Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Introduction To The Concept of Automatic Control
Hochgeladen von
Shamolog0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
13 Ansichten5 Seiten1. An automatic controller measures a variable quantity, compares it to a set point, and performs operations to correct any deviations and maintain the measured value at the set point.
2. Examples of automatic systems include household appliances like refrigerators and thermostats, which sense temperature and turn heating/cooling on or off to maintain a constant temperature.
3. For a system to be automatic, it must form a closed loop with elements that sense a measurement, compare it to a reference, and perform corrective actions based on any differences detected.
Originalbeschreibung:
Intro to Auto Control
Originaltitel
Intro to Auto Control
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden1. An automatic controller measures a variable quantity, compares it to a set point, and performs operations to correct any deviations and maintain the measured value at the set point.
2. Examples of automatic systems include household appliances like refrigerators and thermostats, which sense temperature and turn heating/cooling on or off to maintain a constant temperature.
3. For a system to be automatic, it must form a closed loop with elements that sense a measurement, compare it to a reference, and perform corrective actions based on any differences detected.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
13 Ansichten5 SeitenIntroduction To The Concept of Automatic Control
Hochgeladen von
Shamolog1. An automatic controller measures a variable quantity, compares it to a set point, and performs operations to correct any deviations and maintain the measured value at the set point.
2. Examples of automatic systems include household appliances like refrigerators and thermostats, which sense temperature and turn heating/cooling on or off to maintain a constant temperature.
3. For a system to be automatic, it must form a closed loop with elements that sense a measurement, compare it to a reference, and perform corrective actions based on any differences detected.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
INTRODUCTION TO THE CONCEPT OF
AUTOMATIC CONTROL
Let us begin our discussion of industrial automatic
controls by answering the question, "What is an automatic
controller?" An automatic controller is a mechanism which
measures the value of a variable quantity or condition and
operates to correct or limit the deviation of the measured value
from some selected reference. Note that a measurement must be
taken and an operation must be performed to correct that
measurement, if necessary, to conform to some selected reference. For example, if you can sense what you would do to
Often the selected reference is called the "set point." Another term maintain the speed of an automobile constant over a variable
used in lieu of selected reference is "desired value." Simple devices terrain, then you can understand the performance objectives of
like the light switch on the wall or the throttle of an automobile or an automatic controller. The very things that you would do to
the switch on an electric range can be called "controllers." We did maintain conditions constant must be incorporated in a
not say automatic controllers. These devices require a human controller. It is often said that if we can perform an operation
operator in order to function. If we will agree to consider the manually, we can do it automatically. To do the job as well as a
human operator as a part of the system we may call these good human operator sometimes requires an automatic controller
common everyday examples automatic controllers. In the case of of considerable complexity.
the light switch on the wall, the human operator must be always Some everyday examples of completely automatic systems
present with his fingers on the switch and with his eyes sensing are the household refrigerator, the electric iron, the automatic hot
the lightness of the room. He would operate the switch to turn on water heater, and the automatic heating system in your home.
Control of temperature in the oven of your electric range
the lights when the room reached a certain degree of darkness
constitutes an automatic control system in so far as the oven air
and would operate the switch to turn off the lights when the room
temperature is concerned. The cooking process itself is not a true
reached a certain degree of lightness. This satisfies our definition automatic control system. When a timer clock is provided, the
since a measurement is taken and an operation is performed in duration of cooking must be set so that the oven is automatically
response to it. In the case of a man operating an automobile, he turned off after a prescribed length of time has elapsed. The roast
completes the operations necessary to call it an automatic may or may not be done. To constitute what we would call an
controller. If he desires to operate a car at a constant speed his automatic controller, a measurement of temperature of the roast
eyes would see the measurement of speed on the speedometer (by a thermal element inserted into the central portion) would
and through his mental senses he would determine whether or constitute an indication of cooking completeness. Feeding the
signal of this measurement to a controller which would operate
not the speed deviated from the desired value and operate the
the oven switch would make the cooking process itself automatic.
throttle with his foot if a correction were necessary. One of the
best helps in understanding automatic controllers is to study
what a human operator would do.
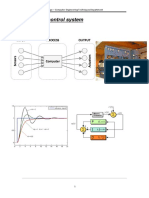
1.1. The closed loop idea
Frequently throughout the text we will find it convenient
to speak of the closed loop. Therefore, in the very beginning it
becomes important to understand what we mean by the system
loop and just what elements are necessary to form a closed loop.
