Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ECE650 Midterm Exam S - 10
Hochgeladen von
MohammedFikryOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ECE650 Midterm Exam S - 10
Hochgeladen von
MohammedFikryCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ain Shams University
Faculty of Engineering Department: Electronics and
Course: ECE 650 Digital Communication II Communications
Semester: Spring 2010 Instructors: Prof. Fawzy Ibrahim
Midterm Exam
Total Grade: 20 Time allowed: 120 Minutes
Question #1
(a) What is the importance of channel coding? Discuss briefly the main idea of the
Linear Block Codes (LBC).
(b) Consider a (7, 4) Linear Block Codes (LBC) generator matrix which is given by:
1 0 0 0 | 1 1 1
0 1 0 0 | 1 1 0
G
0010 | 1 0 1
0 0 0 1 | 0 1 1
(i) For the message vector, M =[1 0 1 1], calculate code vector, C.
(ii) Calculate the parity check matrix, H.
(iii) Let R =[1 0 1 0 0 0 1] is the received vector, calculate error syndrome vector, S
and the message vector, M.
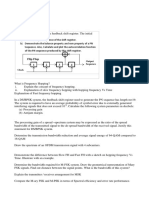
c) For the convolutional encoder shown in Fig. 1, compute the output coded data, y,
when the input data is x = [11011]. (The first input bit is the leftmost element of the x
row vector.)
Fig. 1 A convolutional encoder
ASU ECE 650 MT Exam Page 1 of 2
Question #2
Consider a binary communication system which is used to transmit 10 analog signals
having the same bandwidth using TDM / PCM technique. Each of the analog signals is
sampled, quantized and encoded into binary code words by a non-uniform quantization
PCM technique, applying the "-law", with = 255 and the number of bits, n =8. The
resulting TDM/PCM signal is then transmitted over a transmission channel of 2 MHz
bandwidth. For this system perform the following:
(a) Calculate the peak SNR that can be obtained by this system.
(b) Determine the total channel capacity and the sampling frequency F s at which each of
the analog signals can be sampled.
(c) What is maximum possible value for the highest frequency in the spectrum of the
analog signal?
(d) Looking forward to decrease the PCM bit rate, Differential Pulse Code Modulation
(DPCM) is utilized. Draw the block diagram of a DPCM system and highlight the
advantages and limitations of this approach.
Question #3
a) Consider a digital communication system which consists of 4 binary channels with
transmission rate 200 bytes / sec each, and a Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)
system using a time slot corresponding to one byte from each channel. For this
system, calculate the following:
i) The frame size [bytes]. ii) The frame duration [m sec].
iii) The frame rate [frame / sec]. iv) The bit rate [bits/sec] of the TDM link.
b) Apply the 8-point Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm to calculate the spectrum
X(k) of the discrete periodic (N = 8) signal x(n) having the following samples:
x(n) = {2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1} and then draw the resulting spectrum as function of k, f
and if the sampling time, Ts = 1 ms.
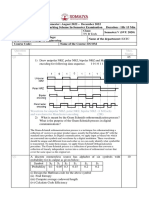
c) Consider the analog waveform w(t) whose spectrum W(f) is a pulse function as shown
in Fig. 3. If the signal amplitude A= 10 and its bandwidth B = 2 kHz, it is required to
convert w(t) into a flat-topped PAM signal by using the sampling rate, fs = 10 kHz
and a pulse duration or width, = 10 s, For this PAM signal do the following:
i) Determine and sketch the magnitude spectrum.
ii) Calculate the value for the first null bandwidth.
Fig. 3 Magnitude spectrum of the input analog signal
ASU ECE 650 MT Exam Page 2 of 2
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- School of Electronics Engineering (Sense)Dokument12 SeitenSchool of Electronics Engineering (Sense)Srividhya SelvakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- School of Electronics Engineering: Specific Instruction To Students (If Any)Dokument2 SeitenSchool of Electronics Engineering: Specific Instruction To Students (If Any)Dinesh ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- R5310406-Digital CommunicationsDokument4 SeitenR5310406-Digital CommunicationssivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Com DA2Dokument2 SeitenCom DA2Alemshet Agizew0% (1)
- DC aDCghskjskksks FjsDokument4 SeitenDC aDCghskjskksks FjsSaiteja GundapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank - NewDokument5 SeitenQuestion Bank - NewJeevanreddy MamillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Final Examination SEMESTER 1 2009 / 2010Dokument7 SeitenCollege of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Final Examination SEMESTER 1 2009 / 2010shahNoch keine Bewertungen
- r05310404 Digital CommunicationsDokument7 Seitenr05310404 Digital CommunicationsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems (ELE 3151) RCSDokument2 SeitenCommunication Systems (ELE 3151) RCSAkshat PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dcom QuestionDokument3 SeitenDcom Questionsushant sahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page 1 of 2Dokument2 SeitenPage 1 of 2ptmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems (ELE 3103) RCS 2017Dokument2 SeitenCommunication Systems (ELE 3103) RCS 2017devangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Information Engineering: 2010/11 Summer Examination Paper, Specimen Solutions and FeedbackDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Information Engineering: 2010/11 Summer Examination Paper, Specimen Solutions and Feedbackcesar767Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sol DCOM 22-23 ISEDokument2 SeitenSol DCOM 22-23 ISEdevansh chotaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Digital Communication1 December 2011Dokument2 SeitenAdvanced Digital Communication1 December 2011Sneha UpadhyayulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 1Syakira WahidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Communication EC501Dokument2 SeitenAnalog Communication EC501Raghavendra LingrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital CommunicationsDokument5 SeitenDigital CommunicationsEcNoch keine Bewertungen
- r05220503 Principles of CommunicationsDokument6 Seitenr05220503 Principles of CommunicationsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Communication Model PaperDokument2 SeitenDigital Communication Model PaperSubrahmanyam ChedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital ComminicationsDokument8 SeitenDigital ComminicationsAkbarSabNoch keine Bewertungen
- NovemberDecember 2020Dokument1 SeiteNovemberDecember 2020PoongodiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dcs Assignment I - A1 Digital AssinmentDokument2 SeitenDcs Assignment I - A1 Digital AssinmentYash GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Assignment I - A1 DIGITAL ASSINMENTDokument2 Seiten3-Assignment I - A1 DIGITAL ASSINMENTRaj GaneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13A04502 Digital Communication SystemsDokument2 Seiten13A04502 Digital Communication SystemsMallikarjuna Rao YamarthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- R07 Set No. 2Dokument8 SeitenR07 Set No. 2Anonymous BHcPexNoch keine Bewertungen
- School of Electronics Engineering (Sense) : Answer Any Three QuestionsDokument9 SeitenSchool of Electronics Engineering (Sense) : Answer Any Three QuestionsIyyaasuu YaadataaNoch keine Bewertungen
- N31 WT31 AssignmentII 2012Dokument1 SeiteN31 WT31 AssignmentII 2012Srinivasan JeganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet SamplingDokument3 SeitenSheet SamplingAhmed MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- rr322205 Communication SystemsDokument7 Seitenrr322205 Communication SystemsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- CT ws10 enDokument23 SeitenCT ws10 enIoana Suciu0% (1)
- 13A04502 Digital Communication SystemsDokument2 Seiten13A04502 Digital Communication SystemsMallikarjuna Rao YamarthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code No: 35095Dokument8 SeitenCode No: 35095SRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- Sheet 5-3Dokument2 SeitenSheet 5-3mostafa3aalyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Information Engineering: 2009/10 Summer Examination Paper and Specimen SolutionsDokument9 SeitenIntroduction To Information Engineering: 2009/10 Summer Examination Paper and Specimen Solutionscesar767Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rr310405 Digital CommunicationsDokument8 SeitenRr310405 Digital CommunicationsSrinivasa Rao GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems (ELE 3103) RCSDokument3 SeitenCommunication Systems (ELE 3103) RCSsagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1: LKC Fes UEET2523 October 2016 Digital CommunicationDokument4 SeitenTest 1: LKC Fes UEET2523 October 2016 Digital CommunicationYenlyn TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Electronics and Communication EngineeringDokument2 SeitenWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Electronics and Communication Engineeringneelima raniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adc QPDokument1 SeiteAdc QPamulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code No: 45088Dokument8 SeitenCode No: 45088SRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Iii Ece I SemDokument45 SeitenIii Ece I SemMacharla DevikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NR 221201 Communication TheoryDokument8 SeitenNR 221201 Communication TheorySrinivasa Rao GNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC 2018Dokument4 SeitenDC 2018Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering AKNUNoch keine Bewertungen
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Digital CommunicationsDokument2 SeitenWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Digital CommunicationsHARIKRISHNA PONNAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Transmission Lab: Communication SystemDokument8 SeitenData Transmission Lab: Communication SystemHoang MaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Test 1 - Answer KeyDokument1 SeiteDC Test 1 - Answer KeyrcherrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Com. Report 20111115 - EnglishDokument23 SeitenWireless Com. Report 20111115 - EnglishHoang MaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECD312:Digital Communication and Systems Assignment: 1 (20 Points)Dokument3 SeitenECD312:Digital Communication and Systems Assignment: 1 (20 Points)V Prakash SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signals and Systems Sample QuestionsDokument10 SeitenSignals and Systems Sample QuestionsSimon Deshte NderituNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC-2019 1Dokument7 SeitenDC-2019 1Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering AKNUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nr310405 Digital Communications Set1Dokument2 SeitenNr310405 Digital Communications Set1Srinivasa Rao GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital CommunicationsgDokument8 SeitenDigital Communicationsgksln100% (1)
- Digital Communication Uq 2011Dokument30 SeitenDigital Communication Uq 2011shankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- VL2022230500824 DaDokument5 SeitenVL2022230500824 DaAditya Bonnerjee 21BEC0384Noch keine Bewertungen
- International Islamic University Malaysia: Midterm Examination SEMESTER II, 2013/2014 SESSIONDokument6 SeitenInternational Islamic University Malaysia: Midterm Examination SEMESTER II, 2013/2014 SESSIONwmhbwhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Case Studies on Signal, Audio and Image Processing Using MatlabVon EverandSome Case Studies on Signal, Audio and Image Processing Using MatlabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Modeling of Wireless Communication SystemsVon EverandAnalytical Modeling of Wireless Communication SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessVon EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- ESC CatalogDokument18 SeitenESC CatalogMohammedFikry100% (1)
- A2000 PDFDokument2 SeitenA2000 PDFMohammedFikry50% (2)
- Computer ArchitectureDokument101 SeitenComputer ArchitectureSoyak_1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual QRAE II CombinedDokument92 SeitenManual QRAE II CombinedNihat DğnNoch keine Bewertungen
- The History of The Arab LeagueDokument2 SeitenThe History of The Arab LeagueMohammedFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Database of Translation Agencies All CountriesDokument3.915 SeitenDatabase of Translation Agencies All CountriesLing Tra67% (3)
- TCB Role Measurement CalibarationDokument68 SeitenTCB Role Measurement CalibarationRidhWanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrument Calibration ExplanationDokument10 SeitenInstrument Calibration ExplanationCris RonaldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goldenbook ArabicDokument7 SeitenGoldenbook ArabicMohammedFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument1 SeiteUntitledMohammedFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- LISAprimer PDFDokument52 SeitenLISAprimer PDFMohammedFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dale Carnegie's Golden BookDokument7 SeitenDale Carnegie's Golden Booktotaleclipse0202Noch keine Bewertungen
- Binary SearchDokument1 SeiteBinary SearchMohammedFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bismillah-e-Rahman-e-Raheem: Complexity of Algorithm and Cost - Time Trade OffDokument14 SeitenBismillah-e-Rahman-e-Raheem: Complexity of Algorithm and Cost - Time Trade OffMohammedFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec20 H PDFDokument4 SeitenLec20 H PDFShivamPradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Binary SearchDokument1 SeiteBinary SearchMohammedFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 8 (Strings and Files)Dokument91 SeitenLesson 8 (Strings and Files)MohammedFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 100 Best Software Engineering Books EverDokument5 SeitenTop 100 Best Software Engineering Books EverMohammedFikry100% (1)
