Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Clinical Micotoxicosis
Hochgeladen von
usaeswoti0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
168 Ansichten4 SeitenAflatoxin hepatic size increase in coagulation enlargement time increase in protocorporal size reduction combining time enlargement enlargement Testicle atrophia Laying reduction Embryo Antibody absorption development delay reduction Sericeous protein reduction Ochratoxin A Kidney weight Corporal Weight loss increase Sexual maturity delay Increased urate.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenAflatoxin hepatic size increase in coagulation enlargement time increase in protocorporal size reduction combining time enlargement enlargement Testicle atrophia Laying reduction Embryo Antibody absorption development delay reduction Sericeous protein reduction Ochratoxin A Kidney weight Corporal Weight loss increase Sexual maturity delay Increased urate.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
168 Ansichten4 SeitenClinical Micotoxicosis
Hochgeladen von
usaeswotiAflatoxin hepatic size increase in coagulation enlargement time increase in protocorporal size reduction combining time enlargement enlargement Testicle atrophia Laying reduction Embryo Antibody absorption development delay reduction Sericeous protein reduction Ochratoxin A Kidney weight Corporal Weight loss increase Sexual maturity delay Increased urate.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
Clinical Mycotoxicosis
Dr.usaeswoti
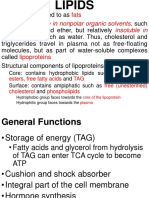
VARIOUS MYCOTOXINS BIOCHEMICAL EFFECTS
Aflatoxin* Hepatic size Increase in coagulation
enlargement time
Increase in proto- Corporal size reduction
combining time Gizzard size
Pro-ventricle size enlargement
enlargement Testicle atrophia
Laying reduction Embryo malformations
Embryo Antibody absorption
development delay reduction
Sericeous protein
reduction
Ochratoxin A* Kidney weight Corporal Weight loss
increase Sexual maturity delay
Increased Urate Laying reduction
deposits
biliary conducts
multiplication
Immunization
defenses reduction
Rubratoxin B* Hepatic Fabricius bag Atrophia
hypertrophy
Embryo
malformation
Diacetoxycirpernol* Lymphatic tissue Spinal cord necropsy
necropsy
Biliary vesicle
necropsy
T-2* Mouth necropsy Hepatic hypertrophy
VII factor and Subcutaneous edema
proto-combining
reduction
Zearalenone* Liver weight
increase Heart weight increase
Kidney weight Estrogenic effect
increase Crest size reduction
Testicle intestinal
fibrosis
Testicle weight
reduction
Citrinin* Renal size Increase in water
enlargement Consumption
Urine production
increase
Penicilloic* Acid Heart muscle Renal necropsy
Sterigmata-cystine alteration
Hepatic necropsy
Penitrem A and B* Neurotoxic
Patulin Hepatic alteration
Note: The combination of two or more mycotoxins, even at LOW levels
can be more toxic than one toxin at a high level and might NOT show
the same symptoms as one mycotoxin.
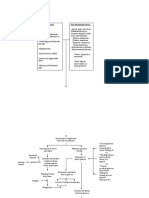
SWINE CLINICAL MYCOTOXICOSIS
(OSWEILER, 1992)
Toxin Category Clinical Effect
Aflatoxin Development / * Growth and feed
grow-out conversion reduction.
* Liver microscopic
lesions, colangio-
hepatitis, hepatic
serological enzymes
enlargement
* Feed consumption
reduction, hardened
hair, hypertony.
* Coagulation apathy,
depression, anorexia.
* Acute hepatitis, and
mortality in 3 to 10
days.
Sow / * No conception effect,
Reproductive Stage normal slow growing
suckling pigs because of
aflatoxin in the milk.
Ochratoxin and Citrinin Grow-out * Moderate renal
lesions. reduction in
weight gain.
* Polydypsia, reduced
growth, glycosuria and
polyuria
Sows / * Normal when they eat
Reproductive Stage on the first month
Tricotecen T-2 and DAS Development * Reduced feed
/Grow-out consumption, oral and
dermal irritation.
* Full rejection and
vomiting.
Deoxynivalenol * Reduced feed
consumption.
