Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 18 - Liver and Biliary Tract
Hochgeladen von
springding0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
25 Ansichten5 Seitenliver
Originaltitel
THE LIVER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenliver
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
25 Ansichten5 SeitenChapter 18 - Liver and Biliary Tract
Hochgeladen von
springdingliver
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
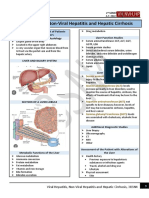
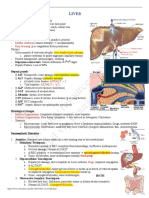
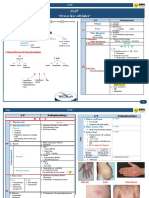
Chapter 18 Liver and Biliary Tract
THE LIVER Hepatocyte degeneration and
has a dual blood supply: the intracellular accumulations
portal vein provides 60% to
Hepatocyte necrosis and
70% of hepatic blood flow, and
apoptosis
the hepatic artery supplies 30%
to 40%
Inflammation
two different concepts: the
hepatic lobule and the hepatic
Regeneration
acinus
Centrilobular - hepatocytes in
the vicinity of the terminal Fibrosis
hepatic vein
TABLE 18-1 -- Laboratory
Periportal - those near the
Evaluation of Liver Disease
portal tract
3 zones: Test
zone 1 being closest to Categor
y Serum Measurement[*]
the vascular supply
zone 3 abutting the Hepatocy Cytosolic
terminal hepatic venule te hepatocellular
and most remote from integrity enzymes[]
the afferent blood supply Serum aspartate
zone 2 being aminotransferase
intermediate (AST)
Classical hexagonal
Serum alanine
Portal triangular
aminotransferase
Kp-1 (CD68) kuppfers cells (ALT)
Low molecular wt. keratin bile
duct cells Serum lactate
dehydrogenase
EMA/CEA canaliculi cells
(LDH)
Space of Disse where fat-
containing hepatic stellate cells Biliary Substances normally
(HSCs) are found
secreted in bile[]
Canals of Hering - connect the
bile canaliculi to bile ductules in Serum bilirubin
the periportal region Total:
unconjugated
General Features of Hepatic plus
Disease conjugated
The major primary diseases of Direct:
the liver: conjugated
viral hepatitis only
alcoholic liver disease Delta:
nonalcoholic fatty liver covalently
disease (NAFLD) linked to
hepatocellular carcinoma albumin
(HCC)
Urine bilirubin
PATTERNS OF HEPATIC INJURY
Chapter 18 Liver and Biliary Tract
Test End-stage liver disease may
Categor occur by insidious destruction of
y Serum Measurement[*] hepatocytes or by repetitive
discrete waves of parenchymal
Serum bile acids damage
The alterations that cause liver
Plasma membrane failure fall into three categories:
enzymes (from Acute liver failure -
damage to bile associated with
canaliculus)[] encephalopathy within 6
Serum alkaline months after the initial
phosphatase diagnosis.
