Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Rates Review Questions ANSWERS
Hochgeladen von
nadia sykesCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Rates Review Questions ANSWERS
Hochgeladen von
nadia sykesCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
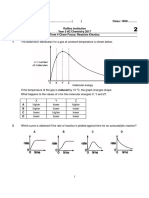
Chemistry 12 (HL) Unit 2 / IB Topics 6 and 16 Review
Rates of Reaction Past Paper Questions
Answers Please do not print
PAST PAPER 2 QUESTIONS
1. (a) rate = k [N2O5]
(b) (i) rate = k[N2O5]
One molecule of [N2O5]
(ii) rate = k[N2O5] [NO3]
But NO3 comes from N2O5 in first step
2
So: rate = k[N2O5] NOTE: Questions
about the half life of a
(c) the time taken for the concentration/amount (of N2O5) to decrease chemical reaction are
to half its original value NOT part of the current
(d) it is constant IB syllabus.
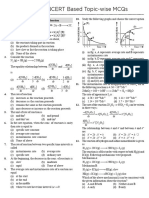
2. (a) (i) change in concentration of reactant (or product) per unit time
(ii) MgCO3 (s) + 2 HCl (aq) MgCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O (l)
(iii)
(iv) new curve reaches same height as original curve AND new curve less steep than original
curve;
volume of gas produced is the same because the same amount of acid is used;
reaction is slower because concentration is decreased;
(b) (i) (from experiments 1 and 2 at constant [H2]), [NO] doubles, rate quadruples;
hence, second order with respect to NO;
(from experiments 2 and 3 at constant [NO]), [H2] doubles, rate doubles;
hence, first order with respect to [4] 2H;
Allow alternative mathematical deductions also.
2
(ii) rate = k [NO] [H2]
-5 -3 2 -3 2
(iii) k = (10.00 x 10 ) / ( (10.00 x 10 ) x (4.00 x 10 ) ) = 2.50 x 10
-2 6 -1
units = mol dm s
(c) (i) step 1
(ii) O (atom) / oxygen atom
Chemistry 12 (HL) Unit 2 / IB Topics 6 and 16 Review
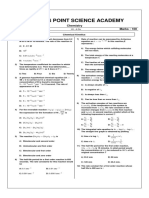
(d) (i) (minimum) energy needed for a reaction to occur
(iii) as temperature increases rate constant increases
(iv) from graph gradient = -Ea / R
measurement of gradient from chosen points on graph;
2
Ea = 1.6 x 10 kJ (or kJ/mol)
3. (a) order of NO = second
[NO] doubled, rate quadrupled
order of Br2 = first
[Br2] doubled, rate of reaction doubled
2
(b) rate = k [NO] [Br2]
-3 -2 2 -3
(c) k = (3.20 x 10 ) / ( (2.00x 10 ) x (5.00 x 10 ) )
3 6 -2 -1
= 1.60 x 10 dm mol s
NOTE: Heterogeneous catalysts
and how they work are not in the
(d) (i) no effect (k changes only with temperature)
current IB syllabus.
(ii) rate decreases (by a factor of 2)
(e) gases adsorb on surface of catalyst / provides surface for the reaction
lowers activation energy / provides alternative pathway for reaction
(f)
NOTE: Ignore the red line.
Chemistry 12 (HL) Unit 2 / IB Topics 6 and 16 Review
2
4. (a) (i) rate = k [NO] [Cl2 ]
(ii) rate of reaction will decrease by a factor of 4;
no effect on the rate constant
(iii)
Note 1: You do not need to worry
about the equilibrium point for the
Kinetics test.
Note 2: The slopes for the NO and
the NOCl curve must be the same
because they are present in equal
amounts in the equation.
(b) Above 775 K: rate = k [NO2][CO];
2
Below 775 K: rate = k [NO2]
(c) zero order reaction;
-3
all concentrations are 1.0 mol dm
+
5. (a) (i) 1. rate = k [CH3COCH3] [H ]
2
2. rate = k [CH3COCH3]
+ 2
3. rate = k [H ]
(ii) 1. [CH3COCH3] doubles, rate doubles and [H]+ doubles, rate doubles; [Br2 ]doubles, no
effect on rate;
+
2. [CH3COCH3] doubles, rate quadruples; [Br2] doubles or [H ] doubles, no effect on rate
+
3. [H ] doubles, rate quadruples; [Br2] doubles or [CH3COCH3] doubles, no effect on rate
The answer given must correspond to the selected expression in 8(a)(i).
(iii) constant half-life;
at least two sets of data to justify statement
-3 -3
e.g concentration decreases from 1.6 to 0.8 mol dm in 10 s; from 0.8 to 0. 4mol dm in
-3
10 s; from 0.4 to 0.2 mol dm in 10 s.
