Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lymphatic System Outline
Hochgeladen von
MelljonhCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lymphatic System Outline
Hochgeladen von
MelljonhCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
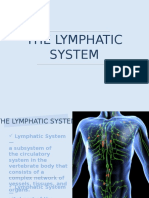
Lymphatic System
- a network of tissues and organs that help rid the body of toxins, waste and other unwanted
materials
- helps to protect us from infection and disease. Its part of the bodys immune system.
Facts/Trivia
There are approximately 500-700 lymph nodes in an adult human.
The largest organ within the lymphatic system is the spleen.
On average, at any time about 1 to 2 liters of lymph fluid circulate in the lymphatics and body
tissue
Medications and vaccines can cause the nodes to swell up
Lymph never stops moving from node to node
Functions
To remove interstitial fluid from tissues
To transport interstitial fluid originally from blood filtrate back to the blood
It absorbs and transports fatty acids and fats as chyle from the digestive system
It transports white blood cells to and from the lymph nodes into the bones
Parts
Adenoid
Although it is often called the adenoids, there is only one adenoid. It is a single, small mass of
lymphatic tissue in the back of the nose that contains lymphocytes. It is also sometimes called the
pharyngeal tonsil.
The adenoid helps the body fight infection by trapping bacteria and viruses.
The adenoid is present in infants and children. It starts to shrink just before puberty so that most
adults dont have the adenoid.
Tonsil
The tonsils are small masses of lymphatic tissue that contain lymphocytes. The palantine tonsils are
in the back of the mouth. We also have another pair of tonsils on the base of the tongue called the
lingual tonsils.
The tonsils help the body fight infection by trapping bacteria and viruses. They also make antibodies.
Thymus
The thymus is in the chest behind the breastbone, or sternum. It is where T cells mature and multiply.
Lymph Node
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped organs that sit along lymph vessels and filter lymph fluid.
Lymph nodes vary in size, but they are usually less than 1 cm. (They can be up to 1.5 cm in size in
the groin.)
There are many lymph nodes throughout the body. The number of lymph nodes varies from one part
of the body to another. Lymph nodes are located in groups in the following major locations:
neck (called cervical lymph nodes)
chest (called thoracic and mediastinal lymph nodes)
armpit (called axillary nodes)
abdomen (called para-aortic, peri-aortic and mesenteric lymph nodes)
groin (called inguinal lymph nodes)
Charmaine S. de Guzman | Christine Joy R. Diala
NS102 | WF | 3:00-4:30
The lymph nodes filter harmful particles from the lymph fluid before returning it to the bloodstream.
These particles include bacteria, viruses and foreign substances. The other main function of the
lymph nodes is to activate the immune system.
Lymph nodes contain 2 types of white blood cells that fight invading micro-organisms. Lymphocytes
attack viruses, bacteria and other micro-organisms. Macrophages surround and destroy foreign
substances, damaged cells and bits of broken cells.
Lymph Vessel
Lymph fluid travels through the body in lymph vessels. There are 3 main types of lymph vessels.
Lymphatic capillaries are tiny, closed-ended tubes through which fluid from body tissues enters the
lymphatic system. Lymphatic vessels are tubes that move lymph fluid to and from the lymph nodes.
Collecting ducts are tubes that return lymph fluid to the bloodstream.
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is soft, spongy tissue in the centre of most bones. It contains immature cells called
stem cells. These stem cells develop into red blood cells, white blood cells or platelets. Red blood
cells carry oxygen to and carbon dioxide from tissues in the body. White blood cells help the body
fight infection and diseases. Platelets help blood to clot.
Spleen
The spleen is the largest lymphatic organ. It is in the upper-left abdomen. The spleen filters the blood
by removing old red blood cells, lymphocytes and invaders (such as viruses and bacteria). The
spleen also stores red blood cells and lymphocytes.
LYMPHOID LEUKEMIA
- a cancer of the blood and bone marrow when abnormal cells in a part of the body begin to grow
out of control
CAUSES TREATMENT PREVENTION
Radiation Exposure Chemotherapy (1) Avoid the
Chemical exposure (hair dyes, benzene, chemotherapy Bone marrow risk factors
drugs) transplant
Viral Infections Stem cell
Race & Gender - usually, African-American transplant
Other risk factors- including cigarette smoking, long exposure
to diesel fuel, pesticides, and electromagnetic field
Lymphoma
abnormal growth of cell in the lymph nodes
RISK FACTORS TREATMENT PREVENTION
Age older than 60 Chemotheraphy Avoid the risk
Weak immune system Radiotheraphy factors
Family history Bone Marrow Transplant
Infections (HIV/Epstein Barr, Hepatitis C) Stem Cell Transplant
Radiation
Charmaine S. de Guzman | Christine Joy R. Diala
NS102 | WF | 3:00-4:30
LYMPHEDEMA
- lymphatic fluid cannot filter & move through the lymph nodes causing clogged
- long term condition where excess fluid (lymph) collects in tissues causing swelling (edema)
TWO MAIN TYPES
(1) Primary- congenial lymphedema
(2) Secondary- occurs as a result of something else (see list of possible causes)
CAUSES TREATMENT PREVENTION
Cancer surgery- removal of Remedial exercise- light After cancer treatment, avoid heavy
lymph nodes to stop the only to encourage activity with the affected limb; rest
spread of cancer movement of the it while recovering.