Serum -glutamyl - fulminant liver failure
transpeptidase when the encephalopathy develops
rapidly, within 2 weeks of the
Serum 5- onset of jaundice, and as sub-
nucleotidase fulminant liver failure when the
encephalopathy develops within 3
Hepatocy Proteins secreted into months of the onset of jaundice
te the blood Chronic liver disease - the
function Serum albumin[] most common route to
Prothrombin hepatic failure
time[] (factors V, - the end point of
VII, X, relentless chronic
prothrombin, hepatitis ending in
fibrinogen) cirrhosis
Hepatic dysfunction
Hepatocyte without overt necrosis
metabolism
Serum ammonia[] Clinical Features:
Aminopyrine Jaundice
breath test Hypoalbuminemia, which
(hepatic predisposes to peripheral
demethylation)[] edema
hyperammonemia, which plays
Galactose
a major role in cerebral
elimination
dysfunction
(intravenous
Fetor hepaticus is a
injection)[]
characteristic body odor that is
variously described as musty
HEPATIC FAILURE or sweet and sour
The most severe clinical Impaired estrogen metabolism
consequence of liver disease and consequent
result of sudden and massive hyperestrogenemia are the
hepatic destruction (fulminant putative causes of palmar
hepatic failure) erythema
the end stage of progressive severely impaired liver function,
chronic damage to the liver patients are highly susceptible
Chapter 18 Liver and Biliary Tract
to encephalopathy and failure
of multiple organ systems Pathogenesis:
The central pathogenic
Three particular complications processes in cirrhosis are death
associated with hepatic failure merit of hepatocytes, extracellular
separate consideration: matrix (ECM) deposition, and
Hepatic encephalopathy - vascular reorganization.[
manifested by a spectrum of types I and III collagen are
disturbances in consciousness, deposited in the space of Disse,
ranging from subtle behavioral creating fibrotic septal tracts
abnormalities, to marked The predominant mechanism of
confusion and stupor, to deep fibrosis is the proliferation of
coma and death hepatic stellate cells and their
- regarded as a disorder activation into highly fibrogenic
of neurotransmission in the cells
central nervous system and
neuromuscular system Clinical features:
Hepatorenal syndrome - The ultimate mechanism of deaths in
refers to the appearance of most cirrhotic patients is (1)
renal failure in individuals with progressive liver failure, (2) a
severe chronic liver disease in complication related to portal
whom there are no intrinsic hypertension, or (3) the development
morphologic or functional of hepatocellular carcinoma
causes for the renal failure
Hepatopulmonary syndrome PORTAL HYPERTENSION
(HPS) - characterized by the The major prehepatic conditions
clinical triad of chronic liver are obstructive thrombosis,
disease, hypoxemia, and intra- narrowing of the portal vein
pulmonary vascular dilations before it ramifies within the
(IVPD) liver, or massive splenomegaly
with increased splenic vein
blood flow
CIRRHOSIS The main post-hepatic causes
Causes: alcohol abuse, viral are severe right-sided heart
hepatitis, and non-alcoholic failure, constrictive pericarditis,
steatohepatitis (NASH) and hepatic vein outflow
three main morphologic obstruction.
characteristics: The dominant intrahepatic
Bridging fibrous septa cause is cirrhosis
* Fibrosis is the The four major clinical
key feature of consequences of portal
progressive damage hypertension are:
to the liver Ascites - the
Parenchymal nodules accumulation of excess
containing hepatocytes fluid in the peritoneal
encircled by fibrosis cavity
Disruption of the Portosystemic Shunts -
architecture of the entire the flow is reversed from
liver portal to systemic
Chapter 18 Liver and Biliary Tract
circulation by dilation of *kernicterus - accumulation of
collateral vessels and unconjugated bilirubin in the
development of new brain
vessels conjugated bilirubin - water-
Splenomegaly soluble, nontoxic, and only
Hepatic encephalopathy loosely bound to albumin;
excess conjugated bilirubin in
JAUNDICE AND CHOLESTASIS plasma can be excreted in urine
The common causes of jaundice Jaundice becomes evident when
are bilirubin overproduction, the serum bilirubin levels rise
hepatitis, and obstruction of the above 2.0 to 2.5 mg/dL
flow of bile
2 major functions of hepatic Two conditions result from specific
bile: defects in hepatocellular bilirubin
emulsification of dietary metabolism:
fat Neonatal Jaundice - transient
of bilirubin, excess and mild unconjugated
cholesterol, xenobiotics hyperbilirubinemia, termed
jaundice and icterus - yellow neonatal jaundice or physiologic
discoloration of the skin and jaundice of the newborn
sclera respectively Hereditary Hyperbilirubinemias
