Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
STPM Physics Chapter 15 Direct Current Circuits
Hochgeladen von
Chris LauCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
STPM Physics Chapter 15 Direct Current Circuits
Hochgeladen von
Chris LauCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
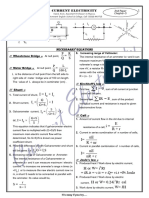
SMK SACRED HEART, SIBU STPM PHYSICS CHAPTER 15 DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUITS
1. Electromotive force (e.m.f.), E
= energy supplied to each coulomb of charge that flows
from the source.
Since its unit is V, from V = E= = =
V1 = V G Itotal = I1 = IG
I1 R1 = IG RG = = =
E=
E = I (R + r)
=1+ 11. Potentiometer (When G = 0)
E= Diagram Formula
R=
2. Potential difference between two points
V= = =constant
=
3. Maximum current
V = E Ir
Imaximum = , r = internal resistance
Due to presence of r , V < E, hence V = IR =
4. Electrical power, P = = constant
P = IV = I2R =
5. Series parallel Hence, =
Type Maximum
Series Voltage
Parallel Current V = IR =
6. Maximum power = = constant
2 2
P=I R=( ) R , when R = r Thus, =
Hence, =
7. Kirchhoffs first law:
The algebraic sum of the currents at a junction of a circuit
is zero. [ Principle of conservation of charge ] = ,
= 0 or Iin = Iout =
8. Kirchhoffs second law: = , V1 = E
In a closed loop, the algebraic sum of = = =1+
the e.m.f.s is equal to the products of
current and resistance. 2 = new length
[Principle of conservation of energy ] when S1 is closed
*Refer to Kirchhoffs Law question analysis
9. Potential and current divider
Poetntial divider Current divider
= =
Itotal = I1 = I2 Vtotal = V1 = V2
= = = Itotal R total = I1 R1 = I2 R2 =
10. Shunt and multiplier
Shunt Multiplier
12. Wheatstone bridge & Metre bridge
Resistor of lower resistance Resistor of high resistance
If R and S are replaced
than that of galvanometer connected in series with the
by wires. Then:
and is connected parallel to galvanometer.
galvanometer PQRS are
resistance
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsVon EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- STPM 2013 Sem 1Dokument7 SeitenSTPM 2013 Sem 1nurulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2Von EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- STPM 2016 Physics 1Dokument16 SeitenSTPM 2016 Physics 1Abdul ShariffNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Physics Experiment 8 Earth S Magnetic Field Second Term PDFDokument2 SeitenSTPM Physics Experiment 8 Earth S Magnetic Field Second Term PDFVishalinie RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Physics Project Presentation SlideDokument15 SeitenSTPM Physics Project Presentation SlideWengMan Sew0% (1)
- 962 Chemistry (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusDokument13 Seiten962 Chemistry (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Physics 2008Dokument26 SeitenSTPM Physics 2008Tang Siew Eng100% (2)
- STPM Physics Experiment 8 Earth S Magnetic Field Second TermDokument2 SeitenSTPM Physics Experiment 8 Earth S Magnetic Field Second Termhonghong_LCHNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Physics Chapter 18 Alternating Current CircuitsDokument2 SeitenSTPM Physics Chapter 18 Alternating Current CircuitsChris Lau100% (1)
- Introduction Coursework STPMDokument4 SeitenIntroduction Coursework STPMSarath KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Baharu 2014 Sem 2 (Mathematics T 954)Dokument21 SeitenSTPM Baharu 2014 Sem 2 (Mathematics T 954)Alex TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics STPM Sem 1 DefinitionDokument2 SeitenPhysics STPM Sem 1 DefinitionBen40% (5)
- STPM Physics Sem 3 Definition ListDokument4 SeitenSTPM Physics Sem 3 Definition ListredroseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Viva f6Dokument11 SeitenAssignment Viva f6Magendren Raman50% (2)
- STPM Physics Chapter 17 Electromagnetic InductionDokument5 SeitenSTPM Physics Chapter 17 Electromagnetic InductionChris Lau100% (1)
- There Are Fifty Questions in This Paper. Answer All Questions. Marks Will Not Be Deducted For Wrong AnswersDokument16 SeitenThere Are Fifty Questions in This Paper. Answer All Questions. Marks Will Not Be Deducted For Wrong AnswersSean100% (1)
- STPM 2021 Sem 3 Mock AnsDokument2 SeitenSTPM 2021 Sem 3 Mock AnsNATASHA NADIA BINTI ABDULLAH MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physic Experiment 6Dokument2 SeitenPhysic Experiment 6JasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM 2014 Sem 1 RealDokument2 SeitenSTPM 2014 Sem 1 Realevacuate clashNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM 954 Math T Coursework 2012 (Sem 1)Dokument32 SeitenSTPM 954 Math T Coursework 2012 (Sem 1)Josh, LRT100% (2)
- STPM Past Year QuestionDokument34 SeitenSTPM Past Year QuestionChris Ng Kien Siong100% (2)
- Physics Project ReportDokument6 SeitenPhysics Project ReportSad FateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Coursework 2016/2017 STPMDokument13 SeitenPhysics Coursework 2016/2017 STPMShi JieNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUGGESTED ANSWER STPM 2011 MATHEMATICS T Paper 2Dokument6 SeitenSUGGESTED ANSWER STPM 2011 MATHEMATICS T Paper 2SKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics (T) VIvaDokument11 SeitenMathematics (T) VIvaJinJinKiraie0% (1)
- Mathematics (T) Coursework: Title: Mathematical Investigation (Am - GM)Dokument1 SeiteMathematics (T) Coursework: Title: Mathematical Investigation (Am - GM)Elil MathhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics STPM Sem 2 FormulaeDokument2 SeitenPhysics STPM Sem 2 FormulaeBen50% (8)
- STPM Chemistry 2011.Dokument8 SeitenSTPM Chemistry 2011.Fu Hong100% (1)
- Endothermic.: A The Forward Reaction IsDokument9 SeitenEndothermic.: A The Forward Reaction IsSatyrKuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Maths T Assignment (Semester 1) 2012Dokument10 SeitenSTPM Maths T Assignment (Semester 1) 2012Nicholas Chong0% (2)
- Ace Ahead Mathematic T Exam Practise Chapter 5Dokument10 SeitenAce Ahead Mathematic T Exam Practise Chapter 5James OoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Formula List STPM (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Dokument0 SeitenPhysics Formula List STPM (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Choe Kok HuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics STPM Sem 3 FormulaeDokument2 SeitenPhysics STPM Sem 3 FormulaeBenNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Chemistry Form 6 Definition ListDokument16 SeitenSTPM Chemistry Form 6 Definition ListCherry T CY100% (1)
- Sem 1 2022 Manual ChemistryDokument9 SeitenSem 1 2022 Manual ChemistryVZYFVVZHVMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checkpoint-14 2 PDFDokument5 SeitenCheckpoint-14 2 PDFJia Xuan100% (3)
- Guide To STPM Pratical Ace Ahead Biology Third Term PDFDokument17 SeitenGuide To STPM Pratical Ace Ahead Biology Third Term PDFViola Voon Li WeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM 2009Dokument19 SeitenSTPM 2009one kilometer100% (2)
- 1 3 0 X 2, 2 3 (3 X), 2 X 3, 0, OtherwiseDokument9 Seiten1 3 0 X 2, 2 3 (3 X), 2 X 3, 0, OtherwiseWendy LohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project STPM 2016Dokument13 SeitenChemistry Project STPM 2016Sabri Bri EDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics STPM Sem 3 DefinitionDokument2 SeitenPhysics STPM Sem 3 DefinitionBen67% (3)
- STPM Maths T 2020 Assignment Conclusion ExampleDokument1 SeiteSTPM Maths T 2020 Assignment Conclusion ExampleLing YiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1 2015Dokument4 SeitenExperiment 1 2015UngHHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument14 SeitenChapter 3Viola Voon Li WeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Physics QuestionDokument10 SeitenSTPM Physics Questionmuhdsabri510% (1)
- STPM 2014 Sem 2 Real AnsDokument1 SeiteSTPM 2014 Sem 2 Real AnsXue Yi LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Physics Chapter 13 Capacitors PDFDokument1 SeiteSTPM Physics Chapter 13 Capacitors PDFChris LauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Electricity: Important ResultsDokument23 SeitenCurrent Electricity: Important ResultsANMOLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula List For Term 2 STPM PhysicsDokument2 SeitenFormula List For Term 2 STPM PhysicsGeethanjali SivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shri Ram Shiksha Mandir: Jindpur, Delhi-36Dokument14 SeitenShri Ram Shiksha Mandir: Jindpur, Delhi-36divyanshu guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC CircuitsDokument22 SeitenDC