Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Safe Work Procedure Bulletin
Hochgeladen von
Andreas 'gondez' SiallaganCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Safe Work Procedure Bulletin
Hochgeladen von
Andreas 'gondez' SiallaganCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
No.
249, 3 of 3
October 2007
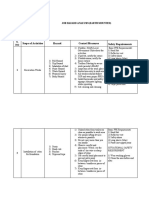
Safe Work Procedures
Developing Safe Work Procedures (SWP)
Safe Work Procedures (SWPs) must be developed and implemented for the work carried out at
your workplace (Section 2.1, Manitoba Workplace Safety and Health Regulation, M.R.
217/2006). SWPs are developed by summarizing the important information you identified while
conducting a Job Hazard Analysis (JHA). Although SWPs may look different depending on your
company, they must capture some basic information. Some SWPs may be more detailed
based on the hazards associated with the job. Some SWPs may include sections such as
scope, qualifications of operators, or materials required, for example. Other SWPs may be more
simplistic, however all SWPs must:
Use positive language (ie. Use words such as ensure or always instead of dont or
never);
Summarize the information gathered in your JHA;
Identify the specific job that the procedure applies to;
Identify who wrote and/or approved the SWP;
Identify the original date it was produced and the latest revision date;
Identify specific hazards you may encounter while performing this job;
Identify Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) or devices required to perform this job safely;
Identify any special equipment or controls that are required (ie. Emergency stops, lock out
procedures);
Describe the step-by-step procedures to perform the task safely;
Refer to or describe the steps to follow in an emergency or during an equipment malfunction;
and
Refer to guidance documents, standards or legislation that applies to the specific task.
If you have more than 20 workers at
your workplace, you are required to
have a Safety and Health Program.
Your SWPs must be referenced in the
section of your Safety and Health
Program that relates to hazard
identification and control (Manitoba
Workplace Safety and Health Act,
W210, Section 7.4(5)(b)).
Page 2 Safe Work Procedures Bltn. 249
EXAMPLE:
(Developed from the JHA sample found in Manitoba Workplace Safety and Health Divisions SAFE Work
Bulletin No. 249, Job Hazard Analysis)
SAFE WORK PROCEDURES - SAMPLE
Woodworking Band Saw
This task may only be performed by trained personnel
Facility: Written By: Approved By: Date Created: Date of Last Revision:
Shop 1 J. Carpenter J. President June 10, 2004 October 5, 2007
Hazards Present: Personal Protective Equipment Additional Training
(PPE) Requirements:
or Devices Required:
Exposed Blade Cuts, Eye Protection Lift/Materials Handling Training
Amputation Hearing Protection Body Posture Training
Electrical Shock Safety Footwear
Noise Disposable Respirator (N95)
Sawdust in Eyes Push Stick or Jig
Sawdust inhaled (possible toxic) Safeguards
MSI Back Injury Dust Collection System
Safe Work Procedure:
1. Don personal protective equipment before beginning the task. Ensure clothing fits appropriately (tight fitting).
2. Ensure saw is unplugged or locked out. Inspect work area to ensure it is clean. Inspect the following for
defects: electrical cords and switches, the blade (by opening up the wheel guards), and all safeguards. If
defects are identified, refer to supervisor for maintenance before continuing. Inspect dust collection system
and ensure it is engaged.
3. Assess the weight and size of the wood. If necessary, obtain assistance. When lifting, use safe lifting
techniques as per lift/materials handling training.
4. Inspect wood to ensure no defects or foreign objects in wood. If defects are identified, place in refuse bin
and continue with alternate piece.
5. Ensure work area is clear of obstructions to prevent twisting and overreaching. Refer to body posture
training.
6. Place wood on platform and measure height of wood. Adjust the guard to 1/8th inch above the height of the
stock of wood being cut.
7. Ensure all safeguards are in place and start the saw. Ensure saw blade is running properly.
8. Hold wood firmly and flat on the platform. Feed the wood into the blade with your body positioned to the side
of the wood. Ensure that hands are kept within the safe zone identified on the platform. Additional
safeguards, such as a jig or push stick, must be used if stock size permits hands to leave the safe zone.
9. Shut off saw. Wait until blade stops. Remove wood from work platform. If wood is near blade, use a push
stick to clear the blade.
10. De-energize and lock out machine to clean off. If there is a large amount of saw dust, wear a disposable
respirator (N95) while cleaning.
If an emergency situation occurs while conducting this task, or there is an equipment malfunction, engage
emergency stop and follow the lock out procedure.