* Full rejection
Zearalenone F-2 Reproductive Sows * vulvovaginitis,
Prolapse
Cycling sows * Persistency of anestra
lutea body.
* Pseudopregnancy
Pregnant sows * Early embryo mortality
when feeding
* 1-3 weeks post-
service.
Fumonisin Swine * Acute lung edema,
hepatitis, lymphoblasts
genesis paralysis,
reduced feed
consumption
VARIOUS MYCOTOXINS BIOCHEMICAL EFFECTS
(SHULLY CHEEKE, 1983)
SYSTEM MYCOTOXINS
* Metabolic System:
- Carbohydrates Aflatoxin, Ochratoxin A, Phomopsin A
metabolism
- Lipids metabolism Aflatoxin, Ochratoxin A, T-2, Citrinin,
Rubratoxin B
- Vitamin assimilation Aflatoxin, dicumarol
- Protein synthesis Aflatoxin, Trichothecenes
- Mitochondrial respiration Aflatoxin, Ochratoxin A, Rubratoxin B,
Patulin
* Endocrine system Aflatoxin, Zearalenone, Ergot, Alkaloids
* Skeletal system Aflatoxin, Ochratoxin A
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Vitamins SummaryDokument5 SeitenVitamins SummaryDanny LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug StudyDarlene Laude GoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug StudyNURSETOPNOTCHER100% (3)
- Zetatechnology Thailand KLEAN Greentech Viv2015Dokument52 SeitenZetatechnology Thailand KLEAN Greentech Viv2015rsuertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ovarian Cancer, The NEw PathophyDokument3 SeitenOvarian Cancer, The NEw PathophylieselannjacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- PATHODokument2 SeitenPATHOad3_aaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 LIPIDS Lee - ModifiedDokument72 Seiten5 LIPIDS Lee - ModifiedPelrNoch keine Bewertungen
- PromDokument33 SeitenPromkisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental FactorsDokument7 SeitenEnvironmental FactorsjayrchinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 2B Nutritional Elements:: Vitamins and Energy BalanceDokument40 SeitenUnit - 2B Nutritional Elements:: Vitamins and Energy BalanceEvet VaxbmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatrics: Treatment of MalnutritionDokument4 SeitenPediatrics: Treatment of Malnutritionapi-3829364Noch keine Bewertungen
- VITAMINSDokument2 SeitenVITAMINSthisswannNoch keine Bewertungen
- ColgyDokument13 SeitenColgyTunazza NaveedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Placenta Previa Case StudyDokument7 SeitenPlacenta Previa Case StudyKing NavsunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asfixia Perinatal, CompendiumDokument7 SeitenAsfixia Perinatal, CompendiumClaudia LópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Work FeliciaDokument3 SeitenGroup Work FeliciaFELICIA KASIMUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elbert A. Mutuc Drug Study BSN III - 1 Group 2Dokument4 SeitenElbert A. Mutuc Drug Study BSN III - 1 Group 2Elbert Aquitania Mutuc RNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inbumin PDFDokument12 SeitenInbumin PDFresa dianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06.2 Inborn Error of Metabolism - Iii B - Trans PDFDokument10 Seiten06.2 Inborn Error of Metabolism - Iii B - Trans PDFAshim AbhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exocrine Pancreas Pathology 1Dokument8 SeitenExocrine Pancreas Pathology 1Natalie HowardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phenylalanine Theonine Histidine Valine Isoleucine Arginine (Semi-Essential in Kids Only) Tryptophan Methionine LysineDokument7 SeitenPhenylalanine Theonine Histidine Valine Isoleucine Arginine (Semi-Essential in Kids Only) Tryptophan Methionine LysineApril BasilioNoch keine Bewertungen
- MefenamicDokument3 SeitenMefenamicassilamorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Clinical Instructor: Ms. Ruby Ann B. Dimayuga, RN, MANDokument19 SeitenHyperemesis Gravidarum: Clinical Instructor: Ms. Ruby Ann B. Dimayuga, RN, MANR Hornilla ArcegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of Diabetes Mellitus: and How Does It Affect Health StatusDokument29 SeitenMechanism of Diabetes Mellitus: and How Does It Affect Health StatusVARITPOL CHAROENYINGPAISALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Docu - Tips Drug StudyDokument14 SeitenDocu - Tips Drug StudyArdel LabadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study KetobestDokument3 SeitenDrug Study KetobestHarold TeodoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Affecting The Male and Female Reproductive SystemDokument24 SeitenDrugs Affecting The Male and Female Reproductive SystemAngelica Pabello100% (2)