Circuitsaykhan5806Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument60 SeitenChapter 3Arif NizarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet and Mind Map For PhysicsDokument19 SeitenFormula Sheet and Mind Map For PhysicsDaksh MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Electricity-Basic by Nurul Amin SirDokument18 SeitenCurrent Electricity-Basic by Nurul Amin SirFardeen KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Year Phsyics Chapter 2Dokument3 Seiten2nd Year Phsyics Chapter 2anieeyaseenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel AC Circuits SPLPDokument47 SeitenParallel AC Circuits SPLPJoey TelinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Points: Unit I - IIDokument10 SeitenKey Points: Unit I - IINarendra SNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 10 Sinusoidal Steady-State Power CalculationsDokument30 SeitenCH 10 Sinusoidal Steady-State Power CalculationsMugerwa CharlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision: Class: 10 Physics Topic: ElectricityDokument35 SeitenRevision: Class: 10 Physics Topic: ElectricitysarathR valsala100% (1)
- STPM Chemistry Topic 18 Carbonyl Compound (Short Notes)Dokument1 SeiteSTPM Chemistry Topic 18 Carbonyl Compound (Short Notes)Chris Lau100% (2)
- STPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes (Short Notes)Dokument2 SeitenSTPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes (Short Notes)Chris LauNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Chemistry Topic 17 Hydroxyl Compound (Short Notes)Dokument1 SeiteSTPM Chemistry Topic 17 Hydroxyl Compound (Short Notes)Chris Lau100% (1)
- STPM Physics Chapter 17 Electromagnetic InductionDokument5 SeitenSTPM Physics Chapter 17 Electromagnetic InductionChris Lau100% (1)
- STPM Chemistry Topic 14 Carbon Chemistry (Short Notes)Dokument1 SeiteSTPM Chemistry Topic 14 Carbon Chemistry (Short Notes)Chris Lau100% (1)
- STPM Physics Chapter 14 Electric CurrentDokument1 SeiteSTPM Physics Chapter 14 Electric CurrentChris LauNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Physics Chapter 18 Alternating Current CircuitsDokument2 SeitenSTPM Physics Chapter 18 Alternating Current CircuitsChris Lau100% (1)
- STPM Physics Chapter 13 Capacitors PDFDokument1 SeiteSTPM Physics Chapter 13 Capacitors PDFChris LauNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Physics Chapter 12 ElectrostaticsDokument1 SeiteSTPM Physics Chapter 12 ElectrostaticsChris Lau100% (3)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 1 Atoms Molecule and Stoichiometry (Physical Chemistry)Dokument15 SeitenSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 1 Atoms Molecule and Stoichiometry (Physical Chemistry)Chris Lau88% (17)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 6D PHASE EQUILIBRIUM PDFDokument14 SeitenSTPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 6D PHASE EQUILIBRIUM PDFChris Lau100% (4)
- STPM Chemistry Past Year Objectives Question (1999-2015)Dokument28 SeitenSTPM Chemistry Past Year Objectives Question (1999-2015)Chris Lau60% (10)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 3 Chemical BondingDokument36 SeitenSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 3 Chemical BondingChris Lau100% (5)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6B Acid Base EquilibriumDokument25 SeitenSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6B Acid Base EquilibriumChris Lau100% (5)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6C Solubility EquilibriumDokument6 SeitenSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6C Solubility EquilibriumChris Lau100% (2)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 5 Reaction KineticsDokument22 SeitenSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 5 Reaction KineticsChris Lau100% (12)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6A Chemical EquilibriumDokument23 SeitenSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6A Chemical EquilibriumChris Lau100% (7)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 4 MATTERDokument31 SeitenSTPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 4 MATTERChris Lau75% (4)
- STPM Chemistry Topic 2 Electronic Structure of AtomsDokument18 SeitenSTPM Chemistry Topic 2 Electronic Structure of AtomsChris Lau67% (3)
- Egx HandoutDokument2 SeitenEgx HandoutNixel SpielNoch keine Bewertungen