REPORT ANY HAZARDOUS SITUATIONS TO YOUR SUPERVISOR
Guidance Documents/ Standards / Applicable
Legislation / Other:
Guidance Documents:
Operators Manual
CSA Standards: This Safe Work Procedure will be reviewed any time
Z432-04 Safeguarding of Machinery the task, equipment, or materials change and at a
Manitoba Workplace Safety and Health Regulation, minimum every three years
M.R. 217/2006:
2.1 Safe Work Procedures
6.1 Personal Protective Equipment
8 Musculoskeletal Injuries (Refer to Safe Work Bulletin #247
12.3, 12.4 Hearing Protection Recognizing MSI Risks &
16.4 Machine and Tool Safety Safe Work Bulletin # 253 MSI Risk
16.5 Safeguards Required. Identification and Assessment
36 Chemical and Biological Substances for more information.)
All procedures obtained from operator manuals or other samples must be thoroughly reviewed to
ensure they are accurate for your workplace and your jobs!
"Cette information existe galement en franais au www.gov.mb.ca/labour/safety/index.fr.html"
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- SHEQ 37.0.90 Fall Protection ProgrammeDokument11 SeitenSHEQ 37.0.90 Fall Protection ProgrammeNkululeko KuneneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forklift Safety Policy and ProcedureDokument3 SeitenForklift Safety Policy and ProcedureChristian Auditor Rivera100% (1)
- Personal Protective EquipmentDokument1 SeitePersonal Protective EquipmentFrancois Johannes BrinkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tower Crane Dismantling JSA HSE ProfessionalsDokument2 SeitenTower Crane Dismantling JSA HSE ProfessionalsnabeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding Oxy A4Dokument2 SeitenWelding Oxy A4LoveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contractor Health and Safety Risk AssessmentDokument70 SeitenContractor Health and Safety Risk AssessmentmakeencvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maeda-Onaka, Joint Venture: Generic Lifting PlanDokument4 SeitenMaeda-Onaka, Joint Venture: Generic Lifting PlanJaycee Pagador100% (1)
- Jsa Installation of HV ApparatusDokument6 SeitenJsa Installation of HV ApparatusLuqman OsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSE Incident Lesson Learnt Eye Injury Charging Lifeboat Air BottlesDokument1 SeiteHSE Incident Lesson Learnt Eye Injury Charging Lifeboat Air BottlesKyaw MinNoch keine Bewertungen
- JHA Jack Hydraulic PalletDokument1 SeiteJHA Jack Hydraulic PalletIndranil Mitra100% (1)
- Hse Plan EngDokument45 SeitenHse Plan EngSayed DarwishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Height ProcedureDokument7 SeitenWork Height ProcedureardodotNoch keine Bewertungen
- BC C Punmia BeamDokument14 SeitenBC C Punmia BeamvikrantgoudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Handling Safe Work InstructionDokument3 SeitenManual Handling Safe Work InstructionUvini IndurangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tower Crane Work Permit ChecklistDokument1 SeiteTower Crane Work Permit Checklistfaisal nadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safe Work Method Statement For Survey Work: CMS Surveyors Pty LTD ABN: 79 096 240 201Dokument18 SeitenSafe Work Method Statement For Survey Work: CMS Surveyors Pty LTD ABN: 79 096 240 201mkash028100% (1)
- Adverse Weather Condition HIRADokument5 SeitenAdverse Weather Condition HIRAVenkadesh PeriathambiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Very Very Good Risk Assessment EnvironmentDokument8 SeitenVery Very Good Risk Assessment EnvironmentSalley Bukhari100% (1)
- Jsa For Piping and Erection RevisedDokument1 SeiteJsa For Piping and Erection RevisedDr AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual HandlingDokument15 SeitenManual HandlingNithun Deenadayalan100% (2)
- JHA Lifting-Moving Heavy ObjectsDokument6 SeitenJHA Lifting-Moving Heavy ObjectsMiguel AugustoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Health Emergency Response ProcedureDokument2 SeitenSafety Health Emergency Response Procedurearjuna rahmat100% (1)
- Incident Report: Proj. N. Unit Document Code Serial NDokument1 SeiteIncident Report: Proj. N. Unit Document Code Serial NSyed Ali HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.4 Attachments - Risk Assessment and Method StatementDokument10 Seiten2.4 Attachments - Risk Assessment and Method StatementFahad MaqsoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Safety Analysis: Calalang Residence J. Fajardo St. Sampaloc ManillaDokument4 SeitenJob Safety Analysis: Calalang Residence J. Fajardo St. Sampaloc ManillaJoey Stanley GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- JHA Handling Materials - ROMODokument3 SeitenJHA Handling Materials - ROMOazroyremyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safe Work Practices SWPDokument66 SeitenSafe Work Practices SWPapi-317342021Noch keine Bewertungen
- COSHH Assessment: Product Name Supplier Date Ref No. Chemical Identification PPE RequirementsDokument2 SeitenCOSHH Assessment: Product Name Supplier Date Ref No. Chemical Identification PPE RequirementsPaulSwinbankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Confined Spaces Management PlanDokument32 SeitenConfined Spaces Management PlanIdris AdeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working at Height Is One of The Hazardous OccupationsDokument6 SeitenWorking at Height Is One of The Hazardous OccupationsHemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Operating Procedures for Parks Machinery and TasksDokument7 SeitenNormal Operating Procedures for Parks Machinery and TasksHafiezul HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loading & Lifting ProcedureDokument5 SeitenLoading & Lifting Procedurekhurram shahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scaffolding-Fixed and Mobile: Safety Operating ProceduresDokument1 SeiteScaffolding-Fixed and Mobile: Safety Operating Proceduresmohammed muzammilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gorgon LNG Jetty Project Working Near Water ProcedureDokument5 SeitenGorgon LNG Jetty Project Working Near Water Procedureiwan azaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Near WaterDokument46 SeitenWorking Near WaterNikil KPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sanesto MG - Risk AssessmentDokument9 SeitenSanesto MG - Risk AssessmentReynaldo Taveras SantanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shiva Enterprises accident logDokument1 SeiteShiva Enterprises accident logRahul KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Authorized Personnel Only PDFDokument1 SeiteAuthorized Personnel Only PDFsubhanmusadiq100% (1)
- Jsa FormDokument3 SeitenJsa Formmiaicarba100% (1)
- BS 1139-1.2-1990Dokument9 SeitenBS 1139-1.2-1990Andreas 'gondez' Siallagan67% (3)
- Akk Jha Installation of Diesel TankDokument3 SeitenAkk Jha Installation of Diesel TankDouglas Delly0% (1)
- 5X5 Matrix RA For Installation Fo CHC-2A Conveyor SystemDokument16 Seiten5X5 Matrix RA For Installation Fo CHC-2A Conveyor SystemSandeep Jain100% (2)
- Workplace Inspection ChecklistDokument5 SeitenWorkplace Inspection ChecklistVepxvia NadiradzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respi-Nclex QuestionsDokument160 SeitenRespi-Nclex QuestionsSophia Rose Delos Santos100% (3)
- VFTO DocumentationDokument119 SeitenVFTO DocumentationSheri Abhishek ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Safety Analysis Pre-Task Briefing: MASAR Project Makkah KSADokument2 SeitenJob Safety Analysis Pre-Task Briefing: MASAR Project Makkah KSAmahammed saleem100% (2)
- JHA No. 06, Manual Excavation and Instalasi Formwork For Barier Pole Dan Concrete Slab HydrantDokument4 SeitenJHA No. 06, Manual Excavation and Instalasi Formwork For Barier Pole Dan Concrete Slab HydrantDarmawan OnradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Njqs Core Audit Module - Rev1.6cDokument14 SeitenNjqs Core Audit Module - Rev1.6cNene UmohNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSA For Refurbishing and Repainting 23oct2017 (Woqod LPG Plant) UpdatedDokument13 SeitenJSA For Refurbishing and Repainting 23oct2017 (Woqod LPG Plant) UpdatedJoseph PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ehv SWP Form Scaffolding RemovalDokument2 SeitenEhv SWP Form Scaffolding RemovalSn AhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Incident Report Form 1 1Dokument3 SeitenEmployee Incident Report Form 1 1api-459048769100% (1)
- Job Hazard Analysis (Earth Mounted Tank)Dokument8 SeitenJob Hazard Analysis (Earth Mounted Tank)jay RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Assessment Checklist: Green TagDokument2 SeitenConstruction Assessment Checklist: Green TagRyan GillespieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accident Investigation PolicyDokument4 SeitenAccident Investigation PolicyNorman AinomugishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HLG HSE SPI FM 051A Rev 00 Lifting Equipment Audit ChecklistDokument1 SeiteHLG HSE SPI FM 051A Rev 00 Lifting Equipment Audit ChecklistLemuel Petronio100% (2)
- Injury Prevention for Bathroom CleaningDokument1 SeiteInjury Prevention for Bathroom CleaningSajid HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refractory Risk AssessmentDokument2 SeitenRefractory Risk AssessmentSehrish JabeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- BP Safety AlertDokument2 SeitenBP Safety AlertRikza AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blinding and De-blinding Safety EssentialsDokument42 SeitenBlinding and De-blinding Safety EssentialsMayur NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSO Cable Drum (02 Sept.'07)Dokument2 SeitenJSO Cable Drum (02 Sept.'07)Francis Enriquez TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safe System Of Work A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandSafe System Of Work A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incident Alert Wrap FailureDokument3 SeitenIncident Alert Wrap FailureAndreas 'gondez' SiallaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Release From Gas Lift Choke Valve PackingDokument2 SeitenGas Release From Gas Lift Choke Valve PackingAndreas 'gondez' SiallaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hinese Olyester Lings: Corrective ActionDokument1 SeiteHinese Olyester Lings: Corrective ActionAndreas 'gondez' SiallaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safe Work Procedures: Safe Business Is Good BusinessDokument4 SeitenSafe Work Procedures: Safe Business Is Good BusinessAndreas 'gondez' SiallaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Man Riding PosterDokument1 SeiteMan Riding PosterAndreas 'gondez' SiallaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Man Riding PosterDokument1 SeiteMan Riding PosterAndreas 'gondez' SiallaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- QUARMEN Prerequisites - SEM1Dokument12 SeitenQUARMEN Prerequisites - SEM1Valérie NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcatel 350 User Guide FeaturesDokument4 SeitenAlcatel 350 User Guide FeaturesFilipe CardosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle Fusion Middleware: CloningDokument25 SeitenOracle Fusion Middleware: CloningSwathiPatluriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Aceh MedikaDokument10 SeitenJurnal Aceh MedikaJessica SiraitNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM105 18to19Dokument30 SeitenCM105 18to19api-3849444100% (2)
- Sample Problems Part FormDokument4 SeitenSample Problems Part FormkenivanabejuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicrotoxOmni Software Version 4Dokument12 SeitenMicrotoxOmni Software Version 4Louise Veronica JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wag Acquisition v. Vubeology Et. Al.Dokument29 SeitenWag Acquisition v. Vubeology Et. Al.Patent LitigationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nestle CompanyDokument5 SeitenNestle CompanymehakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holiday Tradition Lesson PlanDokument2 SeitenHoliday Tradition Lesson Planapi-458585393Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gee1-Lp1 2022-2023Dokument18 SeitenGee1-Lp1 2022-2023Sherrizah AlidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC604(A) Microcontrollers and Embedded Systems Unit 2 SummaryDokument38 SeitenEC604(A) Microcontrollers and Embedded Systems Unit 2 SummaryAbhay AmbuleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emg 1204 Introduction To Materials Science Tutorial I Attempt All These Questions Question OneDokument2 SeitenEmg 1204 Introduction To Materials Science Tutorial I Attempt All These Questions Question Onesteve gateriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life and Works or Rizal - EssayDokument2 SeitenLife and Works or Rizal - EssayQuince CunananNoch keine Bewertungen
- GHB FactsheetDokument2 SeitenGHB FactsheetABC Action NewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Edition of The AJCC - TNM Staging System of Thyroid Cancer - What To Expect (ITCO#2)Dokument5 Seiten8th Edition of The AJCC - TNM Staging System of Thyroid Cancer - What To Expect (ITCO#2)Valentina IndahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lali The Sun Also Rises Final PaperDokument4 SeitenLali The Sun Also Rises Final PaperDaniel AdamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sense Organs Lesson PlanDokument16 SeitenSense Organs Lesson PlanBernard DayotNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Evaluation of Maglev Technology and Its Comparison With High Speed Rail PDFDokument20 SeitenAn Evaluation of Maglev Technology and Its Comparison With High Speed Rail PDFJohanFaqar ZainNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Neyveli Lignite Deposits (Cauvery Basin), India: Organic Composition, Age and Depositional PatternDokument53 SeitenThe Neyveli Lignite Deposits (Cauvery Basin), India: Organic Composition, Age and Depositional PatternAlok SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- FDokument109 SeitenFssissaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Agreement - Zeroid PDFDokument2 SeitenService Agreement - Zeroid PDFYushau Muhammad LawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipofectamine3000 ProtocolDokument2 SeitenLipofectamine3000 ProtocolSamer AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Future TenseDokument6 SeitenFuture TenseMuhammad Ibnu LaksonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3: Batteries: I Ne NR+RDokument3 Seiten3: Batteries: I Ne NR+RIsrael EdeagheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium of Supply and DemandDokument4 SeitenEquilibrium of Supply and DemandJuina Mhay Baldillo ChunacoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bangladesh Red Crescent Society First Aid Kit SpecificationDokument1 SeiteBangladesh Red Crescent Society First Aid Kit SpecificationWORLDWIDE TRANSLATIONNoch keine Bewertungen