- Canine and Feline PancreatitisDokument11 SeitenCanine and Feline Pancreatitistaner_soysuren100% (1)
- Family and Drug MOA Physiologic Effect Indications Side EffectsDokument11 SeitenFamily and Drug MOA Physiologic Effect Indications Side EffectsraquelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease: ReviewDokument4 SeitenParenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease: ReviewdhirazhrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Diseases in NutritionDokument5 SeitenCommon Diseases in NutritionImah ArmildezNoch keine Bewertungen
- #Owajacka CAT 2 GIT With AnswersDokument11 Seiten#Owajacka CAT 2 GIT With AnswersRawlings OtienoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio NotesDokument24 SeitenBio NotesIslam MansourNoch keine Bewertungen
- T. Gastrointestinal DisordersDokument6 SeitenT. Gastrointestinal DisordersJyl Yan SelasorNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANTIPARASITICDokument4 SeitenANTIPARASITICJahn MyrilleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamin D DeficiencyDokument11 SeitenVitamin D DeficiencyElvisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yr5 InsulinTherapyDokument61 SeitenYr5 InsulinTherapyCrystel Tze JingNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG STUDY Sa Surgery WardDokument6 SeitenDRUG STUDY Sa Surgery WardDANIELLA MALARANG MELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 11 - Antifungal DrugsDokument12 SeitenLec 11 - Antifungal DrugsAiqa QaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zootechnics 113 - FirstLEDokument5 SeitenZootechnics 113 - FirstLEGeorge LimbertoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desordenes Metabolicos 2019 IIDokument21 SeitenDesordenes Metabolicos 2019 IIEsnayder Zaravia YauriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamins and Its Types With DetailDokument11 SeitenVitamins and Its Types With DetailSummiyah ShahbazNoch keine Bewertungen
- More Pink . Less Zinc . - Mauro Di BenedettoDokument40 SeitenMore Pink . Less Zinc . - Mauro Di BenedettoAbubakar Tahir RamayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pleural Effusion Case PresentationDokument16 SeitenPleural Effusion Case PresentationDhindee OmahoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bitton 2016Dokument3 SeitenBitton 2016Bilel DhaouadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hipertensi Dalam Kehamilan FK Unizar DR AdipDokument68 SeitenHipertensi Dalam Kehamilan FK Unizar DR AdipAngga FirmansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication ContraindicationsDokument4 SeitenDrug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication ContraindicationsAthena SaturdayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tukak GasterDokument11 SeitenTukak GasterAndrie WigunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Male Age: - 2 Weeks Old Narrowing The Opening of The Pylorus and Eventually Preventing Food From Moving From The Stomach To The IntestineDokument2 SeitenMale Age: - 2 Weeks Old Narrowing The Opening of The Pylorus and Eventually Preventing Food From Moving From The Stomach To The IntestineTeddCamilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- OB PathophysiologyDokument2 SeitenOB PathophysiologyCathy SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Micronutrients Fat Soluble Vitamins 21-01-2022 (21 Jan 2022) Material - I - 21!01!2022 - VitaminsDokument21 Seiten5 Micronutrients Fat Soluble Vitamins 21-01-2022 (21 Jan 2022) Material - I - 21!01!2022 - VitaminsAksh KhandelwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study: Ferrous SulfateDokument1 SeiteDrug Study: Ferrous SulfateLatrell GelacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- LR - XII.A.MNT For Critical Care ConditionsDokument7 SeitenLR - XII.A.MNT For Critical Care ConditionsstitchcruellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Bitot SpotDokument2 SeitenManagement of Bitot SpotEsther EunikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materi Fatty Liver Rsu Hermina & PLNDokument15 SeitenMateri Fatty Liver Rsu Hermina & PLNifa virdiyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Drug Study CefuroximeDokument1 SeiteSample Drug Study CefuroximeHoorise NShineNoch keine Bewertungen
- NFS 382 Final ReviewDokument56 SeitenNFS 382 Final ReviewAya ThairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrient ChartDokument7 SeitenNutrient ChartDanilo Clerigo Sr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Ultimate Special Diet Cooking Book: Excellent Keto Diet, Paleo Diet, Inflammatory Diet, Zero Belly & Renal Diet Recipes (Incl. Delicious Breakfast, Lunch & Dinner Food Recipes)Von EverandThe Ultimate Special Diet Cooking Book: Excellent Keto Diet, Paleo Diet, Inflammatory Diet, Zero Belly & Renal Diet Recipes (Incl. Delicious Breakfast, Lunch & Dinner Food Recipes)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fermented Foods for Health: Use the Power of Probiotic Foods to Improve Your Digestion, Strengthen Your Immunity, and Prevent IllnessVon EverandFermented Foods for Health: Use the Power of Probiotic Foods to Improve Your Digestion, Strengthen Your Immunity, and Prevent IllnessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- Importance of Mycotoxin's Analysis inDokument36 SeitenImportance of Mycotoxin's Analysis inusaeswotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Concept of Value Chain ApproachDokument23 SeitenThe Concept of Value Chain Approachusaeswoti100% (5)
- Molds, Mycotoxins and Their Effect On HorsesDokument10 SeitenMolds, Mycotoxins and Their Effect On HorsesDr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU Philippines100% (1)
- Mycotoxicosis in HorsesDokument26 SeitenMycotoxicosis in Horsesusaeswoti100% (1)
- Assessing The Primary Activities in The Value ChainDokument24 SeitenAssessing The Primary Activities in The Value Chainusaeswoti100% (1)
- Effects of Moldy Feed and Mycotoxins On CattleDokument19 SeitenEffects of Moldy Feed and Mycotoxins On Cattleusaeswoti100% (2)
- Use of Anti-Degnala Liquor and Toxin Binders in Treatment and Control of Endemic Moist Eczematous Syndrome in Cattle in Jhapa District of NepalDokument10 SeitenUse of Anti-Degnala Liquor and Toxin Binders in Treatment and Control of Endemic Moist Eczematous Syndrome in Cattle in Jhapa District of NepalusaeswotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving National AnimalDokument11 SeitenImproving National Animalkellykat64Noch keine Bewertungen
- Socio-Economic Impact of Animal Disease On Sustainable LivelihoodDokument19 SeitenSocio-Economic Impact of Animal Disease On Sustainable Livelihoodusaeswoti100% (2)
- Clinical-Epidemiological Investigation of Moldy Corn Poisoning in at Udayapur District, NepalDokument6 SeitenClinical-Epidemiological Investigation of Moldy Corn Poisoning in at Udayapur District, Nepalusaeswoti100% (2)
- Improvimg National Animal HealthsysteDokument19 SeitenImprovimg National Animal Healthsysteusaeswoti100% (2)
- Low Carbon Economy and Agriculture SystemsDokument9 SeitenLow Carbon Economy and Agriculture SystemsDr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU Philippines100% (2)
- ASSESSMENT OF THE IMMUNOLOGIC PROPERTY OF Fusarium Graminearium in MiceDokument9 SeitenASSESSMENT OF THE IMMUNOLOGIC PROPERTY OF Fusarium Graminearium in Micekedar karkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endemic Moist Facial Eczematous SyndromeDokument10 SeitenEndemic Moist Facial Eczematous SyndromeDr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU PhilippinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Anti-Degnala Liquor and Toxin Binders in Treatment and Control of Endemic Moist Eczematous Syndrome in Cattle in Jhapa District of NepalDokument10 SeitenUse of Anti-Degnala Liquor and Toxin Binders in Treatment and Control of Endemic Moist Eczematous Syndrome in Cattle in Jhapa District of NepalusaeswotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kumri in GoatDokument11 SeitenKumri in GoatDr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU PhilippinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asseessment of The PathogenecityDokument15 SeitenAsseessment of The Pathogenecitykellykat64Noch keine Bewertungen
- ASSESSMENT OF THE IMMUNOLOGIC PROPERTY OF Fusarium GraDokument1 SeiteASSESSMENT OF THE IMMUNOLOGIC PROPERTY OF Fusarium GraDr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU PhilippinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review of Ecosystem ImbalanceDokument11 SeitenA Review of Ecosystem ImbalanceDr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU Philippines100% (1)