(iv) decrease in the colour of the bromine;
+
the acid (H ) is a catalyst;
a catalyst increases rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chemical Equ. (LDA) NMDokument19 SeitenChemical Equ. (LDA) NMkaeshav manivannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsVon EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Kinetic (Graphical Analysis) 21Dokument3 SeitenKinetic (Graphical Analysis) 21滾滾滾滾滾滾Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hi HelloDokument4 SeitenHi Hellotenik68424Noch keine Bewertungen
- B HQW X24 M6 EZK65 IEgl 3 ADokument14 SeitenB HQW X24 M6 EZK65 IEgl 3 ADharshu's GalleryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 StpreboardDokument6 Seiten1 StpreboardJG EDITZNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 Y5 T4 Chem Focus - KineticsDokument4 Seiten2017 Y5 T4 Chem Focus - KineticsxmxmxmxmxmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Answers PDFDokument126 SeitenChemistry Answers PDFNurafiqah FarhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0 Kinetics 2020 - 2021 (Lecturer)Dokument15 Seiten1.0 Kinetics 2020 - 2021 (Lecturer)siti aisyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument6 SeitenChemistryvansh sikriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Equilibrium Assig (Ans) 24 03 21Dokument6 SeitenChemical Equilibrium Assig (Ans) 24 03 21Rushikesh ThoratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry QP2Dokument6 SeitenChemistry QP2Jinendra UvarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE 12 Chemistry Question Term2Dokument4 SeitenCBSE 12 Chemistry Question Term2R roseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetics Note 2023Dokument127 SeitenKinetics Note 2023oliviaadams637Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jee Main 24 Jan 2023 Shift 1 Chemistry Memory Based Paper SolutionDokument9 SeitenJee Main 24 Jan 2023 Shift 1 Chemistry Memory Based Paper SolutionThe Daily PleasureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key - 2610425 - 2024-03-08 06 - 03 - 36 +0000Dokument7 SeitenKey - 2610425 - 2024-03-08 06 - 03 - 36 +0000kishorekumar20010322Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsDokument6 SeitenChm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical Kineticsfiefy zmrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Questions - Chapter 16Dokument8 SeitenSample Questions - Chapter 16Rasel IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- West Bengal University of TechnologyDokument4 SeitenWest Bengal University of Technologysayan_dasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Final CHE1112Dokument13 SeitenPractice Final CHE1112dancer88838Noch keine Bewertungen
- KIITEE Chemistry PaperDokument7 SeitenKIITEE Chemistry PaperPrasan NandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CY1101Dokument3 SeitenCY1101Anurag BaralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic Test 2 RevisionDokument11 SeitenTopic Test 2 RevisionHykal FaridNoch keine Bewertungen
- 31 TT-Poll - C-31 (Chemistry) Chemical KineticsDokument5 Seiten31 TT-Poll - C-31 (Chemistry) Chemical KineticsNandish PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical KineticsDokument15 SeitenChemical KineticsMoksh amberkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 H2 MCT Section B Ans (2023 Edition)Dokument5 Seiten2020 H2 MCT Section B Ans (2023 Edition)HANNAH GOH (TJC)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 Chemistry Sample PaperDokument6 SeitenClass 11 Chemistry Sample PaperDamodar KasukurthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 ChemistryDokument38 Seiten12 ChemistryyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asm1 Chemistry 253147Dokument6 SeitenAsm1 Chemistry 253147deek_jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Log K ®: Section A //X Choose Correct Answer From The Given Options. (Each Carries 1 Mark)Dokument20 SeitenLog K ®: Section A //X Choose Correct Answer From The Given Options. (Each Carries 1 Mark)WhoaretoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsDokument5 SeitenMCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsGabbar100% (1)
- Kinetics Practice QuestionDokument6 SeitenKinetics Practice Question장채윤Noch keine Bewertungen
- SHCC - 2023 - Chem Paper2 - AnnaDokument8 SeitenSHCC - 2023 - Chem Paper2 - AnnaOof GucciNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEMICAL KINETICS FinalDokument6 SeitenCHEMICAL KINETICS FinalBOTHRA CLASSESNoch keine Bewertungen
- T3 Hs Ob MJVN DY4 Ru 2 NSIcDokument23 SeitenT3 Hs Ob MJVN DY4 Ru 2 NSIcYashveer RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grand Btest-Chemistry (Mains) Paper 2Dokument9 SeitenGrand Btest-Chemistry (Mains) Paper 2SouradipNoch keine Bewertungen
- SL Paper 1 MsDokument14 SeitenSL Paper 1 MsKali stringsNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCHCT 133Dokument16 SeitenBCHCT 133Srishti BhandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetics Mc1Dokument6 SeitenKinetics Mc1hylee102594Noch keine Bewertungen
- R 8.314 J Mol K: 22.4 DM 22400 C M 273 K 6.02× 10Dokument5 SeitenR 8.314 J Mol K: 22.4 DM 22400 C M 273 K 6.02× 10ZainabNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP-5 - Student Copy (Chemical Equlibrium)Dokument4 SeitenDPP-5 - Student Copy (Chemical Equlibrium)prashantyadavpky07Noch keine Bewertungen