cholestatis - retention of not Crigler-Najjar
only bilirubin but also other syndrome type I
solutes eliminated in bile hepatic UGT1A1 -
completely absent, and
Bilirubin and Bile Formation the colorless bile contains
Bilirubin is the end product of only trace amounts of
heme degradation; from unconjugated bilirubin
breakdown of senescent red Crigler-Najjar
cells by the mononuclear syndrome type II - a
phagocytic system less severe, nonfatal
Bile acids - the major catabolic disorder in which UGT1A1
products of cholesterol; act as enzyme activity is greatly
highly effective detergents reduced, and the enzyme
is capable of forming only
Pathophysiology of Jaundice monoglucuronidated
Both unconjugated bilirubin and bilirubin
conjugated bilirubin (bilirubin Gilbert syndrome is a
glucuronides) may accumulate relatively common,
systemically benign, inherited
Unconjugated bilirubin - condition presenting with
virtually insoluble in water at mild, fluctuating
physiologic pH and exists in hyperbilirubinemia, in the
tight complexes with serum absence of hemolysis or
albumin. This form cannot be liver disease
excreted in the urine even Dubin-Johnson
when blood levels are high syndrome - an
autosomal recessive
disorder characterized by
Chapter 18 Liver and Biliary Tract
chronic conjugated across the canalicular
hyperbilirubinemia. It is membrane
caused by a defect in
hepatocellular excretion
of bilirubin glucuronides
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hepatobiliary Pathophysiology and DiseasesDokument34 SeitenHepatobiliary Pathophysiology and DiseasesTony NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organ Funt PDFDokument32 SeitenOrgan Funt PDFs.k jamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigations and Their Rationale: in Obstructive JaundiceDokument53 SeitenInvestigations and Their Rationale: in Obstructive JaundiceEvediciNoch keine Bewertungen
- 060 CLIN+PATH+43s Liver+Function+TestDokument43 Seiten060 CLIN+PATH+43s Liver+Function+TestMSKCNoch keine Bewertungen
- HBS Lecture by Dr. Masud JahanDokument13 SeitenHBS Lecture by Dr. Masud Jahanjannatul supti24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Viral HepatitisDokument7 SeitenViral Hepatitisadrian kristopher dela cruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver TransplantationDokument21 SeitenLiver TransplantationRozi RamliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Pathology PDFDokument7 SeitenLiver Pathology PDFjohn smithNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5. Liver Failure GM Eng 2020Dokument46 Seiten5. Liver Failure GM Eng 2020snowrose2609Noch keine Bewertungen
- Askep SirosisDokument73 SeitenAskep SirosisRisma Yuliana PratiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatology (Ekanayaka)Dokument92 SeitenHepatology (Ekanayaka)RusiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pemeriksaan Fungsi HatiDokument46 SeitenPemeriksaan Fungsi HatiNadyaWevtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcoholic Liver Disease & Cirrhosis GuideDokument5 SeitenAlcoholic Liver Disease & Cirrhosis GuideJennyu YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. GALLEBO's Guide to Histopath and Hepatitis VirusesDokument216 SeitenDr. GALLEBO's Guide to Histopath and Hepatitis VirusesFelyne Angelique C. GanoticeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver DiagnosticsDokument10 SeitenLiver DiagnosticsTiny Briones-SallomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC - Liver FunctionDokument5 SeitenCC - Liver FunctionOrhan AsdfghjklNoch keine Bewertungen
- With Ordinary Talent and Extraordinary Perseverance, All Things Are Attainable.Dokument72 SeitenWith Ordinary Talent and Extraordinary Perseverance, All Things Are Attainable.Darin MonerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Function Test (LFT) OverviewDokument26 SeitenLiver Function Test (LFT) Overviewanisa rachmitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Diseases 2.4 (2024)Dokument60 Seiten3 - Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Diseases 2.4 (2024)R. nounNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slides DR Ashgar Approach To LFTs 12.12.2021Dokument47 SeitenSlides DR Ashgar Approach To LFTs 12.12.2021Maryam OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEMERIKSAAN LABORATORIUM UNTUK PENYAKIT HATIDokument23 SeitenPEMERIKSAAN LABORATORIUM UNTUK PENYAKIT HATIgpradheptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CKD Nursing Care Using NANDA, NOC, NICDokument41 SeitenCKD Nursing Care Using NANDA, NOC, NICanggardaerinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asuhan Keperawatan Chronic Kidney Disease (CKDDokument12 SeitenAsuhan