Radiotherapy- use of radiation lymph fluid out of the Avoid sun beds, steam rooms, and
to destroy cancerous tissues limb saunas.
may damage nearby healthy Skincare - to reduce Do not take very hot baths or
tissues such as the lymphatic skin infection showers.
system Manual Lymphatic Do not wear tight fitting clothes.
Infections- it may be viral, Drainage- special Do not wear tight fitting jewelry.
fungal, bacterial, or parasite) massage, also to Don't go barefoot outdoors.
Inflammatory conditions- encourage movement Keep a watch for changes or breaks
permanent damage to of lymph fluid out of in the skin.
lymphatic system from the limb Keep your skin supple by
various inflammatory Multilayer lymphedema moisturizing it every day.
condition (rheumatoid bandaging- support Make sure footwear fits properly.
arthritis, dermatitis, & the muscles and To prevent developing athlete's foot,
eczema) encourage them to use an anti-fungal foot powder.
Cardiovascular disease- move the lymph fluid Use gloves when gardening.
disease that affect the blood out of the limb
flow
Charmaine S. de Guzman | Christine Joy R. Diala
NS102 | WF | 3:00-4:30
LYMPHADENOPATHY
enlargement of the lymph nodes
CAUSES* TREATMENT PREVENTION
Inflammatory condition- inflammation of Treatment Exercise
neighboring organ or body structure or the depends upon Herbal remedies
lymph node itself or lymph vessel particular Enhanced nutrition
Infection - viral, bacterial, fungal condition Drink plenty amount of
Cancer- cancer of the node or blood cell causing the water
within the node enlargement. Lymphatic massage
Immune disorder Proper breathing
*Actually the cause or causes are unknown but there are
identified risk factors
Charmaine S. de Guzman | Christine Joy R. Diala
NS102 | WF | 3:00-4:30
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 50 Life Secrets and Tips - High ExistenceDokument12 Seiten50 Life Secrets and Tips - High Existencesoapyfish100% (1)
- Erika Peters - Complete Idiot's Guide To Walking For Health-Alpha (2001) PDFDokument313 SeitenErika Peters - Complete Idiot's Guide To Walking For Health-Alpha (2001) PDFSiva SubramaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic Drainage TherapyDokument4 SeitenLymphatic Drainage TherapyNikica VidakovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Intermediate Korean Vocabulary and GrammarDokument10 SeitenLow Intermediate Korean Vocabulary and GrammarTuong Van Nguyen100% (3)
- 6.10.13 Intervention For LymphedemaDokument85 Seiten6.10.13 Intervention For LymphedemaAyyappan JayavelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic SystemDokument28 SeitenLymphatic SystemChristine Lorne Aborde100% (1)
- John Dee - Sigillum Dei Aemeth or Seal of The Truth of God EnglishDokument2 SeitenJohn Dee - Sigillum Dei Aemeth or Seal of The Truth of God Englishsatyr70286% (7)
- Know Health Benefits of Bottle Gourd Juice or Lauki Juice - Aspx 2Dokument12 SeitenKnow Health Benefits of Bottle Gourd Juice or Lauki Juice - Aspx 2Sanjay PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Objective of Dress Code PolicyDokument4 SeitenAn Objective of Dress Code PolicySiddhraj Singh KushwahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Brochures and Product Sheets2Dokument36 SeitenAll Brochures and Product Sheets2greeenbeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dalma Training Institute Catalog 2014Dokument28 SeitenDalma Training Institute Catalog 2014Yaniss AlgeriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide To Conducting A Systematic Literature Review ofDokument51 SeitenA Guide To Conducting A Systematic Literature Review ofDarryl WallaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic System 7thDokument14 SeitenLymphatic System 7thAna Sofia Pinzón UlloaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moringa A Miracle Plant Dr. Muhammad AshfaqDokument14 SeitenMoringa A Miracle Plant Dr. Muhammad AshfaqAsfandyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urea Granular 46-0-0Dokument20 SeitenUrea Granular 46-0-0DAPUREAGRO FertilizersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nicole Baldridge, PT, DPT, CLTDokument76 SeitenNicole Baldridge, PT, DPT, CLTAan AlawiyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pages de Senegal - AR Dakar-Diamniadio HighwayDokument34 SeitenPages de Senegal - AR Dakar-Diamniadio HighwayangelsapnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading #2: Participatory Action ResearchDokument45 SeitenReading #2: Participatory Action Researchapi-3723169100% (2)
- Parasitic InfectionsDokument65 SeitenParasitic InfectionsJezreel OrquinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sathish CVDokument2 SeitenSathish CVsathishs79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Company Profile Tanpa AkteDokument60 SeitenCompany Profile Tanpa AkteDamayanti SinagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LymphomaDokument37 SeitenLymphomaMohammed T. Abdul Razak100% (2)
