Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
NCP TABLE
Hochgeladen von
z4ox_AL0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
77 Ansichten5 SeitenOriginaltitel
ncp TABLE
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
77 Ansichten5 SeitenNCP TABLE
Hochgeladen von
z4ox_ALCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
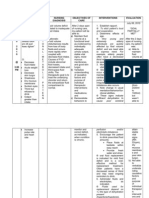
Patient’s name:
room & bed #:
Diagnosis:
physician:
Chief complaint:
DA CUES NURSING NEE OBJECTIVES OF NURSING INTERVENTION EVALUATION
TE DIAGNOSIS D CARE
S Acute pain C At the end of my 1. Note location of surgical July 7, 2010
J >The patient related to O 8 hours span of incision. @
U verbalized, tissue injury G care, my patient ®this can influence the 11 pm
L “Agay!sakit. secondary to N will be able to: amount of postoperative “GOAL
Y Sakit gihapon exploratory I a. report pain pain experienced. PARTIALLY MET”
akong laparotomy T is 2. Note client’s locus of
7, tinahian.” I controlled; control. At the end of my
>”Ayaw lang ®Pain is an V b. follow ®individuals with external 8 hours span of
2 hilabti sa akong unpleasant E prescribed locus of control may take care, my patient
0 tiyan banda kay and highly - pharmacolo little or no responsibility was:
1 sakit.” personal P gical for pain management. a. unable to
0 experience E regimen; 3. Accept the client’s report
O that may be R and description of pain. control of
@ >vertical imperceptibl C c. verbalize ®pain is a subjective pain;
incision below e to others, E nonpharmac experience and cannot be b. able to
3P the sternum while P o-logic felt by others. take all
M bypassing the consuming T methods 4. Observe non-verbal due oral
umbilicus up to all parts of I that provide cues/pain behaviors. medication
2 inches below the person’s O relief. ®observation may/may s for pain
the umbilicus life. It is N not be congruent with or
>guarding of usually a verbal reports or may be analgesics;
abdominal area response to P only indicator present and,
>changes actual tissue A when client is unable to c. able to
position slowly damage, so T verbalize. verbalize,
to avoid pain there may T 5. Monitor skin “dapat
>irritable not be E color/temperature and mag deep
>changes in abnormal R vital signs. breathing
vital sign laboratory or N ®these are usually para dili
especially the radiographic altered in acute pain. mulala ang
cardiac rate and reports 6. Determine client’s sakit sa
pulse rate despite real acceptable level of akong
>sighing pain. pain/pain control levels. samd.”
>grimaced face ®it varies with the
>analgesic individual and situation.
medications 7. Note when pain occurs.
®to medicate
prophylactically, as
appropriate.
8. Provide comfort
measures, and quiet
environment.
®to promote
nonpharmacological pain
management.
9. Instruct in/encourage use
of relaxation techniques
such as focused deep
breathing.
®to distract attention and
reduce tension.
10. Administer
analgesics as ordered.
®to maintain acceptable
level of pain. Notify
physician if regimen
inadequate to meet pain
control goal.
11. Encourage adequate
rest periods.
®to prevent fatigue.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- NCP PresentationDokument16 SeitenNCP Presentationz4ox_ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading AxDokument1 SeiteReading Axz4ox_ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro AssessmentDokument3 SeitenNeuro Assessmentz4ox_ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP TABLEDokument4 SeitenNCP TABLEz4ox_ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antacids, Antireflux Agents & Antiulcerants: Maalox® (Chewtab)Dokument4 SeitenAntacids, Antireflux Agents & Antiulcerants: Maalox® (Chewtab)z4ox_ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP TABLEDokument5 SeitenNCP TABLEz4ox_ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delayed LifeDokument2 SeitenDelayed Lifez4ox_ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erick EriksonDokument2 SeitenErick Eriksonz4ox_ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory TestsDokument13 SeitenLaboratory Testsz4ox_AL100% (1)
- Erick EriksonDokument2 SeitenErick Eriksonz4ox_ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delayed Ax After Blunt Trauma Without Rib FracturesDokument2 SeitenDelayed Ax After Blunt Trauma Without Rib Fracturesz4ox_ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bit DefenderDokument1 SeiteBit Defenderz4ox_ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bit DefenderDokument1 SeiteBit Defenderz4ox_ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- AvastDokument2 SeitenAvastz4ox_ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- AvastDokument2 SeitenAvastz4ox_ALNoch keine Bewertungen