Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
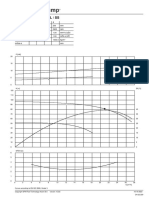
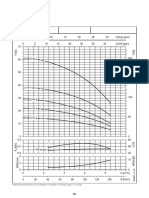
Figure 16.6 Repeat of Figure 16.1 With Appropriate Operating Point Identified
Hochgeladen von
JorgeOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Figure 16.6 Repeat of Figure 16.1 With Appropriate Operating Point Identified
Hochgeladen von
JorgeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CASE STUDIES 389
Material flow rate (tonne/h)
Solids loading
200 160 ratio
120 100
80
16 5 70
60
8 50 Conveying line inlet
40 air velocity (m/s)
12.8 1.6 a 12
12 12.0 b 30
16 20
8 1.2
No
20
go
area 0.8 10
4
0.4 25
0.025
0.052
30
0
0 0.04 0.08
0.12
Air mass flow rate (kg/s)
Figure 16.6 Repeat of Figure 16.1 with appropriate operating point identified.
For a pipeline bore, d of 0.053 m, a conveying line inlet air temperature of
15C (T1 288 K), a conveying line inlet air pressure, p1 of 261.3 kN/m2 abs, and
the above air mass flow rate of 0.021 kg/s, gives:
0.021 288
C min 0.365 m/ s 3.0 m/ s
2
0.053 261.3
This corresponds with the conveying limit on Figure 16.5 for a solids loading ratio in
excess of seventy. The conveying line inlet air velocity, C1, will be 20 per cent
higher and so:
C1 1.2 3.0 3.6 m/s
16.3.1.2 Air only pressure drop for operating point
The air only pressure drop for a pipeline, p, can be determined using Equation
(10.6), reproduced here as Equation (16.2).
0.5 p2 N/ m (16.2)
2 64 f Lm2a 2
pa p
RT
2 2 5
d
Taking the conveying line exit air pressure, p2, to be standard atmospheric pressure
of
101 300 N/m2, the pipeline friction factor, f, to be 0.0045, the length of the test
pipeline,
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- S650 Service - 6987168 enUS SMDokument1.311 SeitenS650 Service - 6987168 enUS SMcarlos andres salazar sanchez75% (4)
- Database Management Systems: Understanding and Applying Database TechnologyVon EverandDatabase Management Systems: Understanding and Applying Database TechnologyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (8)
- GPU Programming in MATLABDokument6 SeitenGPU Programming in MATLABkhaardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airfix 2011 CatalogueDokument132 SeitenAirfix 2011 CatalogueGordon Sorensen0% (1)
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsVon EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Estate Developer Resume SampleDokument1 SeiteReal Estate Developer Resume Sampleresume7.com100% (2)
- Soil Nailing and Rock Anchors ExplainedDokument21 SeitenSoil Nailing and Rock Anchors ExplainedMark Anthony Agnes AmoresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit Report of CompaniesDokument7 SeitenAudit Report of CompaniesPontuChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stage Storage Curve: Clear CellsDokument1 SeiteStage Storage Curve: Clear CellsLuna BejarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRX - Vertical Multistage Inline - 2019-20Dokument1 SeiteTRX - Vertical Multistage Inline - 2019-20Jason Wei Han LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lincoln Electric ESW Strip Cladding GuideDokument26 SeitenLincoln Electric ESW Strip Cladding GuideRenny DevassyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A9C38TDokument1 SeiteA9C38TMuhammad azeemNoch keine Bewertungen
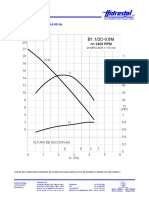
- Curvas de operacion a 60 Hz para electrobomba hidrostalDokument1 SeiteCurvas de operacion a 60 Hz para electrobomba hidrostalLuis RaymundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FC4 Standard Units Pressure CurvesDokument12 SeitenFC4 Standard Units Pressure CurvesTiago Karina ElisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Features of Vortex Drop ShaftsDokument5 SeitenHydraulic Features of Vortex Drop ShaftsCristian GiurgeaNoch keine Bewertungen
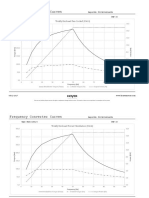
