based on
divide
factors such as:
If a cell doesnt get the go-ahead cues it The G_2 checkpoint
needs at the G_1 checkpoint, it may
leave the cell cycle and enter a resting
state called G_0. Some cells stay
permanently in G_0, while others resume
dividing if conditions improve.
Image of the cell cycle with the G2
checkpoint marked. At the G2 checkpoint,
the cell checks for:
DNA damage The spindle checkpoint
DNA replication completeness
To make sure that cell division goes
smoothly (produces healthy daughter
cells with complete, undamaged DNA),
the cell has an additional checkpoint
before M phase, called the G_2 At this
.
stage, the cell will check:
DNA integrity. Is any of the DNA
damaged?
DNA replication. Was the DNA
completely copied during S phase?
If errors or damage are detected, the cell
will pause at the G_2 checkpoint to allow
for repairs. If the checkpoint mechanisms
detect problems with the DNA, the cell Image of the cell cycle with the spindle
cycle is halted, and the cell attempts to checkpoint marked. At the spindle
either complete DNA replication or repair checkpoint, the cell checks for:
the damaged DNA.
Chromosome attachment to spindle
If the damage is irreparable, the cell may at the metaphase plate
undergo apoptosis, or programmed cell The M checkpoint is also known as
death^2 This self-destruction the spindle checkpoint: here, the cell
mechanism ensures that damaged DNA is examines whether all the sister
not passed on to daughter cells and is chromatids are correctly attached to the
important in preventing cancer. spindle microtubules. Because the
separation of the sister chromatids during
anaphase is an irreversible step, the cycle that influence a cells decision to pause or
will not proceed until all the chromosomes progress at each checkpoint. However,
are firmly attached to at least two spindle you may be wondering what these factors
fibers from opposite poles of the cell. actually do to the cell, or change inside of
it, to cause (or block) progression from
How does this checkpoint work? It seems
one phase of the cell cycle to the next.
that cells don't actually scan the
metaphase plate to confirm that all of the The general answer is that internal and
chromosomes are there. Instead, they external cues trigger signaling pathways
look for "straggler" chromosomes that are inside the cell that activate, or inactivate,
in the wrong place (e.g., floating around in a set of core proteins that move the cell
the cytoplasm. If a chromosome is cycle forward. You can learn more about
misplaced, the cell will pause mitosis, these proteins, and see examples of how
allowing time for the spindle to capture they are affected by cues such as DNA
the stray chromosome. damage, in the article on cell cycle
regulators.
How do the checkpoints
actually work?
This article gives a high-level overview of
cell cycle control, outlining the factors
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chanyeol EXO Punch - Stay With MeDokument3 SeitenChanyeol EXO Punch - Stay With MejayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science COT 2 (4th Quarter)Dokument3 SeitenScience COT 2 (4th Quarter)Rhazel Caballero100% (1)
- Plant PropagationDokument30 SeitenPlant PropagationSheryl BulusanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cognitive Psychology - Memory FactsheetDokument4 SeitenCognitive Psychology - Memory FactsheetAyse Kerim100% (1)
- Genetics A Conceptual Approach 6th Edition by Pierce ISBN Solution ManualDokument5 SeitenGenetics A Conceptual Approach 6th Edition by Pierce ISBN Solution Manualrose100% (22)
- Cell Cycle CheckpointsDokument3 SeitenCell Cycle CheckpointsKristine Grace VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle Checkpoints and DNA Damage ResponseDokument2 SeitenCell Cycle Checkpoints and DNA Damage ResponseAmelyn Lingbawan100% (2)
- Solution Manual For Cell and Molecular Biology 8th Edition Gerald Karp Janet Iwasa Wallace MarshallDokument43 SeitenSolution Manual For Cell and Molecular Biology 8th Edition Gerald Karp Janet Iwasa Wallace Marshallbrianpattersonanpyomzbed100% (40)
- Lesson Plan: ReproductionDokument5 SeitenLesson Plan: ReproductionElizza GuerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 2 Module 12.1Dokument27 SeitenGeneral Biology 2 Module 12.1Jackielyn RosalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Directed Writing Report About The School CanteenDokument4 SeitenDirected Writing Report About The School Canteenjayweinx100% (2)
- Cell cycle checkpoints and regulationDokument17 SeitenCell cycle checkpoints and regulationKamaki RyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Test Written Test GrammarDokument10 SeitenEnglish Test Written Test Grammartarubi53100% (3)
