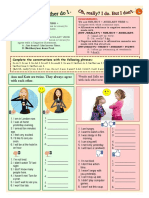
Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Purpose Text
Hochgeladen von
wilmail9Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Purpose Text
Hochgeladen von
wilmail9Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
NARRATIVE Dominant Language Feature
Purpose: To amuse/entertain the readers and to tell a story 1. Introducing group or general aspect
Generic Structure: 2. Using conditional logical connection
1. Orientation 3. Using Simple Present Tense
2. Complication
3. Resolution EXPLANATION
4. Reorientation Purpose: To explain the processes involved in the formation
Dominant Language Features: or working of natural or socio-cultural phenomena.
1. Using Past Tense Generic Structure:
2. Using action verb 1. General statement
3. Chronologically arranged 2. Explanation
3. Closing
RECOUNT Dominant Language Features:
Purpose: to retell something that happened in the past and 1. Using Simple Present Tense
to tell a series of past event 2. Using action verbs
Generic Structure: 3. Using passive voice
1. Orientation 4. Using noun phrase
2. Event(s) 5. Using adverbial phrase
3. Reorientation 6. Using technical terms
Dominant Language Features: 7. Using general and abstract noun
1. Using Past Tense 8. Using conjunction of time and cause-effect.
2. Using action verb
3. Using adjectives ANALYTICAL EXPOSITION
Narrative and recount in some ways are similar. Both are Purpose: To reveal the readers that something is the
telling something in the past so narrative and recount important case
usually apply PAST TENSE; whether Simple Past Tense, Generic Structure:
Simple Past Continuous Tense, or Past Perfect Tense. The 1. Thesis
ways narrative and recount told are in chronological order 2. Arguments
using time or place. Commonly narrative text is found in 3. Reiteration/Conclusion
story book; myth, fable, folklore, etc while recount text is Dominant Language Features:
found in biography. 1. Using modals
The thing that makes narrative and recount different is the 2. Using action verbs
structure in which they are constructed. Narrative uses 3. Using thinking verbs
conflicts among the participants whether natural conflict, 4. Using adverbs
social conflict or psychological conflict. In some ways 5. Using adjective
narrative text combines all these conflicts. In the contrary, 6. Using technical terms
we do not find these conflicts inside recount text. Recount 7. Using general and abstract noun
applies series of event as the basic structure 8. Using connectives/transition
DESCRIPTIVE HORTATORY EXPOSITION
Purpose: to describe a particular person, place or thing in Purpose: to persuade the readers that something should or
detail. should not be the case or be done
Dominant Generic Structure: Generic Structure:
1. Identification 1. Thesis
2. Description 2. Arguments
Language Features: 3. Recommendation
1. Using Simple Present Tense Dominant Language features:
2. Using action verb 1. Using Simple Present Tense
3. Using adverb 2. Using modals
4. Using special technical terms 3. Using action verbs
4. Using thinking verbs
REPORT 5. Using adverbs
Purpose: to presents information about something, as it is. 6. Using adjective
Generic Structure 7. Using technical terms
1. General classification 8. Using general and abstract noun
2. Description 9. Using connectives/transition
Then what is the basic difference between analytical and Dominant Language features:
hortatory exposition. In simple word. Analytical is the 1. Focus on specific participants
answer of How is/will while hortatory is the answer of 2. Using adjectives
How should. Analytical exposition will be best to 3. Using long and complex clauses
describe How will student do for his examination? The 4. Using metaphor
point is the important thing to do. But for the question
How should student do for his exam? will be good to be ANECDOTE
answered with hortatory. It is to convince that the thing Purpose: to share with others an account of an unusual or
should be done amusing incident
Generic Structure:
PROCEDURE 1. Abstract
Purpose: to help readers how to do or make something 2. Orientation
completely 3. Crisis
Generic Structure: 4. Reaction
1. Goal/Aim 5. Coda.
2. Materials/Equipments Dominant Language Features:
3. Steps/Methods 1. Using exclamations, rhetorical question or intensifiers
Dominant Language Features: 2. Using material process
1. Using Simple Present Tense 3. Using temporal conjunctions
2. Using Imperatives sentence
3. Using adverb SPOOF
4. Using technical terms Purpose: to tell an event with a humorous twist and
entertain the readers
DISCUSSION Generic Structure:
Purpose: to present information and opinions about issues 1. Orientation
in more one side of an issue (For/Pros and 2. Event(s)
Against/Cons) 3. Twist
Generic Structure: Dominant Language Features:
1. Issue 1. Using Past Tense
2. Arguments for and against 2. Using action verb
3. Conclusion 3. Using adverb
Dominant Language Features: 4. Chronologically arranged
1. Using Simple Present Tense
2. Use of relating verb/to be NEWS ITEM
3. Using thinking verb Purpose: to inform readers about events of the day which
4. Using general and abstract noun are considered newsworthy or important
5. Using conjunction/transition Dominant Generic Structure:
6. Using modality 1. Newsworthy event(s)
7. Using adverb of manner 2. Background event(s)
3. Sources
REVIEW Dominant Language Features:
Purpose: to critique or evaluate an art work or event for a 1. Short, telegraphic information about story captured in
public audience headline
dominant Generic Structure: 2. Using action verbs
1. Orientation 3. Using saying verbs
2. Evaluation 4. Using adverbs : time, place and manner.
3. Interpretative Recount
4. Evaluation //
5. Evaluative Summation
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Effective FCE Use of English: Word FormationDokument8 SeitenEffective FCE Use of English: Word FormationYozamy TrianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leaving Cert Spanish 2017 Marking SchemeDokument16 SeitenLeaving Cert Spanish 2017 Marking SchemePatricia Caballero MolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Future TenseDokument5 SeitenSimple Future TenseJULITANoch keine Bewertungen
- Reported Speech / Indirect Speech / El Estilo Indirecto: Tell & SayDokument6 SeitenReported Speech / Indirect Speech / El Estilo Indirecto: Tell & SayradgullNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modals of PermisionDokument8 SeitenModals of PermisionKenia Toledo GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tcap Terms To KnowDokument4 SeitenTcap Terms To Knowapi-261646968Noch keine Bewertungen
- Verbals: Gerunds, Infinitives, and ParticiplesDokument2 SeitenVerbals: Gerunds, Infinitives, and ParticiplesEstefaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pivot Idea Lesson Exemplar Alignment With The Module: 10 English 4 3Dokument7 SeitenPivot Idea Lesson Exemplar Alignment With The Module: 10 English 4 3Patrick PelicanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- You've Got To Be Shitting MeDokument7 SeitenYou've Got To Be Shitting MeKelsey StaubNoch keine Bewertungen
- IeltsDokument35 SeitenIeltsTRADE TRADENoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 Writing Argument Essay Practice Step 2 October 2020Dokument3 SeitenLesson 3 Writing Argument Essay Practice Step 2 October 2020Sajad HayderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gsci Gsci GLC 2003 Gwichin Language Dictionary 4thDokument306 SeitenGsci Gsci GLC 2003 Gwichin Language Dictionary 4thNathaniel McFlippersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Four Principal Parts of VerbsDokument1 SeiteFour Principal Parts of VerbsGlyn O. SereñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading and Writing Skills - Patterns of Text DevelopmentDokument14 SeitenReading and Writing Skills - Patterns of Text DevelopmentAJ FulgencioNoch keine Bewertungen
- ModalsDokument14 SeitenModalsclytielejardeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus For Final TermDokument4 SeitenSyllabus For Final TermYammi KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emp - Skills - Communication SkillsDokument7 SeitenEmp - Skills - Communication SkillsChinna SamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key. Reported Speech: Questions and CommandsDokument1 SeiteAnswer Key. Reported Speech: Questions and CommandsAne ValdivielsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 14 General English - Part IIDokument15 SeitenGrade 14 General English - Part IIChamila SenaratneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Verb Agreement ModuleDokument8 SeitenSubject Verb Agreement ModuleJUNAID MASCARANoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Writing NotesDokument16 SeitenFundamentals of Writing NotesSuzy ClaireNoch keine Bewertungen
- OBE Based Course Outline FEDokument4 SeitenOBE Based Course Outline FEMuhammad Ahsan ShahèénNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Compositin McqsDokument43 SeitenEnglish Compositin Mcqsapi-34371568388% (8)
- 2 Unidad 1Dokument16 Seiten2 Unidad 1agustina chervoNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Islamic University Chittagong: Department of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE)Dokument13 SeitenInternational Islamic University Chittagong: Department of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE)Aisha AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passive Voice PDFDokument5 SeitenPassive Voice PDFJohan FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ancient Civilizations Unit PlanDokument19 SeitenAncient Civilizations Unit PlanDrifted Away50% (2)
- Training ModuleDokument259 SeitenTraining Modulepeter ryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- So Do I Neither Do I 85748Dokument3 SeitenSo Do I Neither Do I 85748AngelGijonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2Dokument4 Seiten2Samar ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen