Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
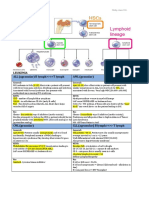
Chart - WBC Disorders
Hochgeladen von
Samuel Rothschild0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
100 Ansichten1 SeiteWBC disorders Leukemia Lymphoma
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenWBC disorders Leukemia Lymphoma
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
100 Ansichten1 SeiteChart - WBC Disorders
Hochgeladen von
Samuel RothschildWBC disorders Leukemia Lymphoma
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
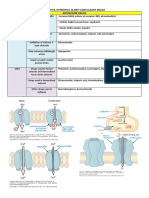
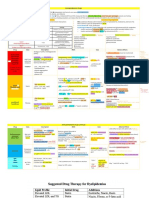
Cell Type Labs + Markers Mutation Presentation + Clinical Features Treatment/ Other
ACUTE LEUKEMIAS -TdT, CD34; >20% blasts
-Fever (from infection), bleeding, fatigue; HSM, painless LAD, + bone pain with mets
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Lymphoid - B-ALL: CD10, CD19, B-ALL: translocations -Mostly in children -B-ALL has excellent
Stem CD20, CD45- t(12;21), t(9;22) -Assoc. w/ Downs (after age 5) response to chemo;
Cells - T-ALL: CD2-8 -B-ALL mets to CNS and requires prophylactic
B-cell: PAX5 testes tx to scrotum + CSF
TdT+, MPO- T-Cell: NOTCH1 -T-ALL usually presents in
teenagers with a thymic mass Good prognosis with
>20% blasts in marrow with Hyperdiploidy: >50 Hyperdiploidy and
punched out nucleoli chromosomes/cell t(12:21)
-thrombocytopenia, anemia,
hypercellular BM, / WBCs
Histo:
Hypercellular
Packed with
lymphoblasts
SCANT basophilic
cytoplasm +
LARGE nuclei
Lymphoblasts vs.
Myeloblasts
More condensed
chromatin, less
conspicuous nuclei,
and smaller amounts
of cytoplasm
lacking granules
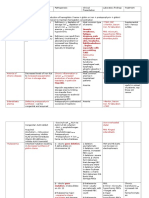
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Myeloid -Acute promyelocytic -Older adults (50-60) APL: ATRA (all-trans-
Stem TdT-, MPO+ leukemia (APL) = -Acute monocytic: infiltration of retinoic acid, a Vit A
Cells t(15;17) RAR gums deriv) maturation
-Auer Rods (crystal disruption, increased risk -Acute megaloblastic: assoc. w/ and death of blasts
aggregates of MPO) of DIC Downs (before age 5); MPO (-)
->20% blasts
-thrombocytopenia, anemia,
hypercellular BM, / WBCs
Acute Promylocytic Leukemia Myeloid t(15:17) Disruption of All-trans-retinoic-acid
Stem retinoic acid receptor (ATRA)
Cells Promylocytes contain many Blocks Myeloid Vitamin A
auer rods which are differentiation
condensed azurophilic
granules. When these
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Acute Myeloproliferative Acute Lymphoproliferative Chronic Myeloproliferative Chronic Lymphoproliferative Plasma Cell NeoplasmDokument1 SeiteAcute Myeloproliferative Acute Lymphoproliferative Chronic Myeloproliferative Chronic Lymphoproliferative Plasma Cell NeoplasmAudreySlitNoch keine Bewertungen
- LeukemiaDokument2 SeitenLeukemiaAyeshaArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breast CancerDokument6 SeitenBreast Cancersarguss14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anemia Flow ChartDokument1 SeiteAnemia Flow ChartCynthiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GI Diarrheal Micro ChartDokument3 SeitenGI Diarrheal Micro ChartEvan MillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateDokument3 SeitenClinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateqselmmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test LFTsDokument2 SeitenTest LFTsostarburstoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anemia Type Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Peripheral Blood Lab FindingsDokument15 SeitenAnemia Type Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Peripheral Blood Lab FindingsDanielle FosterNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC Tumor MC Ca MC 1° Ca BrainDokument12 SeitenMC Tumor MC Ca MC 1° Ca BrainRyan TurnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases - BiochemDokument4 SeitenDiseases - BiochemJay FeldmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small Intestine 01 PDFDokument9 SeitenSmall Intestine 01 PDFfadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Aid