Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Concept Map Hypertension
Hochgeladen von
george pearson0%(1)0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
284 Ansichten1 Seiteyay
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenyay
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0%(1)0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
284 Ansichten1 SeiteConcept Map Hypertension
Hochgeladen von
george pearsonyay
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
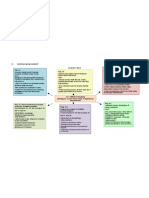
BAKERSFIELD COLLEGE- NURS B20/21
Risk factors Potential complications
PART III: PATHOPHYSIOLOGY CONCEPT MAP
-Being overweight or obese -Aneurysms
-Too much sodium in diet Signs and symptoms -Heart Attack
-Too little potassium in diet -Diagnosis is based on BP readings and can go undetected for years as symptoms -Stroke
-not being physically active usually do not appear until the body is damaged from chronic hypertension. -Peripheral Arterial Disease
-Drinking too much alcohol -Sustained BP reading = SBP of 140mm Hg or more over DBP of 90mm Hg or more -Eye Damage
-Stress -Chronic hypertension can produce signs and symptoms including: -Chronic Kidney Disease
-Diet low in vitamin D -vision changes or blindness (blood vessels in the eyes burst or bleed) -Heart Failure
-Increased risk can come -chest pain (Heart Attack) -Cognitive Changes
from certain chronic -troubled breathing and swelling (Heart Failure) -Left Ventricular
condition including -memory loss and losing focus (Cognitive Changes) Hypertrophy
diabetes, kidney disease,
and sleep apnea
-Age
Disease Process ______Hypertension________
Pathophysiology (Definition / etiology chronicity and prognosis)
Hypertension - chronic elevation of blood pressure that, in the long-term, causes end-organ damage and results in increased morbidity and mortality.
Etiology Primary hypertension has no clear cause and is thought to be linked to genetics, poor diet, and obesity.
- Secondary hypertension is caused by another medical condition that affects the kidneys, arteries, heart or endocrine system. This type can also occur during
pregnancy
Prognosis Hypertension can be controlled with medicine and lifestyle changes if the patient is compliant.
- uncontrolled, patient is at risk for: stroke, heart attack, bleeding, amongst other complications.
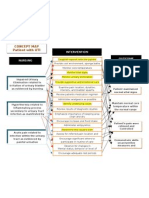
Medical interventions, labs and diagnostic studies Nursing interventions
-Monitor and record orthostatic BP in both arms and thighs routinely.
Medical interventions : medications to treat hypertension include:
-diuretics -Look for general edema, may indicate heart failure, renal or vascular
-angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors impairment
-calcium channel blockers (CCBs)
-angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) -Check presence and quality of central and peripheral pulses
-beta-blockers
General Labs that may be ordered: -Auscultate heart tones and breath sounds (crackles/wheezes may indicate CHF)
-urinalysis (asses kidney function)
-albumin, BUN, and creatinine (monitor kidney dysfunction) -Maintain activity restriction (bed rest/chair rest)
-potassium (some meds cause excessive K loss or retention)
-calcium (parathyroid glands produce an increase in serum calcium) -Observe skin color, moisture, temp, and capillary refill time ( pale, moist skin,
Diagnostic studies: and delayed capillary refill due to vasoconstriction or cardiac decompensation
-ECG (evaluate HR and look for evidence of heart damage) and decreased output)
-Eye exam (look at retina for changes in the blood vessels)
-Physical exam (look for abdominal tenderness, listen for bruits) -Provide calm, restful surroundings, and instruct in relaxation techniques.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hypertension Concept MapDokument1 SeiteHypertension Concept Mapgfhbgfhgf71% (7)
- Clinical Concept MapDokument5 SeitenClinical Concept MapMj FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- TMendoza CriticalCareConceptMap2Dokument5 SeitenTMendoza CriticalCareConceptMap2Theresa Fernandez Mendoza0% (1)
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC Concept MapDokument9 SeitenCC Concept Mapapi-606252228Noch keine Bewertungen
- Waiters Rhabdomyolysis PDFDokument1 SeiteWaiters Rhabdomyolysis PDFmp1757Noch keine Bewertungen
- Small Bowel Obstruction System - DisorderDokument1 SeiteSmall Bowel Obstruction System - DisorderMarina Wasem Netzlaff0% (1)
- Acute PainDokument1 SeiteAcute Painnursing concept mapsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Completed Concept MapDokument4 SeitenCompleted Concept Mapapi-607361848Noch keine Bewertungen
- Small Bowel Obstruction Concept MapDokument1 SeiteSmall Bowel Obstruction Concept MapTessa Claire JaranowskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map Pleural EffusionDokument1 SeiteConcept Map Pleural Effusionapi-341263362Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ricci KeithRN Eating DisorderDokument14 SeitenRicci KeithRN Eating DisorderMichelle RicciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waiters Osteoarthritis PDFDokument1 SeiteWaiters Osteoarthritis PDFmp1757Noch keine Bewertungen
- ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: System DisorderDokument1 SeiteACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: System DisorderDeo FactuarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept MapDokument5 SeitenConcept Mapapi-546509005Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHF Cardiomegaly Volume OverloadDokument1 SeiteCHF Cardiomegaly Volume Overloadnursing concept mapsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Med Surg Week 6Dokument11 SeitenMed Surg Week 6Eunice Cortés100% (1)
- Diagnostic - Procedure DoyleDokument1 SeiteDiagnostic - Procedure Doylemp1757Noch keine Bewertungen
- Community Focused Nursing: Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandCommunity Focused Nursing: Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map StrokeDokument1 SeiteConcept Map StrokeMary GiuntiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothyroidism Concept MapDokument5 SeitenHypothyroidism Concept Mapnursing concept maps0% (1)
- Pku 3 Concept MapDokument3 SeitenPku 3 Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Description: Congestive Heart FailureDokument22 SeitenDescription: Congestive Heart FailurePinklet Arleena CubianNoch keine Bewertungen
- n360 Concept Map Care Plan Week 3 Sheryl SatoDokument15 Seitenn360 Concept Map Care Plan Week 3 Sheryl Satoapi-283363983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing ResumeDokument1 SeiteNursing Resumeapi-545447839Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map 1Dokument5 SeitenConcept Map 1api-396919069Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ampicillin Med InfoDokument1 SeiteAmpicillin Med InfoJan McgovernNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Surgical Nursing IIDokument52 SeitenMedical Surgical Nursing IItwinkle143Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 38: Care of Patients With Diabetes and Hypoglycemia: Multiple ChoiceDokument13 SeitenChapter 38: Care of Patients With Diabetes and Hypoglycemia: Multiple ChoiceNurse UtopiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VSIM Jackson Weber DocumentationDokument2 SeitenVSIM Jackson Weber DocumentationJacqueline LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urosepsis-Sepsis - (KeithRN-Unfolding THIGPEN PDFDokument11 SeitenUrosepsis-Sepsis - (KeithRN-Unfolding THIGPEN PDFOLga A. Thigpen100% (4)
- Care of Pediatric Client With Dermatologic DisorderDokument3 SeitenCare of Pediatric Client With Dermatologic DisorderAraw GabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUR129 Endocrine Concept Mapping InstructorDokument8 SeitenNUR129 Endocrine Concept Mapping InstructorAmber EssmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coreg (Carvedilol)Dokument3 SeitenCoreg (Carvedilol)ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Cord Prolapse March 23Dokument2 SeitenCord Prolapse March 23Kathleen Vargas100% (1)
- Name of Student: - InstructionDokument31 SeitenName of Student: - InstructionPaul Jackson50% (2)
- This Study Resource Was: Maternity Case 5: Fatime SanogoDokument2 SeitenThis Study Resource Was: Maternity Case 5: Fatime SanogoNicole AngelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map Acute PainDokument1 SeiteConcept Map Acute PaincryblrNoch keine Bewertungen
- AmiodaroneDokument2 SeitenAmiodaronekumaninaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intracranial HemorrhageDokument41 SeitenIntracranial Hemorrhagedoctormussieaberra100% (1)
- Concept Map 2Dokument1 SeiteConcept Map 2lanrevoiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nurseslabs MedsurgDokument9 SeitenNurseslabs MedsurgiamdarnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan2Dokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan2gaeLtorvzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care PlanDokument11 SeitenCare PlanAlyssa CardinalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Concept MapDokument2 SeitenNursing Concept MapMary MannNoch keine Bewertungen
- POC and Concepts Maps Week 12Dokument23 SeitenPOC and Concepts Maps Week 12Michelle CollinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCLEX Practice QuestionsDokument12 SeitenNCLEX Practice QuestionsDane WrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care Plan For Excess Fluid Volume ExampleDokument3 SeitenCare Plan For Excess Fluid Volume ExampleVette Angelikka Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care PlanDokument2 SeitenCare PlanLorina Lynne ApelacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric CAP GuidelineDokument1 SeitePediatric CAP GuidelineJohn Vincent Dy OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Management Concept MapDokument1 SeiteNursing Management Concept MapXy-Za Roy Marie100% (1)
- Acetylsalicylic Acid AspirinDokument1 SeiteAcetylsalicylic Acid AspirinE100% (5)
- Fluid Volume Concept MapDokument3 SeitenFluid Volume Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing InterventionsDokument18 SeitenNursing InterventionsMark BellNoch keine Bewertungen
- UTI Patient Concept Map Nursing Diagnosis Interventions OutcomesDokument1 SeiteUTI Patient Concept Map Nursing Diagnosis Interventions OutcomesDon Rieza100% (1)
- Protonix (Pantoprazole)Dokument1 SeiteProtonix (Pantoprazole)CassieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Homework Chapter 1Dokument9 SeitenClass Homework Chapter 1Ela BallıoğluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Superstitious Beliefs of MaranaoDokument13 SeitenSuperstitious Beliefs of MaranaoKhent Ives Acuno SudariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write A Cover Letter For A Training ProgramDokument4 SeitenHow To Write A Cover Letter For A Training Programgyv0vipinem3100% (2)
- Magnetic Suspension System With Electricity Generation Ijariie5381Dokument11 SeitenMagnetic Suspension System With Electricity Generation Ijariie5381Jahnavi ChinnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xtreme 5 (Answer-Key)Dokument120 SeitenXtreme 5 (Answer-Key)arielsergio403Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - The Role of Multimedia in EducationDokument37 SeitenChapter 3 - The Role of Multimedia in EducationGellie Ann Silvestre RapinNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Literature RevisionDokument61 SeitenEnglish Literature RevisionAlex Cobain Glinwood100% (1)
- Bioassay Techniques For Drug Development by Atta-Ur RahmanDokument214 SeitenBioassay Techniques For Drug Development by Atta-Ur RahmanEmpress_MaripossaNoch keine Bewertungen
- In The United States Bankruptcy Court For The District of Delaware in Re:) ) Mervyn'S Holdings, LLC, Et Al.) Case No. 08-11586 (KG) ) ) Debtors.) Affidavit of ServiceDokument19 SeitenIn The United States Bankruptcy Court For The District of Delaware in Re:) ) Mervyn'S Holdings, LLC, Et Al.) Case No. 08-11586 (KG) ) ) Debtors.) Affidavit of ServiceChapter 11 DocketsNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOTAL Income: POSSTORE JERTEH - Account For 2021 Start Date 8/1/2021 End Date 8/31/2021Dokument9 SeitenTOTAL Income: POSSTORE JERTEH - Account For 2021 Start Date 8/1/2021 End Date 8/31/2021Alice NguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Connotative Vs Denotative Lesson Plan PDFDokument5 SeitenConnotative Vs Denotative Lesson Plan PDFangiela goc-ongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Whys Analysis SheetDokument3 Seiten5 Whys Analysis SheetAjay KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Handling - Pre Registration Activity: Submited To-Submitted byDokument12 SeitenGroup Handling - Pre Registration Activity: Submited To-Submitted byharshal kushwahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision and Second Term TestDokument15 SeitenRevision and Second Term TestThu HươngNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEA 1000 Tutorial 1 SolutionDokument12 SeitenGEA 1000 Tutorial 1 SolutionAudryn LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- StoreFront 3.11Dokument162 SeitenStoreFront 3.11AnonimovNoch keine Bewertungen
- January 2008 Ecobon Newsletter Hilton Head Island Audubon SocietyDokument6 SeitenJanuary 2008 Ecobon Newsletter Hilton Head Island Audubon SocietyHilton Head Island Audubon SocietyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Alkazi Collection of Photography Vis PDFDokument68 SeitenThe Alkazi Collection of Photography Vis PDFMochamadRizkyNoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- RITL 2007 (Full Text)Dokument366 SeitenRITL 2007 (Full Text)Institutul de Istorie și Teorie LiterarăNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 ACI Airport Economics Report - Preview - FINAL - WEB PDFDokument12 Seiten2015 ACI Airport Economics Report - Preview - FINAL - WEB PDFDoris Acheng0% (1)
- ABAP Program Types and System FieldsDokument9 SeitenABAP Program Types and System FieldsJo MallickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lumafusion Shortcuts LandscapeDokument2 SeitenLumafusion Shortcuts Landscapepocho clashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan Presentation ON Air Conditioner: Presented By-V.Sowmith REG NO-2121BM010112Dokument16 SeitenBusiness Plan Presentation ON Air Conditioner: Presented By-V.Sowmith REG NO-2121BM010112Kavya Madanu100% (1)
- Young Man Seeks Book to Contact Girl He MetDokument1 SeiteYoung Man Seeks Book to Contact Girl He MetJessie WattsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Paper On The Hells AngelsDokument6 SeitenResearch Paper On The Hells Angelsfvg2xg5r100% (1)
- PCC ConfigDokument345 SeitenPCC ConfigVamsi SuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rebekah Hoeger ResumeDokument1 SeiteRebekah Hoeger ResumerebekahhoegerNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnnovaDokument4 SeitenAnnovabharticNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure For Graduate DIploma in Railway Signalling 2019 v1.0 PDFDokument4 SeitenBrochure For Graduate DIploma in Railway Signalling 2019 v1.0 PDFArun BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Random-Walk-Down-Wall-Street-Malkiel-En-2834 PDFDokument5 SeitenA Random-Walk-Down-Wall-Street-Malkiel-En-2834 PDFTim100% (1)