Keperawatan Chronic Kidney Disease (CKDivo GuloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases of the Liver: Anatomy, Functions and TestsDokument125 SeitenDiseases of the Liver: Anatomy, Functions and TestslindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaundice: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDokument6 SeitenJaundice: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentNestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Function Tests: An OverviewDokument39 SeitenLiver Function Tests: An OverviewchenlieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas PathologyDokument50 SeitenLiver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas PathologybonadnadineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver - Dr. Allam 2021 PDFDokument70 SeitenLiver - Dr. Allam 2021 PDFMohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type of Enzyme Location of The E Normal Value Abnorma L Values InterpretationDokument4 SeitenType of Enzyme Location of The E Normal Value Abnorma L Values InterpretationvisiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patho - Hepatobiliary System AtfDokument21 SeitenPatho - Hepatobiliary System AtfGaurav ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigation of Liver and Biliary DiseaseDokument4 SeitenInvestigation of Liver and Biliary DiseaseNeil Patrick AngelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Cirrhosis Paper PresentationDokument52 SeitenLiver Cirrhosis Paper PresentationNagabharana Hm HollattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Chemistry 2 Liver FunctionsDokument5 SeitenClinical Chemistry 2 Liver FunctionsJen NovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 Liver Tunction TestsDokument41 Seiten07 Liver Tunction TestsPaulina PaskeviciuteNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review of Liver Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument41 SeitenA Review of Liver Anatomy and PhysiologyVaseaPupchin0% (1)
- Acute Renal FailureDokument30 SeitenAcute Renal FailureCarmina SalvañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12Dokument8 SeitenChapter 12newmexicoomfsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver DiseasesDokument53 SeitenLiver DiseasesismailcemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acknowledgement ReceiptDokument21 SeitenAcknowledgement ReceiptdeevoncNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pancreatitis CPCDokument38 SeitenAcute Pancreatitis CPCSariu Ali DidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUR 3032 Pancreatic, Biliary, and Hepatic Disorders Study PlanDokument6 SeitenNUR 3032 Pancreatic, Biliary, and Hepatic Disorders Study PlanThalia FortuneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical Diseases of Liver1Dokument54 SeitenSurgical Diseases of Liver1DR MOHAMED HEALTH CHANNELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal System (Letu Da) PDFDokument74 SeitenGastrointestinal System (Letu Da) PDFNafiul Islam100% (4)
- 12a. Kuliah Aki 2017Dokument36 Seiten12a. Kuliah Aki 2017yussikafernandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pemeriksaan Lab Kelainan Sistem Hepatobilier & PankreasDokument82 SeitenPemeriksaan Lab Kelainan Sistem Hepatobilier & PankreasDhimasAjiZuandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect. 8Dokument30 SeitenLect. 8jayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretation of Liver Function TestsDokument14 SeitenInterpretation of Liver Function TestsNirav SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIVERDokument24 SeitenLIVERFredIanBantolioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labdxtransfinals PDFDokument16 SeitenLabdxtransfinals PDFSubhan Souda MangalasseryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Induced Renal DisorderDokument50 SeitenDrug Induced Renal DisorderYv SantoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portal Hypertension and Cirrhosis: Key ConceptsDokument16 SeitenPortal Hypertension and Cirrhosis: Key ConceptsWa Ode FasridaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatology Case PresentationDokument48 SeitenHepatology Case PresentationHajar HossamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Anatomy and Physiology GuideDokument62 SeitenLiver Anatomy and Physiology Guidehussain AltaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatic EmergenciesDokument76 SeitenHepatic EmergenciesAbdelrahman MokhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Function Test: Maimun ZA Lab Patologi Klinik Fkub-RssaDokument26 SeitenLiver Function Test: Maimun ZA Lab Patologi Klinik Fkub-RssaSaifuddin BadarsyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.acute