In every completely automatic control application, we have a
closed loop. Let us consider an operation which is done manually
and attempt to formulate a closed loop out of it. Figure 1.1 shows
a human subject operating an electric switch to a heater. In this 1.2. Diagram featuring flow of electricity for manual
example the objective is to maintain a constant temperature in control of temperature
the enclosed space. To accomplish this, we have to first measure
the temperature, and the ordinary mercury in glass thermometer Figure 1.2 shows one form of diagram of the
shown is for this purpose. The human operator has one hand on application of Fig. 1.1. This diagram features the energy
the switch and his eyes focused on the thermometer. It is the (electricity) flow with operations of reading the thermometer
coordination of the eyes and hand of the human operator which and operating the switch as "sidelights." A designer of process
make this a closed loop system. The maintenance of the reference equipment would find this type of diagram helpful It shows the
temperature is dependent upon the human operator being alert at wiring diagram from the 110-v service to the switch and then
all times. Now we can see how the loop is closed. The eyes see the to the heater. Also the installer of process equipment could use
temperature and through the mental and body processes a signal diagrams of this type to advantage since all points of
is sent to the hand to operate the switch manually either to connection are shown.
energize the heater when the temperature is low or to de-energize
the heater when the temperature is high. Items necessary to
complete the loop are the electric switch, thermometer, heater,
process or heated space, source of energy, and the human
operator.
1.3. Generalized loop diagram
A more generalized type of closed loop diagram for the
application of Fig. 1.1 is shown in Fig. 1.3. All important
components in the example carry weight in this circuit, such as 1.4. Conversion from manual to automatic operation
the heated chamber or process, the operator, and the final control
We will replace the human operator with a simple device
element or switch. It was described previously that the human
that will make the application automatic. One method of
operator must sense the measurement of temperature, compare
accomplishing this is shown in Fig. 1.4. In place of the mercury
this measurement with the set point, and perform some action on in glass thermometer we will use a sealed thermal system. It
the switch if a deviation or error exists. These functions are consists of a capillary tubing attached to a thermometer bulb at
identified in the figure. one end and to a flexible bellows at the opposite end. The bellows
is fixed at the top. Expansion and contraction of the bellows is
caused by temperature changes within the thermal system. Fills respectively, for the same application where the human operator
used for industrial thermometers are liquids such as mercury, was involved.
xylene, or toluene; gases such as nitrogen, helium, or carbon
dioxide; or mixtures of liquid and vapor such as ethyl chloride,
sulphur dioxide, or freon.
If the temperature within the room falls, the bellows will
contract due to a lowered pressure within the thermal system.
This will continue until the electric contacts are closed, which
energizes the heating element. The length of time required for the
bellows to reverse itself and start expanding depends upon several
factors, among which are the capacity of the heating element, the
resistance to heat flow between the heating element and the air,
the capacity of the air, the resistance to heat flow between air and
thermometer, and the heat capacity of the thermometer bulb. In
the analysis of any automatic control system cognizance must be
taken of the variables such as these which affect its performance.
Diagrams for Automatic Control of Temperature for Fig. 1.4
Figure 1.6
Figure 1.5 is a diagram featuring the energy flow, and Fig. 1.6
is a generalized closed loop diagram of the automatic control
system. These should be compared with Figs. 1.2 and 1.3,
1.5. Open loop systems toasters which operate on a time clock basis. In these toasters,
the length of the period is preset, and no consideration is given to
Now that we have learned what factors or components are the temperature of bread, which would be the measurement
necessary to form a closed loop system, it is worthwhile to necessary to determine whether the proper degree of toasting has
identify and define what we mean by an open loop control system. been attained. There are other important applications of open
There are many applications of open loop systems in modern loop control systems in industry. In food canning, batch processes
appliances. The automatic washing machine which operates on a are operated by a time schedule controller. Here the process such
time basis and is not dependent upon whether or not the clothes as blanching or cooking is started manually and stopped
are clean, is an open loop system. The washer operates for a automatically after a certain period of time by a clock timer
predetermined length of time in the washing, rinsing, and drying switch. No measurement of quality is involved in this circuit, and
positions. No measurement is taken of the condition of the therefore it is not a closed loop system.