- Frequency Converter Curves: Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled (IC411)Dokument2 SeitenFrequency Converter Curves: Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled (IC411)L DKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagrama de MoodyDokument1 SeiteDiagrama de MoodySanti SotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temperature at The Midplane of An Infi Nite Slab of Thickness 2 DDokument3 SeitenTemperature at The Midplane of An Infi Nite Slab of Thickness 2 Dski097Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diagrama de Moody (White)Dokument1 SeiteDiagrama de Moody (White)Jose DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProductComparison - 27 06 2023 - 15 54 40Dokument1 SeiteProductComparison - 27 06 2023 - 15 54 40stefancuandreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRX - Vertical Multistage Inline - 2019-16Dokument1 SeiteTRX - Vertical Multistage Inline - 2019-16Jason Wei Han LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT2 12 30Dokument3 SeitenPT2 12 30daniguzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 1. Plot of R vs. PDokument5 SeitenFigure 1. Plot of R vs. PKaye CaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Undfos Vertical Multistage Centrifugal Pump - Kurva - Technical Data - CRI-CRN 1sDokument2 SeitenUndfos Vertical Multistage Centrifugal Pump - Kurva - Technical Data - CRI-CRN 1s'Budi Kaos HitamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co-Cu MOF outperforms Pt/C for oxygen reductionDokument17 SeitenCo-Cu MOF outperforms Pt/C for oxygen reductionCB Dong SuwonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SunonDokument4 SeitenSunonEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TC 0.32128703 Horas TP 0.75959409 Horas L 4030 M TR 1.26852213 Horas S 0.27Dokument6 SeitenTC 0.32128703 Horas TP 0.75959409 Horas L 4030 M TR 1.26852213 Horas S 0.27Rafael SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marlow Industries Inc. Marlow Industries Inc. Marlow Industries Inc. Marlow Industries IncDokument2 SeitenMarlow Industries Inc. Marlow Industries Inc. Marlow Industries Inc. Marlow Industries IncJavad ArabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Added: 9.78 ML of Ethyl Acetate in 1 Liter Water Added: 4G of Naoh in 1000Ml or 1 Liter WaterDokument8 SeitenAdded: 9.78 ML of Ethyl Acetate in 1 Liter Water Added: 4G of Naoh in 1000Ml or 1 Liter WaterABHAY PARASHARNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Transfer Characteristics of CMOS Gates and Pass TransistorsDokument6 SeitenDC Transfer Characteristics of CMOS Gates and Pass Transistorswajid aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- WP5 12Dokument2 SeitenWP5 12zain_zedanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aula4 Turb in Fluids Dissipation LawDokument23 SeitenAula4 Turb in Fluids Dissipation LawTomás CarreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- TECHNICAL Lowara EHM-td-En 50 HZ Part60Dokument1 SeiteTECHNICAL Lowara EHM-td-En 50 HZ Part60Alberto GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
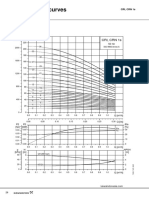
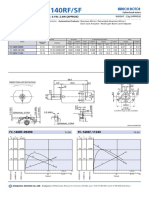
- FC 140rfsf PDFDokument1 SeiteFC 140rfsf PDFtomasykNoch keine Bewertungen
- End of Life Product Not Recommended For New Design: RotationDokument1 SeiteEnd of Life Product Not Recommended For New Design: RotationEdwin David Tamayo AlzateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determine Inductance of The Lead: English Units Metric EquivalentDokument2 SeitenDetermine Inductance of The Lead: English Units Metric EquivalentfourwheelerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long Lead Acid Battery 12v 7ahDokument2 SeitenLong Lead Acid Battery 12v 7ahmuhammad irfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph 1Dokument4 SeitenGraph 1Shazeem HoseinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wuhan Intepower 6GFMJ-150Dokument2 SeitenWuhan Intepower 6GFMJ-150Lê Hữu ÁiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crane GirderDokument3 SeitenCrane GirderMohamed Alaa ElsheriefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eb Ssep 1.1 13Dokument1 SeiteEb Ssep 1.1 13vandana sathishNoch keine Bewertungen