Liver Failure Without AudioDokument42 Seiten3.acute Liver Failure Without AudioMohamed ElkadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anesthetic Consideration For Patients With Obstructive JaundiceDokument47 SeitenAnesthetic Consideration For Patients With Obstructive JaundiceagatakassaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Kidney Injuri: Professor Ibrahim UmmateDokument46 SeitenAcute Kidney Injuri: Professor Ibrahim UmmateElvis obajeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast Facts: Acute and Recurrent Pancreatitis: Using evidence to support treatmentVon EverandFast Facts: Acute and Recurrent Pancreatitis: Using evidence to support treatmentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signaling Pathways in Liver DiseasesVon EverandSignaling Pathways in Liver DiseasesJean-Francois DufourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Femur 151205075833 Lva1 App6891Dokument14 SeitenFemur 151205075833 Lva1 App6891springdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wound ManagementDokument19 SeitenWound ManagementspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPM16TH Intrapartum and Immediate Postpartum CareDokument25 SeitenCPM16TH Intrapartum and Immediate Postpartum CarespringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attia General Surgery Review ManualDokument158 SeitenAttia General Surgery Review Manualbphage100% (2)
- Airway MGTDokument8 SeitenAirway MGTspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airway MGTDokument8 SeitenAirway MGTspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine CPG On The Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Adults-2015 Update - Part 2 PDFDokument140 SeitenPhilippine CPG On The Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Adults-2015 Update - Part 2 PDFspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaerobic BacteriaDokument16 SeitenAnaerobic BacteriaPriti Go0% (1)
- Intracranial and Spinal Tumors 10 ItemsDokument2 SeitenIntracranial and Spinal Tumors 10 ItemsspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spirometry IntrepretationDokument1 SeiteSpirometry IntrepretationspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaerobic BacteriaDokument16 SeitenAnaerobic BacteriaPriti Go0% (1)
- Intracranial and Spinal Tumors 10 ItemsDokument2 SeitenIntracranial and Spinal Tumors 10 ItemsspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia Gi NotesDokument34 SeitenPedia Gi NotesspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- MJ Legal FundamentalsDokument2 SeitenMJ Legal FundamentalsspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zako HematologyDokument35 SeitenZako Hematologydoctormehmeteren8292Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Secondhand SmokeDokument3 SeitenWhat Is Secondhand SmokespringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- GlaucomaDokument5 SeitenGlaucomaspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIGOCEDokument11 SeitenFIGOCEAldwin TanuwijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spirometry IntrepretationDokument1 SeiteSpirometry IntrepretationspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indirect Inguinal Hernias Are The Most Common Groin Hernias in Men and WomenDokument2 SeitenIndirect Inguinal Hernias Are The Most Common Groin Hernias in Men and WomenspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 - Memorial AcclamationDokument1 Seite07 - Memorial AcclamationspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glycogen Metabolism Index CardDokument3 SeitenGlycogen Metabolism Index CardspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- RNA VirusesDokument11 SeitenRNA VirusesKate Alyssa CatonNoch keine Bewertungen
- ShapesDokument10 SeitenShapesRosalind GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Must Know Parasitology TermsDokument22 SeitenMust Know Parasitology TermsvillajanellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MUST To KNOW in Medical Technology Laws EthicsDokument12 SeitenMUST To KNOW in Medical Technology Laws EthicsRona Salando100% (3)
- Neeraj's Notes Plan A Trip: USMLE CS: Step-1: Arrange The DocumentsDokument0 SeitenNeeraj's Notes Plan A Trip: USMLE CS: Step-1: Arrange The DocumentsvarrakeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Let The Saints Be JoyfulDokument1 SeiteLet The Saints Be JoyfulspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digging Up The Bones - MicrobiologyDokument31 SeitenDigging Up The Bones - MicrobiologyMossa Di Base100% (1)