PharmacoDokument61 SeitenFirst Aid PharmacogirNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPTOMED-HW2-Diabetic Retinopathy PDFDokument3 SeitenOPTOMED-HW2-Diabetic Retinopathy PDFDanalie SalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiology Arteritis ChartDokument3 SeitenCardiology Arteritis ChartM PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin and MSK EverythingDokument31 SeitenSkin and MSK EverythingBernard HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microcytic AnemiaDokument2 SeitenMicrocytic AnemiaLanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arteriolar Dilator Decreases After Load Ejection FractionDokument1 SeiteArteriolar Dilator Decreases After Load Ejection FractionJack GuccioneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. A. Samy TAG Bone Diseases - 1Dokument2 SeitenDr. A. Samy TAG Bone Diseases - 1Herato MenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematologic MalignanciesDokument5 SeitenHematologic MalignanciesPrisbert W. AlejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SketchyPath ChecklistDokument1 SeiteSketchyPath ChecklistFajar Raza100% (1)
- Week 7. Renal Pathology Continued.Dokument9 SeitenWeek 7. Renal Pathology Continued.Amber LeJeuneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Main DrugsDokument14 SeitenPharmacology Main DrugsSabir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 07 Microbiology Mycobacterium Skin InfectionDokument6 Seiten2011 07 Microbiology Mycobacterium Skin InfectionCristinaConcepcionNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.1d - Pathology of The Pituitary - Nov.10 - Dr. GalangDokument4 Seiten4.1d - Pathology of The Pituitary - Nov.10 - Dr. GalangMiel Raphael AranillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenDokument5 SeitenTumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenAngela ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Chart #3 - Italics OnlyDokument27 SeitenMicro Chart #3 - Italics Onlyapi-26938624100% (1)
- LOOK! Neuroscience Brainstorm 2010Dokument32 SeitenLOOK! Neuroscience Brainstorm 2010genome12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- IV Fluid ChartDokument2 SeitenIV Fluid Chartbenny christantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical SignsDokument26 SeitenClinical SignswiraandiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotics Chart 1Dokument7 SeitenAntibiotics Chart 1Vee MendNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY WebpathDokument35 SeitenENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY Webpathapi-3766657Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionDokument1 SeitePathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionMicroposterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zanki (Complete) + R/medicalschoolanki Microbiology ErrataDokument70 SeitenZanki (Complete) + R/medicalschoolanki Microbiology ErrataedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step 1 DrugsDokument46 SeitenStep 1 DrugsZebram ZeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Path DumpsDokument44 SeitenPath DumpsAndleeb ImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casts inDokument1 SeiteCasts ingregoryvoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurology Musculoskeletal (MedicalBooksVN - Com)Dokument4 SeitenNeurology Musculoskeletal (MedicalBooksVN - Com)Jonathan AiresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Profiles: CyclophosphamideDokument12 SeitenDrugs Profiles: Cyclophosphamidejhk0428Noch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of The Epilepsies: Purpose: For Clinical DiagnosisDokument25 SeitenClassification of The Epilepsies: Purpose: For Clinical Diagnosisayu rifqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tumour Marker For Medincine ResidentsDokument58 SeitenTumour Marker For Medincine ResidentsSandeep NarayananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DDokument28 SeitenAntihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Normal Kidney: Pediatrics 2 The Urinary System and Urinary Tract InfectionsDokument4 SeitenThe Normal Kidney: Pediatrics 2 The Urinary System and Urinary Tract Infectionssarguss14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Most Common : WWW - Med.usf - Edu/ Jmensch/downloads - HTMDokument3 SeitenMost Common : WWW - Med.usf - Edu/ Jmensch/downloads - HTMazul2233Noch keine Bewertungen