- TransformationsDokument34 SeitenTransformationsRigo Martinez MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Questions and AnswersDokument26 SeitenJava Questions and AnswersMohammedFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics & CommunicationDokument12 SeitenElectronics & CommunicationMohammedFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- I S D N: Ntegrated Ervices Igital EtworkDokument24 SeitenI S D N: Ntegrated Ervices Igital EtworkMohammedFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 (N, K) Linear Block Codes Over GF (Q)Dokument13 Seiten3.1 (N, K) Linear Block Codes Over GF (Q)MohammedFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- UserManual ch7,8Dokument19 SeitenUserManual ch7,8wleaderheeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC/DC Converters: Not Recommended For New Design inDokument3 SeitenDC/DC Converters: Not Recommended For New Design insaberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Megawin Switchgear: Numerical Over Current ProtectionDokument4 SeitenMegawin Switchgear: Numerical Over Current ProtectionRock hackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9 USB To PIC Microcontroller InterfaceDokument8 SeitenLecture 9 USB To PIC Microcontroller Interfaceaaaa100% (1)
- Option EntryDokument6 SeitenOption EntryManoj RajahulliNoch keine Bewertungen
- CR310 ManualDokument236 SeitenCR310 Manualelisio_fonsecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Order ExampleDokument25 Seiten2nd Order ExampleMagdy RiadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPC555UMDokument966 SeitenMPC555UMRafael FávaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components OFA ComputerDokument29 SeitenComponents OFA ComputerRobert S. DeligeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- SATIP-P-103-01 Rev 6Dokument30 SeitenSATIP-P-103-01 Rev 6VISAKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Voltage CoilsDokument20 SeitenHigh Voltage CoilsMarco SussuaranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Askey rtl0200 5g NR Cpe DatasheetDokument2 SeitenAskey rtl0200 5g NR Cpe DatasheetMSI IngenieriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 BEE AC ListDokument16 Seiten9 BEE AC ListKarthek EyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ULN2001, ULN2002 ULN2003, ULN2004: DescriptionDokument17 SeitenULN2001, ULN2002 ULN2003, ULN2004: DescriptionAlberto CorralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- D-2 Power Vent ManualDokument24 SeitenD-2 Power Vent ManualJon BondNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edson - Vacuum Tube Oscillators 1953 PDFDokument494 SeitenEdson - Vacuum Tube Oscillators 1953 PDFrichi78yobsNoch keine Bewertungen
- BTS Power Control R10Dokument17 SeitenBTS Power Control R10Achmad SalsabilNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZN551Dokument2 SeitenZN551Darnell GracenNoch keine Bewertungen
- B-63494EN - 01 - Fin (Dual Check Safety Ops Man)Dokument268 SeitenB-63494EN - 01 - Fin (Dual Check Safety Ops Man)nzbradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volume II - Ericsson Field Guide For UTRAN P1-Lite: Feature Parameters and Best PracticesDokument71 SeitenVolume II - Ericsson Field Guide For UTRAN P1-Lite: Feature Parameters and Best Practicessara y santi becerra barreto100% (2)
- Digital Integrated Circuit ApplicationsDokument3 SeitenDigital Integrated Circuit ApplicationsShammu KandepuNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Silicone Conformal Coating For PCBDokument19 SeitenWhat Is Silicone Conformal Coating For PCBjackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Correpcion de Error U4 Xerox 5020Dokument2 SeitenCorrepcion de Error U4 Xerox 5020Victor Michel Cribilleros GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- OTC000005 OTN Introduction ISSUE1.00Dokument73 SeitenOTC000005 OTN Introduction ISSUE1.00Mohammed Kumayl100% (1)
- Valliammai Enginering College Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument6 SeitenValliammai Enginering College Department of Mechanical EngineeringMani KandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GS70 - MSI-1771 Disassembly GuideDokument17 SeitenGS70 - MSI-1771 Disassembly GuideCatalin FinkelsteinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual: 40VM Series Indoor Units and Controllers For Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) Heat Pump SystemDokument80 SeitenService Manual: 40VM Series Indoor Units and Controllers For Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) Heat Pump SystemNasim KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procuct-Catalogue-Active-Next-Generation Ang STD Eng R02 0Dokument50 SeitenProcuct-Catalogue-Active-Next-Generation Ang STD Eng R02 0Nethaji MsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10.Tủ Điện DB-B-MDFDokument7 Seiten10.Tủ Điện DB-B-MDFthanh sang đinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pure DataDokument11 SeitenPure Datatcsaxtc0% (1)