- Cancer in The Philippines Vol. IV Part 1 PDFDokument78 SeitenCancer in The Philippines Vol. IV Part 1 PDFspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar Pustaka: Tahun 2009 Dan 2010Dokument3 SeitenDaftar Pustaka: Tahun 2009 Dan 2010yoga paripurnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adult Intussusception: A Retrospective ReviewDokument5 SeitenAdult Intussusception: A Retrospective ReviewkameliasitorusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indikasi EgdDokument3 SeitenIndikasi EgdAhmad MirzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complications of CholelithiasisDokument25 SeitenComplications of CholelithiasisGibson RamseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NO Particular Pages 1. 2 2. Problem Statement 3 3. Literature Review 4-6 4. Discussion 7-13 5. Conclusion 14 6. Reference List 15 7. Attachment 16-17Dokument17 SeitenNO Particular Pages 1. 2 2. Problem Statement 3 3. Literature Review 4-6 4. Discussion 7-13 5. Conclusion 14 6. Reference List 15 7. Attachment 16-17Fardzli MatjakirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastritis and Peptic Ulcer Disease: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument23 SeitenGastritis and Peptic Ulcer Disease: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentLisnawati Nur Farida100% (1)
- Anorectal Malformations: DR BenakDokument22 SeitenAnorectal Malformations: DR Benakbenak shivalingappaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Guide To The Frog DissectionDokument3 SeitenStudent Guide To The Frog Dissectionapi-233187566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDokument20 SeitenPeptic Ulcer DiseaseALNAKINoch keine Bewertungen
- Artigo 2023 ELASTOGRAFIADokument6 SeitenArtigo 2023 ELASTOGRAFIAFrankNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1991 - McTavish, Buckley, Heel - Omeprazole An Updated Review of Its Pharmacology and Therapeutic Use in Acid-Related DisordersDokument33 Seiten1991 - McTavish, Buckley, Heel - Omeprazole An Updated Review of Its Pharmacology and Therapeutic Use in Acid-Related DisordersKTKL RSABNoch keine Bewertungen
- 008 Plain X-Ray AbdomenDokument7 Seiten008 Plain X-Ray AbdomenAthul GurudasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastro PanelDokument8 SeitenGastro PanelgemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bing Soal Us SmaDokument4 SeitenBing Soal Us SmaElma FatmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute PancreatitisDokument76 SeitenAcute PancreatitisKamran Khan Khalil100% (1)
- LiverDokument29 SeitenLiverHasan AsdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constipation: Causes, Prevention Tips & Natural RemediesDokument2 SeitenConstipation: Causes, Prevention Tips & Natural RemediesPrashant jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal Distention inDokument45 SeitenAbdominal Distention inArif Rahman DmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholestatic Disease in PregnancyDokument25 SeitenCholestatic Disease in Pregnancyarifbotwin100% (1)
- Harrisons Principles of Internal Medicine 21st Edition Vol 1 Vol Split PDF 1694700703964Dokument73 SeitenHarrisons Principles of Internal Medicine 21st Edition Vol 1 Vol Split PDF 1694700703964Clorinda RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Calculous CholecystitisDokument9 SeitenAcute Calculous CholecystitisWinstonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematemesis and MelaenaDokument16 SeitenHematemesis and MelaenaPooja ShashidharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIT Conditions - StudentsDokument57 SeitenGIT Conditions - StudentsShamal KoyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prehension, Mastication, and DeglutitionDokument3 SeitenPrehension, Mastication, and DeglutitionAnjelica Louise MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Pediatric GI Function CorrectDokument126 SeitenMicrosoft PowerPoint - Pediatric GI Function CorrectArchanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- G.augustin - Acute Abdomen During Pregnancy - 2014Dokument584 SeitenG.augustin - Acute Abdomen During Pregnancy - 2014Constantin BudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemorrhoidectomy From Group 5Dokument22 SeitenHemorrhoidectomy From Group 5joel david knda mj100% (1)
- DIGESTIVE SYSTEM REVIEWER - BPEd1-1Dokument2 SeitenDIGESTIVE SYSTEM REVIEWER - BPEd1-1Mira AurumtinNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mesentery: Structure, Function, and Role in DiseaseDokument11 SeitenThe Mesentery: Structure, Function, and Role in DiseaseIsaacQueirozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safe Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy An Illustrated AtlasDokument171 SeitenSafe Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy An Illustrated AtlasText OK100% (2)