- PATH All TA Reviews Answers and Notes11Dokument718 SeitenPATH All TA Reviews Answers and Notes11Andleeb Imran100% (1)
- Ultimate Pharm GuideDokument41 SeitenUltimate Pharm GuideeanguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alarm Symptoms of Hematoonco in Pediatrics: Dr. Cece Alfalah, M.Biomed, Sp.A (K) Pediatric Hematology and OncologyDokument22 SeitenAlarm Symptoms of Hematoonco in Pediatrics: Dr. Cece Alfalah, M.Biomed, Sp.A (K) Pediatric Hematology and OncologyMuhammad ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7sgdfgf PDFDokument438 Seiten7sgdfgf PDFPratik JadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiseizure, Sedative & HypnoticsDokument8 SeitenAntiseizure, Sedative & HypnoticsThulasi tootsieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentry PDFDokument17 SeitenIntegumentry PDFMehul RathoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bot Med Final CHARTDokument33 SeitenBot Med Final CHARTapi-26938624100% (3)
- Genetic Disorders-Www - Qworld.co - inDokument13 SeitenGenetic Disorders-Www - Qworld.co - inQworld100% (1)
- Kidney Part 1Dokument5 SeitenKidney Part 1sarguss14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Decreased Levels of Iron by Diet or Hemorrhage Impaired Heme SynthesisDokument8 SeitenDecreased Levels of Iron by Diet or Hemorrhage Impaired Heme SynthesisSamuel RothschildNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ninja - Antihyperlipidemics PDFDokument3 SeitenNinja - Antihyperlipidemics PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Bipolar Disorder Background: Hypomania Has The Same Symptoms of Mania Without Psychotic SymptomsDokument2 SeitenBipolar Disorder Background: Hypomania Has The Same Symptoms of Mania Without Psychotic SymptomshumdingerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephrotic Nephritic SyndromsDokument4 SeitenNephrotic Nephritic SyndromsKimiwari100% (2)
- Abx FinalDokument3 SeitenAbx Finalyanks1120Noch keine Bewertungen
- Immunopharmacology: GlucocorticoidsDokument9 SeitenImmunopharmacology: GlucocorticoidsCas BuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abernathy Contents PDFDokument7 SeitenAbernathy Contents PDFSamuel RothschildNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abernathy Contents PDFDokument7 SeitenAbernathy Contents PDFSamuel RothschildNoch keine Bewertungen
- UVA Family QuestionsDokument30 SeitenUVA Family QuestionsSamuel RothschildNoch keine Bewertungen
- UVA Family Questions W/ AnswersDokument60 SeitenUVA Family Questions W/ AnswersSamuel Rothschild0% (1)
- UVA Family QuestionsDokument30 SeitenUVA Family QuestionsSamuel RothschildNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decreased Levels of Iron by Diet or Hemorrhage Impaired Heme SynthesisDokument8 SeitenDecreased Levels of Iron by Diet or Hemorrhage Impaired Heme SynthesisSamuel RothschildNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decreased Levels of Iron by Diet or Hemorrhage Impaired Heme SynthesisDokument8 SeitenDecreased Levels of Iron by Diet or Hemorrhage Impaired Heme SynthesisSamuel RothschildNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 1111@jocd 13505Dokument15 Seiten10 1111@jocd 13505Dr. Hilder HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holistic Approach To Mental HealthDokument38 SeitenHolistic Approach To Mental HealthabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nevid CH14 TBDokument71 SeitenNevid CH14 TBAngela MarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determinants of Utilization of MaternalDokument24 SeitenDeterminants of Utilization of MaternalPraise NehumambiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet: Texclad 2Dokument7 SeitenSafety Data Sheet: Texclad 2Om Prakash RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leaflet Writing TasksDokument10 SeitenLeaflet Writing TasksNeal ColpittsNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiPAP Full FlowchartDokument1 SeiteBiPAP Full FlowchartArjun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Deterioration and Its ControlDokument4 SeitenFood Deterioration and Its ControlArul Kamalakumar100% (3)