clothes. Another example is embodied in some of our automatic
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 003 - Option B Chapter 14 Engineering Physics PDFDokument62 Seiten003 - Option B Chapter 14 Engineering Physics PDFyuke kristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Control SystemDokument11 SeitenHistory of Control Systemarvinlorenz100% (1)
- Building Controls I - An Introduction To Building Controls-TranscriptDokument11 SeitenBuilding Controls I - An Introduction To Building Controls-Transcriptjacksonli100% (1)
- Introductory Concepts: ErrorDokument5 SeitenIntroductory Concepts: ErrorbismilishfaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument30 SeitenUnit 1Rajasekaran RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medule 1 Lect 1Dokument12 SeitenMedule 1 Lect 1Aram Nasih MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 1 MechatronicsDokument15 SeitenUNIT 1 MechatronicsMuthuvel M82% (17)
- Control SystemDokument8 SeitenControl SystemEire SimanjuntakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control EngineeringDokument7 SeitenControl Engineeringuet158Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer Practice ProblemsDokument3 SeitenHeat Transfer Practice ProblemsCody WaltonNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Process Control: Dr. Ahmed Kamal El-DINDokument21 SeitenTo Process Control: Dr. Ahmed Kamal El-DINJooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logic Control: Logic or Sequential Controls Feedback Linear Fuzzy Logic Logic Not ControllableDokument6 SeitenLogic Control: Logic or Sequential Controls Feedback Linear Fuzzy Logic Logic Not ControllableSRI NANDANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 FTDokument40 SeitenChapter 8 FTUthaiyavani RajendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 2401 Mechatronics Unit 1 NotesDokument60 SeitenMe 2401 Mechatronics Unit 1 NotesSivagami PunithavathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control SystemDokument6 SeitenControl SystemkirandasNoch keine Bewertungen
- FinalllllllDokument47 SeitenFinalllllllSoresa JemalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control SystemDokument7 SeitenControl SystemLeo LonardelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Controls System Group 1Dokument17 SeitenFundamentals of Controls System Group 1Louie CamposNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEA-430 Introduction To Mechatronics: D R. Abdul Attayyab Khan Email AddressDokument16 SeitenEEA-430 Introduction To Mechatronics: D R. Abdul Attayyab Khan Email AddressAamir MansoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechatronics Unit 1 & 4 Notes PDFDokument86 SeitenMechatronics Unit 1 & 4 Notes PDFSt. Anne's CET (EEE Department)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pid Feedforward ControllerDokument6 SeitenPid Feedforward ControllermitudevilNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Control The Speed of Three Phase Induction MotorDokument6 SeitenHow To Control The Speed of Three Phase Induction MotorakramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Control Unit 1Dokument16 SeitenProcess Control Unit 1Carn JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Sol CH 1Dokument5 SeitenTutorial Sol CH 1Nabila Agnasia DesmaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto 221chapter 2Dokument6 SeitenAuto 221chapter 2Ben Aldrian Tariao IbañezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pid Versus On-Off Control, Why Use A Valve Positioner?: MeasurementDokument13 SeitenPid Versus On-Off Control, Why Use A Valve Positioner?: MeasurementVale BajoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading CONTROL SYSTEM Brandol SarayDokument6 SeitenReading CONTROL SYSTEM Brandol SarayBrandol Andrey SarayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemical Engineering B.SC, University of DebrecenDokument6 SeitenBiochemical Engineering B.SC, University of DebrecenArifuzzamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- General: P - A - R - TCDokument18 SeitenGeneral: P - A - R - TCMohamed MosaedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Control: The ProcessDokument7 SeitenIntroduction To Control: The ProcessshajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1Dokument6 SeitenCH 1Dineshsingh ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 - Introduction: PretestDokument18 SeitenUnit 1 - Introduction: Pretestariel mentawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Part 1Dokument5 SeitenControl Part 1Su Yen YapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Control SystemsDokument8 SeitenIntroduction To Control Systemsraduja93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Control System - المنهج المقرر PDFDokument122 SeitenControl System - المنهج المقرر PDFTariq ZeyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Furnace Control SystemDokument9 SeitenFurnace Control SystemMUHAMMAD ASJAD AAMIR AAMIR AMINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction of Control EngineeringDokument21 SeitenIntroduction of Control EngineeringAshvani ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Systems: Closed - Loop System and Open - Loop SystemDokument4 SeitenControl Systems: Closed - Loop System and Open - Loop SystemKaylaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control System PresentationDokument15 SeitenControl System PresentationecegianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Instrumentation: Learning OutcomeDokument12 SeitenIntroduction To Instrumentation: Learning OutcomeMandeep MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation and ControlDokument41 SeitenInstrumentation and ControlAnonymous 5ZR8rH3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Title: Design and Analysis of Digital Temperature Control SystemDokument4 SeitenTitle: Design and Analysis of Digital Temperature Control SystemVISHNU DOUND VDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Loops: An Open Loop Control SystemDokument17 SeitenControl Loops: An Open Loop Control Systemget_engineer05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecturer: Ms. Santhiya School of EngineeringDokument13 SeitenLecturer: Ms. Santhiya School of EngineeringsanthiyaperemelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Exchanger Part 3Dokument19 SeitenHeat Exchanger Part 3Mohamed AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application o FeedbackDokument4 SeitenApplication o FeedbackPatoriku KunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Engineering Department College of Engineering and Technology Adigrat UniversityDokument33 SeitenChemical Engineering Department College of Engineering and Technology Adigrat Universitykibrom atsbhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pump ED 101: PID ControlDokument6 SeitenPump ED 101: PID ControlAjay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Close Loop Control Sys IntroDokument7 SeitenClose Loop Control Sys IntroDwi Mulyanti DwimulyantishopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Washing MachineDokument8 SeitenWashing MachineHieu Nguyen TrungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Types of Switch: Closed Loop SystemDokument18 SeitenDifferent Types of Switch: Closed Loop SystemPamNoch keine Bewertungen
- KE30501 Lab 1 - Open and Close Loop SystemDokument24 SeitenKE30501 Lab 1 - Open and Close Loop SystemAlvin Tung Kwong ChoongNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS LabReport 8Dokument10 SeitenCS LabReport 8Muhammad AfzaalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controllers and Sensors: Block 6 Control Hardware: Electric /pneumatic ActuationDokument12 SeitenControllers and Sensors: Block 6 Control Hardware: Electric /pneumatic ActuationUche Avriel Asimov OputaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control of Temperature, Humidity, Pressure, Flow Rate, Level or PH Process VariablesDokument8 SeitenControl of Temperature, Humidity, Pressure, Flow Rate, Level or PH Process VariablessaravananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Close & Open Loop SystemDokument6 SeitenClose & Open Loop SystemAdonis NicolasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control System NOTESDokument9 SeitenControl System NOTESSTUDENTS OF DOE CUSATNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Systems Analysis and Control D Coughanowr 3rd Ed 2Dokument6 SeitenProcess Systems Analysis and Control D Coughanowr 3rd Ed 2bismilishfaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Notes - As Unit 3Dokument4 SeitenClass Notes - As Unit 3aqsaleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control SystemDokument21 SeitenControl SystemKarthik SuvarnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- San MateoDokument1 SeiteSan MateoShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard ListDokument9 SeitenStandard ListShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 QuestionDokument3 Seiten4 QuestionShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMM 1Dokument1 SeiteCMM 1ShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tyu 17Dokument2 SeitenTyu 17ShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDEDokument12 SeitenMDEShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Handling Manual: Transport Safety and Security Chemical Risk and Hazard Analysis BBDokument2 SeitenChemical Handling Manual: Transport Safety and Security Chemical Risk and Hazard Analysis BBShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- RtyDokument1 SeiteRtyShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- San MateoDokument1 SeiteSan MateoShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Operating Proportional Controller - Liquid LevelDokument2 SeitenSelf-Operating Proportional Controller - Liquid LevelShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pin Codes 5y55y5y5 Aathathath Athath5 54yybnyw4y64 W46n46uw W6m57w 7m7m78w Away Insert Page Lay OutDokument1 SeitePin Codes 5y55y5y5 Aathathath Athath5 54yybnyw4y64 W46n46uw W6m57w 7m7m78w Away Insert Page Lay OutShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid FuelsDokument2 SeitenSolid FuelsShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Hygiene .3Dokument2 SeitenIndustrial Hygiene .3ShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proportional Control .1Dokument2 SeitenProportional Control .1ShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- UP MSmathDokument2 SeitenUP MSmathShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primavera Project Planner Reference ManualDokument774 SeitenPrimavera Project Planner Reference ManualPancho Javier SerenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Information: Spur Gears Gear NomenclatureDokument18 SeitenEngineering Information: Spur Gears Gear NomenclatureShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThermodynamicsDokument3 SeitenThermodynamicsShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide Questions Final Exam 2016Dokument4 SeitenGuide Questions Final Exam 2016ShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiffusionDokument23 SeitenDiffusionShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- For EPT Non-Passers: Chemistry Calculation With Organic ChemistryDokument2 SeitenFor EPT Non-Passers: Chemistry Calculation With Organic ChemistryShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passport Applicationform 2015Dokument2 SeitenPassport Applicationform 2015genesisrdomingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquid FuelsDokument8 SeitenLiquid FuelsShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- HT Pipe SPDokument2 SeitenHT Pipe SPShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer SPDokument2 SeitenHeat Transfer SPShamolog100% (1)
- Compressor Problem SetDokument21 SeitenCompressor Problem SetShamologNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duct DesignDokument46 SeitenDuct DesignPushp Dutt100% (3)
- Physics Episode 6 PDFDokument42 SeitenPhysics Episode 6 PDFRaging PhoenixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Del Code - BrightDokument275 SeitenManual Del Code - BrightDilson Loaiza CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fan Laws: Table 1 Fan Laws Parameters Variable ‘n' Speed Variable ‘ρ' Density Variable ‘d' Impeller Diameter p Q PpowDokument3 SeitenFan Laws: Table 1 Fan Laws Parameters Variable ‘n' Speed Variable ‘ρ' Density Variable ‘d' Impeller Diameter p Q Ppowgeetikag_23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Beam Calculator Online (Calculate The Reactions, Draws Bending Moment, Shear Force, Axial Force) PDFDokument5 SeitenBeam Calculator Online (Calculate The Reactions, Draws Bending Moment, Shear Force, Axial Force) PDFEngr Ishfaque TunioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Stability Analysis of A Tethered AerostatDokument8 SeitenDynamic Stability Analysis of A Tethered AerostatNick SetarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB Electronic Products and Relays CM-Three-phase en 1111Dokument24 SeitenABB Electronic Products and Relays CM-Three-phase en 1111babaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction Heat Transfer Arpaci.Dokument551 SeitenConduction Heat Transfer Arpaci.Abhimanyu Ghosh100% (4)
- Chapter ThreeDokument21 SeitenChapter ThreeProf. Dr. Hassan N. Al-ObaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument4 SeitenPhysicsKhurshaid AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Notes For Soil MechanicsDokument26 SeitenShort Notes For Soil MechanicsColdWinterKid50% (2)
- Equate: 665 0.051Q 200 0.42Q, Solve Q 31.4 FT /s (A) Figure 11.7a: P GQH/ 62.4 (31.4) (615) /0.78 550 - (B)Dokument1 SeiteEquate: 665 0.051Q 200 0.42Q, Solve Q 31.4 FT /s (A) Figure 11.7a: P GQH/ 62.4 (31.4) (615) /0.78 550 - (B)BarbaraGuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hygromax: VersionsDokument10 SeitenHygromax: VersionsmendoncasegundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Montalk - Dimensional Shift - The Physics of 2012 - Fringe ScienceDokument4 SeitenMontalk - Dimensional Shift - The Physics of 2012 - Fringe ScienceKamal HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Heat Exchanger DesignDokument972 SeitenFundamentals of Heat Exchanger DesignNgô Linh Đan80% (5)
- Unit One Formulae and Definitions Module 1: Mechanics D: Base Quantity Base Unit ImensionsDokument27 SeitenUnit One Formulae and Definitions Module 1: Mechanics D: Base Quantity Base Unit ImensionsUnexpected TheoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2 MarkschemeDokument6 SeitenTopic 2 MarkschemeGajendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Project Finite Element AnalysisDokument41 SeitenFinal Project Finite Element AnalysisAkhil KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- WWW - Physics.ox - Ac.uk - Olympiad - Downloads - PastPapers - BPhO - Round - 1 - PRT - 1 - 2014 PDFDokument7 SeitenWWW - Physics.ox - Ac.uk - Olympiad - Downloads - PastPapers - BPhO - Round - 1 - PRT - 1 - 2014 PDFMadAm JaJaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 PlateTheory 08 VibrationsDokument6 Seiten06 PlateTheory 08 Vibrationsvhj gbhjNoch keine Bewertungen
- QueDokument29 SeitenQuedeva1007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science Module 1 For Students.Dokument10 SeitenPhysical Science Module 1 For Students.YUH JBWDHGNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXP - 4 Chip MorphologyDokument2 SeitenEXP - 4 Chip MorphologyRaju SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- William Liller - Space AstrophysicsDokument290 SeitenWilliam Liller - Space Astrophysicsmuhamad dimas arifin a.k.a Ahmd El ArfNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Chapter Iii) : Earthquake Records and Measuring InstrumentsDokument7 Seiten(Chapter Iii) : Earthquake Records and Measuring InstrumentsDominic FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emulsions Questions and AnswersDokument3 SeitenEmulsions Questions and AnswersAhmad FarhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument7 SeitenChemistryVic Rizenn Isidore BobilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tipler and Mosca Physics For Scientists and Engineers Solutions Manual Chapter 13Dokument102 SeitenTipler and Mosca Physics For Scientists and Engineers Solutions Manual Chapter 13Nate LinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of LightDokument8 SeitenProperties of LightSha BtstaNoch keine Bewertungen