- Memorandum of Understanding (Mou)Dokument5 SeitenMemorandum of Understanding (Mou)Prasad PoluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expression of InterestDokument2 SeitenExpression of InterestYogesh YogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic SystemDokument3 SeitenLymphatic SystemKuldeep Monga100% (1)
- Lymphatic System and ImmunityDokument4 SeitenLymphatic System and ImmunityBlessed May PastranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Castigliano's 2nd TheoremDokument29 SeitenCastigliano's 2nd TheoremMiddle East100% (4)
- How To Use The Matrix To Address Chronic Health ConditionsDokument9 SeitenHow To Use The Matrix To Address Chronic Health ConditionsLaura Diana BarthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lymphatic SystemDokument23 SeitenThe Lymphatic SystemMERIDIAN SEESNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Food Affects Mental Health - The New York TimesDokument3 SeitenHow Food Affects Mental Health - The New York TimesAlexa Valentina RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- MahayanaDokument26 SeitenMahayanaAleza Menorca100% (1)
- G.R. No. 201354 September 21, 2016Dokument11 SeitenG.R. No. 201354 September 21, 2016Winston YutaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anthelmintic DrugsDokument35 SeitenAnthelmintic DrugsRamla KashifNoch keine Bewertungen
- MQM100 MultipleChoice Chapter2Dokument9 SeitenMQM100 MultipleChoice Chapter2Nakin KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Do We Fall IllDokument15 SeitenWhy Do We Fall IllShiv ShivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moringa - DR Kathiresan-NIRDPRDokument14 SeitenMoringa - DR Kathiresan-NIRDPRJoel WilliamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curcumin - The Spice That Can Potentially Help Your HealthDokument4 SeitenCurcumin - The Spice That Can Potentially Help Your HealthAngelLight26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Model Letter Intent enDokument1 SeiteModel Letter Intent enSylvanas SyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic Citizenship Programme - DominicaDokument6 SeitenEconomic Citizenship Programme - DominicaCITIZENSHIP AND RESIDENCY PROGRAMMES WORLDWIDENoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitic Infections Affected Body Parts Causative Agents Mode OF Transmission Signs AND Symptoms Drug of ChoiceDokument23 SeitenParasitic Infections Affected Body Parts Causative Agents Mode OF Transmission Signs AND Symptoms Drug of ChoiceCindy Mae de la TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autism Awareness CampaignDokument23 SeitenAutism Awareness Campaignapi-371173669Noch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop LayoutDokument2 SeitenWorkshop LayoutEMELITO COLENTUMNoch keine Bewertungen
- BVAA Valve User Issue 13 PDFDokument88 SeitenBVAA Valve User Issue 13 PDFrakacyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial InvoiceDokument1 SeiteCommercial InvoiceTokunbo ElegbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functionalization of GrapheneDokument59 SeitenFunctionalization of GrapheneDiego Alejandro Hurtado BalcazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioplastic Pilot Plant - BIDokument2 SeitenBioplastic Pilot Plant - BIMohamad DinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orange and Blue Depressed Man Mental Health PosterDokument1 SeiteOrange and Blue Depressed Man Mental Health PosterDanette FileNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPR & AED Update FinalDokument24 SeitenCPR & AED Update FinalYulianti MaulanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Largest Losses - Refinery Refinery Losses in Five-Year PeriodsDokument1 SeiteLargest Losses - Refinery Refinery Losses in Five-Year PeriodsDave CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gene Therapy TechnologyDokument6 SeitenGene Therapy TechnologyIlham Azizam100% (1)
- BiohazardDokument14 SeitenBiohazardsujan maharjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RoundupDokument8 SeitenRoundupNina100% (1)
- Immune SystemDokument32 SeitenImmune SystemZero OrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic System HandoutsDokument3 SeitenLymphatic System HandoutsApril Joy T. GrijaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latest DnhoDokument22 SeitenLatest DnhoFELICIA0% (1)