- S6 Test 5Dokument7 SeitenS6 Test 5XD XDNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument4 SeitenChemistryRaghav KaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSC Chemistry 2014 Part 1Dokument2 SeitenHSC Chemistry 2014 Part 1Sachin DedhiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0162.Dokument4 SeitenWa0162.Saish ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Kinetics PDFDokument5 SeitenChemical Kinetics PDFBrahmanand TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Record1Dokument12 SeitenMath Record1SABARISH SABARISHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Kinetics AssignmentDokument15 SeitenChemical Kinetics AssignmentVanshdip RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 GasesDokument3 Seiten8 Gasesmatty kafwimbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper - 1 (Theory) : ChemistryDokument7 SeitenPaper - 1 (Theory) : Chemistrykaithabjeet singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020Dokument17 SeitenChemistry: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020QSQFNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Advanced 2018 Chemistry Sample Question Paper1Dokument7 SeitenJEE Advanced 2018 Chemistry Sample Question Paper1misostudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- XII Chemistry EveningDokument15 SeitenXII Chemistry EveningAyush Kumar singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- WPP-1 Without XIIDokument2 SeitenWPP-1 Without XIIAaryan KeshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Paper (Senior) PDFDokument4 SeitenPractice Paper (Senior) PDFABHIROOP REDDYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Target Publications: Board Question Paper: July 2022Dokument4 SeitenTarget Publications: Board Question Paper: July 2022Liyutsa ZirangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Mock IIT Advanced Test - 1/JEE-2018/Paper - 2: (Chemistry)Dokument10 SeitenSolutions To Mock IIT Advanced Test - 1/JEE-2018/Paper - 2: (Chemistry)rajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCH 2109 - Chemistry IDokument2 SeitenSCH 2109 - Chemistry Iraymond muneneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical KineticsDokument22 SeitenChemical KineticsDarnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- India Case StudiesDokument14 SeitenIndia Case StudiesmampiiiiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energetics 3 Practice Problems Mar 2013Dokument2 SeitenEnergetics 3 Practice Problems Mar 2013nadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energetics Review Answers March 2014 RevDokument4 SeitenEnergetics Review Answers March 2014 Revnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MexicoDokument28 SeitenMexiconadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energetics Cycle1 - PracticeProblemsDokument4 SeitenEnergetics Cycle1 - PracticeProblemsnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energetics 3 Practice Problems Mar 2013 AnswersDokument2 SeitenEnergetics 3 Practice Problems Mar 2013 Answersnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetics - Graphs: Sketch Volume-Time Graphs ForDokument3 SeitenKinetics - Graphs: Sketch Volume-Time Graphs Fornadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 6: Kinetics 6. 1 Rates of ReactionDokument7 SeitenTopic 6: Kinetics 6. 1 Rates of Reactionnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rate LawDokument3 SeitenRate Lawnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 16 Past Paper Questions 2011Dokument15 SeitenTopic 16 Past Paper Questions 2011nadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetics - Graphs To KnowDokument4 SeitenKinetics - Graphs To Knownadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphs On Rates of ReactionsDokument1 SeiteGraphs On Rates of Reactionsnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rates Review Questions (HL)Dokument8 SeitenRates Review Questions (HL)nadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practicetopic 6 Paper 2 KeyDokument8 SeitenPracticetopic 6 Paper 2 Keynadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practicetopic 6 Paper 2.pagesDokument8 SeitenPracticetopic 6 Paper 2.pagesnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year I-Unit 8 Test: IB Mathematics HLDokument6 SeitenYear I-Unit 8 Test: IB Mathematics HLnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practicetopics 6 Paper 1.pagesDokument13 SeitenPracticetopics 6 Paper 1.pagesnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetics NotesDokument19 SeitenKinetics Notesnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practicetopics 6 Paper 1 KeyDokument13 SeitenPracticetopics 6 Paper 1 Keynadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Practice Exam A: PAPER 1: Do Not Use A Calculator or The Data Booklet. Allow 23 Minutes. 1Dokument10 SeitenMini Practice Exam A: PAPER 1: Do Not Use A Calculator or The Data Booklet. Allow 23 Minutes. 1nadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Practice Exam A - Answers: Have You Taken The Practice Exam in Full Given The Time Allowed?Dokument5 SeitenMini Practice Exam A - Answers: Have You Taken The Practice Exam in Full Given The Time Allowed?nadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Test - Complex NumbersDokument14 SeitenMath Test - Complex Numbersnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year I-Unit 2 Test: IB Mathematics HLDokument9 SeitenYear I-Unit 2 Test: IB Mathematics HLnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit6 Test 2010Dokument12 SeitenUnit6 Test 2010nadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year I-Unit 5 Test: IB Mathematics HLDokument6 SeitenYear I-Unit 5 Test: IB Mathematics HLnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Word Search Puzzle - AnimalsDokument1 SeiteWord Search Puzzle - Animalsnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Binomial Theorem - Sec 4 A MathDokument50 SeitenOn Binomial Theorem - Sec 4 A Mathnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Mathematics HL Year I-Unit 1 TestDokument9 SeitenIB Mathematics HL Year I-Unit 1 Testnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weather Notes For GeographyDokument3 SeitenWeather Notes For Geographynadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC110R 1 S N 2265000001 Up PDFDokument330 SeitenPC110R 1 S N 2265000001 Up PDFLuis Gustavo Escobar MachadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HandbookDokument6 SeitenHandbookAryan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schools Division of Roxas CityDokument4 SeitenSchools Division of Roxas CityHuge Propalde EstolanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Habits Across Generations: Before ReadingDokument3 SeitenDigital Habits Across Generations: Before ReadingSharina RamallahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Consideration in Leadership and ManagementDokument6 SeitenEthical Consideration in Leadership and ManagementGlizzle Macaraeg67% (3)
- Group Interative Art TherapyDokument225 SeitenGroup Interative Art TherapyRibeiro CatarinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- List Acreditated JournalDokument2.124 SeitenList Acreditated JournalSetiyo PrajokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guarantor Indemnity For Illness or DeathDokument2 SeitenGuarantor Indemnity For Illness or Deathlajaun hindsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Death Obituary Cause of Death Ookht PDFDokument4 SeitenDeath Obituary Cause of Death Ookht PDFMayerRhodes8Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Phase Synchronous-Rectified Buck Controller For Mobile GPU PowerDokument18 Seiten2-Phase Synchronous-Rectified Buck Controller For Mobile GPU PowerMax Assistência TécnicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- So 2nd Ed Adv Read Extra U4Dokument2 SeitenSo 2nd Ed Adv Read Extra U4hector1817Noch keine Bewertungen
- November 2013 (v3) QP - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSEDokument12 SeitenNovember 2013 (v3) QP - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSEAfra AhamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- DM - BienAir - CHIROPRO 980 - EngDokument8 SeitenDM - BienAir - CHIROPRO 980 - Engfomed_twNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Analysis: Beth OwensDokument8 SeitenCase Analysis: Beth OwensPhillip CookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dig Inn Early Summer MenuDokument2 SeitenDig Inn Early Summer MenuJacqueline CainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5.4 - Incapacity As A Ground For DismissalDokument15 SeitenUnit 5.4 - Incapacity As A Ground For DismissalDylan BanksNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACLS Post Test (Copy) 낱말 카드 - QuizletDokument18 SeitenACLS Post Test (Copy) 낱말 카드 - Quizlet김민길Noch keine Bewertungen
- Air MassesDokument22 SeitenAir MassesPrince MpofuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing 7 BulletsDokument4 SeitenMaternal and Child Health Nursing 7 BulletsHoneylie PatricioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saa6d107e 1CC S N 26540705 Up - Parts Book Do Motor GD655-5Dokument164 SeitenSaa6d107e 1CC S N 26540705 Up - Parts Book Do Motor GD655-5kit101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)Dokument1 SeiteDysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)Bheru LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Period of Intuitive NursingDokument4 SeitenPeriod of Intuitive NursingJhey-ar Toledo100% (1)
- Dirty Dozen List of Endocrine DisruptorsDokument4 SeitenDirty Dozen List of Endocrine DisruptorsMariuszNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tda12110h1 N300Dokument1 SeiteTda12110h1 N300rolandseNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument18 SeitenUntitledSpace HRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Health & TravelDokument18 SeitenMental Health & TravelReyza HasnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye Essentials Cataract Assessment Classification and ManagementDokument245 SeitenEye Essentials Cataract Assessment Classification and ManagementKyros1972Noch keine Bewertungen
- BURNS GeneralDokument59 SeitenBURNS GeneralValluri MukeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seachem Laboratories, Inc. Safety Data SheetDokument10 SeitenSeachem Laboratories, Inc. Safety Data SheetJorge Restrepo HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTHE Comments On APG's Proposal No. 9090/3181-L&T-Detailed Engineering Services For EPCC-1-AVU Unit, Barauni RefineryDokument9 SeitenLTHE Comments On APG's Proposal No. 9090/3181-L&T-Detailed Engineering Services For EPCC-1-AVU Unit, Barauni RefineryajayNoch keine Bewertungen