- Lesson 6 - Cell Cycle and CheckpointsDokument6 SeitenLesson 6 - Cell Cycle and CheckpointsReuben Al'jaldi100% (1)
- Cell Cycle CheckpointsDokument3 SeitenCell Cycle CheckpointsAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle Handouts - PDF (Highlighted)Dokument4 SeitenCell Cycle Handouts - PDF (Highlighted)Shien VarronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell DivisionDokument3 SeitenCell DivisionKaith Ashlee De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3 BiologyDokument5 SeitenWeek 3 BiologyAngelo ReambonanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO-301 Safdar Ali (DC210400273)Dokument7 SeitenBIO-301 Safdar Ali (DC210400273)Shazia AslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell ModificationsDokument8 SeitenCell ModificationsKriezhel Kim TadleNoch keine Bewertungen
- General-Biology Notes PerezDokument4 SeitenGeneral-Biology Notes PerezAshley PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 4 Cell CycleDokument24 SeitenUNIT 4 Cell CycleChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle Checkpoints and PhasesDokument6 SeitenCell Cycle Checkpoints and PhasesJoyce NoblezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell CycleDokument15 SeitenCell CycleRhea GulayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle Regulation - Control Points (Part I)Dokument24 SeitenCell Cycle Regulation - Control Points (Part I)Amara TargaryenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2. Topic 1 B2 Control of The Cell CycleDokument10 SeitenModule 2. Topic 1 B2 Control of The Cell CycleRey Donn VILLABLANCANoch keine Bewertungen
- GB1 - W4 Module 2 1st QTR 1Dokument145 SeitenGB1 - W4 Module 2 1st QTR 1AyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle Lecture ReviewerDokument2 SeitenCell Cycle Lecture ReviewerIgnacio, Moira Jomille K.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell CycleDokument81 SeitenCell CycleSandara AsinguaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell CycleDokument2 SeitenCell CycleGlenda ArajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell Cycle Worksheet KEYDokument3 SeitenThe Cell Cycle Worksheet KEYCamille Sison-AlmirolNoch keine Bewertungen
- The key stages and regulation of the cell cycle/TITLEDokument24 SeitenThe key stages and regulation of the cell cycle/TITLEimarotusshoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulation of Cell Division: DR Sri WidyartiDokument49 SeitenRegulation of Cell Division: DR Sri WidyartiMaheer JoefrieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument52 SeitenUnit 1Dsce BtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ii M.Sc. Botany Cell and Molecular Biology Unit: Ii Cell CycleDokument36 SeitenIi M.Sc. Botany Cell and Molecular Biology Unit: Ii Cell CycleDeblina JanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDokument4 SeitenCell Cycle and Cell Divisionchar montejeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiologyDokument3 SeitenBiologyVIVEK100% (1)
- BiologyDokument3 SeitenBiologyVIVEKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handouts Gen. Bio Oct 3 6 2022Dokument14 SeitenHandouts Gen. Bio Oct 3 6 2022Mark Kenneth CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fallsem2018-19 Bit1001 TH Smv110 Vl2018191000249 Reference Material I Cell CycleDokument15 SeitenFallsem2018-19 Bit1001 TH Smv110 Vl2018191000249 Reference Material I Cell CycleJatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Cell Cycle and MitosisDokument1 Seite4 Cell Cycle and MitosisJasmine FloreceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division and Genetic Inheritance - FormattedDokument24 SeitenCell Division and Genetic Inheritance - FormattedAISHA MUHAMMADNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1cell CycleDokument19 Seiten1cell CycleUrdu KahaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checkpoint FinalDokument1 SeiteCheckpoint FinalSantanu DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELL CYCLE PPT KimDokument33 SeitenCELL CYCLE PPT KimNeo RilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell CycleDokument22 SeitenCell CycleMUHAMMAD KHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phases of The Cell CycleDokument25 SeitenPhases of The Cell CycleThaira HerniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell CycleDokument26 SeitenCell CycleMa. Theresa AgsaoayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.1 and 8.2 Group AssignmentDokument7 Seiten8.1 and 8.2 Group AssignmentDaniel CondreayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Notes - Cell