- C 3126 MT 3 4p: Technical SpecificationDokument8 SeitenC 3126 MT 3 4p: Technical SpecificationRodolfo AriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Misr Raymond Foundations: Soil Investigation DepartmentDokument2 SeitenMisr Raymond Foundations: Soil Investigation Departmentm.askarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNWX651-F65 3.7kW 4P-220VT50Hz-1: ModelDokument1 SeiteCNWX651-F65 3.7kW 4P-220VT50Hz-1: ModelGiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tech Schlumberger Charts 11 Rcor, Rint.p7Dokument1 SeiteTech Schlumberger Charts 11 Rcor, Rint.p7Gyra LuthmanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tornado LLT Rint-9BDokument1 SeiteTornado LLT Rint-9BDarknight OWONoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Modelling of A 245Kv 40ka H Ybrid Gas Circuit BreakerDokument20 SeitenComputer Modelling of A 245Kv 40ka H Ybrid Gas Circuit Breakerbylee3894Noch keine Bewertungen
- CN 32-250Dokument1 SeiteCN 32-250Sachin ParasharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pearson's Correlation Coefficients (Elements) - Pliensbachian - Lower Toarcian Peniche SectionDokument2 SeitenPearson's Correlation Coefficients (Elements) - Pliensbachian - Lower Toarcian Peniche SectionArroyo Romero WilmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchor YS.Dokument2 SeitenAnchor YS.RizkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power your life with reliable lead-acid batteriesDokument28 SeitenPower your life with reliable lead-acid batteriesЗинаNoch keine Bewertungen
- IstruDokument4 SeitenIstruAndrés Jonathan Cepeda GuerronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moody DiagramDokument2 SeitenMoody DiagramImad HabeebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 15Dokument1 SeiteZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 15Pierre-Cécil KönigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph of Characteristic CurveDokument7 SeitenGraph of Characteristic CurvePooja waniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acqua Tedela Pump Series - 1Dokument22 SeitenAcqua Tedela Pump Series - 1Janzzen CrudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primer NivelDokument1 SeitePrimer NivelDANESKA ABIGAIL AVALOS VELASQUEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP Series: Air PumpDokument1 SeiteHP Series: Air PumpCakEmUsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Depletion Actual: Out Ig in IgDokument8 SeitenDepletion Actual: Out Ig in IgnitinsethiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zener Diode-Load Regulator 2Dokument1 SeiteZener Diode-Load Regulator 2Kaushal Kumar GulatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Identification Using Neutron Porosity and Bulk Density LogsDokument20 SeitenFluid Identification Using Neutron Porosity and Bulk Density LogsAhmad Fuad SalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foto Diodo Infrarrojo Receptor 5mmDokument1 SeiteFoto Diodo Infrarrojo Receptor 5mmcreative_26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer AssignmentDokument679 SeitenComputer Assignmentjahanvi vermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- +C Series: Pure Lead Carbon BatteryDokument2 Seiten+C Series: Pure Lead Carbon BatteryAhmed ZeharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Fan DatasheetDokument2 SeitenDC Fan DatasheetTalha NasrNoch keine Bewertungen
- TECHNICAL Lowara EHM TD en 50 HZ Part166Dokument1 SeiteTECHNICAL Lowara EHM TD en 50 HZ Part166Alberto GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing Spreadsheet Vs LRFD Tables: Truss Tr23 YP 16-Apr Sample ConnectionDokument6 SeitenTesting Spreadsheet Vs LRFD Tables: Truss Tr23 YP 16-Apr Sample ConnectionJose Sosa CarmeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rigging PlantDokument1 SeiteRigging PlantJorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure Ref: Left Hand End: Fixed Pinned Fixed PinnedDokument3 SeitenStructure Ref: Left Hand End: Fixed Pinned Fixed PinnedIngenieria Estructural AplicadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acfm vs. SCFM vs. IcfmDokument9 SeitenAcfm vs. SCFM vs. IcfmJose SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- RP42 2 PDFDokument24 SeitenRP42 2 PDFJorge100% (1)