- TDJ 609015 172717deh 65FT2Dokument1 SeiteTDJ 609015 172717deh 65FT2Marcos SarzuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Abbreviations-A320Dokument58 SeitenList of Abbreviations-A320Midun Mohan100% (1)
- Marki Mixer Basics Primer-MinDokument12 SeitenMarki Mixer Basics Primer-MinMalc SellarsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protection Relays: Jola Spezialschalter K. Mattil Co. KGDokument16 SeitenProtection Relays: Jola Spezialschalter K. Mattil Co. KGMiftah SalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Est2 Installation and Service ManualDokument142 SeitenEst2 Installation and Service ManualJason Eric YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- q2 Chs 9 Module 1 Week 1Dokument6 Seitenq2 Chs 9 Module 1 Week 1Chris John Dave RosarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- HT-XQ100: Stylish Home Theater SystemDokument2 SeitenHT-XQ100: Stylish Home Theater SystemJoko NugrohoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PM-9000 Service ManualDokument80 SeitenPM-9000 Service ManualVictorHernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supraja DocumentDokument73 SeitenSupraja DocumentAnonymous gWVMMa588pNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethernet Network Redundancy in SCADA and Real-Time Automation PlatformsDokument14 SeitenEthernet Network Redundancy in SCADA and Real-Time Automation PlatformssavijolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Communication Chapter 11Dokument5 SeitenDigital Communication Chapter 11MIsh GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANT-20 ManualDokument12 SeitenANT-20 Manualranju022Noch keine Bewertungen
- PHC Electronica PDFDokument80 SeitenPHC Electronica PDFarchangel_07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pocket ZX Handheld ZX SpectrumDokument15 SeitenPocket ZX Handheld ZX SpectrumDavid ClodeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fonte SDN 10-24-100CDokument6 SeitenFonte SDN 10-24-100CKennedy TavaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- DX 5704V XCS Install ManualDokument44 SeitenDX 5704V XCS Install ManualAnish ParameswaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esys Flasher User's ManualDokument8 SeitenEsys Flasher User's ManualThiago Techscan Henrique TechscanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Computer Science & Engineering First Internal Assessment Test, October 2020 - 21Dokument1 SeiteDepartment of Computer Science & Engineering First Internal Assessment Test, October 2020 - 21Sri SriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eaton RCD DRCMDokument5 SeitenEaton RCD DRCMrajpre12130% (1)
- Lab 1Dokument4 SeitenLab 1Matt SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing For Cisco Internetwork Solutions Lab Guide (CCDA DESGN 640-864) v2.1Dokument95 SeitenDesigning For Cisco Internetwork Solutions Lab Guide (CCDA DESGN 640-864) v2.1axidnet100% (2)
- Atf 36077Dokument4 SeitenAtf 36077hendpraz88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Micross Technical PresentationDokument28 SeitenMicross Technical PresentationRaja KalyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic GSM NotesDokument5 SeitenBasic GSM NotesHtet Myet NaingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 - Electronic Control of Linear-To-circular Polarization Conversion Using A Reconfigurable MetasurfaceDokument6 Seiten2017 - Electronic Control of Linear-To-circular Polarization Conversion Using A Reconfigurable Metasurfaceab4azizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radar Atlas 1000 Operational Manual Ver 2 2Dokument168 SeitenRadar Atlas 1000 Operational Manual Ver 2 2Sergey Vertyanov100% (1)
- ExternalSpecialist SEARCH RESULTDokument6 SeitenExternalSpecialist SEARCH RESULTSea RouteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configuring Straight-Through Ethernet Cable: Learning Activity SheetDokument9 SeitenConfiguring Straight-Through Ethernet Cable: Learning Activity SheetJay AnunciacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Complete Response Function and System Parameters For A Loudspeaker With Passive Radiator PDFDokument17 SeitenThe Complete Response Function and System Parameters For A Loudspeaker With Passive Radiator PDFMajo JaimesNoch keine Bewertungen