Cycle and MitosisDokument26 SeitenBiology Notes - Cell Cycle and MitosisAnjehyn ElleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Project:The Cell Cycle Group Number: 672: Name of MembersDokument16 SeitenBiology Project:The Cell Cycle Group Number: 672: Name of MembersNadhirah MohamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle (Scitable)Dokument2 SeitenCell Cycle (Scitable)LibrofiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell BiologyDokument24 SeitenCell BiologySheelendra Mangal BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- X G2 CheckpointDokument1 SeiteX G2 CheckpointNicole De VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle 2Dokument20 SeitenCell Cycle 2Louelle RazonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle Regulation TitleDokument5 SeitenCell Cycle Regulation TitleYuree ChoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module - : Title: Cell CycleDokument11 SeitenGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module - : Title: Cell CycleAron Chua FababeirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research How Checkpoints and Cyclins Help To Regulate The Cell CycleDokument1 SeiteResearch How Checkpoints and Cyclins Help To Regulate The Cell Cyclegiansamra2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology Lec 8Dokument15 SeitenCell Biology Lec 8Mushtaq HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument48 SeitenLecture 1NIMRAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Written Report IN Biology 1: "Prokaryotic Cell Division"Dokument5 SeitenWritten Report IN Biology 1: "Prokaryotic Cell Division"Rodel Barro AlwitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle ScriptDokument4 SeitenCell Cycle Scriptlalala lalalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell CycleDokument9 SeitenCell Cyclestevensb055Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell CycleDokument31 SeitenCell CycleMariah Missy DatuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eukaryotic Cell CycleDokument96 SeitenEukaryotic Cell CycleRaghav Oberoi100% (1)
- Q1 GenBio1 SLKWeek3 EditDokument20 SeitenQ1 GenBio1 SLKWeek3 EditInele Ellia AgReNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18 Cell Cycle Regulation-SDokument6 Seiten18 Cell Cycle Regulation-SChiyokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell Cycle and Its Regulation in 40 CharactersDokument4 SeitenThe Cell Cycle and Its Regulation in 40 CharactersExcellent KhozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Biology and Laboratory RulesDokument142 SeitenIntroduction to Biology and Laboratory RulesRouXuanChangNoch keine Bewertungen
- It Must Be Halloween: 1. DiscussDokument5 SeitenIt Must Be Halloween: 1. DiscussjayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Scene at A Crowded Shopping MallDokument4 SeitenThe Scene at A Crowded Shopping MalljayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talking About Money: 1. DiscussDokument4 SeitenTalking About Money: 1. Discussjayweinx100% (1)
- Novel: King Arthur: Theme: courage 勇敢Dokument3 SeitenNovel: King Arthur: Theme: courage 勇敢jayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- January 1Dokument49 SeitenJanuary 1LAMCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing The IntroductionDokument3 SeitenWriting The IntroductionjayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- How A Typical Five-Paragraph Essay Is Written SCDokument4 SeitenHow A Typical Five-Paragraph Essay Is Written SCjayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- 体面Dokument1 Seite体面jayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- My HeroDokument7 SeitenMy HerojayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- f5 110319Dokument3 Seitenf5 110319jayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- CW Compilation (2017 Trials)Dokument4 SeitenCW Compilation (2017 Trials)FBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pep. Set 4 PT3 2016 PDFDokument2 SeitenPep. Set 4 PT3 2016 PDFjayweinx100% (1)
- Mid Year f2 2016Dokument14 SeitenMid Year f2 2016jayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
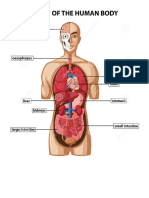