- Plano GeneralDokument1 SeitePlano GeneralJorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acfm vs. SCFM vs. IcfmDokument9 SeitenAcfm vs. SCFM vs. IcfmJose SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 3-Structural Bolts PDFDokument45 SeitenChap 3-Structural Bolts PDFAndang85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Desarme 300 Compact, Cabezales y Muebles PDFDokument12 SeitenDesarme 300 Compact, Cabezales y Muebles PDFJorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matching a Vendor's HRSG in THERMOFLEXDokument30 SeitenMatching a Vendor's HRSG in THERMOFLEXRafraf EzdineNoch keine Bewertungen
- (DO-CYT-T1-16) - KASSAHUN ComparisionDokument126 Seiten(DO-CYT-T1-16) - KASSAHUN ComparisionMohammed AdaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ts 391 IltDokument5 SeitenTs 391 IltFunnypoumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Memo in Motion For ContemptDokument118 SeitenMemo in Motion For ContemptMark SternNoch keine Bewertungen
- Restaurant P&L ReportDokument4 SeitenRestaurant P&L Reportnqobizitha giyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH Measurement TechniqueDokument5 SeitenPH Measurement TechniquevahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Science Practical File WorkDokument34 SeitenComputer Science Practical File WorkArshdeep SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics of Fluid-Conveying Beams: Governing Equations and Finite Element ModelsDokument22 SeitenDynamics of Fluid-Conveying Beams: Governing Equations and Finite Element ModelsDario AcevedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emiish Me: Answer BookDokument7 SeitenEmiish Me: Answer BookNickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python Lecture PSBCDokument83 SeitenPython Lecture PSBCPedro RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Financial Ratios of Manufacturing CompaniesDokument61 SeitenAnalysis of Financial Ratios of Manufacturing CompaniesNine ZetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Claim Form - Group Health InsuranceDokument5 SeitenClaim Form - Group Health Insurancevizag mdindiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wasbi Bank AnalysisDokument18 SeitenWasbi Bank AnalysisHamadia KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LK BMHS 30 September 2021Dokument71 SeitenLK BMHS 30 September 2021samudraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and Mechanism of The Deformation of Grade 2 Titanium in Plastometric StudiesDokument8 SeitenStructure and Mechanism of The Deformation of Grade 2 Titanium in Plastometric StudiesJakub BańczerowskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CXS 310-2013 - PomegranateDokument5 SeitenCXS 310-2013 - PomegranateFranz DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rodriguez, Joseph Lorenz Ceit-08-402ADokument7 SeitenRodriguez, Joseph Lorenz Ceit-08-402AJOSEPH LORENZ RODRIGUEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grand Viva Question For Ece StudentDokument17 SeitenGrand Viva Question For Ece Studentapi-35904739086% (7)
- Papi AdbDokument50 SeitenPapi AdbSilvio Figueiredo0% (1)
- Christmasworld Trend Brochure 2024Dokument23 SeitenChristmasworld Trend Brochure 2024Ольга ffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lunakleen: Standard Type Hepa FilterDokument1 SeiteLunakleen: Standard Type Hepa FilterRyan Au YongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Railway Reservation System Er DiagramDokument4 SeitenRailway Reservation System Er DiagramPenki Sarath67% (3)
- Igbt Irg 4p254sDokument9 SeitenIgbt Irg 4p254sMilagros Mendieta VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TMA - ExerciseDokument3 SeitenTMA - ExercisemorrisioNoch keine Bewertungen