- Lymphatic SystemDokument22 SeitenLymphatic SystemKim, Seyoung Cristine G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic SystemDokument22 SeitenLymphatic SystemJohn MenesesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immune SystemDokument7 SeitenImmune SystemDAYANIS GELVEZ GONZALEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brown Navy Professional Museum of Art Trifold BrochureDokument2 SeitenBrown Navy Professional Museum of Art Trifold BrochureIrene MaterumNoch keine Bewertungen
- C. Lymphatic DisordersDokument18 SeitenC. Lymphatic DisordersaileenmarjlimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathogenic Flagellates: (Quick Review) and Still Capture The Pertinent InformationDokument23 SeitenPathogenic Flagellates: (Quick Review) and Still Capture The Pertinent Informationryanjt178Noch keine Bewertungen
- BLS - The Detailed Online Five GuideDokument23 SeitenBLS - The Detailed Online Five GuidepeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic System Group 9Dokument25 SeitenLymphatic System Group 9LanceRedanicanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lympathic SystemDokument18 SeitenLympathic Systemn7sspyywc6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Immunity 1Dokument6 SeitenImmunity 1Tori RolandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic - System - HDN 3Dokument42 SeitenLymphatic - System - HDN 3Rashini FernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Borne DiseasesDokument7 SeitenVector Borne DiseasesAbuzar KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatics: Terminal Lymphatic Capillaries, Which Have High Porosity AbsorbDokument10 SeitenLymphatics: Terminal Lymphatic Capillaries, Which Have High Porosity AbsorbRadhika SethuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic Disorders: DR - Rehab GwadaDokument30 SeitenLymphatic Disorders: DR - Rehab GwadaMohamed ElMeligieNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMI Equipment Services and Solutions, Inc. Biomedical Engineering DepartmentDokument11 SeitenAMI Equipment Services and Solutions, Inc. Biomedical Engineering Departmentvandolph siribanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 87844-Chapter 1. The Psychology of TourismDokument28 Seiten87844-Chapter 1. The Psychology of TourismVENA LANDERONoch keine Bewertungen
- Niper SyllabusDokument9 SeitenNiper SyllabusdirghayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operations Research Letters: Meichun Lin, Woonghee Tim Huh, Guohua WanDokument8 SeitenOperations Research Letters: Meichun Lin, Woonghee Tim Huh, Guohua WanQuỳnh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Content: SAP Fiori Implementation (SAPX03)Dokument3 SeitenCourse Content: SAP Fiori Implementation (SAPX03)Jathin Varma KanumuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7: Identifying and Understanding ConsumersDokument3 SeitenChapter 7: Identifying and Understanding ConsumersDyla RafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PREETI and RahulDokument22 SeitenPREETI and Rahulnitinkhandelwal2911Noch keine Bewertungen
- HF CharactersDokument5 SeitenHF CharactersAudri DebnathNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Naruto Char.Dokument40 SeitenList of Naruto Char.Keziah MecarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- SakalDokument33 SeitenSakalKaran AsnaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality of Life After Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients With Chronic RhinosinusitisDokument15 SeitenQuality of Life After Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients With Chronic RhinosinusitisNarendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kematian Di ICUDokument24 SeitenKematian Di ICURahmida RahmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mag Issue137 PDFDokument141 SeitenMag Issue137 PDFShafiq Nezat100% (1)
- Brand Zara GAP Forever 21 Mango H&M: Brand Study of Zara Nancys Sharma FD Bdes Batch 2 Sem 8 Brand-ZaraDokument2 SeitenBrand Zara GAP Forever 21 Mango H&M: Brand Study of Zara Nancys Sharma FD Bdes Batch 2 Sem 8 Brand-ZaraNancy SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energizing Your ScalesDokument3 SeitenEnergizing Your ScalesjohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leverage My PptsDokument34 SeitenLeverage My PptsMadhuram SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brent Berlin-Covert Categories and Folk TaxonomyDokument10 SeitenBrent Berlin-Covert Categories and Folk TaxonomyKawita ChuachengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalyst 3750 Series Switches TroubleshootDokument19 SeitenCatalyst 3750 Series Switches TroubleshootSugumar DuraisamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TestFunda - Puzzles 1Dokument39 SeitenTestFunda - Puzzles 1Gerald KohNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMBROSE PINTO-Caste - Discrimination - and - UNDokument3 SeitenAMBROSE PINTO-Caste - Discrimination - and - UNKlv SwamyNoch keine Bewertungen