- Anatomy of Human BodyDokument1 SeiteAnatomy of Human BodyjayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Co-CurricularDokument3 SeitenReport On Co-CurricularjayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ibmyp2 10Dokument11 SeitenIbmyp2 10jayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ujian Sumatif 1 Ting 1 2017Dokument8 SeitenUjian Sumatif 1 Ting 1 2017jayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 CBA HEART ATTACK GUIDEDokument5 Seiten5 CBA HEART ATTACK GUIDEjayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul 2 PDF July 13 2009 9 39 PM 181kDokument10 SeitenModul 2 PDF July 13 2009 9 39 PM 181kArun ManiamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of Human BodyDokument1 SeiteAnatomy of Human BodyjayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebraic Expressions ExerciseDokument18 SeitenAlgebraic Expressions ExerciseLi Ann ChungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line EeeeDokument1 SeiteLine EeeejayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tips 2017 SPM EngDokument13 SeitenTips 2017 SPM EngjayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Here are the algebraic expressions for the given statements:2 more than x = x + 26 less than x = x - 6 k more than x = x + kx minus t = x - tx added t = x + tDokument52 SeitenHere are the algebraic expressions for the given statements:2 more than x = x + 26 less than x = x - 6 k more than x = x + kx minus t = x - tx added t = x + tjayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- C1 Maths F1 Topical Test 1Dokument3 SeitenC1 Maths F1 Topical Test 1jayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- f3 Bi Conjuction, Application LetterDokument7 Seitenf3 Bi Conjuction, Application LetterjayweinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Chapter 4 F1Dokument5 SeitenExercise Chapter 4 F1Nadwah HasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Somatic Embryogenesis PDFDokument12 SeitenSomatic Embryogenesis PDFTica DuyênNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics Basic Terms ModelansDokument2 SeitenGenetics Basic Terms ModelansNoora AttariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 12 - Life Science - Part A - Test 1 - 8 Feb 2024Dokument15 SeitenGrade 12 - Life Science - Part A - Test 1 - 8 Feb 2024Heinricht FourieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acrosome ReactionDokument4 SeitenAcrosome ReactionKuldip DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice: Choose Best (2.5 Points Each, 80Dokument7 SeitenMultiple Choice: Choose Best (2.5 Points Each, 80Florence BamigbolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Signaling - The ComponentsDokument7 SeitenCell Signaling - The Componentsk10 Lớp Dinh DưỡngNoch keine Bewertungen
- G5 Science - Q1-W7 - Puberty ChangesDokument25 SeitenG5 Science - Q1-W7 - Puberty ChangesMarimel GuillenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wolpert, L. - 1994 - Do We Understand DevelopmentDokument2 SeitenWolpert, L. - 1994 - Do We Understand DevelopmentcontulmmivNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Bio CH 1Dokument6 SeitenClass 12 Bio CH 1AbhishekDwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloning - Pros & ConsDokument6 SeitenCloning - Pros & ConsAaesta PriyestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell SignalingDokument38 SeitenCell SignalingTukai KulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDokument33 SeitenLesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologySherwin YenogacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asexual ReproductionDokument12 SeitenAsexual ReproductionJoyce DometitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELL CYCLE Cancer 1Dokument25 SeitenCELL CYCLE Cancer 1nur.fauziyah.99Noch keine Bewertungen
- GEN. BIOLOGY 1: CELL CYCLE AND MEIOSISDokument5 SeitenGEN. BIOLOGY 1: CELL CYCLE AND MEIOSISAna Carmela MortelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth and Life Science Q2 LP 3Dokument7 SeitenEarth and Life Science Q2 LP 3Jhoana OrenseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Luis Abonce-Llanos - Karyotypes & Chromosomes Amoeba Sisters QuestionsDokument2 SeitenLuis Abonce-Llanos - Karyotypes & Chromosomes Amoeba Sisters QuestionsLuis Abonce-LlanosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xi Biology Term 2 MCQDokument94 SeitenXi Biology Term 2 MCQkiruthikpranav46Noch keine Bewertungen
- The 5 Stages of Intermittent Fasting - LIFE Apps - LIVE and LEARNDokument8 SeitenThe 5 Stages of Intermittent Fasting - LIFE Apps - LIVE and LEARNPetra CtiborNoch keine Bewertungen
- WORKSHEET 5.10 Cell & Mitosis Crossword PuzzleDokument4 SeitenWORKSHEET 5.10 Cell & Mitosis Crossword PuzzleNurul Huda IsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embriology Hewan Michael J. F. Barresi Scott F. Gilbert Developm (B-Ok - Xyz) (2) (PDF - Io)Dokument60 SeitenEmbriology Hewan Michael J. F. Barresi Scott F. Gilbert Developm (B-Ok - Xyz) (2) (PDF - Io)Afriani AfidahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mischief MakerDokument5 SeitenThe Mischief Makerapi-550006187Noch keine Bewertungen