- Chapter 3.2 Futures HedgingDokument19 SeitenChapter 3.2 Futures HedginglelouchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schools Division of Roxas CityDokument4 SeitenSchools Division of Roxas CityHuge Propalde EstolanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Positioning Strategy - Mineral WaterDokument2 SeitenPositioning Strategy - Mineral WaterRakesh SelvamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy, Physiology & Health EducationDokument2 SeitenAnatomy, Physiology & Health Educationsantosh vaishnaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire BehaviourDokument4 SeitenFire BehaviourFirezky CuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 2281 1990Dokument8 SeitenIso 2281 1990jesus torresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final PR 2 CheckedDokument23 SeitenFinal PR 2 CheckedCindy PalenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonsai TreesDokument19 SeitenBonsai TreesMayur ChoudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- WAM IPM Mechanical Pressure Gauge BrochureDokument4 SeitenWAM IPM Mechanical Pressure Gauge BrochureOliver ConlonNoch keine Bewertungen
- DoveDokument11 SeitenDovekattyperrysherryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lpalmer ResumeDokument4 SeitenLpalmer Resumeapi-216019096Noch keine Bewertungen
- Installation and Operation Manual: Proact™ Ii Electric Powered Actuator and DriverDokument32 SeitenInstallation and Operation Manual: Proact™ Ii Electric Powered Actuator and DriverDjebali MouradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keandalan Bangunan Rumah SusunDokument9 SeitenKeandalan Bangunan Rumah SusunDewi ARimbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Term Biology Ss3Dokument20 Seiten2nd Term Biology Ss3Wisdom Lawal (Wizywise)Noch keine Bewertungen
- ARS122 Engine Spare Part Catalogue PDFDokument134 SeitenARS122 Engine Spare Part Catalogue PDFIrul Umam100% (1)
- Life Orientation Grade 11 Revision Term 2 - 2021 FinalDokument16 SeitenLife Orientation Grade 11 Revision Term 2 - 2021 FinalTeeshan VerappenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing 7 BulletsDokument4 SeitenMaternal and Child Health Nursing 7 BulletsHoneylie PatricioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piaget Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentDokument2 SeitenPiaget Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentSeph TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pentacon Six-02Dokument28 SeitenPentacon Six-02Melissa Moreira TYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osma Osmadrain BG Pim Od107 Feb 2017pdfDokument58 SeitenOsma Osmadrain BG Pim Od107 Feb 2017pdfDeepakkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 36 Petroland PD Serie DKDokument7 Seiten36 Petroland PD Serie DKBayu RahmansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Compressor CP9149-05Dokument5 SeitenAir Compressor CP9149-05Andrés RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epidemiology of Injury in Powerlifting: Retrospective ResultsDokument2 SeitenEpidemiology of Injury in Powerlifting: Retrospective ResultsJavier Estelles MuñozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crude TBP Country United Arab Emirates Distillation: MurbanDokument2 SeitenCrude TBP Country United Arab Emirates Distillation: MurbanHaris ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5.4 - Incapacity As A Ground For DismissalDokument15 SeitenUnit 5.4 - Incapacity As A Ground For DismissalDylan BanksNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Defend The Faith Without Raising Your VoiceDokument139 SeitenHow To Defend The Faith Without Raising Your VoiceCleber De Souza Cunha100% (2)
- 20 Best Cognac CocktailsDokument1 Seite20 Best Cognac CocktailsHL XanticNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2019Dokument64 SeitenJune 2019Eric SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microporous WikiDokument2 SeitenMicroporous WikiIris BalcarceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz BowlDokument36 SeitenQuiz BowlSherry GonzagaNoch keine Bewertungen