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA HydrocephalusDokument2 SeitenDAFTAR PUSTAKA HydrocephalusRahma darisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jawaban Tugas Bahasa Inggris - Sandrina Herawati PutriDokument4 SeitenJawaban Tugas Bahasa Inggris - Sandrina Herawati PutriPuskesmas PanonganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuromitos PDFDokument9 SeitenNeuromitos PDFAriel JaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Positioning and Its ImportanceDokument22 SeitenPositioning and Its ImportanceDeepika PatidarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pengaruh Kegel Exercise Terhadap Inkontinensia Urine Pada Ibu Postpartum MultiparaDokument8 SeitenPengaruh Kegel Exercise Terhadap Inkontinensia Urine Pada Ibu Postpartum MultiparaYunita RahayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strasinger, Susan King, Di Lorenzo, Marjorie Schaub - Urinalysis and Body Fluids 7th EdDokument426 SeitenStrasinger, Susan King, Di Lorenzo, Marjorie Schaub - Urinalysis and Body Fluids 7th EdJocelle89% (9)
- Hemet City Manager Christopher LopezDokument15 SeitenHemet City Manager Christopher LopezHemetUpdatesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant 6 3: Risk Assessment For Lifting OperationsDokument4 SeitenPlant 6 3: Risk Assessment For Lifting OperationsIdris AdeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders DSM - V Ocd and Related DisordersDokument2 SeitenObsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders DSM - V Ocd and Related DisordersJaaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRVPF AGPP Baseline Study Report For Uganda Power AnalysisDokument43 SeitenCRVPF AGPP Baseline Study Report For Uganda Power AnalysisKayita InnocentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Therapy AssessmentDokument38 SeitenPhysical Therapy Assessmentnikki98% (56)
- NURS FPX 6618 Assessment 3 Disaster Plan With Guidelines For ImplementationDokument5 SeitenNURS FPX 6618 Assessment 3 Disaster Plan With Guidelines For Implementationjoohnsmith070Noch keine Bewertungen
- VapeDokument2 SeitenVapeVanessa MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 & 2 PDFDokument15 SeitenChapter 1 & 2 PDF11D3 CHUA , Jasmine B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Health Declaration Form A1 Whole PageDokument1 SeiteHealth Declaration Form A1 Whole PageFedelyn SemenianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kalipay: B. Mendoza ST., Bgy. Kalipay, Puerto Princesa City, PalawanDokument43 SeitenKalipay: B. Mendoza ST., Bgy. Kalipay, Puerto Princesa City, PalawanShōya IshidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SweetDachs Sales Contract-15Dokument3 SeitenSweetDachs Sales Contract-15Katelyn ShirkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narcissism - Gral Def - 1 of TH 3 Triadic Dark Perosnality Traits With Psychopathy & Machiavellism - Wi EN 17sep2014Dokument23 SeitenNarcissism - Gral Def - 1 of TH 3 Triadic Dark Perosnality Traits With Psychopathy & Machiavellism - Wi EN 17sep2014jffm7147Noch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1. IdentificationDokument9 SeitenSafety Data Sheet: Section 1. IdentificationJosePPMolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leistner 2000 PDFDokument6 SeitenLeistner 2000 PDFProf C.S.PurushothamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radford High Athletic ComplexDokument27 SeitenRadford High Athletic ComplexHNNNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Family Guide To Getting Over OCD Reclaim Your Life and Help Your Loved One (Jonathan S. Abramowitz)Dokument259 SeitenThe Family Guide To Getting Over OCD Reclaim Your Life and Help Your Loved One (Jonathan S. Abramowitz)Ines Maria MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen