Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Anatomy
Hochgeladen von
Vaibhav Karoliya0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten11 SeitenH
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenH
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten11 SeitenAnatomy
Hochgeladen von
Vaibhav KaroliyaH
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 11
Accessory obturator artery is a branch
of inferior epigastric artery, which itself
is given by external iliac artery.
Lacunar ligament is medial boundary of
femoral ring and accessory obturator
artery may lie on that in some
percentage of population.
In reduction of femoral hernia, we must
be careful of accessory obturator artery,
while we cut lacunar ligament to
enlarge the femoral ring to reduce the
hernia.
Inguinal hernia (direct or indirect) lies
supero-medial to pubic tubercle, and
enters the scrotum. Whereas, femoral
hernia lies infero lateral to pubic
tubercle and enters the thigh region.
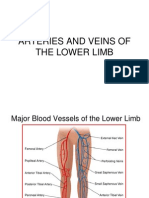
Femoral vein lies lateral to femoral
ring. (JIPMER2016).
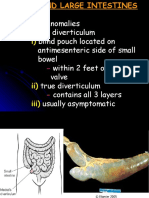
In femoral hernia, the intestine may
enter the femoral ring, and the femoral
canal to reach thigh region, and lie
inferolateral to pubic tubercle.
The most medial content of femoral
triangle is the inguinal lymphatics. The
arrangement of structures ( medial to
lateral) are: Inguinal lymphatics -
Femoral vein, femoral artery, femoral
nerve.
Femoral nerve lies outside the femoral
sheath.
Inferior epigastric artery enters the
rectus sheath, and is a landmark to
differentiate between direct and indirect
inguinal hernia.
Limbus fossa ovalis is present in the
septum secundum and at its floor is
seen the septum primum.
Fusion between septum primum and
septum secundum takes place at about
3 months after birth.
The vas deferens is usually derived
from the superior vesical artery, and
occasionally from the inferior vesical
artery, both branches of the internal
iliac artery.
Note: It may also arise from middle
rectal artery.
Ligamenta denticulatum is made up of
piamater. It lies on each side between
the dorsal and ventral nerve roots,
forming narrow ribbon-like transparent
bands.
The lateral margin of each ligamentum
denticulatum sends
21 teeth-like projections, which pass
through subarachnoid space and
arachnoid mater to gain attachment on
the inner surface of the dural tube
between the points of emergence of
two adjacent spinal nerves.
Note: Ligamentum denticulatum
attaches to duramater.
Ligamenta denticulatum helps to
anchor the spinal cord in the middle of
the subarachnoid space.
The first tooth of ligamentum
denticulatum is at the level of the
foramen magnum, while the last tooth
lies between T12 and L1 spinal nerves
Each ovary lies in the ovarian fossa (of
Waldeyer) on the lateral pelvic wall
below the pelvic brim.
The ovarian fossa is a slight peritoneal
depression bounded
Posteriorly by the ureter and internal
iliac vessels (and origin of uterine
artery). retroperitoneal structures
Anteriorly by the external iliac vessels.
Inferiorly by the uterine tubes (in the
free margin of broad ligament).
The obturator nerve and vessels cross
the floor of the fossa.
Capitate bone articulates with Second
metacarpal Lunate Trapezoid Scaphoid
Pisiform (a sesamoid bone) ossifies at
9-12 years of age.
Optic vesicle derived from an
evagination developing on either side
of the forebrain ( neuroectoderm) of
the early embryo, from which the
percipient parts of the eye are formed.
Rotator cuff (formed by SITS muscles)
stablizes it postero-superiorly, but
weak antero-inferiorly - Shoulder
dislocations are more commonly
antero - inferior. ( Subscapularis is the
forgotten muscle in rotator cuff).
Bicipital Groove Contents:
Tendon of long head of biceps brachii
enclosed in the synovial sheath
Ascending branch of anterior
circumflex humeral artery
Pectoralis Major on the lateral lip of
the groove.
Teres Major on the medial lip of the
groove.
Latissimus dorsi in the floor of the
groove.
Levator ani muscle is subdivided into
named portions according to their
attachments and the pelvic viscera to
which they are related (
pubococcygeus, iliococcygeus
and puborectalis).
Ischiococcygeus muscle is a component
of pelvic diaphragm, but is not included
under levator ani muscle.
Hiltons law: The nerve supplying a
joint also supplies the muscles that
move the joint and the skin covering
the insertion of such muscles.
Sites of sesamoid bones:
In the knee - the patella (within the
quadriceps tendon)
In the hand - two sesamoid bones in
the distal portions of the first
metacarpal bone (within the tendons
of adductor pollicis and
flexor pollicis brevis).
In the wrist - The pisiform of the wrist
is a sesamoid bone (within the tendon
of flexor carpi ulnaris), develops at age
912.
In the foot - two sesamoid bones in
the distal portions of the first
metatarsal bone (within the tendons of
flexor hallucis brevis.
In the ear - the lenticular process of
incus is a sesamoid bone and therefore
is considered the fourth ossicle of
middle ear.
Traction epiphyses are extra capsular
Pressure epiphyses are intra capsular
Deltoid tuberosity is not an epiphysis
(it is present on the shaft/diaphysis)
Epiphysis on the head of first
metacarpal is an example of aberrant
epiphysis.!
Elastic cartilage is present at E3 -
External ear/Eustachian
tube/Epiglottis. It is also seen at the
tip of the arytenoid, corniculate &
cuneiform cartilages (Larynx).
Ventricles of brain are lined by
ependyma (ciliated columnar
epithelium)
Otic placode is a thickening on
ectoderm which appears at day 20
25, and develops into components
of ear.
Trophoblast differentiates into cyto
and syncytiotrophoblast at post
fertilization day 6-8.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CNS Degeneration, Demyelination AnDokument82 SeitenCNS Degeneration, Demyelination AnVaibhav Karoliya100% (1)
- BreastDokument5 SeitenBreastVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Born Error of Metabolism (IEM) : DR Mohammad Khassawneh Assistant Professor of PediatricsDokument31 SeitenIn Born Error of Metabolism (IEM) : DR Mohammad Khassawneh Assistant Professor of PediatricsVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PharmacoDokument62 SeitenPharmacoVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal SeizuresDokument62 SeitenNeonatal SeizuresVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.J. Medical College, Ahmedabad Internship Completion CertificateDokument2 SeitenB.J. Medical College, Ahmedabad Internship Completion CertificateVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grand Rounds: Andy Chien, MD, PHD University of Washington Division of DermatologyDokument75 SeitenGrand Rounds: Andy Chien, MD, PHD University of Washington Division of DermatologyVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamins and Vitamin-Like Substances: PathwaysDokument12 SeitenVitamins and Vitamin-Like Substances: PathwaysAdnan QureshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTN managment-JNC7Dokument37 SeitenHTN managment-JNC7Vaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PeritonitisDokument21 SeitenPeritonitisVaibhav Karoliya100% (1)
- Epilepsy MGDokument91 SeitenEpilepsy MGVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Path Review Questions 3Dokument10 SeitenRenal Path Review Questions 3Vaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VentilatorsDokument28 SeitenVentilatorsKlaue Neiv CallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Board Review - Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyDokument16 SeitenBoard Review - Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Surgery Review - JFRDokument60 SeitenPediatric Surgery Review - JFRVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Path BOARTD ReviDokument36 SeitenRenal Path BOARTD ReviVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sandy SalmonelDokument14 SeitenSandy SalmonelVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friday Harb CancerDokument62 SeitenFriday Harb CancerVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small and Large IntestineDokument82 SeitenSmall and Large IntestineVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tetanus: Philip L. Pokorski, Ph.D. University of Michigan-Dearborn Department of BiologyDokument14 SeitenTetanus: Philip L. Pokorski, Ph.D. University of Michigan-Dearborn Department of BiologyVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paraoxonase TalkDokument27 SeitenParaoxonase TalkVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatology TestingDokument28 SeitenRheumatology TestingVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KOL Hypertesnion With CV Problems Associated ConditionsDokument61 SeitenKOL Hypertesnion With CV Problems Associated ConditionsVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prof. Bari Kaplan MD - . 2-4-2003Dokument7 SeitenProf. Bari Kaplan MD - . 2-4-2003Hamsa ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNS Review Pre Exam MS1Dokument10 SeitenCNS Review Pre Exam MS1Vaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac BiomarDokument34 SeitenCardiac BiomarVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lupus NephritDokument29 SeitenLupus NephritVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Board Review - CHFDokument14 SeitenBoard Review - CHFVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thrombocytes &plateletsDokument18 SeitenThrombocytes &plateletsVaibhav KaroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Surgery Cases GPDokument29 SeitenSurgery Cases GPSudeep Kumar Meena100% (1)
- Cardiology Notes (Chris Andersen, ICUPrimaryPrep - Com) PDFDokument16 SeitenCardiology Notes (Chris Andersen, ICUPrimaryPrep - Com) PDFPkernNoch keine Bewertungen
- (PPT) Anatomy 2.5 Lower Limbs - Blood and Nerve Supply - Dr. Tan PDFDokument110 Seiten(PPT) Anatomy 2.5 Lower Limbs - Blood and Nerve Supply - Dr. Tan PDFPreeti Joan BuxaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- House OfficerDokument32 SeitenHouse Officerapi-3705046100% (1)
- Femoral Triangle - Borders, Contents and Mnemonics - KenhubDokument7 SeitenFemoral Triangle - Borders, Contents and Mnemonics - Kenhubو عجلت اليك ربي لترضيNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Bio MedDokument3 SeitenA Bio MedMeghann MarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy 2009-2018 PastPapers PDFDokument32 SeitenAnatomy 2009-2018 PastPapers PDFYasif AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Anterolateral Thigh FlapDokument6 Seiten14 Anterolateral Thigh FlapAngga Putra100% (1)
- Topography of Lower LimbDokument10 SeitenTopography of Lower LimbMarina CretuNoch keine Bewertungen
- BloodvesselsoflowerlimbDokument48 SeitenBloodvesselsoflowerlimbshyam shankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DVT Ultrasound Made Easy Step-By-Step GuideDokument37 SeitenDVT Ultrasound Made Easy Step-By-Step GuideEL SHITANoch keine Bewertungen
- MANTA™ Vascular Closure Device: Instructions For UseDokument30 SeitenMANTA™ Vascular Closure Device: Instructions For UseXunyao LuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Groin DissectionDokument19 SeitenGroin Dissectiondewiswahyu100% (1)
- CPC Practice Exam ADokument11 SeitenCPC Practice Exam AJamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCEM Anatomy MCQ PDFDokument44 SeitenMCEM Anatomy MCQ PDFUgeshwaran Aristotle Reddy100% (1)
- Chronic Limb IschemiaDokument29 SeitenChronic Limb IschemiaSadia NaveedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rutherford JVS 2000 Venous Severity Scoring AdjunctDokument6 SeitenRutherford JVS 2000 Venous Severity Scoring AdjunctMilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Surgery QuizDokument4 SeitenCardiovascular Surgery Quizjeevan more100% (2)
- Final Onc Paper 1Dokument13 SeitenFinal Onc Paper 1api-645453685Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Do Radial Coronary AngiogramDokument5 SeitenHow To Do Radial Coronary AngiogramnarasimhahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ilioinguinal Lymphadenectomy: Douglas F. MilamDokument7 SeitenIlioinguinal Lymphadenectomy: Douglas F. Milamurovjr vajiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse Points Nursing Assessment PDFDokument8 SeitenPulse Points Nursing Assessment PDFERANoch keine Bewertungen
- Cannula (Medtronic)Dokument119 SeitenCannula (Medtronic)Anca Anca50% (2)
- X-Ray For Medical StudentsDokument68 SeitenX-Ray For Medical StudentsSyahirul AfifiNoch keine Bewertungen
- L14-Arteries of The Lower Limb-DoneDokument47 SeitenL14-Arteries of The Lower Limb-Doneyakuza444Noch keine Bewertungen
- 23 Inguinofemoral, Iliac-Obturator, and Popliteal Lymphadenectomy For MelanomaDokument19 Seiten23 Inguinofemoral, Iliac-Obturator, and Popliteal Lymphadenectomy For MelanomajuanrangoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetic Foot CmeDokument29 SeitenDiabetic Foot CmeAli emillyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology Veins of The Lower LimbsDokument3 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology Veins of The Lower LimbsRoel John Atamosa CasilacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolic and Endocrine 2010 With AnswersDokument15 SeitenMetabolic and Endocrine 2010 With AnswersWenzy CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vascular Note by Joel ArudchelvamDokument52 SeitenVascular Note by Joel ArudchelvamJoel Arudchelvam100% (1)